Featured
-
-
Article |
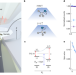 Imaging the Meissner effect in hydride superconductors using quantum sensors
Imaging the Meissner effect in hydride superconductors using quantum sensors
In order to explore superconductivity in hydride materials, local magnetometry inside a diamond anvil cell is performed with sub-micron spatial resolution at megabar pressures using nitrogen-vacancy colour centres.
- P. Bhattacharyya
- , W. Chen
- & N. Y. Yao
-
Article
| Open Access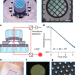 Room-temperature quantum optomechanics using an ultralow noise cavity
Room-temperature quantum optomechanics using an ultralow noise cavity
A room-temperature demonstration of optomechanical squeezing of light and measurement of mechanical motion approaching the Heisenberg limit using a phononic-engineered membrane-in-the-middle cavity with ultralow noise.
- Guanhao Huang
- , Alberto Beccari
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
Article |
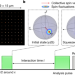 Scalable spin squeezing in a dipolar Rydberg atom array
Scalable spin squeezing in a dipolar Rydberg atom array
In the dipolar XY model, quench dynamics from a polarized initial state lead to spin squeezing that improves with increasing system size, and two refinements show further enhanced squeezing and extended lifetime of the squeezed state by freezing its dynamics.
- Guillaume Bornet
- , Gabriel Emperauger
- & Antoine Browaeys
-
Article |
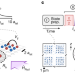 Realizing spin squeezing with Rydberg interactions in an optical clock
Realizing spin squeezing with Rydberg interactions in an optical clock
Spin squeezing in an optical atomic clock based on arrays of neutral atoms is used to realize measurement performance below the standard quantum limit.
- William J. Eckner
- , Nelson Darkwah Oppong
- & Adam M. Kaufman
-
Article |
 Quantum-enhanced sensing on optical transitions through finite-range interactions
Quantum-enhanced sensing on optical transitions through finite-range interactions
A method is described for the generation of large-scale entanglement that can be used for quantum-enhanced sensing even when systems are limited to short-range interactions in experiments with up to 51 trapped ions.
- Johannes Franke
- , Sean R. Muleady
- & Christian F. Roos
-
Article |
 Quantum-limited optical time transfer for future geosynchronous links
Quantum-limited optical time transfer for future geosynchronous links
Laser-based time transfer with near quantum-limited acquisition and timing is demonstrated that can support femtosecond precision over 102 dB link loss, more than sufficient for future time transfer to geosynchronous orbits for future optical clock networks.
- Emily D. Caldwell
- , Jean-Daniel Deschenes
- & Laura C. Sinclair
-
Article |
 Topological lattices realized in superconducting circuit optomechanics
Topological lattices realized in superconducting circuit optomechanics
Optomechanical lattices in one and two dimensions with exceptionally low disorder are realized, showing how the optomechanical interaction can be exploited for direct measurements of the Hamiltonian, beyond the tight-binding approximation.
- Amir Youssefi
- , Shingo Kono
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
Article |
 Distributed quantum sensing with mode-entangled spin-squeezed atomic states
Distributed quantum sensing with mode-entangled spin-squeezed atomic states
A spatially distributed, atomic clock network entangled via quantum nondemolition measurements offers better precision and lower noise compared to an equivalent mode-separable network, and the improvements scale with network size.
- Benjamin K. Malia
- , Yunfan Wu
- & Mark A. Kasevich
-
Article
| Open Access Entanglement-enhanced matter-wave interferometry in a high-finesse cavity
Entanglement-enhanced matter-wave interferometry in a high-finesse cavity
A matter-wave interferometer is demonstrated with an interferometric phase noise below the standard quantum limit, combining two core concepts of quantum mechanics, that a particle can simultaneously be in two places at once and entanglement between distinct particles.
- Graham P. Greve
- , Chengyi Luo
- & James K. Thompson
-
Article |
 Free-space dissemination of time and frequency with 10−19 instability over 113 km
Free-space dissemination of time and frequency with 10−19 instability over 113 km
By using 1 W optical frequency combs and nanowatt-level linear optical sampling modules, a time–frequency dissemination over a free-space link of 113 km is achieved with a stability of less than 4 × 10−19 at 10,000 s.
