Featured
-
-
Letter |
 A structural transition in physical networks
A structural transition in physical networks
A modelling framework is presented to determine the optimal layout and physical properties of networks in which the nodes and links have physical sizes and intersections between components is prohibited.
- Nima Dehmamy
- , Soodabeh Milanlouei
- & Albert-László Barabási
-
Letter |
 Electronic noise due to temperature differences in atomic-scale junctions
Electronic noise due to temperature differences in atomic-scale junctions
A fundamental electronic noise—beyond electronic thermal noise and voltage-activated shot noise—that is generated by temperature differences across nanoscale conductors is demonstrated, with possible implications for thermometry and electronics.
- Ofir Shein Lumbroso
- , Lena Simine
- & Oren Tal
-
Letter |
 Sorting ultracold atoms in a three-dimensional optical lattice in a realization of Maxwell’s demon
Sorting ultracold atoms in a three-dimensional optical lattice in a realization of Maxwell’s demon
An experiment inspired by Maxwell’s ‘demon’ thought experiment uses a series of reversible operations to fully fill a three-dimensional optical lattice with ultracold atoms and realize a low-entropy state.
- Aishwarya Kumar
- , Tsung-Yao Wu
- & David S. Weiss
-
Letter |
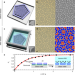 A Brownian quasi-crystal of pre-assembled colloidal Penrose tiles
A Brownian quasi-crystal of pre-assembled colloidal Penrose tiles
A lithographic patterning and release method is used to create a dense, fluctuating, Brownian system of mobile colloidal kite- and dart-shaped Penrose tiles over large areas that retains quasi-crystalline order.
- Po-Yuan Wang
- & Thomas G. Mason
-
Letter |
 Resonant domain-wall-enhanced tunable microwave ferroelectrics
Resonant domain-wall-enhanced tunable microwave ferroelectrics
The domain-wall structure and dynamics are found to enhance, rather than inhibit, the high-frequency performance of an intrinsically tunable material, obtaining ultralow loss and exceptional frequency selectivity.
- Zongquan Gu
- , Shishir Pandya
- & Jonathan E. Spanier
-
Letter |
 Hot streaks in artistic, cultural, and scientific careers
Hot streaks in artistic, cultural, and scientific careers
The career trajectories of around 30,000 artists, film directors and scientists show that individuals in each domain have ‘hot streaks’ during which their works have increased impact, despite showing no increase in productivity.
- Lu Liu
- , Yang Wang
- & Dashun Wang
-
Letter |
 Addressing the minimum fleet problem in on-demand urban mobility
Addressing the minimum fleet problem in on-demand urban mobility
An optimal computationally efficient solution to the problem of finding the minimum taxi fleet size using a vehicle-sharing network is presented.
- M. M. Vazifeh
- , P. Santi
- & C. Ratti
-
Letter |
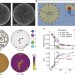 Freezing on a sphere
Freezing on a sphere
Freezing on a spherical surface is shown to proceed by the sequestration of defects into 12 icosahedrally coordinated ‘seas’ that enable the formation of a crystalline ‘continent’ with long-range orientational order.
- Rodrigo E. Guerra
- , Colm P. Kelleher
- & Paul M. Chaikin
-
Letter |
 Global patterns of tropical forest fragmentation
Global patterns of tropical forest fragmentation
Satellite data and modelling reveal that tropical forest fragments have similar size distributions across continents, and that forest fragmentation is close to a critical point, beyond which fragment numbers will strongly increase.
- Franziska Taubert
- , Rico Fischer
- & Andreas Huth
-
Letter |
 Granular materials flow like complex fluids
Granular materials flow like complex fluids
The relaxation dynamics of granular materials is more like that of complex fluids than that of thermal glass-forming systems, owing to the absence of the ‘cage effect’.
