Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Photosynthesis-dependent H2O2 transfer from chloroplasts to nuclei provides a high-light signalling mechanism
Photosynthesis-dependent H2O2 transfer from chloroplasts to nuclei provides a high-light signalling mechanism
Multiple plastid-derived signals have been proposed but not shown to move to the nucleus to promote plant acclimation to fluctuating light. Here the authors use a fluorescent hydrogen peroxide sensor to provide evidence that H2O2 is transferred directly from chloroplasts to nuclei to control nuclear gene expression.
- Marino Exposito-Rodriguez
- , Pierre Philippe Laissue
- & Philip M. Mullineaux
-
Article
| Open Access Plastid thylakoid architecture optimizes photosynthesis in diatoms
Plastid thylakoid architecture optimizes photosynthesis in diatoms
Phytoplankton and plant plastids have distinct evolutionary origins and membrane organization. Here Floriet al. show that diatom photosynthetic complexes spatially segregate into interconnected subdomains within loose thylakoid stacks enabling fast diffusion of electron carriers and efficient photosynthesis
- Serena Flori
- , Pierre-Henri Jouneau
- & Giovanni Finazzi
-
Article
| Open Access Exchange pathways of plastoquinone and plastoquinol in the photosystem II complex
Exchange pathways of plastoquinone and plastoquinol in the photosystem II complex
Plastoquinone (PLQ) shuttles electrons between photosystem II (PSII) and cytochrome b6f. Here the authors perform molecular dynamics simulations and propose that PLQ enters the exchange cavity of PSII by a promiscuous diffusion mechanism whereby three different channels each act as entry and exit points.
- Floris J. Van Eerden
- , Manuel N. Melo
- & Siewert J. Marrink
-
Article
| Open Access Redesigning the QA binding site of Photosystem II allows reduction of exogenous quinones
Redesigning the QA binding site of Photosystem II allows reduction of exogenous quinones
Devices that harness electron flow from photosynthetic organisms generally compromise host photosynthesis. Here, the authors show that, by redesigning the QAsite of Photosystem II, it is possible to reroute electrons to an exogenous quinone while maintaining endogenous photosynthetic electron transfer in a green alga.
- Han-Yi Fu
- , Daniel Picot
- & Francis-André Wollman
-
Article
| Open Access Augmenting light coverage for photosynthesis through YFP-enhanced charge separation at the Rhodobacter sphaeroides reaction centre
Augmenting light coverage for photosynthesis through YFP-enhanced charge separation at the Rhodobacter sphaeroides reaction centre
Photosynthesis uses only a limited range of solar radiation. Here, Graysonet al. genetically incorporated the yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) chromophore into a bacterial photosystem, and show that energy harvested by reaction centre–YFP complexes can augment photosynthesis in vivo.
- Katie J. Grayson
- , Kaitlyn M. Faries
- & C. Neil Hunter
-
Review Article
| Open Access Photon management for augmented photosynthesis
Photon management for augmented photosynthesis
Photosynthetic microalgae could provide an ecologically sustainable route to produce solar biofuels and high-value chemicals. Here, the authors review various optical management strategies used to manipulate the incident light in order to increase the efficiency of microalgae biofuel production.
- Matthew D. Ooms
- , Cao Thang Dinh
- & David Sinton
-
Article
| Open Access A voltage-dependent chloride channel fine-tunes photosynthesis in plants
A voltage-dependent chloride channel fine-tunes photosynthesis in plants
Plants have evolved to maximize energy capture while protecting their photosynthetic machinery in response to rapid variation in light conditions. Here, the authors describe a chloroplast voltage-dependent anion channel that contributes to photoprotection by fine-tuning the ion balance across the thylakoid membrane.
- Andrei Herdean
- , Enrico Teardo
- & Björn Lundin
-
Article
| Open Access Identification and characterization of multiple rubisco activases in chemoautotrophic bacteria
Identification and characterization of multiple rubisco activases in chemoautotrophic bacteria
The CO2-fixing enzyme rubisco requires motor proteins known as rubisco activases to remove inhibitors bound to its active site. Here the authors describe a new class of rubisco activase present in chemoautotrophic bacteria that belongs to the MoxR family of AAA+ ATPases.
- Yi-Chin Candace Tsai
- , Maria Claribel Lapina
- & Oliver Mueller-Cajar
-
Article
| Open Access Energetics of proton release on the first oxidation step in the water-oxidizing enzyme
Energetics of proton release on the first oxidation step in the water-oxidizing enzyme
The availability of crystal structures of photosystem II opens up the possibility of gaining insights into its mechanism. Here, the authors use a computational approach and propose a deprotonation event at O4 followed by long-range proton-transfer along a chain of strongly bonded water molecules.
