Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access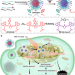 A hydrogen sulphide-responsive and depleting nanoplatform for cancer photodynamic therapy
A hydrogen sulphide-responsive and depleting nanoplatform for cancer photodynamic therapy
Abnormal levels of intracellular hydrogen sulphide (H2S) have been associated with different pathological conditions, including cancer. Here the authors report the design of a H2S-responsive and -depleting nanoplatform that, combined with NIR-II photodynamic properties, can be used for H2S imaging and cancer therapy.
- Yuqi Zhang
- , Jing Fang
- & Haibin Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Electron transfer-triggered imaging of EGFR signaling activity
Electron transfer-triggered imaging of EGFR signaling activity
Here, the authors design a nanoprobe for in vivo imaging of electronic transfer, consisting of a ferrocene-DNA polymer to transfer electrons to luminescent nanoparticles, changing their optical signal. Using this probe, they map activation of EGFR signalling during tumour treatment.
- Jie Tan
- , Hao Li
- & Quan Yuan
-
Article
| Open Access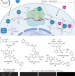 Minimal genetically encoded tags for fluorescent protein labeling in living neurons
Minimal genetically encoded tags for fluorescent protein labeling in living neurons
Site-specific labelling of proteins can be performed with unnatural amino acids combined with bioorthogonal click chemistry. Here the authors establish this in living neurons, using neurofilament light chain; they show combination with CRISPR/Cas9 engineering to tag the endogenous protein.
- Aleksandra Arsić
- , Cathleen Hagemann
- & Ivana Nikić-Spiegel
-
Article
| Open Access Smart facemask for wireless CO2 monitoring
Smart facemask for wireless CO2 monitoring
While facemasks are recommended to prevent the spread of SARS-CoV-2, potential adverse effects may occur upon prolonged usage. Here the authors develop and evaluate an opto-chemical sensor incorporated into a smart FFP2-type facemask for wireless, real-time CO2 monitoring.
- P. Escobedo
- , M. D. Fernández-Ramos
- & A. J. Palma
-
Article
| Open Access Simultaneous two-photon imaging of action potentials and subthreshold inputs in vivo
Simultaneous two-photon imaging of action potentials and subthreshold inputs in vivo
The authors present a geneticallyencoded voltage indicator to specifically measure subthreshold membrane potentials. They combine two-photon imaging of voltage and calcium to map epileptic seizures progression through cortical circuits.
- Yuki Bando
- , Michael Wenzel
- & Rafael Yuste
-
Article
| Open Access A turquoise fluorescence lifetime-based biosensor for quantitative imaging of intracellular calcium
A turquoise fluorescence lifetime-based biosensor for quantitative imaging of intracellular calcium
Currently, genetically encoded calcium indicators are not suitable for direct quantification. Here the authors engineer a fluorescence lifetime imaging calcium biosensor, Turquoise Calcium Fluorescence LIfeTime Sensor (Tq-Ca-FLITS), and measure intracellular calcium concentrations in human-derived organoids.
- Franka H. van der Linden
- , Eike K. Mahlandt
- & Joachim Goedhart
-
Article
| Open Access A genetically encoded fluorescent biosensor for extracellular l-lactate
A genetically encoded fluorescent biosensor for extracellular l-lactate
l-lactate is an important intercellular energy currency. Here the authors report a genetically encoded biosensor eLACCO1.1 to monitor extracellular l-lactate; they use eLACCO1.1 to image extracellular l-lactate in cultured mammalian cells and brain tissue.
- Yusuke Nasu
- , Ciaran Murphy-Royal
- & Robert E. Campbell
-
Article
| Open Access A H2O2-activatable nanoprobe for diagnosing interstitial cystitis and liver ischemia-reperfusion injury via multispectral optoacoustic tomography and NIR-II fluorescent imaging
A H2O2-activatable nanoprobe for diagnosing interstitial cystitis and liver ischemia-reperfusion injury via multispectral optoacoustic tomography and NIR-II fluorescent imaging
Fluorescent imaging in the second biological window has advantages for in vivo applications. Here, the authors synthesise a molecular nanoprobe which activates upon binding H2O2, generating both strong fluorescent NIR-II emission and ultrasound signal for multi-mode imaging of inflammatory diseases.
