Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access An index of access to essential infrastructure to identify where physical distancing is impossible
An index of access to essential infrastructure to identify where physical distancing is impossible
Lack of private infrastructure remains a major challenge potentially hampering a societies’ ability to contain the transmission of communicable diseases. Areas at high risk in Africa are identified based on access to essential basic infrastructure.
- Isabel Günther
- , Kenneth Harttgen
- & Jürg Utzinger
-
Article
| Open Access A federated graph neural network framework for privacy-preserving personalization
A federated graph neural network framework for privacy-preserving personalization
Mainstream personalization methods rely on centralized Graph Neural Network learning on global graphs, which have considerable privacy risks due to the privacy-sensitive nature of user data. Here, the authors present a federated GNN framework for both effective and privacy-preserving personalization.
- Chuhan Wu
- , Fangzhao Wu
- & Xing Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Risk caused by the propagation of earthquake losses through the economy
Risk caused by the propagation of earthquake losses through the economy
The integration of risk analysis and spatial CGE modeling frameworks allowed for measuring the direct and indirect consequences of extreme events via novel probabilistic risk indicators which incorporate elements of uncertainty and systemic effects
- J. A. León
- , M. Ordaz
- & I. F. Araújo
-
Article
| Open Access Modelling armed conflict risk under climate change with machine learning and time-series data
Modelling armed conflict risk under climate change with machine learning and time-series data
Using machine learning, the authors reveal that stable background conditions explain most variation in armed conflict risk worldwide. Positive temperature deviations and precipitation extremes also increase the risk of conflict onset and incidence.
- Quansheng Ge
- , Mengmeng Hao
- & Tobias Ide
-
Comment
| Open AccessA broader perspective on the economics of malaria prevention and the potential impact of SARS-CoV-2
Economic evaluations of public health interventions to prevent malaria should consider the adoption of wider perspectives and the inclusion of non-health impacts, particularly economic development outcomes, such as education. This is especially relevant in malaria elimination settings and in the context of the current SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.
- Elisa Sicuri
- , Francesco Ramponi
- & Francisco Saúte
-
Article
| Open Access Using sero-epidemiology to monitor disparities in vaccination and infection with SARS-CoV-2
Using sero-epidemiology to monitor disparities in vaccination and infection with SARS-CoV-2
Continued monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 at the population level is important for identifying at-risk groups. Here the authors analyse data from a serological surveillance platform in San Francisco and find considerable variation in infection and vaccination history by race/ethnicity and socioeconomic status.
- Isobel Routledge
- , Saki Takahashi
- & Isabel Rodríguez-Barraquer
-
Article
| Open Access Indigenous oyster fisheries persisted for millennia and should inform future management
Indigenous oyster fisheries persisted for millennia and should inform future management
‘Commercial fisheries have decimated keystone species, including oysters in the past 200 years. Here, the authors examine how Indigenous oyster harvest in North America and Australia was managed across 10,000 years, advocating for effective future stewardship of oyster reefs by centering Indigenous peoples.’
- Leslie Reeder-Myers
- , Todd J. Braje
- & Torben C. Rick
-
-
Article
| Open Access Accuracy prompts are a replicable and generalizable approach for reducing the spread of misinformation
Accuracy prompts are a replicable and generalizable approach for reducing the spread of misinformation
Prompting people to consider accuracy can improve the quality of news they share online. Here, using an internal meta-analysis, the authors show that this effect is replicable and generalizes across headlines, types of accuracy prompt, and various participant characteristics.
- Gordon Pennycook
- & David G. Rand
-
Article
| Open Access A computational theory of the subjective experience of flow
A computational theory of the subjective experience of flow
Flow is a desired but elusive state characterized by the subjective experience of immersion and engagement in an activity. Here, the authors develop and empirically validate a formal model that specifies variables and computations involved in the subjective experience of flow.
- David E. Melnikoff
- , Ryan W. Carlson
- & Paul E. Stillman
-
Article
| Open Access Economic shocks predict increases in child wasting prevalence
Economic shocks predict increases in child wasting prevalence
Economic shocks may lead to food insecurity and therefore acute child malnutrition (wasting). Here, the authors use data from Demographic Health Surveys to estimate impacts of past economic shocks on wasting and project possible effects of shocks related to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Derek D. Headey
- & Marie T. Ruel
-
Article
| Open Access Cumulative lifetime stressor exposure assessed by the STRAIN predicts economic ambiguity aversion
Cumulative lifetime stressor exposure assessed by the STRAIN predicts economic ambiguity aversion
Uncertainty is a factor in most decisions. Here the authors quantify tolerance for two forms of economic uncertainty—risk and ambiguity—and show that greater lifetime stressor exposure (as assessed by a comprehensive lifetime stressor exposure inventory) was associated with higher aversion to decisions involving ambiguity, but not risk.
