Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Ultracompact mirror device for forming 20-nm achromatic soft-X-ray focus toward multimodal and multicolor nanoanalyses
Ultracompact mirror device for forming 20-nm achromatic soft-X-ray focus toward multimodal and multicolor nanoanalyses
Optics used for X-ray focusing suffer from wavelength dependent effects like chromatic aberration. Here the authors demonstrate fabrication of a ultracompact Kirkpatrick-Baez mirror and use it for achromatic focusing to 20 nm spot for the soft X-ray at 2-keV photon energy.
- Takenori Shimamura
- , Yoko Takeo
- & Hidekazu Mimura
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast entropy production in pump-probe experiments
Ultrafast entropy production in pump-probe experiments
Ultrafast spectroscopy enables characterization and control of non-equilibrium states. Here the authors introduce a stochastic thermodynamics approach to calculate entropy production in a material under ultrafast excitation, using ionic displacement data from time-resolved X-ray scattering experiments.
- Lorenzo Caprini
- , Hartmut Löwen
- & R. Matthias Geilhufe
-
Article
| Open Access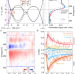 Enhanced optical conductivity and many-body effects in strongly-driven photo-excited semi-metallic graphite
Enhanced optical conductivity and many-body effects in strongly-driven photo-excited semi-metallic graphite
Strong optical excitation near band extrema can drive novel correlated states. Here the authors report a non-equilibrium many-body state in graphite driven by a strong excitation near van Hove singularity, yielding a tenfold increase in optical conductivity attributed to carrier excitations in the flat bands.
- T. P. H. Sidiropoulos
- , N. Di Palo
- & J. Biegert
-
Article
| Open Access Prediction on X-ray output of free electron laser based on artificial neural networks
Prediction on X-ray output of free electron laser based on artificial neural networks
Methods to characterize the free-electron laser pulses are evolving and their performances are also improving. Here the authors demonstrate a method based on the artificial neural networks to predict the output pulses of the X-ray free-electron laser by considering the electron beam parameters as input.
- Kenan Li
- , Guanqun Zhou
- & Anne Sakdinawat
-
Article
| Open Access Probing three-dimensional mesoscopic interfacial structures in a single view using multibeam X-ray coherent surface scattering and holography imaging
Probing three-dimensional mesoscopic interfacial structures in a single view using multibeam X-ray coherent surface scattering and holography imaging
The authors observe X-ray coherent scattering speckles from substrate-supported planar patterns in grazing incidence reflection geometry, which constitutes hard X-ray holograms revealing three-dimensional high-resolution structural information in a single image.
- Miaoqi Chu
- , Zhang Jiang
- & Jin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access An X-ray free-electron laser with a highly configurable undulator and integrated chicanes for tailored pulse properties
An X-ray free-electron laser with a highly configurable undulator and integrated chicanes for tailored pulse properties
Since their initial operation, free-electron lasers are regularly upgraded in their performance and parameter control. Here the authors present the first lasing results of the soft X-ray free-electron laser beamline of the Paul Scherrer Institute, demonstrating different modes of operation and polarisation control of the tailored soft X-ray pulses.
- Eduard Prat
- , Andre Al Haddad
- & Tobias Weilbach
-
Article
| Open Access Alvarez varifocal X-ray lens
Alvarez varifocal X-ray lens
Development of synchroton facilities increases the demand of optics for focusing X-ray beam to achieve diffraction-limited focusing onto samples. Here, the authors demonstrated an X-ray optical element based on visible light Alvarez varifocal lens providing precise performance focusing elements.
- Vishal Dhamgaye
- , David Laundy
- & Kawal Sawhney
-
Article
| Open Access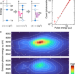 Two-dimensional Kβ-Kα fluorescence spectrum by nonlinear resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
Two-dimensional Kβ-Kα fluorescence spectrum by nonlinear resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy is a powerful tool to investigate atomic properties. Here the authors report a two-dimensional fluorescence spectrum of copper metal using X-ray nonlinear scattering and find two-hole satellite feature resulting from atomic transitions.
