Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access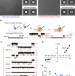 A quantized mechanism for activation of pannexin channels
A quantized mechanism for activation of pannexin channels
Pannexins are oligomeric plasma membrane channels that allow permeation of ions and large molecules. Here the authors show that human Pannexin 1 activation is a multistep event, where modification of each monomer opens the channel to a unique conductance state and fine tunes its activity.
- Yu-Hsin Chiu
- , Xueyao Jin
- & Douglas A. Bayliss
-
Article
| Open Access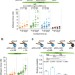 αV-class integrins exert dual roles on α5β1 integrins to strengthen adhesion to fibronectin
αV-class integrins exert dual roles on α5β1 integrins to strengthen adhesion to fibronectin
Interaction of fibronectin with αv-class and α5β1 integrins results in formation of cell adhesion complexes, but the initial events (<120 s) remain unclear. Here, the authors show that αv-class integrins bind fibronectin faster than α5β1 integrins and subsequently signal to α5ß1 integrins to strengthen the adhesion.
- Mitasha Bharadwaj
- , Nico Strohmeyer
- & Daniel J. Müller
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscopy of bacterial cells immobilized by holographic optical tweezers
Nanoscopy of bacterial cells immobilized by holographic optical tweezers
Nanoscopy of non-adherent cells is currently not possible, due to their movement in solution. Here the authors immobilize and manipulate fixedE. coli by multiple optical traps; their holographic optical tweezers enable dSTORM imaging of orthogonal planes via 3D realignment of the sample.
- Robin Diekmann
- , Deanna L. Wolfson
- & Thomas Huser
-
Article
| Open Access KCNE1 induces fenestration in the Kv7.1/KCNE1 channel complex that allows for highly specific pharmacological targeting
KCNE1 induces fenestration in the Kv7.1/KCNE1 channel complex that allows for highly specific pharmacological targeting
Specificity of inhibitors of voltage-gated ion channels is crucial for their use as therapeutics. Here, the authors show that adamantane derivatives interact with a specific binding site on fenestrations that only become available when accessory subunits are bound to the channel.
- Eva Wrobel
- , Ina Rothenberg
- & Guiscard Seebohm
-
Article
| Open Access Nicotinamide is an endogenous agonist for a C. elegans TRPV OSM-9 and OCR-4 channel
Nicotinamide is an endogenous agonist for a C. elegans TRPV OSM-9 and OCR-4 channel
TRPV are cation channels activated by physical and chemical stimuli. Here the authors show that nicotinamide is a soluble, endogenous agonist for orthologous TRPV channels fromC. elegans and Drosophila, unveiling a metabolic-based regulation for TRPV channel activity.
- Awani Upadhyay
- , Aditya Pisupati
- & Wendy Hanna-Rose
-
Article
| Open Access Confocal reference free traction force microscopy
Confocal reference free traction force microscopy
Traction force microscopy is an effective method of measuring forces between cells and their environment, but requires removing the cells to obtain a reference image. Here the authors use nanodrip printing of quantum dots into compliant substrates to provide a regular array of fiducial spots, removing the need for a reference image.
- Martin Bergert
- , Tobias Lendenmann
- & Aldo Ferrari
-
Article
| Open Access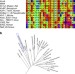 Structural and functional characterization of a calcium-activated cation channel from Tsukamurella paurometabola
Structural and functional characterization of a calcium-activated cation channel from Tsukamurella paurometabola
Tetrameric cationic channels specificity is determined by the sequence and structural conformation of their selectivity filter. Here, the authors show that a cationic channel from Tsukamurella paurometabola is non-selective due to a Ca2+-binding motif within its unusual proline-rich filter.
- Balasundaresan Dhakshnamoorthy
- , Ahmed Rohaim
- & Benoît Roux
-
Article
| Open Access Iso-acoustic focusing of cells for size-insensitive acousto-mechanical phenotyping
Iso-acoustic focusing of cells for size-insensitive acousto-mechanical phenotyping
Acoustophoresis, a method to manipulate individual cells based on their acoustic properties is confounded by a strong dependency on cell size. Here the authors present iso-acoustic focussing, a way to separate cells in a microfluidic chamber according to their effective acoustic impedance, independent of their size.
- Per Augustsson
- , Jonas T. Karlsen
- & Joel Voldman
-
Article
| Open Access OptoDyCE as an automated system for high-throughput all-optical dynamic cardiac electrophysiology
OptoDyCE as an automated system for high-throughput all-optical dynamic cardiac electrophysiology
The efficiency of preclinical drug testing and characterization of cellular function can be improved through the use of optogenetic tools. Here Klimas et al. present and validate OptoDyCE, a fully automated system for all-optical high-throughput cardiac electrophysiology.
- Aleksandra Klimas
- , Christina M. Ambrosi
- & Emilia Entcheva
-
Article
| Open Access Rotational manipulation of single cells and organisms using acoustic waves
Rotational manipulation of single cells and organisms using acoustic waves
The precise rotational manipulation of single cells is technically challenging and relies on the optical, magnetic and electrical properties of the biospecimen. Here the authors develop an acoustic-based, on-chip manipulation method that can rotate single microparticles, cells and organisms.