- Binquan Kou
- , Yixin Cao
- & Yujie Wang
-
Letter |
 Chaotic dynamics in nanoscale NbO2 Mott memristors for analogue computing
Chaotic dynamics in nanoscale NbO2 Mott memristors for analogue computing
A relaxation oscillator incorporating nanoscale niobium dioxide memristors that exhibit both a current- and a temperature-controlled negative differential resistance produces chaotic dynamics that aid biomimetic computing.
- Suhas Kumar
- , John Paul Strachan
- & R. Stanley Williams
-
Letter |
 Experimental characterization of a quantum many-body system via higher-order correlations
Experimental characterization of a quantum many-body system via higher-order correlations
Experimental measurements of higher-order correlation functions in many-body systems provide insight into a non-trivial quantum field theory and how it can be implemented in a cold-atom quantum simulation.
- Thomas Schweigler
- , Valentin Kasper
- & Jörg Schmiedmayer
-
Article |
 A living mesoscopic cellular automaton made of skin scales
A living mesoscopic cellular automaton made of skin scales
A mesoscopic cellular automaton arising from a microscopic reaction–diffusion system as a function of skin thickness is observed in ocellated lizards, showing that cellular automata are not merely abstract computational systems, but can directly correspond to processes generated by biological evolution.
- Liana Manukyan
- , Sophie A. Montandon
- & Michel C. Milinkovitch
-
Letter |
 Topological defects control collective dynamics in neural progenitor cell cultures
Topological defects control collective dynamics in neural progenitor cell cultures
The cell flow and defects within the alignment pattern of cultured mouse neural progenitor cells are described.
- Kyogo Kawaguchi
- , Ryoichiro Kageyama
- & Masaki Sano
-
Letter |
 Weak synchronization and large-scale collective oscillation in dense bacterial suspensions
Weak synchronization and large-scale collective oscillation in dense bacterial suspensions
Cells in dense bacterial suspensions can self-organize into highly robust collective oscillatory motion, while individual cells move in an erratic manner; their interaction is modelled to reveal a weak synchronization mechanism.
- Chong Chen
- , Song Liu
- & Yilin Wu
-
Letter |
 Emergence of a turbulent cascade in a quantum gas
Emergence of a turbulent cascade in a quantum gas
The gradual development of a turbulent cascade in a weakly interacting homogeneous Bose gas is observed on application of a periodic driving force.
- Nir Navon
- , Alexander L. Gaunt
- & Zoran Hadzibabic
-
Letter |
 Autocatalytic, bistable, oscillatory networks of biologically relevant organic reactions
Autocatalytic, bistable, oscillatory networks of biologically relevant organic reactions
A few-component network of biologically relevant, organic reactions displays bistability and oscillations, without an enzymatic catalyst.
- Sergey N. Semenov
- , Lewis J. Kraft
- & George M. Whitesides
-
Letter |
 Combinatorial design of textured mechanical metamaterials
Combinatorial design of textured mechanical metamaterials
Lattices of cubic building blocks that deform anisotropically and that are designed to fit together like a three-dimensional jigsaw puzzle are 3D printed to create aperiodic, frustration-free, mechanical metamaterials; these metamaterials act as programmable shape-shifters and are able to perform pattern analysis.
- Corentin Coulais
- , Eial Teomy
- & Martin van Hecke
-
Letter |
 Ablation-cooled material removal with ultrafast bursts of pulses
Ablation-cooled material removal with ultrafast bursts of pulses
Ablation cooling is demonstrated as an effective means of removing material using successive bursts of laser pulses with short intraburst delay times; the technique allows the overall pulse energy to be decreased, overcoming negative thermal effects during the ablation process.
- Can Kerse
- , Hamit Kalaycıoğlu
- & Fatih Ömer Ilday
-
Letter |
 Mean first-passage times of non-Markovian random walkers in confinement
Mean first-passage times of non-Markovian random walkers in confinement
An analytical method of determining the mean first-passage time (the time taken by a random walker in confinement to reach a target point) is presented for a Gaussian non-Markovian random walker, thus revealing the importance of memory effects in first-passage statistics.