- Kenji Tamasaku
- , Munetaka Taguchi
- & Tetsuya Ishikawa
-
Article
| Open Access Self-wavelength shifting in two-dimensional perovskite for sensitive and fast gamma-ray detection
Self-wavelength shifting in two-dimensional perovskite for sensitive and fast gamma-ray detection
Efficient light extraction in perovskite X/γ-ray scintillators is hindered by the small Stokes shift of exciton luminescence. Here, Jin et al. exploit the intrinsic strain in 2D perovskite as “self-wavelength shifting” to reduce the self-absorption effect without sacrificing the device response speed.
- Tong Jin
- , Zheng Liu
- & Guangda Niu
-
Article
| Open Access A sensitive high repetition rate arrival time monitor for X-ray free electron lasers
A sensitive high repetition rate arrival time monitor for X-ray free electron lasers
In time-resolved measurements it is crucial to know the time delay between the exciting and probing light pulses. Here the authors demonstrate a self-referencing common-path interferometer method measuring the arrival time between the X-ray free electron laser and the optical pulse to the target and thus their inherent timing jitter.
- Michael Diez
- , Henning Kirchberg
- & Christian Bressler
-
Article
| Open Access Solution-grown BiI/BiI3 van der Waals heterostructures for sensitive X-ray detection
Solution-grown BiI/BiI3 van der Waals heterostructures for sensitive X-ray detection
Many of the most sensitive X-ray detectors are based on toxic elements such as lead, limiting their safe applications. Here, the authors report the realization of sensitive X-ray detectors based on solution-grown thick BiI/BiI3/BiI van der Waals heterostructures, showing a detection limit down to 34 nGy s−1 and high stability.
- Renzhong Zhuang
- , Songhua Cai
- & Shenghuang Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Attosecond-Angstrom free-electron-laser towards the cold beam limit
Attosecond-Angstrom free-electron-laser towards the cold beam limit
Free-electron lasers (FELs) can produce bright X-ray pulses, but require high quality electron beams. Here the authors show how to generate and preserve ultrabright electron beams from plasma-based accelerators for ultra-compact, high-brightness X-ray FELs.
- A. F. Habib
- , G. G. Manahan
- & B. Hidding
-
Article
| Open Access Realizing nearly-zero dark current and ultrahigh signal-to-noise ratio perovskite X-ray detector and image array by dark-current-shunting strategy
Realizing nearly-zero dark current and ultrahigh signal-to-noise ratio perovskite X-ray detector and image array by dark-current-shunting strategy
The high dark current of perovskite photodetectors hinders the full potential of perovskites as active material for X-ray detectors. Here, Jin et al. provide a strategy to reduce the dark current to zero and massively enhance the signal-to-noise ratio of perovskite X-ray detectors and photodetectors.
- Peng Jin
- , Yingjie Tang
- & Yang (Michael) Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced detection of threat materials by dark-field x-ray imaging combined with deep neural networks
Enhanced detection of threat materials by dark-field x-ray imaging combined with deep neural networks
Dark-field X-ray imaging is sensitive to the microstructure of a material. Here, the authors combine this with a neural network algorithm to provide efficient material discrimination, e.g., of explosives vs non-threat materials.
- T. Partridge
- , A. Astolfo
- & A. Olivo
-
Article
| Open Access Generation of ultrahigh-brightness pre-bunched beams from a plasma cathode for X-ray free-electron lasers
Generation of ultrahigh-brightness pre-bunched beams from a plasma cathode for X-ray free-electron lasers
Laser-produced plasma can be used for acceleration and tuning of particle beams. Here the authors discuss the generation of a bunched electron beam using simulations and its application to X-ray free-electron laser.
- Xinlu Xu
- , Fei Li
- & Warren B. Mori
-
Article
| Open Access An achromatic X-ray lens
An achromatic X-ray lens
X-ray diffractive and refractive optical elements suffer from chromatic aberrations, limiting high-resolution X-ray microscopes mainly to bright synchrotron sources. Here, the authors experimentally realise an achromatic X-ray lens by combing a focusing diffractive Fresnel zone plate and a defocusing refractive lens.
