Featured
-
-
Article |
 Coherent control of a surface structural phase transition
Coherent control of a surface structural phase transition
A structural phase transition from metal to insulator on a solid surface is controlled by an ultrafast sequence of optical pulses.
- Jan Gerrit Horstmann
- , Hannes Böckmann
- & Claus Ropers
-
Article |
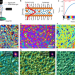 Observation of branched flow of light
Observation of branched flow of light
Branched flow of light is experimentally observed inside a thin soap membrane, where smooth variations of the membrane thickness transform the light beam into branched filaments of enhanced intensity that keep dividing as the waves propagate.
- Anatoly Patsyk
- , Uri Sivan
- & Miguel A. Bandres
-
Article |
 Laser picoscopy of valence electrons in solids
Laser picoscopy of valence electrons in solids
Laser-generated high-harmonic emission is used to image the valence potential and electron density in magnesium fluoride and calcium fluoride at the picometre scale, enabling direct probing of material properties.
- H. Lakhotia
- , H. Y. Kim
- & E. Goulielmakis
-
Article |
 Frequency combs induced by phase turbulence
Frequency combs induced by phase turbulence
Wave destabilization is demonstrated in semiconductor ring lasers operating at low pumping levels, where ultrafast gain recovery leads to the emergence of a frequency comb regime owing to phase turbulence.
- Marco Piccardo
- , Benedikt Schwarz
- & Federico Capasso
-
Article |
 Topological polaritons and photonic magic angles in twisted α-MoO3 bilayers
Topological polaritons and photonic magic angles in twisted α-MoO3 bilayers
The photonic dispersion of phonon polaritons in bilayers of α-phase molybdenum trioxide can undergo tunable topological transitions at magic interlayer twist angles.
- Guangwei Hu
- , Qingdong Ou
- & Andrea Alù
-
Article |
 Controlling free electrons with optical whispering-gallery modes
Controlling free electrons with optical whispering-gallery modes
The coupling between light and relativistic free electrons is enhanced through phase matching of electrons with optical whispering-gallery modes in dielectric microspheres and through extended modal lifetimes.
- Ofer Kfir
- , Hugo Lourenço-Martins
- & Claus Ropers
-
Article |
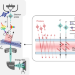 Coherent interaction between free electrons and a photonic cavity
Coherent interaction between free electrons and a photonic cavity
The strong interaction of coherent free electrons with a photonic-crystal cavity enables the measurement of the lifetimes of the cavity modes and provides a technique for multidimensional near-field imaging and spectroscopy.
- Kangpeng Wang
- , Raphael Dahan
- & Ido Kaminer
-
Article |
 Observation of Laughlin states made of light
Observation of Laughlin states made of light
Pairs of photons in the Laughlin state are created by mimicking a fractional quantum Hall system using the synthetic magnetic field induced by a twisted optical cavity and Rydberg-mediated polariton interactions.
- Logan W. Clark
- , Nathan Schine
- & Jonathan Simon
-
Article |
 Spin squeezing of 1011 atoms by prediction and retrodiction measurements
Spin squeezing of 1011 atoms by prediction and retrodiction measurements
A squeezed collective state of 1011 rubidium atoms is generated by quantum non-demolition measurements, and the accuracy of the estimation of their collective spin is improved using past quantum state retrodiction.
- Han Bao
- , Junlei Duan
- & Yanhong Xiao
-
Article |
 Exploring dynamical phase transitions with cold atoms in an optical cavity
Exploring dynamical phase transitions with cold atoms in an optical cavity
Interactions between light and an ensemble of strontium atoms in an optical cavity can serve as a testbed for studying dynamical phase transitions, which are currently not well understood.
- Juan A. Muniz
- , Diego Barberena
- & James K. Thompson
-
Article |
 Control and single-shot readout of an ion embedded in a nanophotonic cavity
Control and single-shot readout of an ion embedded in a nanophotonic cavity
Single ytterbium ion qubits in nanophotonic cavities have long coherence times and can be optically read out in a single shot, establishing them as excellent candidates for optical quantum networks.
- Jonathan M. Kindem
- , Andrei Ruskuc
- & Andrei Faraon
-
Article |
 Experimental demonstration of memory-enhanced quantum communication
Experimental demonstration of memory-enhanced quantum communication
A solid-state spin memory is used to demonstrate quantum repeater functionality, which has the potential to overcome photon losses involved in long-distance transmission of quantum information.
- M. K. Bhaskar
- , R. Riedinger
- & M. D. Lukin
-
Article |
 Entanglement of two quantum memories via fibres over dozens of kilometres
Entanglement of two quantum memories via fibres over dozens of kilometres
The entanglement of two atomic-ensemble quantum memories via optical fibres, enabled by the use of cavity enhancement and quantum frequency conversion, is demonstrated over dozens of kilometres.