- Junjie Chen
- , Longqi Chen
- & Yanli Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access A Fabry-Pérot cavity coupled surface plasmon photodiode for electrical biomolecular sensing
A Fabry-Pérot cavity coupled surface plasmon photodiode for electrical biomolecular sensing
Surface plasmon resonance is well established for biosensing applications, but commonly limited by complex optical detection. Here, the authors present a plasmonic sensor integrated in a photovoltaic cell, which generates an electronic signal sensitive to the solution refractive index via plasmon interaction
- Giles Allison
- , Amrita Kumar Sana
- & Hironori Suzuki
-
Article
| Open Access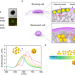 High-spatial and colourimetric imaging of histone modifications in single senescent cells using plasmonic nanoprobes
High-spatial and colourimetric imaging of histone modifications in single senescent cells using plasmonic nanoprobes
The authors demonstrate a colourimetric imaging method using plasmonic nanoparticles for visualisation of heterochromatin histone markers. Based on the distance-dependent coupling effect, resulting in spectral shifts, they observe reorganisation of histone markers caused by oncogene-induced senescence.
- Hyun Ji An
- , Yun Kim
- & Inhee Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Protocell arrays for simultaneous detection of diverse analytes
Protocell arrays for simultaneous detection of diverse analytes
Simultaneous detection of multiple analytes from a sample is currently difficult. Here the authors present protocell arrays in a customisable platform integrating cell-free expression with a polymer-based aqueous two-phase system; they use this for detection of chemically diverse targets from biofluids.
- Yan Zhang
- , Taisuke Kojima
- & Mark P. Styczynski
-
Article
| Open Access A plug-and-play platform of ratiometric bioluminescent sensors for homogeneous immunoassays
A plug-and-play platform of ratiometric bioluminescent sensors for homogeneous immunoassays
Many current immunoassays require multiple washing, incubation and optimization steps. Here the authors present Ratiometric Plug-and-Play Immunodiagnostics (RAPPID), a generic assay platform that uses ratiometric bioluminescent detection to allow sandwich immunoassays to be performed directly in solution.
- Yan Ni
- , Bas J. H. M. Rosier
- & Maarten Merkx
-
Article
| Open Access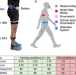 Sensing leg movement enhances wearable monitoring of energy expenditure
Sensing leg movement enhances wearable monitoring of energy expenditure
Current methods to estimate energy expenditure are either infeasible for everyday use or associated with significant errors. Here the authors present a Wearable System using inertial measurement units worn on the shank and thigh that estimates metabolic energy expenditure in real-time during common steady-state and time-varying activities.
- Patrick Slade
- , Mykel J. Kochenderfer
- & Steven H. Collins
-
Article
| Open Access Fluorescence umpolung enables light-up sensing of N-acetyltransferases and nerve agents
Fluorescence umpolung enables light-up sensing of N-acetyltransferases and nerve agents
The electron-withdrawing target (EWT)-induced fluorescence quenching is an unsolved issue in intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) fluorophores that limits their applicability. Here, the authors report a simple and generalizable strategy to reverse the EWT-induced quenching mode into light-up mode, by introducing an indazole building block between the π-bridge and the donor in the ICT scaffold.
- Chenxu Yan
- , Zhiqian Guo
- & Wei-Hong Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Unravelling cytosolic delivery of cell penetrating peptides with a quantitative endosomal escape assay
Unravelling cytosolic delivery of cell penetrating peptides with a quantitative endosomal escape assay
Our understanding of cytosolic delivery is hindered by existing methods for quantification which suffer from being indirect and showing low sensitivity. Here the authors report a SLEEQ (Split Luciferase Endosomal Escape Quantification) assay to assess cytosolic delivery of cell-penetrating peptides.
- Serena L. Y. Teo
- , Joshua J. Rennick
- & Colin W. Pouton
-
Article
| Open Access An l-2-hydroxyglutarate biosensor based on specific transcriptional regulator LhgR
An l-2-hydroxyglutarate biosensor based on specific transcriptional regulator LhgR
L-2-hydroxyglutarate (L-2-HG) is an important metabolite but its regulation is poorly understood. Here the authors report an L-2-HG FRET biosensor based on the allosteric transcription factor, LhgR, to monitor L-2-HG in cells and biological samples.
- Zhaoqi Kang
- , Manman Zhang
- & Ping Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Protein analysis of extracellular vesicles to monitor and predict therapeutic response in metastatic breast cancer
Protein analysis of extracellular vesicles to monitor and predict therapeutic response in metastatic breast cancer
A thermophoretic aptasensor can be used to profile cancer-associated proteins of extracellular vesicles (EVs) in patients’ plasma. Here, the authors use this technique to develop an EV-signature able to discriminate metastatic breast cancer, monitor treatment response, and predict patients’ progression-free survival.