- Daniel Ahmed
- , Adem Ozcelik
- & Tony Jun Huang
-
Article
| Open Access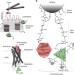 Identifying and quantifying two ligand-binding sites while imaging native human membrane receptors by AFM
Identifying and quantifying two ligand-binding sites while imaging native human membrane receptors by AFM
Functional analysis of membrane proteins would benefit from the combination of imaging with ligand characterisation. Here, Pfreundschuh et al. use specialised atomic force microscopy tips to image and quantify the binding of two ligands at the same time.
- Moritz Pfreundschuh
- , David Alsteens
- & Daniel J. Müller
-
Article
| Open Access Electrical behaviour of dendritic spines as revealed by voltage imaging
Electrical behaviour of dendritic spines as revealed by voltage imaging
Dendritic spines located on individual neurons process information, but our understanding of the electrical behaviour of spines is still limited. Here, the authors use voltage-sensitive dye imaging techniques to monitor electrical signals from thin basal spines and show that synapses are not electrically isolated by the spine neck.
- Marko A. Popovic
- , Nicholas Carnevale
- & Dejan Zecevic
-
Article |
 Biophysical mechanisms that maintain biodiversity through trade-offs
Biophysical mechanisms that maintain biodiversity through trade-offs
Trade-offs between life history traits are key to understanding biodiversity. Here, the authors use population genetics models and experimental microbial evolution to show that trade-off geometry can be deduced from fundamental biological principles, and used to predict biodiversity stability.
- Justin R. Meyer
- , Ivana Gudelj
- & Robert Beardmore
-
Article |
 Camera-based three-dimensional real-time particle tracking at kHz rates and Ångström accuracy
Camera-based three-dimensional real-time particle tracking at kHz rates and Ångström accuracy
Particle tracking with ultra-high resolution in optical and magnetic tweezers has so far relied on laser detection through photodiodes. Here, Huhle et al. demonstrate three-dimensional particle tracking with Ångström accuracy and real-time GPU-accelerated data processing at kHz rates using camera-based imaging.
- Alexander Huhle
- , Daniel Klaue
- & Ralf Seidel
-
Article |
 Transparent and flexible low noise graphene electrodes for simultaneous electrophysiology and neuroimaging
Transparent and flexible low noise graphene electrodes for simultaneous electrophysiology and neuroimaging
Monitoring neuronal activity of large populations of neurons at high-temporal and spatial resolution is important to understand neurophysiology but requires improved tools and methods. Here the authors develop a transparent and flexible electrode based on graphene that allows them to combine electrophysiological recordings with calcium imaging.
- Duygu Kuzum
- , Hajime Takano
- & Brian Litt
-
Article |
 A distinct sodium channel voltage-sensor locus determines insect selectivity of the spider toxin Dc1a
A distinct sodium channel voltage-sensor locus determines insect selectivity of the spider toxin Dc1a
β-Diguetoxin-Dc1a, a component of desert bush spider venom, targets insect voltage-gated sodium channels, but not those of humans. Bende et al. find that American, but not German cockroaches are sensitive to the toxin, and identify two residues in the voltage-sensor domain that underlie this difference.
- Niraj S. Bende
- , Sławomir Dziemborowicz
- & Frank Bosmans
-
Article
| Open Access The stimulus-evoked population response in visual cortex of awake monkey is a propagating wave
The stimulus-evoked population response in visual cortex of awake monkey is a propagating wave
Propagating waves of cortical neuronal activity are implicated in various cognitive processes and have been observed in anaesthetised animals. Here, the authors demonstrate the existence of propagating waves in awake monkeys during visual stimulation, and show that they are mediated by horizontal fibres in the cortex.
- Lyle Muller
- , Alexandre Reynaud
- & Alain Destexhe
-
Article |
 Integrated circuit-based electrochemical sensor for spatially resolved detection of redox-active metabolites in biofilms
Integrated circuit-based electrochemical sensor for spatially resolved detection of redox-active metabolites in biofilms
The direct detection of metabolites secreted by cells can indicate how cellular dynamics affects population development. Here, the authors present an integrated circuit-based method for electrochemical imaging of redox-active signalling molecules with spatial resolution within bacterial colonies.
- Daniel L. Bellin
- , Hassan Sakhtah
- & Kenneth L. Shepard
-
Article |
 Iridium oxide nanotube electrodes for sensitive and prolonged intracellular measurement of action potentials
Iridium oxide nanotube electrodes for sensitive and prolonged intracellular measurement of action potentials
Nanoelectrode intracellular recording of action potential may be used to study cell electrophysiology. Here, the authors demonstrate vertical nanotube electrodes which improve recording quality and duration, as the cell membrane wraps the nanotubes surfaces and protrudes into their hollow centres.