- Yong Yu
- , Fei Ma
- & Jian-Wei Pan
-
Article |
 Attosecond pulse shaping using a seeded free-electron laser
Attosecond pulse shaping using a seeded free-electron laser
Generation of intense attosecond waveforms with independently controllable amplitude and phase is performed by using a seeded free-electron laser.
- Praveen Kumar Maroju
- , Cesare Grazioli
- & Giuseppe Sansone
-
Article |
 Phonon heat transfer across a vacuum through quantum fluctuations
Phonon heat transfer across a vacuum through quantum fluctuations
Conventionally, heat transfer occurs by conduction, convection or radiation, but has also been theoretically predicted to occur through quantum fluctuations across a vacuum; this prediction has now been confirmed experimentally.
- King Yan Fong
- , Hao-Kun Li
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Article |
 A general theoretical and experimental framework for nanoscale electromagnetism
A general theoretical and experimental framework for nanoscale electromagnetism
A general framework for incorporating and correcting for nonclassical electromagnetic phenomena in nanoscale systems is presented.
- Yi Yang
- , Di Zhu
- & Marin Soljačić
-
Article |
 Observation of the exceptional-point-enhanced Sagnac effect
Observation of the exceptional-point-enhanced Sagnac effect
precisely controllable integrated optical gyroscope based on stimulated Brillouin scattering is used to study non-Hermitian physics, revealing a four-fold enhancement of the Sagnac scale factor near exceptional points.
- Yu-Hung Lai
- , Yu-Kun Lu
- & Kerry Vahala
-
Article |
 Non-Hermitian ring laser gyroscopes with enhanced Sagnac sensitivity
Non-Hermitian ring laser gyroscopes with enhanced Sagnac sensitivity
A method based on non-Hermitian singularities, or exceptional points, is established and used to increase the Sagnac scale factor and enhance the sensitivity of ring-laser gyroscopes.
- Mohammad P. Hokmabadi
- , Alexander Schumer
- & Mercedeh Khajavikhan
-
Article |
 A gated quantum dot strongly coupled to an optical microcavity
A gated quantum dot strongly coupled to an optical microcavity
Strong coupling between a gated semiconductor quantum dot and an optical microcavity is observed in an ultralow-loss frequency-tunable microcavity device.
- Daniel Najer
- , Immo Söllner
- & Richard J. Warburton
-
Letter |
 X-ray pumping of the 229Th nuclear clock isomer
X-ray pumping of the 229Th nuclear clock isomer
Excitation to the second excited state of 229Th is used to populate the metastable state 229mTh, enabling accurate determination of the isomer’s energy, half-life and excitation linewidth.
- Takahiko Masuda
- , Akihiro Yoshimi
- & Koji Yoshimura
-
Letter |
 Giant nonreciprocal second-harmonic generation from antiferromagnetic bilayer CrI3
Giant nonreciprocal second-harmonic generation from antiferromagnetic bilayer CrI3
Large second-harmonic generation is observed in antiferromagnetic bilayers of CrI3, providing information about the microscopic origin of layered antiferromagnetism and motivating the use of two-dimensional magnets in nonlinear optical devices.
- Zeyuan Sun
- , Yangfan Yi
- & Shiwei Wu
-
Letter |
 Global entangling gates on arbitrary ion qubits
Global entangling gates on arbitrary ion qubits
Multi-qubit entangling gates are realized by simultaneously driving multiple motional modes of a linear chain of trapped ions with modulated external fields, achieving a fidelity of about 93 per cent with four qubits.
- Yao Lu
- , Shuaining Zhang
- & Kihwan Kim
-
Letter |
 Nonlinear optics in the fractional quantum Hall regime
Nonlinear optics in the fractional quantum Hall regime
Nonlinear optical measurements in a two-dimensional electron system embedded in an optical cavity show enhanced polariton–polariton interactions in the fractional quantum Hall regime.
- Patrick Knüppel
- , Sylvain Ravets
- & Atac Imamoglu
-
Letter |
 Interacting Floquet polaritons
Interacting Floquet polaritons
Frequency modulation is used to create ‘Floquet polaritons’—strongly interacting quasi-particles that exist in a customizable set of modes.
- Logan W. Clark
- , Ningyuan Jia
- & Jonathan Simon
-
Letter |
 Light-wave dynamic control of magnetism
Light-wave dynamic control of magnetism
The magnetic properties of a ferromagnetic layer stack are controlled on attosecond timescales through optically induced spin and orbital momentum transfer, demonstrating a coherent regime of ultrafast magnetism.