- Keisuke Saito
- , A. William Rutherford
- & Hiroshi Ishikita
-
Article |
 IM30 triggers membrane fusion in cyanobacteria and chloroplasts
IM30 triggers membrane fusion in cyanobacteria and chloroplasts
Thylakoid membranes are critical components of chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. Here, Hennig et al. demonstrate that IM30, a conserved chloroplast and cyanobacterial protein, binds to thylakoid membranes and can trigger membrane destabilization and fusion in a Mg2+dependent manner.
- Raoul Hennig
- , Jennifer Heidrich
- & Dirk Schneider
-
Article
| Open Access Arabidopsis uses two gluconeogenic gateways for organic acids to fuel seedling establishment
Arabidopsis uses two gluconeogenic gateways for organic acids to fuel seedling establishment
During seed germination plants use gluconeogenesis to mobilize noncarbohydrate energy reserves. Here Eastmond et al. show that plants, unlike other eukaryotes, do not solely rely on a gluconeogenic pathway via the enzyme PCK but also use a second pathway relying on PPDK.
- Peter J. Eastmond
- , Holly M. Astley
- & Julian M. Hibberd
-
Article |
 A megacomplex composed of both photosystem reaction centres in higher plants
A megacomplex composed of both photosystem reaction centres in higher plants
Plants have two types of photosystem reaction centres, PSI and PSII, that are traditionally thought to be spatially separate. Here, Yokono et al. show in Arabidopsisthat around half of PSII physically interacts with PSI to efficiently transfer excitation energy between the complexes, and this interaction is regulated by light.
- M. Yokono
- , A. Takabayashi
- & A. Tanaka
-
Article
| Open Access The evolution of photosynthesis in chromist algae through serial endosymbioses
The evolution of photosynthesis in chromist algae through serial endosymbioses
The chromalveolate hypothesis proposes that chromist algae became photosynthetic through a single endosymbiosis in a common ancestor. Here, Stiller et al. use a novel statistical approach to propose that instead, the major chromist algae arose as a result of three specific serial plastid transfers.
- John W. Stiller
- , John Schreiber
- & Jinling Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Ion antiport accelerates photosynthetic acclimation in fluctuating light environments
Ion antiport accelerates photosynthetic acclimation in fluctuating light environments
Plants must respond rapidly to unpredictable variations in light intensity to maximize photosynthetic efficiency. Here Armbruster et al.identify a potassium antiporter that is critical for accelerating proton fluxes across thylakoid membranes and minimizing energy loss in fluctuating light conditions.
- Ute Armbruster
- , L. Ruby Carrillo
- & Martin C. Jonikas
-
Article
| Open Access Coordinated regulation of photosynthesis in rice increases yield and tolerance to environmental stress
Coordinated regulation of photosynthesis in rice increases yield and tolerance to environmental stress
Improving photosynthetic efficiency to increase crop yield is an important goal of plant breeders. Here, Ambavaram et al.identify a transcription factor that is a key regulator of photosynthetic carbon metabolism in rice and show that its overexpression enhances grain yield.
- Madana M. R. Ambavaram
- , Supratim Basu
- & Andy Pereira
-
Article |
 The role of charge-transfer states in energy transfer and dissipation within natural and artificial bacteriochlorophyll proteins
The role of charge-transfer states in energy transfer and dissipation within natural and artificial bacteriochlorophyll proteins
Non-photochemical quenching is the process by which photosynthetic organisms can protect themselves from damage caused by high-intensity light. Here, the authors use Stark spectroscopy to determine the influence of the protein environment on charge transfer in non-photochemical quenching.
- Md. Wahadoszamen
- , Iris Margalit
- & Dror Noy
-
Article |
 Economic photoprotection in photosystem II that retains a complete light-harvesting system with slow energy traps
Economic photoprotection in photosystem II that retains a complete light-harvesting system with slow energy traps
Photosystem II possesses a protection mechanism to prevent damage when exposed to high-intensity light. Here, the authors analyze the functional consequences of structural changes associated with this process, and show that protection does not undermine energy capture by open reaction centres.
- Erica Belgio
- , Ekaterina Kapitonova
- & Alexander V. Ruban
-
Article |
 Taking snapshots of photosynthetic water oxidation using femtosecond X-ray diffraction and spectroscopy
Taking snapshots of photosynthetic water oxidation using femtosecond X-ray diffraction and spectroscopy
Photosystem II is the biosynthetic machinery that allows the conversion of water to oxygen using light. Here, the authors combine X-ray emission and diffraction data to probe the structural changes that take place during photosystem II catalysis.
- Jan Kern
- , Rosalie Tran
- & Vittal K. Yachandra
-
Article
| Open Access Substrate–water exchange in photosystem II is arrested before dioxygen formation
Substrate–water exchange in photosystem II is arrested before dioxygen formation
The oxygen-evolving complex of photosystem II converts water into oxygen during photosynthesis, but how this process occurs is not yet fully understood. Here, the authors use modified complexes with reduced reaction rates to study the process of oxygen evolution in more detail.