- Adam Kubec
- , Marie-Christine Zdora
- & Christian David
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing nano-scale lattice distortions in implanted material with 3D Bragg ptychography
Revealing nano-scale lattice distortions in implanted material with 3D Bragg ptychography
Atomic point defects formed by irradiation can dramatically alter material properties, but are difficult to probe, limiting understanding of their impact. Here, the authors introduce an x-ray microscopy approach, based on Bragg ptychography, to visualise the distortion caused by these otherwise invisible defects.
- Peng Li
- , Nicholas W. Phillips
- & Virginie Chamard
-
Article
| Open Access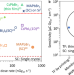 Determination of X-ray detection limit and applications in perovskite X-ray detectors
Determination of X-ray detection limit and applications in perovskite X-ray detectors
The limit of X-ray detection is an important figure of merit for X-ray detectors, yet the suitability of method adopted from Currie’s 1968 paper and the following international standard is in doubt. Here, the authors propose a statistical model that correlates dark current and photo-current, show how it can be used to determine detection limit.
- Lei Pan
- , Shreetu Shrestha
- & Lei R. Cao
-
Article
| Open Access Demonstration of a compact plasma accelerator powered by laser-accelerated electron beams
Demonstration of a compact plasma accelerator powered by laser-accelerated electron beams
Particle accelerators based on laser- or electron-driven plasma waves promise compact sources for relativistic electron bunches. Here, Kurz and Heinemann et al. demonstrate a hybrid two-stage configuration, combining the individual features of both accelerating schemes.
- T. Kurz
- , T. Heinemann
- & A. Irman
-
Article
| Open Access Control of quantum electrodynamical processes by shaping electron wavepackets
Control of quantum electrodynamical processes by shaping electron wavepackets
Here the authors show that radiation emitted by individual electrons can be controlled by shaping the electron wavepacket. They present feasible examples for applications including collimated and monochromatic X-ray emission from specially shaped electrons.
- Liang Jie Wong
- , Nicholas Rivera
- & Ido Kaminer
-
Article
| Open Access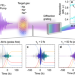 Measuring the frequency chirp of extreme-ultraviolet free-electron laser pulses by transient absorption spectroscopy
Measuring the frequency chirp of extreme-ultraviolet free-electron laser pulses by transient absorption spectroscopy
Free-electron laser pulses generated from self-amplification of spontaneous emission scheme vary from one another in their characteristics. Here the authors demonstrate a transient absorption spectroscopy method to characterize the frequency chirp of the FEL pulses.
- Thomas Ding
- , Marc Rebholz
- & Thomas Pfeifer
-
Article
| Open Access Automation and control of laser wakefield accelerators using Bayesian optimization
Automation and control of laser wakefield accelerators using Bayesian optimization
Laser wakefield accelerators are compact sources of ultra-relativistic electrons which are highly sensitive to many control parameters. Here the authors present an automated machine learning based method for the efficient multi-dimensional optimization of these plasma-based particle accelerators.
- R. J. Shalloo
- , S. J. D. Dann
- & M. J. V. Streeter
-
Article
| Open Access Laser-driven x-ray and proton micro-source and application to simultaneous single-shot bi-modal radiographic imaging
Laser-driven x-ray and proton micro-source and application to simultaneous single-shot bi-modal radiographic imaging
Here the authors show a synchronized single-shot bi-modal x-ray and proton source based on laser-generated plasma. This source can be useful for radiographic and tomographic imaging.
- T. M. Ostermayr
- , C. Kreuzer
- & J. Schreiber
-
Article
| Open Access Hot electrons in a nanowire hard X-ray detector
Hot electrons in a nanowire hard X-ray detector
Designing efficient nanowire chip-based electrical and optical devices remains a challenge. Here, the authors present an axial p-n junction GaAs nanowire X-ray detector that enables achieving a spatial resolution of 200 nm; probing the internal electrical field and observing hot electron effects at the nanoscale.
- Maximilian Zapf
- , Maurizio Ritzer
- & Carsten Ronning
-
Article
| Open Access Diffractive small angle X-ray scattering imaging for anisotropic structures
Diffractive small angle X-ray scattering imaging for anisotropic structures
Mesoscale investigations of material microarchitecture using small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) methods have been limited by long measurement times. Here, the authors present an X-ray diffractive optics method which enables single shot acquisition of SAXS signals over large areas.
