Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembled photonic cavities with atomic-scale confinement
Self-assembled photonic cavities with atomic-scale confinement
Silicon photonic nanocavities based on surface forces and conventional lithography and etching are developed, demonstrating pioneering technology that integrates atomic dimensions with the scalability of planar semiconductors.
- Ali Nawaz Babar
- , Thor August Schimmell Weis
- & Søren Stobbe
-
News |
 IBM releases first-ever 1,000-qubit quantum chip
IBM releases first-ever 1,000-qubit quantum chip
The company announces its latest huge chip — but will now focus on developing smaller chips with a fresh approach to ‘error correction’.
- Davide Castelvecchi
-
Article |
 Exploring large-scale entanglement in quantum simulation
Exploring large-scale entanglement in quantum simulation
On a 51-ion quantum simulator, we investigate locality of entanglement Hamiltonians for a Heisenberg chain, demonstrating Bisognano–Wichmann predictions of quantum field theory applied to lattice many-body systems, and observe the transition from area- to volume-law scaling of entanglement entropies.
- Manoj K. Joshi
- , Christian Kokail
- & Peter Zoller
-
Nature Careers Podcast |
 Scientific illustration: striking the balance between creativity and accuracy
Scientific illustration: striking the balance between creativity and accuracy
A misleading image in a medical textbook could have life and death implications, but some disciplines can deploy myth and metaphor to convey their science through art.
- Julie Gould
-
Article |
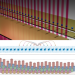 Continuous symmetry breaking in a trapped-ion spin chain
Continuous symmetry breaking in a trapped-ion spin chain
A one-dimensional trapped-ion quantum simulator with up to 23 spins is used to demonstrate a continuous symmetry-breaking phase that relies on long-range interactions.
- Lei Feng
- , Or Katz
- & Christopher Monroe
-
Article |
 Quantum gas mixtures and dual-species atom interferometry in space
Quantum gas mixtures and dual-species atom interferometry in space
Using upgraded hardware of the multiuser Cold Atom Lab (CAL) aboard the International Space Station (ISS), Bose–Einstein condensates (BECs) of two atomic isotopes are simultaneously created and used to demonstrate interspecies interactions and dual species atom interferometry in space.
- Ethan R. Elliott
- , David C. Aveline
- & Jason R. Williams
-
Career Feature |
 The future is quantum: universities look to train engineers for an emerging industry
The future is quantum: universities look to train engineers for an emerging industry
With quantum technologies heading for the mainstream, undergraduate courses are preparing the workforce of the future.
- Sophia Chen
-
Spotlight |
 Keeping secrets in a quantum world
Keeping secrets in a quantum world
Cryptographers are preparing for new quantum computers that will break their ciphers.
- Neil Savage
-
News & Views |
 Magnetic atoms push interactions to new lengths for quantum simulation
Magnetic atoms push interactions to new lengths for quantum simulation
Lasers, and a cold ensemble of magnetic atoms, have been used to mimic a complex quantum system characterized by long-range interactions — an essential ingredient for realizing realistic models of many quantum materials.
- P. Blair Blakie
- & Barbara Capogrosso-Sansone
-
Research Briefing |
 Large-scale nanowire camera with a single-photon sensitivity
Large-scale nanowire camera with a single-photon sensitivity
Superconducting detectors are a leading technology for the detection of single photons, but have been limited in the number of pixels that they can offer. A 400,000-pixel superconducting nanowire single-photon detector camera provides an improvement by a factor of 400 compared with the current state of the art.
-
Article |
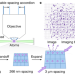 Dipolar quantum solids emerging in a Hubbard quantum simulator
Dipolar quantum solids emerging in a Hubbard quantum simulator
The realization of dipolar quantum solids with an ultracold gas of magnetic atoms in an optical lattice ushers in quantum simulation of many-body systems with long-range anisotropic interactions.
- Lin Su
- , Alexander Douglas
- & Markus Greiner
-
News & Views |
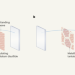 Searching for phase transitions in the dark
Searching for phase transitions in the dark
An electrically insulating quantum material turns metallic when placed between two semi-reflecting mirrors — even if there is no illumination between them. This discovery paves the way for engineering other phase transitions.