- Håkan Nilsson
- , Fabrice Rappaport
- & Johannes Messinger
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic protein conformations preferentially drive energy transfer along the active chain of the photosystem II reaction centre
Dynamic protein conformations preferentially drive energy transfer along the active chain of the photosystem II reaction centre
Cofactor-mediated energy and electron transfer in photosystem II occurs preferentially through one branch of the reaction centre, despite there being a symmetric path available. Here, the authors use computational methods to determine the influence of protein conformation on this selectivity.
- Lu Zhang
- , Daniel-Adriano Silva
- & Xuhui Huang
-
Article |
 Translation-independent circadian control of the cell cycle in a unicellular photosynthetic eukaryote
Translation-independent circadian control of the cell cycle in a unicellular photosynthetic eukaryote
Photosynthetic unicellular eukaryotes undergo cell division more frequently at night. Miyagishima et al.show that circadian control of the cell division cycle in unicellular red algae is mediated by phosphorylation of E2F, and that nocturnal cell division protects these cells from photosynthetic oxidative stress.
- Shin-ya Miyagishima
- , Takayuki Fujiwara
- & Mami Nakamura
-
Article
| Open Access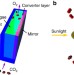 Solar spectral conversion for improving the photosynthetic activity in algae reactors
Solar spectral conversion for improving the photosynthetic activity in algae reactors
Algae beds are a promising resource for bio-energy and gas production, but their productivity is often limited by solar energy harvesting efficiency. Wondraczek et al. promote algal growth by using photoluminescent phosphor, which shifts the light spectrum to better match the algal adsorption band.
- Lothar Wondraczek
- , Miroslaw Batentschuk
- & Christoph J. Brabec
-
Article
| Open Access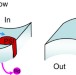 Cyclic electron flow is redox-controlled but independent of state transition
Cyclic electron flow is redox-controlled but independent of state transition
The switch from linear to cyclic electron flow has long been thought to rely on the migration of antenna proteins from Photosystem II to Photosystem I. Takahashi et al. report that this is not the case and that cyclic electron flow is tuned by the intrachloroplastic redox power.
- Hiroko Takahashi
- , Sophie Clowez
- & Fabrice Rappaport
-
Article
| Open Access Greater efficiency of photosynthetic carbon fixation due to single amino-acid substitution
Greater efficiency of photosynthetic carbon fixation due to single amino-acid substitution
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, the key enzyme of C4 photosynthesis, evolved from an ancestral isoform in C3 plants and has a reduced feedback inhibition. Paulus et al.show that enhanced inhibitor tolerance of C4 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase is achieved by a single amino-acid exchange.
- Judith Katharina Paulus
- , Daniel Schlieper
- & Georg Groth
-
Article
| Open Access Phytoplankton growth after a century of dormancy illuminates past resilience to catastrophic darkness
Phytoplankton growth after a century of dormancy illuminates past resilience to catastrophic darkness
Global darkness from an asteroid impact 65.5 million years ago led to massive extinction of oceanic phytoplankton, but coastal groups survived. Ribeiroet al.revive coastal dinoflagellates after a century of dormancy, suggesting phytoplankton survived the extinction and helped restore photosynthesis in the ocean.
- Sofia Ribeiro
- , Terje Berge
- & Marianne Ellegaard
-
Article
| Open Access Photosynthetic growth despite a broken Q-cycle
Photosynthetic growth despite a broken Q-cycle
The Q-cycle is thought to be an essential energetic component of the photosynthetic electron-transfer chain. Here, Chlamydomonas mutants with an inactive Q-cycle but normal levels ofb6fcomplexes are shown to display photosynthetic growth, demonstrating the dispensability of the Q-cycle in the oxygenic photosynthetic chain.
- Alizée Malnoë
- , Francis-André Wollman
- & Fabrice Rappaport
-
Article |
 High rates of photobiological H2 production by a cyanobacterium under aerobic conditions
High rates of photobiological H2 production by a cyanobacterium under aerobic conditions
Hydrogen production using photosynthetic bacteria is an appealing energy source, but typically the bacteria require anaerobic conditions. Here, the authors report a wild-type cyanobacterium strain that shows very high rates of hydrogen production under aerobic environmental conditions.
- Anindita Bandyopadhyay
- , Jana Stöckel
- & Himadri B. Pakrasi
-
Article |
 Mutualistic mycorrhiza-like symbiosis in the most ancient group of land plants
Mutualistic mycorrhiza-like symbiosis in the most ancient group of land plants
Symbiotic fungi are thought to have assisted plants in their colonization of the land. In this study, it is shown that mycorrhizal fungi symbiosis with liverwort, a member of an ancient clade of land plants, promotes photosynthetic carbon uptake and growth, supporting the role of fungi in 'the greening of the Earth'.
- Claire P. Humphreys
- , Peter J. Franks
- & David J. Beerling

 Mapping the ultrafast flow of harvested solar energy in living photosynthetic cells
Mapping the ultrafast flow of harvested solar energy in living photosynthetic cells