- Qi Shen
- , Jian-Yu Guan
- & Jian-Wei Pan
-
Article |
 An elementary quantum network of entangled optical atomic clocks
An elementary quantum network of entangled optical atomic clocks
An elementary quantum network of two entangled atomic clocks is demonstrated; the high fidelity and speed of entanglement generation show that entangled clocks can offer practical enhancement for metrology.
- B. C. Nichol
- , R. Srinivas
- & D. M. Lucas
-
Article |
 Quantized current steps due to the a.c. coherent quantum phase-slip effect
Quantized current steps due to the a.c. coherent quantum phase-slip effect
Direct observation of the physical dual a.c. Josephson effect, a series of quantized current steps in a superconducting nanowire, is reported and may offer a way to establish new metrological standards for currents.
- Rais S. Shaikhaidarov
- , Kyung Ho Kim
- & Oleg V. Astafiev
-
Article
| Open Access Continuous Bose–Einstein condensation
Continuous Bose–Einstein condensation
Continuous, indefinitely lasting Bose–Einstein condensation, sustained by amplification through Bose-stimulated gain of atoms from a thermal bath, creates a continuous-wave condensate of strontium atoms.
- Chun-Chia Chen
- , Rodrigo González Escudero
- & Florian Schreck
-
Article |
 Optimal metrology with programmable quantum sensors
Optimal metrology with programmable quantum sensors
A new approach to generating quantum sensors with close-to-optimal performance is demonstrated experimentally through Ramsey interferometry with (up to) N = 26 entangled atoms on a trapped-ion quantum computer, without a priori knowledge of the device or its noise environment.
- Christian D. Marciniak
- , Thomas Feldker
- & Thomas Monz
-
Article |
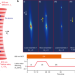 Differential clock comparisons with a multiplexed optical lattice clock
Differential clock comparisons with a multiplexed optical lattice clock
Multiple ultracold ensembles of strontium atoms are trapped in the same optical lattice, realizing a multiplexed optical clock where precision measurements can benefit from having all atoms share the same trapping light and clock laser.
- Xin Zheng
- , Jonathan Dolde
- & Shimon Kolkowitz
-
Article |
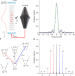 Resolving the gravitational redshift across a millimetre-scale atomic sample
Resolving the gravitational redshift across a millimetre-scale atomic sample
Reducing the fractional uncertainty over the measurement of the frequency of an ensemble of trapped strontium atoms enables observation of the gravitational redshift at the submillimetre scale.
- Tobias Bothwell
- , Colin J. Kennedy
- & Jun Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated photonics enables continuous-beam electron phase modulation
Integrated photonics enables continuous-beam electron phase modulation
A silicon nitride microresonator is used for coherent phase modulation of a transmission electron microscope beam, with future applications in combining high-resolution microscopy with spectroscopy, holography and metrology.
- Jan-Wilke Henke
- , Arslan Sajid Raja
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Direct limits for scalar field dark matter from a gravitational-wave detector
Direct limits for scalar field dark matter from a gravitational-wave detector
Using a gravitational-wave detector to listen for dark matter signatures, a direct search for scalar field dark matter was conducted and new upper limits are set on the coupling constants.
- Sander M. Vermeulen
- , Philip Relton
- & Holger Wittel
-
Article |
 Demonstration of a trapped-ion atomic clock in space
Demonstration of a trapped-ion atomic clock in space
Operating in space, NASA’s Deep Space Atomic Clock, a trapped-ion clock, is shown to have long-term stability and drift that are an order of magnitude better than current space clocks.
- E. A. Burt
- , J. D. Prestage
- & T. A. Ely
-
Article |
 Accurately computing the electronic properties of a quantum ring
Accurately computing the electronic properties of a quantum ring
As a blueprint for high-precision quantum simulation, an 18-qubit algorithm that consists of more than 1,400 two-qubit gates is demonstrated, and reconstructs the energy eigenvalues of the simulated one-dimensional wire to a precision of 1 per cent.