- Matias Kagias
- , Zhentian Wang
- & Marco Stampanoni
-
Article
| Open Access Core-level nonlinear spectroscopy triggered by stochastic X-ray pulses
Core-level nonlinear spectroscopy triggered by stochastic X-ray pulses
Free electron X-ray laser pulses, generated by self-amplified spontaneous emission, are stochastic in nature. Here the authors present a reconstruction method for 2D spectroscopy while preserving the intrinsic properties of the incident pulses and apply it to a study towards X-ray intensity induced effects.
- Yves Kayser
- , Chris Milne
- & Jakub Szlachetko
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent X-ray measurement of step-flow propagation during growth on polycrystalline thin film surfaces
Coherent X-ray measurement of step-flow propagation during growth on polycrystalline thin film surfaces
Monitoring growth dynamics of crystalline thin materials progressively is crucial to understand the mechanism. Here, the authors develop a local step flow model to investigate the growth of C60 films on graphene coated over silicon substrates that correlates the step-edge velocity with its terrace lengths using the X-ray photon correlation spectroscopy.
- Randall L. Headrick
- , Jeffrey G. Ulbrandt
- & Karl F. Ludwig Jr.
-
Article
| Open Access Ab initio nonrigid X-ray nanotomography
Ab initio nonrigid X-ray nanotomography
Radiation induced sample deformation can be a limiting factor for X-ray imaging resolution at the nanoscale. The authors report a tomographic model that estimates and accounts for morphological changes during data acquisition and enables reconstruction of a high-resolution image ab initio.
- Michal Odstrcil
- , Mirko Holler
- & Manuel Guizar-Sicairos
-
Article
| Open Access Full-field structured-illumination super-resolution X-ray transmission microscopy
Full-field structured-illumination super-resolution X-ray transmission microscopy
Modern high-resolution X-ray microscopy techniques suffer from limited field-of-view or longer acquisition times. Here the authors use structured illumination to enable fast, full-field super-resolution transmission microscopy, even for optically thick specimens and at hard X-ray energies.
- Benedikt Günther
- , Lorenz Hehn
- & Franz Pfeiffer
-
Article
| Open Access Realization of wafer-scale nanogratings with sub-50 nm period through vacancy epitaxy
Realization of wafer-scale nanogratings with sub-50 nm period through vacancy epitaxy
Fabrication of wafer-scale nanogratings for X-ray spectroscopy is difficult especially for very high line densities. The authors use vacancy epitaxy to fabricate sub-50-nm-periodicity gratings, coated with multilayers for efficient operation, for use in ultra-high resolution x-ray spectroscopy.
- Qiushi Huang
- , Qi jia
- & Xin Ou
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of picosecond melting and disintegration of metallic nanoparticles
Direct observation of picosecond melting and disintegration of metallic nanoparticles
Laser-matter interaction has been intensively studied in equilibrium states, but irreversible processes in a highly nonequilibrium state at nanoscales remains elusive due to experimental challenges. Here, Ihm et al. image heterogeneous melting of gold nanoparticles with nanometer and picosecond resolution.
- Yungok Ihm
- , Do Hyung Cho
- & Changyong Song
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast photonic micro-systems to manipulate hard X-rays at 300 picoseconds
Ultrafast photonic micro-systems to manipulate hard X-rays at 300 picoseconds
It is desirable to improve spatiotemporal control of light generated by synchrotron user facilities or table-top X-ray sources. Here the authors demonstrate manipulation of hard X-rays using microelectro mechanical systems (MEMS) oscillators on timescales of 300 ps, approaching the synchrotron pulse width.
- Pice Chen
- , Il Woong Jung
- & Jin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Spectral interferometry with waveform-dependent relativistic high-order harmonics from plasma surfaces
Spectral interferometry with waveform-dependent relativistic high-order harmonics from plasma surfaces
High-order harmonic generation is explored in gases, solids and plasmas with moderate to high intensity lasers. Here the authors show spectral interferometry of HHG from relativistic plasma and its potential as a source of intense isolated attosecond pulses.