- Edoardo Baldini
-
Article
| Open Access Measurement-induced entanglement and teleportation on a noisy quantum processor
Measurement-induced entanglement and teleportation on a noisy quantum processor
Measurement-induced phases of quantum information have been observed in a system of 70 superconducting qubits.
- J. C. Hoke
- , M. Ippoliti
- & P. Roushan
-
Article
| Open Access Erasure conversion in a high-fidelity Rydberg quantum simulator
Erasure conversion in a high-fidelity Rydberg quantum simulator
Erasure conversion and detection are used in a Rydberg quantum simulator to create Bell states with high fidelity, competitive with other state-of-the-art platforms.
- Pascal Scholl
- , Adam L. Shaw
- & Manuel Endres
-
Article
| Open Access High-fidelity parallel entangling gates on a neutral-atom quantum computer
High-fidelity parallel entangling gates on a neutral-atom quantum computer
The realization of two-qubit entangling gates with 99.5% fidelity on up to 60 rubidium atoms in parallel is reported, surpassing the surface-code threshold for error correction and laying the groundwork for neutral-atom quantum computers.
- Simon J. Evered
- , Dolev Bluvstein
- & Mikhail D. Lukin
-
Article |
 High-fidelity gates and mid-circuit erasure conversion in an atomic qubit
High-fidelity gates and mid-circuit erasure conversion in an atomic qubit
This study reports gates between qubits encoded in the nuclear spin state of Yb atoms trapped in optical tweezers, reaching very high fidelity and demonstrating mid-circuit conversion of errors into erasure errors.
- Shuo Ma
- , Genyue Liu
- & Jeff D. Thompson
-
News |
 New kind of quantum computer made using high-resolution microscope
New kind of quantum computer made using high-resolution microscope
Individual atoms on a surface do their first basic calculation.
- Davide Castelvecchi
-
Research Briefing |
 Testing the limits of the standard model of particle physics with a heavy, highly charged ion
Testing the limits of the standard model of particle physics with a heavy, highly charged ion
Quantum electrodynamics, the archetypical theory of electromagnetic interactions, describes the behaviour of charged particles and photons using quantum field theory. Measuring the g factor of a bound electron in a hydrogen-like tin ion (118Sn49+) provides one of the most stringent tests so far of quantum electrodynamics in strong electric fields.
-
Article
| Open Access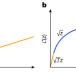 Universality in long-distance geometry and quantum complexity
Universality in long-distance geometry and quantum complexity
Many different homogeneous metrics on Lie groups, which may have markedly different short-distance properties, are shown to exhibit nearly identical distance functions at long distances, suggesting a large universality class of definitions of quantum complexity.
- Adam R. Brown
- , Michael H. Freedman
- & Leonard Susskind
-
Article
| Open Access A quantum engine in the BEC–BCS crossover
A quantum engine in the BEC–BCS crossover
This study reports the creation of a model thermodynamic engine that is fuelled by the energy difference resulting from changing the statistics of a quantum gas from bosonic to fermionic.
- Jennifer Koch
- , Keerthy Menon
- & Artur Widera
-
Article
| Open Access Resonant X-ray excitation of the nuclear clock isomer 45Sc
Resonant X-ray excitation of the nuclear clock isomer 45Sc
Resonant X-ray excitation of the 45Sc nuclear isomeric state was achieved by irradiation of a Sc-metal foil with 12.4-keV photon pulses from a state-of-the-art X-ray free-electron laser, allowing a high-precision determination of the transition energy.
- Yuri Shvyd’ko
- , Ralf Röhlsberger
- & Tomasz Kolodziej
-
Research Briefing |
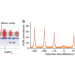 A step closer to repeaters for quantum networks
A step closer to repeaters for quantum networks
Loss of photons over long-distance connections limits the development of quantum networks, necessitating the use of quantum ‘repeater’ systems to boost signals between network nodes. Erbium ions incorporated into calcium tungstate crystals have been found to emit photons in the telecommunications frequency band that are indistinguishable from each other, and thus show promise for use in such repeaters.
-
Article |
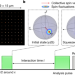 Scalable spin squeezing in a dipolar Rydberg atom array
Scalable spin squeezing in a dipolar Rydberg atom array
In the dipolar XY model, quench dynamics from a polarized initial state lead to spin squeezing that improves with increasing system size, and two refinements show further enhanced squeezing and extended lifetime of the squeezed state by freezing its dynamics.