- Candace M. Raio
- , Benjamin B. Lu
- & Paul Glimcher
-
Comment
| Open Access Community voices: NIH working toward inclusive excellence by promoting and supporting women in science
Community voices: NIH working toward inclusive excellence by promoting and supporting women in science
The U. S. National Institutes of Health is committed to addressing gender discrimination and fostering inclusive excellence, which is critical for the advancement of creativity and innovation in science. Strategies and processes aimed at achieving these goals are discussed.
- Kelly G. Ten Hagen
- , Carrie Wolinetz
- & Marie A. Bernard
-
Comment
| Open AccessCommunity voices: Achieving real diversity in STEM requires the ability to transform institutions
Resilience is often invoked to address systemic marginalization (e.g. racism) in academia but inadvertently maintains harmful systems. We argue that the ability to transform systems, as opposed to persevering within them, must be prioritized to make real, lasting change.
- Jory C. Lerback
- , Monique M. Holt
- & Stephanie Alvarez
-
Article
| Open Access Identifying regions for enhanced control of gambiense sleeping sickness in the Democratic Republic of Congo
Identifying regions for enhanced control of gambiense sleeping sickness in the Democratic Republic of Congo
Gambiense human African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness or gHAT) has been targeted for elimination of transmission by 2030. Here, the authors project impacts of gHAT interventions in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and derive a priority list of health zones requiring enhanced control to achieve this target.
- Ching-I Huang
- , Ronald E. Crump
- & Kat S. Rock
-
Article
| Open Access Assessing the climate change exposure of foreign direct investment
Assessing the climate change exposure of foreign direct investment
This study finds that foreign firms tend to shy away from countries with higher physical climate risks than do local firms. Chinese FDI is significantly more exposed to most physical climate risks than non-Chinese FDI across countries.
- Xia Li
- & Kevin P. Gallagher
-
Article
| Open Access Geographically dispersed zoonotic tuberculosis in pre-contact South American human populations
Geographically dispersed zoonotic tuberculosis in pre-contact South American human populations
‘Pre-contact era humans from coastal South America were infected by Mycobacterium pinnipedii, most likely, through contact with infected pinnipeds. Here, the authors investigate the presence of M. pinnipedii in pre-contact era humans from inland South America and explore potential scenarios of human-to-human or animal-mediated transmission.’
- Åshild J. Vågene
- , Tanvi P. Honap
- & Kirsten I. Bos
-
Comment
| Open Access Resilience-by-Design and Resilience-by-Intervention in supply chains for remote and indigenous communities
Resilience-by-Design and Resilience-by-Intervention in supply chains for remote and indigenous communities
Indigenous and remote communities face difficulties in times of supply chain disruption. Here the authors comment on challenges faced by the Tribal Population of Noepe (Martha’s Vineyard) and argue for the inclusion of Resilience-by-Design and Resilience-by-Intervention in supply chain management.
- Emerson Mahoney
- , Maureen Golan
- & Igor Linkov
-
Article
| Open Access Modeling assortative mating and genetic similarities between partners, siblings, and in-laws
Modeling assortative mating and genetic similarities between partners, siblings, and in-laws
Assortative mating could violate the assumption of random mating used in many genetic studies. Here, the authors study more than 25,000 Norwegian families to find genetic similarity between partners, siblings, and in-laws in genetic factors related to educational attainment, height, and depression.
- Fartein Ask Torvik
- , Espen Moen Eilertsen
- & Eivind Ystrom
-
Article
| Open Access Cost-effectiveness of sleeping sickness elimination campaigns in five settings of the Democratic Republic of Congo
Cost-effectiveness of sleeping sickness elimination campaigns in five settings of the Democratic Republic of Congo
Gambiense human African trypanosomiasis has been targeted for elimination of transmission by 2030. Here, the authors assess the cost-effectiveness of elimination strategies in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and find that those which lead to elimination of transmission might also be considered cost-effective by conventional thresholds.