- Fei Tian
- , Shaohua Zhang
- & Jiashu Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Simultaneous readout of multiple FRET pairs using photochromism
Simultaneous readout of multiple FRET pairs using photochromism
Performing multiple FRET measurements at once can be challenging. Here the authors report a method to discriminate between overlapping FRET pairs, even if the fluorophores display almost identical absorption and emission spectra, based on the photochromism of the donor fluorophores.
- Thijs Roebroek
- , Wim Vandenberg
- & Peter Dedecker
-
Article
| Open Access Melanoma subpopulations that rapidly escape MAPK pathway inhibition incur DNA damage and rely on stress signalling
Melanoma subpopulations that rapidly escape MAPK pathway inhibition incur DNA damage and rely on stress signalling
BRAF inhibitors are used to treat late-stage melanoma patients harbouring BRAF mutations. Here the authors track the responses of single melanoma cells to BRAF inhibitors and show that a subset of cells rapidly escapes drug via non-genetic mechanisms and incurs DNA damage.
- Chen Yang
- , Chengzhe Tian
- & Sabrina L. Spencer
-
Article
| Open Access pHmScarlet is a pH-sensitive red fluorescent protein to monitor exocytosis docking and fusion steps
pHmScarlet is a pH-sensitive red fluorescent protein to monitor exocytosis docking and fusion steps
A number of pH-sensitive fluorescent proteins exist which enable monitoring of some but not all steps of exocytosis. Here the authors engineer a bright, photostable red pH-sensitive fluorescent protein, pHmScarlet, to allow visualisation of the docking and fusion events of exocytosis.
- Anyuan Liu
- , Xiaoshuai Huang
- & Pingyong Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Incorporation of sensing modalities into de novo designed fluorescence-activating proteins
Incorporation of sensing modalities into de novo designed fluorescence-activating proteins
Fluorescent protein reporters based on GFP exist, but have intrinsic disadvantages. Here the authors incorporate pH, Ca2+ and protein–protein interaction sensing modalities into de novo designed mini-fluorescence-activating proteins (mFAPs), with increased photostability and smaller size, which bind a range of DFHBI chromophore variants.
- Jason C. Klima
- , Lindsey A. Doyle
- & David Baker
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid electrochemical detection of coronavirus SARS-CoV-2
Rapid electrochemical detection of coronavirus SARS-CoV-2
Currently the most common method of COVID-19 diagnosis is by qRT-PCR which is slow and requires expensive instrumentation. Here the authors report an electrochemical biosensor based on isothermal rolling circle amplification for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 in clinical samples.
- Thanyarat Chaibun
- , Jiratchaya Puenpa
- & Benchaporn Lertanantawong
-
Comment
| Open Access Illuminating cellular formaldehyde
Illuminating cellular formaldehyde
Writing in Nature communications, Zhu and collaborators reported the development of a genetically encoded sensor for the detection of formaldehyde in cells and tissues. This tool has great potential to transform formaldehyde research; illuminating a cellular metabolite that has remained elusive in live structures.
- Carla Umansky
- , Agustín E. Morellato
- & Lucas B. Pontel
-
Article
| Open Access Genetically encoded formaldehyde sensors inspired by a protein intra-helical crosslinking reaction
Genetically encoded formaldehyde sensors inspired by a protein intra-helical crosslinking reaction
In order to understand the role of formaldehyde in living systems, real-time monitoring is required. Here the authors report a genetically encoded, reaction-based formaldehyde sensor (FAsor) that enables visualisation of formaldehyde in mammalian cells and tissues.
- Rongfeng Zhu
- , Gong Zhang
- & Peng R. Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Disposable silicon-based all-in-one micro-qPCR for rapid on-site detection of pathogens
Disposable silicon-based all-in-one micro-qPCR for rapid on-site detection of pathogens
Designing efficient, rapid and low-cost diagnostic technologies targeting nucleic acids remains a challenge. Here the authors present a disposable silicon-based integrated Point-of-Need transducer produced in a standard wet lab and able to chemically-amplify and detect pathogen-specific sequences of nucleic acids quantitatively in real-time.