- Dmitrii Kormin
- , Antonin Borot
- & Laszlo Veisz
-
Article
| Open Access Probing warm dense matter using femtosecond X-ray absorption spectroscopy with a laser-produced betatron source
Probing warm dense matter using femtosecond X-ray absorption spectroscopy with a laser-produced betatron source
Understanding the ultrafast dynamics of materials under extreme conditions is challenging. Here the authors use a femtosecond betatron X-ray source to investigate the solid to dense plasma phase transition in copper using XAS with unprecedented time resolution.
- B. Mahieu
- , N. Jourdain
- & L. Lecherbourg
-
Article
| Open Access In situ coherent diffractive imaging
In situ coherent diffractive imaging
Coherent diffractive imaging (CDI) allows for high resolution imaging without lenses. Here, Lo et al. develop in situ CDI with real-time imaging and a corresponding low-dose requirement, with expected applications in the physical and life sciences.
- Yuan Hung Lo
- , Lingrong Zhao
- & Jianwei Miao
-
Article
| Open Access Towards ultrafast dynamics with split-pulse X-ray photon correlation spectroscopy at free electron laser sources
Towards ultrafast dynamics with split-pulse X-ray photon correlation spectroscopy at free electron laser sources
X-ray photon correlation spectroscopy has been mainly used to measure slow dynamics using synchrotron sources. Here the authors demonstrate the split-and- delay pulse set-up to study nanosecond dynamics of gold nanoparticles using XPCS with free electron laser pulses.
- W. Roseker
- , S. O. Hruszkewycz
- & G. Grübel
-
Article
| Open Access Monovalent manganese based anodes and co-solvent electrolyte for stable low-cost high-rate sodium-ion batteries
Monovalent manganese based anodes and co-solvent electrolyte for stable low-cost high-rate sodium-ion batteries
Sodium ion batteries offer more cost-effective storage than lithium and could be used for grid-scale energy storage. Here, the authors demonstrate a full cell based on a MnHCMn anode and an organic-aqueous cosolvent electrolyte. X-ray spectroscopy evidence further suggests the presence of Mn(I).
- Ali Firouzi
- , Ruimin Qiao
- & Colin D. Wessells
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing hole trapping in zinc oxide nanoparticles by time-resolved X-ray spectroscopy
Revealing hole trapping in zinc oxide nanoparticles by time-resolved X-ray spectroscopy
Metal-oxide nanostructures are used in a range of light-driven applications, yet the fundamentals behind their properties are poorly understood. Here the authors probe photoexcited zinc oxide nanoparticles using time-resolved X-ray spectroscopy, identifying photocatalytically-active hole traps as oxygen vacancies in the lattice.
- Thomas J. Penfold
- , Jakub Szlachetko
- & Christopher J. Milne
-
Article
| Open Access In situ single-shot diffractive fluence mapping for X-ray free-electron laser pulses
In situ single-shot diffractive fluence mapping for X-ray free-electron laser pulses
Free electron laser beam profile characterization is usually performed separately from the actual measurements and this leads to considerable uncertainty in the results. Here the authors demonstrate the simultaneous measurement of the FEL beam profile with the experiment by using integrated gratings.
- Michael Schneider
- , Christian M. Günther
- & Stefan Eisebitt
-
Article
| Open Access Picometer polar atomic displacements in strontium titanate determined by resonant X-ray diffraction
Picometer polar atomic displacements in strontium titanate determined by resonant X-ray diffraction
It is a challenge to measure changes in the crystal structures in picometer scale and the associated phase. Here the authors demonstrate the lattice expansion and polar distortions of oxygen deficient SrTiO3 using a resonance X-ray scattering technique.
- Carsten Richter
- , Matthias Zschornak
- & Dirk C. Meyer
-
Article
| Open Access 53-attosecond X-ray pulses reach the carbon K-edge
53-attosecond X-ray pulses reach the carbon K-edge
Isolated attosecond pulses are produced using high harmonic generation and sources of these pulses often suffer from low photon flux in soft X-ray regime. Here the authors demonstrate efficient generation and characterization of 53 as pulses with photon energy near the water window.