- Marina Antillon
- , Ching-I Huang
- & Fabrizio Tediosi
-
Article
| Open Access Cooperation in alternating interactions with memory constraints
Cooperation in alternating interactions with memory constraints
In many instances of reciprocity, individuals cooperate in turns. Here, the authors analyze the equilibria and the dynamics of such alternating games, and in particular describe all strategies with one-round memory that maintain cooperation.
- Peter S. Park
- , Martin A. Nowak
- & Christian Hilbe
-
Comment
| Open AccessRelevance of international partnerships in the implementation of the UN Sustainable Development Goals
Sustainable Development Goal 17 focuses on partnerships that can enable the achievement of other SDGs. In this comment the authors examine the obstacles to the success of SDG 17 and suggest measures to overcome these.
- Walter Leal Filho
- , Tony Wall
- & Julianna Ramirez
-
Article
| Open Access Cost-effectiveness of routine adolescent vaccination with an M72/AS01E-like tuberculosis vaccine in South Africa and India
Cost-effectiveness of routine adolescent vaccination with an M72/AS01E-like tuberculosis vaccine in South Africa and India
The M72/AS01E tuberculosis vaccine has shown 50% efficacy in preventing pulmonary TB disease in infected 18–50 year olds. Here, the authors demonstrate that, in most scenarios modelled, vaccination of adolescents would also be cost effective in two high incidence settings, South Africa and India.
- Rebecca C. Harris
- , Matthew Quaife
- & Richard G. White
-
Article
| Open Access Self-reported COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy and uptake among participants from different racial and ethnic groups in the United States and United Kingdom
Self-reported COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy and uptake among participants from different racial and ethnic groups in the United States and United Kingdom
The authors show differences in self-reported vaccine hesitancy and uptake among participants from different racial and ethnic groups in the United States and in the United Kingdom during the initial phase of the COVID-19 vaccine rollout.
- Long H. Nguyen
- , Amit D. Joshi
- & Andrew T. Chan
-
Article
| Open Access National identity predicts public health support during a global pandemic
National identity predicts public health support during a global pandemic
Understanding collective behaviour is an important aspect of managing the pandemic response. Here the authors show in a large global study that participants that reported identifying more strongly with their nation reported greater engagement in public health behaviours and support for public health policies in the context of the pandemic.
- Jay J. Van Bavel
- , Aleksandra Cichocka
- & Paulo S. Boggio
-
Article
| Open Access Interaction data are identifiable even across long periods of time
Interaction data are identifiable even across long periods of time
Large amounts of interaction data are collected by messaging apps, mobile phone carriers, and social media. Creţu et al. propose a behavioral profiling attack model and show that the stability of people’s interaction networks over time can allow individuals to be re-identified in interaction datasets.
- Ana-Maria Creţu
- , Federico Monti
- & Yves-Alexandre de Montjoye
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access On the difficulty of achieving Differential Privacy in practice: user-level guarantees in aggregate location data
On the difficulty of achieving Differential Privacy in practice: user-level guarantees in aggregate location data
- Florimond Houssiau
- , Luc Rocher
- & Yves-Alexandre de Montjoye
-
Article
| Open Access Options for reforming agricultural subsidies from health, climate, and economic perspectives
Options for reforming agricultural subsidies from health, climate, and economic perspectives
Springmann and Freund use an integrated modelling framework to show that coupling agricultural subsidies to producing foods with beneficial health and environmental characteristics can improve population health and lower greenhouse gas emissions without reducing economic welfare.
- M. Springmann
- & F. Freund
-
Article
| Open Access Trend towards virtual and hybrid conferences may be an effective climate change mitigation strategy
Trend towards virtual and hybrid conferences may be an effective climate change mitigation strategy
Moving conferences from in-person to virtual and hybrid modes may have emissions reductions benefits. Here the authors find that the switch to virtual and hybrid conferencing reduces the carbon footprint by 94% when it comes to the switch to virtual conferencing, and 67% for hybrid conferences with carefully selected hubs.
- Yanqiu Tao
- , Debbie Steckel
- & Fengqi You
-
Article
| Open Access Brain network coupling associated with cognitive performance varies as a function of a child’s environment in the ABCD study
Brain network coupling associated with cognitive performance varies as a function of a child’s environment in the ABCD study
Previous research suggests that, for children and adults, there is an association between better performance on cognitive tests and less functional connectivity between two brain networks. Here, the authors find that this association does not hold in a sample of children from households in poverty, highlighting the need for more diverse samples to incorporate a range of childhood environments in developmental cognitive neuroscience.