- Ziliang Carter Lin
- , Chong Xie
- & Bianxiao Cui
-
Article |
 Engineering protein thermostability using a generic activity-independent biophysical screen inside the cell
Engineering protein thermostability using a generic activity-independent biophysical screen inside the cell
Methods to improve protein stability are important in the biopharmaceutical industry. Here, the authors describe a high-throughput screen to increase protein thermostability and identify thermostable variants from a broad range of proteins.
- Ignacio Asial
- , Yue Xiang Cheng
- & Tobias Cornvik
-
Article |
 Activation of the central nervous system induced by micro-magnetic stimulation
Activation of the central nervous system induced by micro-magnetic stimulation
Magnetic stimulation is used therapeutically for neurological disorders, but its effectiveness is hindered by efficacy and safety limitations due to large device sizes. Here the authors show that sub-millimetre, micro-magnetic coils effectively stimulate hamster cochlear neurons, with minimal side effects.
- Hyun-Joo Park
- , Giorgio Bonmassar
- & John T. Gale
-
Article |
 Tracking axonal action potential propagation on a high-density microelectrode array across hundreds of sites
Tracking axonal action potential propagation on a high-density microelectrode array across hundreds of sites
Optical techniques that are used to study neuronal action potential propagation are limited by phototoxicity and photobleaching. Here the authors describe a microelectrode system that allows simultaneous stimulation and recordings of action potential propagation across hundreds of sites in cultured neurons.
- Douglas J. Bakkum
- , Urs Frey
- & Andreas Hierlemann
-
Article |
 Trapping red blood cells in living animals using optical tweezers
Trapping red blood cells in living animals using optical tweezers
Optical tweezers based on focused laser beams are widely used for biophysical measurements of single molecules in vitro. Here Zhong et al. use infrared optical tweezers to trap and manipulate red blood cells within subdermal capillaries in living mice.
- Min-Cheng Zhong
- , Xun-Bin Wei
- & Yin-Mei Li
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo recordings of brain activity using organic transistors
In vivo recordings of brain activity using organic transistors
Flexible organic electronic devices have the potential to serve as biosensors in living animals. Khodagholy et al. show that organic transistors can be used to record brain activity in rats and demonstrate that they have a superior signal-to-noise ratio compared with electrodes due to local signal amplification.
- Dion Khodagholy
- , Thomas Doublet
- & George G. Malliaras
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of an inhibitory restraint of seizure activity in humans
Evidence of an inhibitory restraint of seizure activity in humans
Seizure activity in the brain is characterized by the recruitment of cortical neuronal activity. Schevon and colleagues study seizure activity in human subjects and find that the recruitment of neurons is hypersynchronous and that there is an intrinsic restraint on the propagation of this activity.
- Catherine A. Schevon
- , Shennan A. Weiss
- & Andrew J. Trevelyan
-
Article
| Open Access Switching of myosin-V motion between the lever-arm swing and Brownian search-and-catch
Switching of myosin-V motion between the lever-arm swing and Brownian search-and-catch
The motor protein myosin-V transports cargo along actin filaments, but the biophysical mechanisms by which myosin-V generates force are unclear. Here, optical tweezers and a DNA handle are used to study the forces generated by myosin-V: the mechanism of force generation is found to depend on the load applied.
- Keisuke Fujita
- , Mitsuhiro Iwaki
- & Toshio Yanagida
-
Article
| Open Access Freely orbiting magnetic tweezers to directly monitor changes in the twist of nucleic acids
Freely orbiting magnetic tweezers to directly monitor changes in the twist of nucleic acids
Rotational motion and torsional strain affects DNA replication, transcription and repair. Lipfertet al. have developed a new technique that uses freely orbiting magnetic tweezers to measure equilibrium fluctuations and determine the twist of tethered nucleic acid molecules.
- Jan Lipfert
- , Matthew Wiggin
- & Nynke H. Dekker
-
Article
| Open Access Errors in the measurement of voltage-activated ion channels in cell-attached patch-clamp recordings
Errors in the measurement of voltage-activated ion channels in cell-attached patch-clamp recordings
Voltage-activated ion channels can be measured in neurons using the cell-attached patch-clamp technique. Williams and Wozny show that this technique is prone to errors that are caused by the flow of current through the ion channels; a method to correct for these discrepancies is described.
- Stephen R. Williams
- & Christian Wozny
-
Article |
 Measurement of cochlear power gain in the sensitive gerbil ear
Measurement of cochlear power gain in the sensitive gerbil ear
The cochlear amplifier in the inner ear is thought to mediate sensitivity to soft sounds, but this power gain has not been measured directly. Renet aluse an interferometer to measure the volume displacement and velocity of the cochlear partition and demonstrate experimentally that the cochlea amplifies soft sounds.
- Tianying Ren
- , Wenxuan He
- & Peter G. Gillespie

 Vector assembly of colloids on monolayer substrates
Vector assembly of colloids on monolayer substrates