- T. Guérin
- , N. Levernier
- & R. Voituriez
-
Letter |
 Intrinsic ferroelectric switching from first principles
Intrinsic ferroelectric switching from first principles
Molecular dynamics simulations of 90° domain walls in PbTiO3 are used to construct a nucleation-and-growth-based analytical model that quantifies the dynamics of many types of domain walls in various ferroelectrics, suggesting intrinsic domain-wall motion as a universal mechanism for ferroelectric switching.
- Shi Liu
- , Ilya Grinberg
- & Andrew M. Rappe
-
Letter
| Open Access The role of low-volatility organic compounds in initial particle growth in the atmosphere
The role of low-volatility organic compounds in initial particle growth in the atmosphere
The growth of nucleated organic particles has been investigated in controlled laboratory experiments under atmospheric conditions; initial growth is driven by organic vapours of extremely low volatility, and accelerated by more abundant vapours of slightly higher volatility, leading to markedly different modelled concentrations of atmospheric cloud condensation nuclei when this growth mechanism is taken into account.
- Jasmin Tröstl
- , Wayne K. Chuang
- & Urs Baltensperger
-
Letter |
 Direct observation of dynamic shear jamming in dense suspensions
Direct observation of dynamic shear jamming in dense suspensions
Dense suspensions of hard granular particles can transform from liquid-like to solid-like when perturbed; a state diagram is mapped out that reveals how this transformation can occur via dynamic jamming at sufficiently large shear stress while leaving the particle density unchanged.
- Ivo R. Peters
- , Sayantan Majumdar
- & Heinrich M. Jaeger
-
-
-
Letter |
 Universal resilience patterns in complex networks
Universal resilience patterns in complex networks
An analytical framework is proposed for a complex network to accurately predict its dynamic resilience and unveil the network characteristics that can enhance or diminish resilience.
- Jianxi Gao
- , Baruch Barzel
- & Albert-László Barabási
-
Letter |
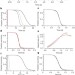 The temporal scaling of Caenorhabditis elegans ageing
The temporal scaling of Caenorhabditis elegans ageing
A diverse range of molecular and genetic manipulations all alter lifespan distributions of Caenorhabditis elegans by an apparent stretching or shrinking of time.
- Nicholas Stroustrup
- , Winston E. Anthony
- & Walter Fontana
-
Letter |
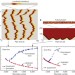 The rise of fully turbulent flow
The rise of fully turbulent flow
Experiments, asymptotic theory and computer simulations of wall-bounded shear flow uncover a bifurcation scenario that explains the transition from localized turbulent patches to fully turbulent flow.
- Dwight Barkley
- , Baofang Song
- & Björn Hof
-
Letter |
 Universal Fermi liquid crossover and quantum criticality in a mesoscopic system
Universal Fermi liquid crossover and quantum criticality in a mesoscopic system
Zero-temperature quantum phase transitions and their associated quantum critical points are believed to underpin the exotic finite-temperature behaviours of many strongly correlated electronic systems, but identifying the microscopic origins of these transitions can be challenging and controversial; Keller et al. (see also the related paper by Iftikhar et al.) show how such behaviours can be engineered into nanoelectronic quantum dots, which permit both precise experimental control of the quantum critical behaviour and its exact theoretical characterization.
- A. J. Keller
- , L. Peeters
- & D. Goldhaber-Gordon
-
Letter |
 Multi-gigaelectronvolt acceleration of positrons in a self-loaded plasma wakefield
Multi-gigaelectronvolt acceleration of positrons in a self-loaded plasma wakefield
A particle accelerator that is two orders of magnitude more efficient than conventional radio-frequency accelerators is described in which positrons (rather than electrons) at the front of a bunch transfer their energy to a substantial number of positrons at the rear of the same bunch by exciting a wakefield in the plasma.
- S. Corde
- , E. Adli
- & G. Yocky
-
Letter |
 Influence maximization in complex networks through optimal percolation
Influence maximization in complex networks through optimal percolation
A rigorous method to determine the most influential superspreaders in complex networks is presented—involving the mapping of the problem onto optimal percolation along with a scalable algorithm for big-data social networks—showing, unexpectedly, that many weak nodes can be powerful influencers.