- Monica E. Ellwood-Lowe
- , Susan Whitfield-Gabrieli
- & Silvia A. Bunge
-
Article
| Open Access Financial stability in response to climate change in a northern temperate economy
Financial stability in response to climate change in a northern temperate economy
Climate change will impact the global economy. Here, the authors propose a framework to evaluate its effect on economies across multiple regional and temporal scales, and project decreased financial stability in a northern temperate economy.
- Kayla Stan
- , Graham A. Watt
- & Arturo Sanchez-Azofeifa
-
Article
| Open Access A meritocratic network formation model for the rise of social media influencers
A meritocratic network formation model for the rise of social media influencers
Dynamical development process of various social network platforms shows emergence and transformation of user communities. The authors model social network formation processes considering the meritocratic perspective, where users make their decisions based on the user-generated content.
- Nicolò Pagan
- , Wenjun Mei
- & Florian Dörfler
-
Article
| Open Access The reduction of race and gender bias in clinical treatment recommendations using clinician peer networks in an experimental setting
The reduction of race and gender bias in clinical treatment recommendations using clinician peer networks in an experimental setting
Race and gender bias in healthcare contribute to health disparities. Here the authors show in an experimental setting that structured information sharing networks among clinicians can reduce race and gender bias in medical decisions.
- Damon Centola
- , Douglas Guilbeault
- & Jingwen Zhang
-
Comment
| Open Access Impacts of climate change to African indigenous communities and examples of adaptation responses
Impacts of climate change to African indigenous communities and examples of adaptation responses
Climate change negatively impacts the livelihoods of indigenous communities across the world, including those located on the African continent. This Comment reports on how five African indigenous communities have been impacted by climate change and the adopted adaptation mechanisms.
- Walter Leal Filho
- , Newton R. Matandirotya
- & Richard Achia Mbih
-
Article
| Open Access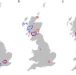 The geography of intergenerational social mobility in Britain
The geography of intergenerational social mobility in Britain
Intergenerational preconditions and historical conferment of opportunity play a role in social mobility. This study considers the geography of relative deprivation to show how different family groups across Great Britain experience different intergenerational outcomes.
- Paul A. Longley
- , Justin van Dijk
- & Tian Lan
-
Article
| Open Access ENSO impacts child undernutrition in the global tropics
ENSO impacts child undernutrition in the global tropics
The El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) influences the weather around the world and, therefore, has strong impacts on society. Here, the authors show that ENSO is associated with child nutrition in many countries, with warmer El Niño conditions leading to more child undernutrition in large parts of the developing world.
- Jesse K. Anttila-Hughes
- , Amir S. Jina
- & Gordon C. McCord
-
Article
| Open Access Scientific prizes and the extraordinary growth of scientific topics
Scientific prizes and the extraordinary growth of scientific topics
Scientific revolutions have famously inspired scientists and innovation but large-scale analyses of scientific revolutions in modern science are rare. Here, the authors investigate one possible factor connected with a topic’s extraordinary growth—scientific prizes.
- Ching Jin
- , Yifang Ma
- & Brian Uzzi
-
Article
| Open Access Shifting parental beliefs about child development to foster parental investments and improve school readiness outcomes
Shifting parental beliefs about child development to foster parental investments and improve school readiness outcomes
Parents’ investments in their children are a critical input in the production of early skills, yet those investments differ across socioeconomic backgrounds. Here the authors show that variations in parental beliefs about the impact of such investments can be one of the sources of investment disparities, and report interventions that can potentially shift those beliefs.
- John A. List
- , Julie Pernaudet
- & Dana L. Suskind
-
Article
| Open Access How social relationships shape moral wrongness judgments
How social relationships shape moral wrongness judgments
Moral judgments depend on relational context, with different normative cooperative expectations – relational norms – embedded in different social relationships, such as parent-child, romantic partners, siblings, or acquaintances. Here, the authors show how relational norms for care, hierarchy, reciprocity, and mating are embedded in a set of everyday social relationships in the United States, and use this information to predict out-of-sample moral judgments in relational context.
- Brian D. Earp
- , Killian L. McLoughlin
- & Molly J. Crockett
-
Article
| Open Access Collective patterns of social diffusion are shaped by individual inertia and trend-seeking
Collective patterns of social diffusion are shaped by individual inertia and trend-seeking
Social convention change due to diffusion is often described by agent-based models focusing on the role of social coordination. In this work the authors uncover two additional individual-level mechanisms, trend-seeking and inertia, that can critically shape the collective behavior of the population.