- Estefania Nunez-Bajo
- , Alexander Silva Pinto Collins
- & Firat Güder
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasensitive antibody-aptamer plasmonic biosensor for malaria biomarker detection in whole blood
Ultrasensitive antibody-aptamer plasmonic biosensor for malaria biomarker detection in whole blood
Reliable plasmonic biosensors with high throughput and ease of use are highly sought after. Here, the authors report a plasmon-enhanced fluorescence antibody-aptamer biosensor based on a gold nanoparticle array, and demonstrate its use for effective specific detection of a malaria marker, at femtomolar level, in whole blood.
- Antonio Minopoli
- , Bartolomeo Della Ventura
- & Raffaele Velotta
-
Article
| Open Access Client proximity enhancement inside cellular membrane-less compartments governed by client-compartment interactions
Client proximity enhancement inside cellular membrane-less compartments governed by client-compartment interactions
Membrane-less organelles or compartments are considered to be dynamic reaction centers for spatiotemporal control of diverse cellular processes. Here authors report quantitative measurements of changes in protein interactions for the proteins recruited into membrane-less compartments (termed client proteins) in living cells.
- Daesun Song
- , Yongsang Jo
- & Yongwon Jung
-
Article
| Open Access A molecular sensor to quantify the localization of proteins, DNA and nanoparticles in cells
A molecular sensor to quantify the localization of proteins, DNA and nanoparticles in cells
Determining the trafficking of intracellular material is commonly done by colocalisation analysis using microscopy. Here the authors monitor trafficking of select cargo by measuring the conversion of quenched SNAP-tag substrates by subcellularly-localised SNAP-tag and detection by flow cytometry.
- Laura I. FitzGerald
- , Luigi Aurelio
- & Angus P. R. Johnston
-
Article
| Open Access Two-color nanoscopy of organelles for extended times with HIDE probes
Two-color nanoscopy of organelles for extended times with HIDE probes
High density environmentally sensitive (HIDE) probes allow for long time-lapse super-resolution imaging of live cells. Here the authors develop a second HIDE probe with a bio-orthogonal labelling strategy to enable two-color nanoscopy of two organelles over extended periods.
- Ling Chu
- , Jonathan Tyson
- & Derek K. Toomre
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplexed Optical Sensors in Arrayed Islands of Cells for multimodal recordings of cellular physiology
Multiplexed Optical Sensors in Arrayed Islands of Cells for multimodal recordings of cellular physiology
Existing fluorescent protein-based sensor measurements are limited to 4 or fewer simultaneously recorded modalities due to spectral overlap. Here the authors introduce Multiplexed Optical Sensors in Arrayed Islands of Cells (MOSAIC), which enables parallel recording of tens of physiological parameters using dense arrays of cell islands, each expressing a different fluorescent sensor.
- Christopher A. Werley
- , Stefano Boccardo
- & Adam E. Cohen
-
Article
| Open Access A STING-based biosensor affords broad cyclic dinucleotide detection within single living eukaryotic cells
A STING-based biosensor affords broad cyclic dinucleotide detection within single living eukaryotic cells
Cyclic dinucleotides are conserved second messengers but current detection methods are limited. Here the authors engineer a Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) based biosensor, BioSTING, which gives real-time in vitro detection of these nucleotides.
- Alex J. Pollock
- , Shivam A. Zaver
- & Joshua J. Woodward
-
Article
| Open Access A general approach to engineer positive-going eFRET voltage indicators
A general approach to engineer positive-going eFRET voltage indicators
Genetically encoded voltage indicators (GEVIs) allow visualisation of fast action potentials in neurons but most are bright at rest and dimmer during an action potential. Here, the authors engineer electrochromic FRET GEVIs with fast, bright and positive-going fluorescence signals for in vivo imaging.
- Ahmed S. Abdelfattah
- , Rosario Valenti
- & Eric R. Schreiter
-
Article
| Open Access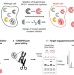 Chemical genetics strategy to profile kinase target engagement reveals role of FES in neutrophil phagocytosis
Chemical genetics strategy to profile kinase target engagement reveals role of FES in neutrophil phagocytosis
Chemical tools to monitor drug-target engagement of endogenous enzymes are essential for preclinical target validation. Here, the authors present a chemical genetics strategy to study target engagement of endogenous kinases, achieving specific labeling and inactivation of FES kinase to provide insights into FES’ role in neutrophil phagocytosis.