- C. Neill
- , T. McCourt
- & V. Smelyanskiy
-
Article |
 A quantum enhanced search for dark matter axions
A quantum enhanced search for dark matter axions
A quantum enhanced search for dark matter that uses vacuum squeezing to overcome the quantum noise limit finds no evidence of dark matter axions in a well motivated mass range.
- K. M. Backes
- , D. A. Palken
- & H. Wang
-
Article |
 Entanglement on an optical atomic-clock transition
Entanglement on an optical atomic-clock transition
A many-atom state of trapped 171Yb atoms that are entangled on an optical atomic-clock transition overcomes the standard quantum limit, providing a proof-of-principle demonstration towards entanglement-based optical atomic clocks.
- Edwin Pedrozo-Peñafiel
- , Simone Colombo
- & Vladan Vuletić
-
Article |
 Half-minute-scale atomic coherence and high relative stability in a tweezer clock
Half-minute-scale atomic coherence and high relative stability in a tweezer clock
A tweezer clock containing about 150 88Sr atoms achieves trapping and optical excited-state lifetimes exceeding 40 seconds, and shows relative fractional frequency stability similar to that of leading atomic clocks.
- Aaron W. Young
- , William J. Eckner
- & Adam M. Kaufman
-
Article |
 Determination of the fine-structure constant with an accuracy of 81 parts per trillion
Determination of the fine-structure constant with an accuracy of 81 parts per trillion
The fine-structure constant is determined with an accuracy of 81 parts per trillion using matter-wave interferometry to measure the rubidium atom recoil velocity.
- Léo Morel
- , Zhibin Yao
- & Saïda Guellati-Khélifa
-
Article |
 Imaging viscous flow of the Dirac fluid in graphene
Imaging viscous flow of the Dirac fluid in graphene
Viscous Dirac fluid flow in room-temperature graphene is imaged using quantum diamond magnetometry, revealing a parabolic Poiseuille profile for electron flow in a high-mobility graphene channel near the charge-neutrality point.
- Mark J. H. Ku
- , Tony X. Zhou
- & Ronald L. Walsworth
-
Article |
 Spin squeezing of 1011 atoms by prediction and retrodiction measurements
Spin squeezing of 1011 atoms by prediction and retrodiction measurements
A squeezed collective state of 1011 rubidium atoms is generated by quantum non-demolition measurements, and the accuracy of the estimation of their collective spin is improved using past quantum state retrodiction.
- Han Bao
- , Junlei Duan
- & Yanhong Xiao
-
Article |
 Coherent laser spectroscopy of highly charged ions using quantum logic
Coherent laser spectroscopy of highly charged ions using quantum logic
The precision of laser spectroscopy of highly charged ions is improved by eight orders of magnitude by cooling trapped, highly charged ions and using quantum logic spectroscopy, thereby enabling tests of fundamental physics.
- P. Micke
- , T. Leopold
- & P. O. Schmidt
-
Article |
 Atomic-scale imaging of a 27-nuclear-spin cluster using a quantum sensor
Atomic-scale imaging of a 27-nuclear-spin cluster using a quantum sensor
An individual electron is used as a quantum sensor to realize atomic-scale magnetic resonance imaging.
- M. H. Abobeih
- , J. Randall
- & T. H. Taminiau
-
Letter |
 Quantum-enhanced sensing of a single-ion mechanical oscillator
Quantum-enhanced sensing of a single-ion mechanical oscillator
Number-state superpositions of the harmonic motion of a trapped beryllium ion are used to measure the oscillation frequency with quantum-enhanced sensitivity, achieving a mode-frequency uncertainty of about 10−6.
- Katherine C. McCormick
- , Jonas Keller
- & Dietrich Leibfried
-
Letter |
 Tracking the precession of single nuclear spins by weak measurements
Tracking the precession of single nuclear spins by weak measurements
Periodic weak measurements of just a few carbon-13 nuclear spins in diamond demonstrate sensitive, high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy at the molecular level.
- K. S. Cujia
- , J. M. Boss
- & C. L. Degen
-
Letter |
 Hypersonic Bose–Einstein condensates in accelerator rings
Hypersonic Bose–Einstein condensates in accelerator rings
Bose–Einstein condensates are transported at hypersonic speeds over a distance of 15 cm in a neutral-atom accelerator ring while preserving their internal coherence.