- Guillaume Bornet
- , Gabriel Emperauger
- & Antoine Browaeys
-
Article |
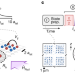 Realizing spin squeezing with Rydberg interactions in an optical clock
Realizing spin squeezing with Rydberg interactions in an optical clock
Spin squeezing in an optical atomic clock based on arrays of neutral atoms is used to realize measurement performance below the standard quantum limit.
- William J. Eckner
- , Nelson Darkwah Oppong
- & Adam M. Kaufman
-
Article |
 Indistinguishable telecom band photons from a single Er ion in the solid state
Indistinguishable telecom band photons from a single Er ion in the solid state
Er3+ is implanted into CaWO4, a material with non-polar site symmetry free of background rare earth ions, to realize reduced optical spectral diffusion in nanophotonic devices, representing a step towards making telecom band quantum repeater networks with single ions.
- Salim Ourari
- , Łukasz Dusanowski
- & Jeff D. Thompson
-
Article |
 Quantum-enhanced sensing on optical transitions through finite-range interactions
Quantum-enhanced sensing on optical transitions through finite-range interactions
A method is described for the generation of large-scale entanglement that can be used for quantum-enhanced sensing even when systems are limited to short-range interactions in experiments with up to 51 trapped ions.
- Johannes Franke
- , Sean R. Muleady
- & Christian F. Roos
-
Essay |
 Could the Universe be a giant quantum computer?
Could the Universe be a giant quantum computer?
Computational rules might describe the evolution of the cosmos better than the dynamical equations of physics — but only if they are given a quantum twist.
- David L. Chandler
-
Article
| Open Access Reversible spin-optical interface in luminescent organic radicals
Reversible spin-optical interface in luminescent organic radicals
We report organic molecules showing both efficient luminescence and near-unity generation yield of excited states with high spin multiplicity, simultaneously supporting a high efficiency of initialization, spin manipulations and light-based readout at room temperature.
- Sebastian Gorgon
- , Kuo Lv
- & Emrys W. Evans
-
Research Briefing |
 Emergent ferromagnetic states revealed in a geometrically frustrated triangular lattice
Emergent ferromagnetic states revealed in a geometrically frustrated triangular lattice
The ordering of magnetic moments in a strongly correlated system depends on the lattice they inhabit, with triangular lattices yielding exotic phases through an effect called geometrical frustration. Experiments demonstrate that ultracold atoms in such lattices show frustration and, surprisingly, display an ordering called ferromagnetism when mobile charges are present.
-
Article |
 Frustration- and doping-induced magnetism in a Fermi–Hubbard simulator
Frustration- and doping-induced magnetism in a Fermi–Hubbard simulator
The magnetic phases of the geometrically frustrated triangular lattice Hubbard model are directly investigated using ultracold fermionic atoms, indicating a possible transition to ferromagnetism at a filling of 1.2.
- Muqing Xu
- , Lev Haldar Kendrick
- & Markus Greiner
-
Article |
 Universal equation of state for wave turbulence in a quantum gas
Universal equation of state for wave turbulence in a quantum gas
Equilibrium-like state variables, related by an equation of state, are identified in a study of turbulent cascade of matter waves in a far-from-equilibrium ultracold atomic Bose gas.
- Lena H. Dogra
- , Gevorg Martirosyan
- & Zoran Hadzibabic
-
News & Views |
 The particle-physics breakthrough that paved the way for the Higgs boson
The particle-physics breakthrough that paved the way for the Higgs boson
The discovery of ‘weak neutral currents’ at Europe’s particle-physics research centre CERN 50 years ago was a decisive step towards establishing the standard model of particle physics — a journey that continues to this day.
- Pippa Wells
-
-
Comment |
 How to introduce quantum computers without slowing economic growth
How to introduce quantum computers without slowing economic growth
To smooth the path of the quantum revolution, researchers and governments must predict and prepare for the traps ahead.
- Chander Velu
- & Fathiro H. R. Putra
-
News & Views |
 A fast quantum route to random numbers
A fast quantum route to random numbers
Using a quantum computer to speed up one step in a textbook approach to generating random numbers proves to be a savvy strategy, and one that could make good use of quantum computers that will be available in the near future.