- Tom van der Wel
- , Riet Hilhorst
- & Mario van der Stelt
-
Article
| Open Access Single-atom Ni-N4 provides a robust cellular NO sensor
Single-atom Ni-N4 provides a robust cellular NO sensor
The monitoring of nitric oxide is important to a number of disease states and biomedical applications. Here, the authors report on a single nickel atom catalyst based sensor for detecting nitric oxide production from cells.
- Min Zhou
- , Ying Jiang
- & Lanqun Mao
-
Article
| Open Access A deep-learned skin sensor decoding the epicentral human motions
A deep-learned skin sensor decoding the epicentral human motions
Real-time monitoring human motions normally demands connecting a large number of sensors in a complicated network. To make it simpler, Kim et al. decode the motion of fingers using a flexible sensor attached on wrist that measures skin deformation with the help of a deep-learning architecture.
- Kyun Kyu Kim
- , InHo Ha
- & Seung Hwan Ko
-
Article
| Open Access A pocket-escaping design to prevent the common interference with near-infrared fluorescent probes in vivo
A pocket-escaping design to prevent the common interference with near-infrared fluorescent probes in vivo
Near-infrared fluorescent probes hold great potential for biomedical imaging but most bind to albumin, generating unspecific fluorescence. Here the authors identify the acceptor (A) group as responsible and design a new A group that avoids capture by albumin, and apply it to imaging liver fibrosis in vivo.
- Panfei Xing
- , Yiming Niu
- & Chunming Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Developing a highly efficient hydroxytyrosol whole-cell catalyst by de-bottlenecking rate-limiting steps
Developing a highly efficient hydroxytyrosol whole-cell catalyst by de-bottlenecking rate-limiting steps
Whole-cell catalyst-based hydroxytyrosol production is low. Here, the authors increase the efficiency of its production in E. coli by de-bottlenecking two enzymatic steps catalyzed by monooxygenase and tyramine oxidase using structure-based enzyme redesign or in vivo-directed evolution with the aid of a newly developed biosensor.
- Jun Yao
- , Yang He
- & Shuang-Yan Tang
-
Article
| Open Access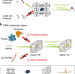 Size-selective molecular recognition based on a confined DNA molecular sieve using cavity-tunable framework nucleic acids
Size-selective molecular recognition based on a confined DNA molecular sieve using cavity-tunable framework nucleic acids
Size-selective discrimination is an issue in biosensing. Here, the authors report on a size selective DNA nanocage which excludes agents based on size and protects the probes against degradation, and demonstrate the discrimination between mature and precursor miRNA.
- Xiaoyi Fu
- , Guoliang Ke
- & Weihong Tan
-
Article
| Open Access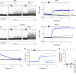 Optogenetic manipulation of calcium signals in single T cells in vivo
Optogenetic manipulation of calcium signals in single T cells in vivo
The ability to manipulate and monitor calcium signaling in cells in vivo would provide insights into signaling in an endogenous context. Here the authors develop a two-photon-responsive calcium actuator and reporter combination to monitor the effect of calcium actuation on T cell migration, adhesion and chemokine release in vivo.
- Armelle Bohineust
- , Zacarias Garcia
- & Philippe Bousso
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene-based sensing of oxygen transport through pulmonary membranes
Graphene-based sensing of oxygen transport through pulmonary membranes
Changes in the pulmonary membrane, caused by bacterial infection, form part of the pathology of pneumonia. Here, the authors report on a graphene-based oxygen sensor which is used along with X-ray diffraction and AFM to measure the structural changes and changes in oxygen permeability of pulmonary membranes associated with bacterial pneumonia.
- Mijung Kim
- , Marilyn Porras-Gomez
- & Cecilia Leal
-
Article
| Open Access CMOS-based bio-image sensor spatially resolves neural activity-dependent proton dynamics in the living brain
CMOS-based bio-image sensor spatially resolves neural activity-dependent proton dynamics in the living brain
Protons have been discovered to play a role in neuronal signaling, but current methods to measure pH in the brain of animal models are limited. Here the authors develop a miniaturized proton image sensor that fits into a living mouse brain and can measure pH changes at micrometer and millisecond resolution scales.