- Saurabh Pandey
- , Hector Mas
- & Wolf von Klitzing
-
Letter |
 Measurement of quantum back action in the audio band at room temperature
Measurement of quantum back action in the audio band at room temperature
Future gravitational-wave detectors are expected to be limited by quantum back action, which is now found in the audio band in a low-loss optomechanical system.
- Jonathan Cripe
- , Nancy Aggarwal
- & Thomas Corbitt
-
Letter |
 Optical clock comparison for Lorentz symmetry testing
Optical clock comparison for Lorentz symmetry testing
Agreement between two single-ion clocks is demonstrated experimentally at the 10−18 level over a six-month period, confirming a key postulate of Einstein’s theory of relativity with hundredfold-improved precision.
- Christian Sanner
- , Nils Huntemann
- & Sergey G. Porsev
-
Letter |
 Emergence of multi-body interactions in a fermionic lattice clock
Emergence of multi-body interactions in a fermionic lattice clock
Clock spectroscopy of ultracold strontium atoms in a three-dimensional optical lattice is used to observe the onset of multi-body interactions that result from the underlying pairwise interactions between atoms.
- A. Goban
- , R. B. Hutson
- & J. Ye
-
Letter |
 Space-borne Bose–Einstein condensation for precision interferometry
Space-borne Bose–Einstein condensation for precision interferometry
A Bose–Einstein condensate is created in space that has sufficient stability to enable its characteristic dynamics to be studied.
- Dennis Becker
- , Maike D. Lachmann
- & Ernst M. Rasel
-
Letter |
 High-resolution magnetic resonance spectroscopy using a solid-state spin sensor
High-resolution magnetic resonance spectroscopy using a solid-state spin sensor
High-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy at the scale of single cells is achieved by combining a magnetometer consisting of an ensemble of nitrogen–vacancy centres with a narrowband synchronized readout protocol.
- David R. Glenn
- , Dominik B. Bucher
- & Ronald L. Walsworth
-
Letter |
 Quantum back-action-evading measurement of motion in a negative mass reference frame
Quantum back-action-evading measurement of motion in a negative mass reference frame
By coupling a mechanical object to an ensemble of atomic spins with negative effective mass, the object’s position can be measured without the usual quantum back-action perturbation of its momentum.
- Christoffer B. Møller
- , Rodrigo A. Thomas
- & Eugene S. Polzik
-
Letter |
 Preparation and coherent manipulation of pure quantum states of a single molecular ion
Preparation and coherent manipulation of pure quantum states of a single molecular ion
By exploiting a co-trapped Ca+ ion, a single CaH+ ion is prepared in pure quantum states, which are coherently manipulated, using a protocol that could easily be extended to other molecular ion species.
- Chin-wen Chou
- , Christoph Kurz
- & Dietrich Leibfried
-
Letter |
 Simultaneous tracking of spin angle and amplitude beyond classical limits
Simultaneous tracking of spin angle and amplitude beyond classical limits
Simultaneous precise measurement of the non-commuting observables spin angle and spin amplitude is achieved by directing the error due to quantum measurement back-action into an unmeasured spin component.
- Giorgio Colangelo
- , Ferran Martin Ciurana
- & Morgan W. Mitchell
-
Letter |
 Quantum dynamics of simultaneously measured non-commuting observables
Quantum dynamics of simultaneously measured non-commuting observables
Simultaneous measurement of two incompatible observables in a superconducting qubit placed in a cavity shows that the quantum dynamics of the system is governed by the uncertainty principle and that the wavefunction collapse is replaced by persistent diffusion.
- Shay Hacohen-Gourgy
- , Leigh S. Martin
- & Irfan Siddiqi
-
Letter |
 A sensitive electrometer based on a Rydberg atom in a Schrödinger-cat state
A sensitive electrometer based on a Rydberg atom in a Schrödinger-cat state
A highly sensitive electrometer is reported that is based on a Schrödinger-cat state in a Rydberg atom, that reaches a sensitivity beyond the standard quantum limit and can compete with state-of-the-art electric field measurements performed using electromechanical resonators and single-electron transistors.