- Mohan Sarovar
-
Article |
 Generation of genuine entanglement up to 51 superconducting qubits
Generation of genuine entanglement up to 51 superconducting qubits
A scalable approach is provided for preparing and verifying intermediate-scale genuine entanglement on a 66-qubit superconducting quantum processor.
- Sirui Cao
- , Bujiao Wu
- & Jian-Wei Pan
-
Article |
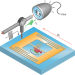 Single-electron spin resonance detection by microwave photon counting
Single-electron spin resonance detection by microwave photon counting
Spectroscopic measurements of individual rare-earth ion electron spins are performed by detecting their microwave fluorescence, with the method coming close to practical single-electron spin resonance at millikelvin temperatures.
- Z. Wang
- , L. Balembois
- & E. Flurin
-
Article |
 Quantum-enhanced Markov chain Monte Carlo
Quantum-enhanced Markov chain Monte Carlo
A quantum algorithm is introduced that performs Markov chain Monte Carlo to sample from the Boltzmann distribution of Ising models, demonstrating, through experiments and simulations, a polynomial speedup compared with classical alternatives.
- David Layden
- , Guglielmo Mazzola
- & Sarah Sheldon
-
News & Views |
 Clocks synchronized at the quantum limit
Clocks synchronized at the quantum limit
Time signals have been transmitted across 300 kilometres with an accuracy and precision limited only by the quantum nature of photons. The feat promises to revolutionize high-precision science using satellites.
- David Gozzard
-
Article |
 Quantum-limited optical time transfer for future geosynchronous links
Quantum-limited optical time transfer for future geosynchronous links
Laser-based time transfer with near quantum-limited acquisition and timing is demonstrated that can support femtosecond precision over 102 dB link loss, more than sufficient for future time transfer to geosynchronous orbits for future optical clock networks.
- Emily D. Caldwell
- , Jean-Daniel Deschenes
- & Laura C. Sinclair
-
Article |
 Realization of a fractional quantum Hall state with ultracold atoms
Realization of a fractional quantum Hall state with ultracold atoms
Using ultracold atoms trapped in an optical lattice, a Laughlin-like fractional quantum Hall state is prepared and mapped out on a microscopic level.
- Julian Léonard
- , Sooshin Kim
- & Markus Greiner
-
Research Highlight |
 Particle of sound put in two places at once
Particle of sound put in two places at once
Scientists place a phonon into superposition, paving the way for its use in quantum computers.
-
News & Views |
 Quantum computer scales up by mitigating errors
Quantum computer scales up by mitigating errors
A post-processing technique for handling errors has enabled a quantum computer comprising 127 quantum bits to calculate the physical properties of a complex model system — a task that cannot be performed by a classical computer.
- Göran Wendin
- & Jonas Bylander
-
News |
 IBM quantum computer passes calculation milestone
IBM quantum computer passes calculation milestone
‘Benchmark’ experiment suggests quantum computers could have useful real-world applications within two years.
- Davide Castelvecchi
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for the utility of quantum computing before fault tolerance
Evidence for the utility of quantum computing before fault tolerance
Experiments on a noisy 127-qubit superconducting quantum processor report the accurate measurement of expectation values beyond the reach of current brute-force classical computation, demonstrating evidence for the utility of quantum computing before fault tolerance.
- Youngseok Kim
- , Andrew Eddins
- & Abhinav Kandala
-
Essay |
 Particle, wave, both or neither? The experiment that challenges all we know about reality
Particle, wave, both or neither? The experiment that challenges all we know about reality
Thomas Young’s double-slit experiment originally served to prove that light is a wave — but later quantum versions have made for a much fuzzier picture.
- Anil Ananthaswamy
-
Spotlight |
 Towards quantum machine learning
Towards quantum machine learning
Jungsang Kim discusses his interest in the pioneering technology.
- Michael Brooks
-
Outlook |
 Rewriting the quantum-computer blueprint
Rewriting the quantum-computer blueprint
An architecture for quantum computers based on parity is attracting money from government and industry.
- Edwin Cartlidge
-
Outlook |
 Commercializing quantum computers step by step
Commercializing quantum computers step by step
Alongside developing a quantum computer, one group of scientists is selling its components to other researchers.
- Edwin Cartlidge

 Single-molecule electron spin resonance by means of atomic force microscopy
Single-molecule electron spin resonance by means of atomic force microscopy