- Flaviano Morone
- & Hernán A. Makse
-
Letter |
 Metastable liquid–liquid transition in a molecular model of water
Metastable liquid–liquid transition in a molecular model of water
A stable crystal phase and two metastable liquid phases of the ST2 model of water exist at the same deeply supercooled condition, and the two liquids undergo a first-order liquid–liquid transition that meets stringent thermodynamic criteria.
- Jeremy C. Palmer
- , Fausto Martelli
- & Pablo G. Debenedetti
-
Letter |
 Quantum chaos in ultracold collisions of gas-phase erbium atoms
Quantum chaos in ultracold collisions of gas-phase erbium atoms
An ultracold gas of erbium atoms is shown to have many scattering resonances whose quantum fluctuations exhibit chaotic behaviour resulting from the anisotropy of the atoms’ interactions.
- Albert Frisch
- , Michael Mark
- & Svetlana Kotochigova
-
Letter |
 Emergence of macroscopic directed motion in populations of motile colloids
Emergence of macroscopic directed motion in populations of motile colloids
Populations of millions of colloidal rolling particles are shown to self-organize to achieve coherent motion; comparison between experiment and theory based on the microscopic interactions between these ‘rollers’ suggests that hydrodynamic interactions promote the emergence of the collective motion.
- Antoine Bricard
- , Jean-Baptiste Caussin
- & Denis Bartolo
-
Perspective |
 Globally networked risks and how to respond
Globally networked risks and how to respond
Strongly connected and interdependent networks create risks of global-scale catastrophic failure; to make networked risks more manageable, it is suggested to establish a ‘Global Systems Science’.
- Dirk Helbing
-
News & Views |
 Quantum interference heats up
Quantum interference heats up
A thermal effect predicted more than 40 years ago was nearly forgotten, while a related phenomenon stole the limelight. Now experimentally verified, the effect could spur the development of heat-controlling devices. See Letter p.401
- Raymond W. Simmonds
-
News & Views |
 Synchronized tumbling particles
Synchronized tumbling particles
Magnetic particles have been made that undergo synchronized oscillations when suspended in liquid in a rotating magnetic field. This discovery links the fields of nonlinear dynamics and materials science. See Letter p.578
- Sabine H. L. Klapp
-
News & Views |
 The fridge gate
The fridge gate
Logic gates are the elementary building blocks of computers. The finding that a single logic gate may drive a refrigerator is a beautiful demonstration that information-processing devices can have useful thermodynamic properties.
- Renato Renner
-
Letter |
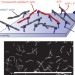 Polar patterns of driven filaments
Polar patterns of driven filaments
Collective motion is a ubiquitous self-organization phenomenon that can be observed in systems ranging from flocks of animals to the cytoskeleton. Similarities between these systems suggest that there are universal underlying principles. This idea can be tested with 'active' or 'driven' fluids, but so far such systems have offered limited parameter control. Here, an active fluid is studied that contains only a few components — actin filaments and molecular motors — allowing the control of all relevant system parameters.
- Volker Schaller
- , Christoph Weber
- & Andreas R. Bausch
-
News & Views |
 Closing in on evaders
Closing in on evaders
A simple model highlights the pros and cons of chasing — and escaping — in groups. It shows that, for a given number of prey animals, an optimal number of predators exists that maximizes the success of the catch.
- Tamás Vicsek
-
News & Views |
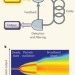 Optoelectronic chaos
Optoelectronic chaos
Optoelectronic circuits with delayed feedback provide a convenient bench-top platform to study a wide range of nonlinear dynamic systems, from ultrastable clocks to complex chaotic devices.
- Laurent Larger
- & John M. Dudley

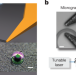 Real-time vibrations of a carbon nanotube
Real-time vibrations of a carbon nanotube Metastability and no criticality
Metastability and no criticality