- Florian Siegrist
- , Julia A. Gessner
- & Martin Schultze
-
Letter |
 Temporal and spectral fingerprints of ultrafast all-coherent spin switching
Temporal and spectral fingerprints of ultrafast all-coherent spin switching
Antenna-enhanced terahertz pulses ballistically switch spins in antiferromagnetic TmFeO3 with minimal energy dissipation between metastable minima of the anisotropy potential, as characterized by unique temporal and spectral fingerprints.
- S. Schlauderer
- , C. Lange
- & R. Huber
-
Letter |
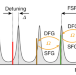 Resonant electro-optic frequency comb
Resonant electro-optic frequency comb
A low-power, fixed microwave signal in combination with an optical-pump signal generates an optical frequency comb that spans the whole wavelength range of the telecommunications C-band, with possible applications ranging from spectroscopy to optical communications.
- Alfredo Rueda
- , Florian Sedlmeir
- & Harald G. L. Schwefel
-
Letter |
 Electric field correlation measurements on the electromagnetic vacuum state
Electric field correlation measurements on the electromagnetic vacuum state
Electro-optic detection in a nonlinear crystal is used to measure coherence properties of vacuum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field and deduce the spectrum of the ground state of electromagnetic radiation.
- Ileana-Cristina Benea-Chelmus
- , Francesca Fabiana Settembrini
- & Jérôme Faist
-
Letter |
 Visualizing vibrational normal modes of a single molecule with atomically confined light
Visualizing vibrational normal modes of a single molecule with atomically confined light
The vibrational normal modes in a single molecule are imaged using tip-enhanced Raman spectromicroscopy performed in the atomistic near-field.
- Joonhee Lee
- , Kevin T. Crampton
- & V. Ara Apkarian
-
Letter |
 Ultrafast spin-lasers
Ultrafast spin-lasers
Room-temperature modulation frequencies exceeding 200 GHz are demonstrated in birefringent semiconductor spin-lasers by coupling the spin of the charge carriers to the light polarization.
- Markus Lindemann
- , Gaofeng Xu
- & Nils C. Gerhardt
-
Letter |
 Measurement of quantum back action in the audio band at room temperature
Measurement of quantum back action in the audio band at room temperature
Future gravitational-wave detectors are expected to be limited by quantum back action, which is now found in the audio band in a low-loss optomechanical system.
- Jonathan Cripe
- , Nancy Aggarwal
- & Thomas Corbitt
-
Letter |
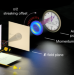 Attosecond angular streaking and tunnelling time in atomic hydrogen
Attosecond angular streaking and tunnelling time in atomic hydrogen
Simulation and measurement of the photoionization of atomic hydrogen at attosecond resolution confirm that the tunnelling of the ejected electron is instantaneous.
- U. Satya Sainadh
- , Han Xu
- & I. V. Litvinyuk
-
Letter |
 Random anti-lasing through coherent perfect absorption in a disordered medium
Random anti-lasing through coherent perfect absorption in a disordered medium
Coherent perfect absorption in a disordered medium is demonstrated experimentally in the microwave regime through the realization of a random anti-laser that absorbs engineered radiation with near-perfect efficiency.
- Kevin Pichler
- , Matthias Kühmayer
- & Stefan Rotter
-
Letter |
 Photonic topological insulator in synthetic dimensions
Photonic topological insulator in synthetic dimensions
A spatially oscillating two-dimensional waveguide array is used to realize a photonic topological insulator in synthetic dimensions with modal-space edge states, unidirectionality and robust topological protection.
- Eran Lustig
- , Steffen Weimann
- & Mordechai Segev
-
Letter |
 Near-field photonic cooling through control of the chemical potential of photons
Near-field photonic cooling through control of the chemical potential of photons
The ‘negative luminescence’ of a reverse-biased photodiode is harnessed to draw thermal energy from a nearby solid object, thereby realizing photonic cooling without the use of coherent laser radiation.
- Linxiao Zhu
- , Anthony Fiorino
- & Pramod Reddy
-
Letter |
 Waveguide-coupled single collective excitation of atomic arrays
Waveguide-coupled single collective excitation of atomic arrays
Waveguide quantum electrodynamics is used to couple a single collective excitation of an atomic array to a nanoscale waveguide; the excitation is stored and later read out, generating guided single photons on demand.
- Neil V. Corzo
- , Jérémy Raskop
- & Julien Laurat
-
Letter |
 The ultrafast Einstein–de Haas effect
The ultrafast Einstein–de Haas effect
Femtosecond time-resolved X-ray diffraction reveals that in the ultrafast demagnitization of ferromagnetic iron, about 80% of the angular momentum lost from the spins is transferred to the lattice on a sub-picosecond timescale.
- C. Dornes
- , Y. Acremann
- & S. L. Johnson
-
Letter |
 An ultrafast symmetry switch in a Weyl semimetal
An ultrafast symmetry switch in a Weyl semimetal
Terahertz light pulses induce transitions between a topological and a trivial phase in the Weyl semimetal WTe2 through an interlayer shear strain.