- Mengbin Ye
- , Lorenzo Zino
- & Ming Cao
-
Article
| Open Access Collaborative management of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam increases economic benefits and resilience
Collaborative management of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam increases economic benefits and resilience
Integrating river system and economy-wide models in a dynamic, iterative, bidirectional fashion allows assessing some economic impacts of interventions in river systems. Here the authors use this framework to compare water resources management strategies for the Nile in a quest for efficient use of the river’s limited and stressed water resources.
- Mohammed Basheer
- , Victor Nechifor
- & Julien J. Harou
-
Article
| Open Access Neutral bots probe political bias on social media
Neutral bots probe political bias on social media
Social media platforms moderating misinformation have been accused of political bias. Here, the authors use neutral social bots to show that, while there is no strong evidence for such a bias, the content to which Twitter users are exposed depends strongly on the political leaning of early Twitter connections.
- Wen Chen
- , Diogo Pacheco
- & Filippo Menczer
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence from a long-term experiment that collective risks change social norms and promote cooperation
Evidence from a long-term experiment that collective risks change social norms and promote cooperation
Large-scale cooperation is needed to reduce existential risks like those posed by pandemics and climate change. Here the authors demonstrate that social norms can emerge and sustain cooperation in situations of collective risk and that the level of risk influences the strength of the norms.
- Aron Szekely
- , Francesca Lipari
- & Giulia Andrighetto
-
Article
| Open Access Blue food demand across geographic and temporal scales
Blue food demand across geographic and temporal scales
Global demand for “blue food” is growing. In this quantitative synthesis, the authors analyse global seafood demand and project trends to 2050, finding considerable regional variation in the relationship between wealth and consumption.
- Rosamond L. Naylor
- , Avinash Kishore
- & Beatrice Crona
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding the onset of hot streaks across artistic, cultural, and scientific careers
Understanding the onset of hot streaks across artistic, cultural, and scientific careers
Despite their ubiquitous nature across a wide range of creative domains, it remains unclear if there is any regularity underlying the beginning of successful periods in a career. Here, the authors develop computational methods to trace the career outputs of artists, film directors, and scientists and explore how they move in their creative space along their career trajectory.
- Lu Liu
- , Nima Dehmamy
- & Dashun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Climatic windows for human migration out of Africa in the past 300,000 years
Climatic windows for human migration out of Africa in the past 300,000 years
It is still unclear when and by which route modern humans expanded out of Africa. Here, Beyer et al. use paleoclimate reconstructions and estimates of human precipitation requirements to evaluate the survivability of spatial and temporal migration corridors to Eurasia over the last 300,000 years.
- Robert M. Beyer
- , Mario Krapp
- & Andrea Manica
-
Article
| Open Access Professional actors demonstrate variability, not stereotypical expressions, when portraying emotional states in photographs
Professional actors demonstrate variability, not stereotypical expressions, when portraying emotional states in photographs
It has long been hypothesized that certain emotional states are universally expressed with specific facial movements. Here the authors provide evidence that facial expressions of those emotional states are, in fact, varied among individuals rather than stereotyped.
- Tuan Le Mau
- , Katie Hoemann
- & Lisa Feldman Barrett
-
Comment
| Open Access Global catastrophic risk from lower magnitude volcanic eruptions
Global catastrophic risk from lower magnitude volcanic eruptions
Globalisation supports the clustering of critical infrastructure systems, sometimes in proximity to lower-magnitude (VEI 3–6) volcanic centres. In this emerging risk landscape, moderate volcanic eruptions might have cascading, catastrophic effects. Risk assessments ought to be considered in this light.
- Lara Mani
- , Asaf Tzachor
- & Paul Cole
-
Article
| Open Access Grassland ecological compensation policy in China improves grassland quality and increases herders’ income
Grassland ecological compensation policy in China improves grassland quality and increases herders’ income
China has introduced a payment-for-ecosytsem-services program called GECP which is focused on pastoral communities in grassland areas. Here, the authors combine remote sensing and household survey data to find small improvement in grassland quality and a significant positive effects on the income of herders.
- Lingling Hou
- , Fang Xia
- & Scott Rozelle

 Universality out of order
Universality out of order