- Adrien Facon
- , Eva-Katharina Dietsche
- & Sébastien Gleyzes
-
Letter |
 Non-destructive state detection for quantum logic spectroscopy of molecular ions
Non-destructive state detection for quantum logic spectroscopy of molecular ions
Detecting the quantum states of molecules is harder than detecting those of atoms; here, a way around this problem is found by co-trapping a molecular and an atomic ion, using the state of the atomic ion to non-destructively determine that of the molecular ion.
- Fabian Wolf
- , Yong Wan
- & Piet O. Schmidt
-
Letter |
 Measurement noise 100 times lower than the quantum-projection limit using entangled atoms
Measurement noise 100 times lower than the quantum-projection limit using entangled atoms
Quantum entanglement is thought to offer great promise for improving measurement precision; now a spin-squeezing implementation with cold atoms offers levels of sensitivity unavailable with any competing conventional method, sensing microwave induced rotations a factor of 70 beyond the standard quantum limit.
- Onur Hosten
- , Nils J. Engelsen
- & Mark A. Kasevich
-
Letter |
 Multi-element logic gates for trapped-ion qubits
Multi-element logic gates for trapped-ion qubits
Harnessing the entanglement of different ionic species could bring new flexibility in quantum computing, and now two groups independently demonstrate entanglement between different atomic species; Tan et al. achieve entanglement between different elements, whereas the related paper by Ballance et al. shows entanglement between different atomic isotopes, together demonstrating a first step towards mixed-species quantum logic.
- T. R. Tan
- , J. P. Gaebler
- & D. J. Wineland
-
Letter |
 Measurement-based control of a mechanical oscillator at its thermal decoherence rate
Measurement-based control of a mechanical oscillator at its thermal decoherence rate
A position sensor is demonstrated that is capable of resolving the zero-point motion of a nanomechanical oscillator in the timescale of its thermal decoherence; it achieves an imprecision that is four orders of magnitude below that at the standard quantum limit and is used to feedback-cool the oscillator to a mean photon number of five.
- D. J. Wilson
- , V. Sudhir
- & T. J. Kippenberg
-
Letter |
 Spin–motion entanglement and state diagnosis with squeezed oscillator wavepackets
Spin–motion entanglement and state diagnosis with squeezed oscillator wavepackets
A single atom is used to create squeezed ‘Schrödinger’s cat’ states, which could be useful for quantum computation and interferometry.
- Hsiang-Yu Lo
- , Daniel Kienzler
- & Jonathan P. Home
-
Letter |
 State preservation by repetitive error detection in a superconducting quantum circuit
State preservation by repetitive error detection in a superconducting quantum circuit
A quantum error correction scheme is demonstrated in a system of superconducting qubits, and repeated quantum non-demolition measurements are used to track errors and reduce the failure rate; increasing the system size from five to nine qubits improves the failure rate further.
- J. Kelly
- , R. Barends
- & John M. Martinis
-
Letter |
 Michelson–Morley analogue for electrons using trapped ions to test Lorentz symmetry
Michelson–Morley analogue for electrons using trapped ions to test Lorentz symmetry
An electronic analogue of a Michelson–Morley experiment, in which an electron wave packet bound inside a calcium ion is split into two parts and subsequently recombined, demonstrates that the relative change in orientation of the two parts that results from the Earth’s rotation reveals no anisotropy in the electron dispersion; this verification of Lorentz symmetry improves on the precision of previous tests by a factor of 100.
- T. Pruttivarasin
- , M. Ramm
- & H. Häffner
-
Letter |
 Mapping the optimal route between two quantum states
Mapping the optimal route between two quantum states
Reconstruction of the quantum trajectories of a superconducting circuit that evolves under the competing influences of continuous weak measurement and Rabi drive makes it possible to deduce the most probable path through quantum state space.
- S. J. Weber
- , A. Chantasri
- & I. Siddiqi

 Laser spectroscopy of triply charged 229Th isomer for a nuclear clock
Laser spectroscopy of triply charged 229Th isomer for a nuclear clock