- Jie Li
- , Xiaoming Ren
- & Zenghu Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Single-stage plasma-based correlated energy spread compensation for ultrahigh 6D brightness electron beams
Single-stage plasma-based correlated energy spread compensation for ultrahigh 6D brightness electron beams
Controlling and improving electron beam parameters are crucial for their application in free electron laser and X-ray sources. Here the authors generate quality electron beams with reduced energy spread from plasma accelerators by using a tailored escort electron bunch with the main accelerating bunch.
- G. G. Manahan
- , A. F. Habib
- & B. Hidding
-
Article
| Open Access Direct and simultaneous observation of ultrafast electron and hole dynamics in germanium
Direct and simultaneous observation of ultrafast electron and hole dynamics in germanium
Understanding excited carrier dynamics in semiconductors is central to the continued development of optoelectronic devices. Using extreme ultraviolet transient absorption spectroscopy, Zürchet al. directly and simultaneously observe ultrafast electron and hole dynamics in germanium thin films.
- Michael Zürch
- , Hung-Tzu Chang
- & Stephen R. Leone
-
Article
| Open Access Attosecond interferometry with self-amplified spontaneous emission of a free-electron laser
Attosecond interferometry with self-amplified spontaneous emission of a free-electron laser
Phase-sensitive measurements are important to gain insights of light-matter interactions and require phase-controlled pulses. Here the authors demonstrate the phase control and interferometric autocorrelation on a free electron laser using SASE pulse pair created with a split and delay unit.
- Sergey Usenko
- , Andreas Przystawik
- & Tim Laarmann
-
Article
| Open Access Perfect X-ray focusing via fitting corrective glasses to aberrated optics
Perfect X-ray focusing via fitting corrective glasses to aberrated optics
X-ray optics are notoriously challenging to fabricate due to the strict tolerances that result from the short wavelength of radiation. Here, Seibothet al. carefully quantify aberrations in complex X-ray lenses and correct them with an easy-to-fabricate broadband phase plate.
- Frank Seiboth
- , Andreas Schropp
- & Christian G. Schroer
-
Article
| Open Access Electromagnon dispersion probed by inelastic X-ray scattering in LiCrO2
Electromagnon dispersion probed by inelastic X-ray scattering in LiCrO2
Whilst terahertz optical spectroscopy allows for the study of coupled spin and lattice excitations, it is limited in momentum space. Here, the authors use inelastic x-ray scattering to demonstrate strong magnon-phonon coupling and electromagnon excitations across the Brillouin zone of LiCrO2.
- Sándor Tóth
- , Björn Wehinger
- & Christian Rüegg
-
Article
| Open Access Phase retrieval by coherent modulation imaging
Phase retrieval by coherent modulation imaging
Robust coherent diffractive imaging generally requires many exposures that may damage samples. Here, the authors develop a single-shot X-ray imaging method applicable to general samples for materials and biological sciences, also enabling imaging of dynamic processes, using a pulsed X-ray laser.
- Fucai Zhang
- , Bo Chen
- & Ian K. Robinson
-
Article
| Open Access 0.5-keV Soft X-ray attosecond continua
0.5-keV Soft X-ray attosecond continua
Attosecond soft X-ray pulses hold promise for probing electronic dynamics in real time, but it is challenging to achieve element sensitivity while maintaining temporal resolution. Teichmann et al. report the cover of carbon, nitrogen and oxygen absorption edges with an isolated pulse supporting 13 as duration.
- S. M. Teichmann
- , F. Silva
- & J. Biegert
-
Correspondence
| Open Access Correspondence: Quantitative evaluation of X-ray dark-field images for microcalcification analysis in mammography
Correspondence: Quantitative evaluation of X-ray dark-field images for microcalcification analysis in mammography
- Kai Scherer
- , Lorenz Birnbacher
- & Franz Pfeiffer

 Reconfigurable perovskite X-ray detector for intelligent imaging
Reconfigurable perovskite X-ray detector for intelligent imaging