- Edbert J. Sie
- , Clara M. Nyby
- & Aaron M. Lindenberg
-
Letter |
 Measurement of the Casimir torque
Measurement of the Casimir torque
The theoretically predicted Casimir torque, which causes charge-neutral, birefringent materials to rotate towards a preferred alignment, is measured.
- David A. T. Somers
- , Joseph L. Garrett
- & Jeremy N. Munday
-
Letter |
 Extreme-ultraviolet refractive optics
Extreme-ultraviolet refractive optics
A refractive lens and a refractive prism for extreme-ultraviolet radiation have been developed that use the deflection of the radiation in an inhomogeneous jet of atoms.
- L. Drescher
- , O. Kornilov
- & B. Schütte
-
Letter |
 Atomic clock performance enabling geodesy below the centimetre level
Atomic clock performance enabling geodesy below the centimetre level
Improved techniques allow the measurement of a frequency difference with an uncertainty of the order of 10–19 between two independent atomic optical lattice clocks, suggesting that they may be able to improve state-of-the-art geodetic techniques.
- W. F. McGrew
- , X. Zhang
- & A. D. Ludlow
-
Letter |
 Superfluorescence from lead halide perovskite quantum dot superlattices
Superfluorescence from lead halide perovskite quantum dot superlattices
Cooperative quantum effects in superlattices of quantum dots made of caesium lead halide perovskite give rise to superfluorescence, with the individual emitters interacting coherently to give intense bursts of light.
- Gabriele Rainò
- , Michael A. Becker
- & Thilo Stöferle
-
Letter |
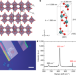 In-plane anisotropic and ultra-low-loss polaritons in a natural van der Waals crystal
In-plane anisotropic and ultra-low-loss polaritons in a natural van der Waals crystal
Observation of the anisotropic propagation of polaritons along the surface of layered, semiconducting α-MoO3 confirms the existence of this phenomenon in natural materials.
- Weiliang Ma
- , Pablo Alonso-González
- & Qiaoliang Bao
-
Letter |
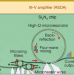 Battery-operated integrated frequency comb generator
Battery-operated integrated frequency comb generator
Integrating an optical Kerr frequency comb source with an electronically excited laser pump produces a battery-powered comb generator that does not require external lasers, moveable optics or laboratory set-ups.
- Brian Stern
- , Xingchen Ji
- & Michal Lipson
-
Letter |
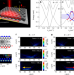 Exciton-polariton topological insulator
Exciton-polariton topological insulator
A part-light, part-matter exciton-polariton topological insulator is created in an array of semiconductor microcavities.
- S. Klembt
- , T. H. Harder
- & S. Höfling
-
Letter |
 Subcycle observation of lightwave-driven Dirac currents in a topological surface band
Subcycle observation of lightwave-driven Dirac currents in a topological surface band
Time- and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy reveals how Dirac fermions in the band structure of the topological surface state of Bi2Te3 are accelerated by the carrier wave of a terahertz-frequency light pulse.
- J. Reimann
- , S. Schlauderer
- & R. Huber
-
Letter |
 Device-independent quantum random-number generation
Device-independent quantum random-number generation
Genuine, unpredictable quantum random-number generation that is provably secure against quantum and classical adversaries is demonstrated, certified by the loophole-free violation of a Bell inequality.
- Yang Liu
- , Qi Zhao
- & Jian-Wei Pan
-
Letter |
 A topological source of quantum light
A topological source of quantum light
Topologically protected edge states realized in a square array of ring resonators are used to demonstrate a robust source of heralded single photons produced by spontaneous four-wave mixing.
- Sunil Mittal
- , Elizabeth A. Goldschmidt
- & Mohammad Hafezi
-
Letter |
 All-inorganic perovskite nanocrystal scintillators
All-inorganic perovskite nanocrystal scintillators
All-inorganic perovskite nanocrystals containing caesium and lead provide low-cost, flexible and solution-processable scintillators that are highly sensitive to X-ray irradiation and emit radioluminescence that is colour-tunable across the visible spectrum.
- Qiushui Chen
- , Jing Wu
- & Xiaogang Liu
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Atom optics
- High-harmonic generation
- Magneto-optics
- Micro-optics
- Nanophotonics and plasmonics
- Nonlinear optics
- Polaritons
- Quantum optics
- Single photons and quantum effects
- Slow light
- Solitons
- Sub-wavelength optics
- Supercontinuum generation
- Terahertz optics
- Transformation optics
- Ultrafast photonics
- X-rays

 A subradiant optical mirror formed by a single structured atomic layer
A subradiant optical mirror formed by a single structured atomic layer