- Hiroshi Horiuchi
- , Masakazu Agetsuma
- & Junichi Nabekura
-
Article
| Open Access Elucidating target specificity of the taccalonolide covalent microtubule stabilizers employing a combinatorial chemical approach
Elucidating target specificity of the taccalonolide covalent microtubule stabilizers employing a combinatorial chemical approach
Taccalonolide microtubule stabilizers covalently bind β-tubulin and overcome taxane resistance mechanisms. Here, the authors synthesized fluorogenic taccalonolide probes and investigated the specificity of taccalonolide binding to β-tubulin and the molecular interactions between drug and target,
- Lin Du
- , Samantha S. Yee
- & April L. Risinger
-
Article
| Open Access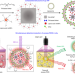 Photosynthesis-inspired H2 generation using a chlorophyll-loaded liposomal nanoplatform to detect and scavenge excess ROS
Photosynthesis-inspired H2 generation using a chlorophyll-loaded liposomal nanoplatform to detect and scavenge excess ROS
Hydrogen can be used to reduce the concentration of reactive oxygen species (ROS), but its delivery to diseased tissues is challenging due to its low solubility. Here the authors develop a photosynthesis-inspired FRET nanocomplex to detect and scavenge local excess of ROS in the tissue using photocatalytic hydrogen production.
- Wei-Lin Wan
- , Bo Tian
- & Hsing-Wen Sung
-
Article
| Open Access An artificial metalloenzyme biosensor can detect ethylene gas in fruits and Arabidopsis leaves
An artificial metalloenzyme biosensor can detect ethylene gas in fruits and Arabidopsis leaves
Existing methods to detect ethylene in plant tissue typically require gas chromatography or use ethylene-dependent gene expression as a proxy. Here Vong et al. show that an artificial metalloenzyme-based ethylene probe can be used to detect ethylene in plants with improved spatiotemporal resolution.
- Kenward Vong
- , Shohei Eda
- & Katsunori Tanaka
-
Article
| Open Access Thermodynamics and kinetics guided probe design for uniformly sensitive and specific DNA hybridization without optimization
Thermodynamics and kinetics guided probe design for uniformly sensitive and specific DNA hybridization without optimization
Optimisation of nucleic acid probes and blocker strands can be laborious. Here the authors construct a theoretical model of competitive DNA hybridisation to design DNA probes for optimisation-free mutation detection.
- Xin Chen
- , Na Liu
- & Xianjin Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Simultaneous measurement of excitation-contraction coupling parameters identifies mechanisms underlying contractile responses of hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes
Simultaneous measurement of excitation-contraction coupling parameters identifies mechanisms underlying contractile responses of hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes
Cardiomyocytes obtained from human induced pluripotent stem cells are increasingly used for drug testing, but they are not always predictive of the heart contractile responses. Here the authors develop a method to measure cytosolic calcium, action potentials and contraction simultaneously, to achieve higher sensitivity for drug screenings.
- Berend J. van Meer
- , Ana Krotenberg
- & Christine L. Mummery
-
Article
| Open Access Electrical pulse-induced electrochemical biosensor for hepatitis E virus detection
Electrical pulse-induced electrochemical biosensor for hepatitis E virus detection
Detection of viral biomarkers is important for disease treatment and prevention. Here, the authors report on a system that uses an electrical pulse-induced electrochemical sensor for the detection of hepatitis E virus, and demonstrate potential application of the device.
- Ankan Dutta Chowdhury
- , Kenshin Takemura
- & Enoch Y. Park
-
Article
| Open Access Degron-tagged reporters probe membrane topology and enable the specific labelling of membrane-wrapped structures
Degron-tagged reporters probe membrane topology and enable the specific labelling of membrane-wrapped structures
Visualising certain organelles and their dynamics is challenging in living cells. Here the authors co-opt selective degradation to label membrane-bound compartments in worm embryos and mammalian cells, revealing membrane topology during cell division.
- Katharina B. Beer
- , Gholamreza Fazeli
- & Ann M. Wehman
-
Article
| Open Access A fast and specific fluorescent probe for thioredoxin reductase that works via disulphide bond cleavage
A fast and specific fluorescent probe for thioredoxin reductase that works via disulphide bond cleavage
Thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) plays a crucial part in regulating cellular redox homeostasis. Here, the authors developed a fluorescent probe composed of a five-membered disulphide, a coumarin fluorophore and a urea linker that detects TrxR activity with fast response and high selectivity.
- Xinming Li
- , Baoxin Zhang
- & Jianguo Fang

 Absolute measurement of cellular activities using photochromic single-fluorophore biosensors and intermittent quantification
Absolute measurement of cellular activities using photochromic single-fluorophore biosensors and intermittent quantification