News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 CRTC3 links catecholamine signalling to energy balance
CRTC3 links catecholamine signalling to energy balance
β-adrenergic receptor signalling in adipocytes stimulates energy expenditure via cAMP-dependent increases in lipolysis and fatty-acid oxidation, and this signalling mechanism is thought to be disrupted in obesity. Here, the cAMP-responsive CREB coactivator Crtc3 is shown to promote obesity in mice by attenuating β adrenergic receptor signalling in adipose tissue.
- Youngsup Song
- , Judith Altarejos
- & Marc Montminy
-
News |
 Slim spoils for obesity drugs
Slim spoils for obesity drugs
Drug makers struggle to find viable treatments for global epidemic.
- Heidi Ledford
-
News |
 Growth factor makes a comeback in cystic fibrosis
Growth factor makes a comeback in cystic fibrosis
Work in pigs points to culprit and potential treatment for growth retardation.
- Virginia Hughes
-
News |
 Fat fathers affect daughters' health
Fat fathers affect daughters' health
Female offspring of male rats on bad diets are more likely to develop diabetes-like disease.
- Geoff Marsh
-
Research Highlights |
Epigenetics: Mapping methylation
-
Research Highlights |
Immunology: Killer cells help
-
Article |
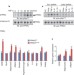 Anti-diabetic drugs inhibit obesity-linked phosphorylation of PPARγ by Cdk5
Anti-diabetic drugs inhibit obesity-linked phosphorylation of PPARγ by Cdk5
PPARγ ligands are used to control diabetes, but their anti-diabetic actions are puzzling. Here the authors show that phosphorylation of PPARγ by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) in mice is linked to obesity induced by high-fat feeding, and that inhibition of the effect in humans by the drug rosiglitazone is closely associated with its anti-diabetic effects. Several anti-diabetic PPARγ ligands directly inhibit the effect, and thus support a more normal non-diabetic pattern of gene expression.
- Jang Hyun Choi
- , Alexander S. Banks
- & Bruce M. Spiegelman
-
Editorial |
Effective approach
The controversy surrounding diabetes drugs highlights the importance of comparative studies.
-
News & Views |
 New life for antidiabetic drugs
New life for antidiabetic drugs
Antidiabetic drugs that activate the protein PPARγ had a bright start but soon lost their appeal because of undesirable side effects. Subtle modifications may once again make them suitable for treating diabetes.
- Riekelt H. Houtkooper
- & Johan Auwerx
-
News |
 Diabetes drugs offered fresh start
Diabetes drugs offered fresh start
As FDA advisers vote for restrictions on Avandia, researchers reveal a way to make such drugs safer.
- Heidi Ledford
-
News |
 Evidence mounts against diabetes drug
Evidence mounts against diabetes drug
Studies continue to find heart-attack risk.
- Heidi Ledford
-
News |
 Strange lesions after stem-cell therapy
Strange lesions after stem-cell therapy
Unproven treatment results in mysterious masses.
- David Cyranoski
-
Letter |
 Disruption of the clock components CLOCK and BMAL1 leads to hypoinsulinaemia and diabetes
Disruption of the clock components CLOCK and BMAL1 leads to hypoinsulinaemia and diabetes
Circadian rhythms control many physiological functions. During periods of feeding, pancreatic islets secrete insulin to maintain glucose homeostasis — a rhythmic process that is disturbed in people with diabetes. These authors show that pancreatic islets contain their own clock: they have self-sustained circadian oscillations of CLOCK and BMAL1 genes and proteins, which are vital for the regulation of circadian rhythms. Without this clock, a cascade of cellular failure and pathology initiates the onset of diabetes mellitus.
- Biliana Marcheva
- , Kathryn Moynihan Ramsey
- & Joseph Bass
-
News |
 Twin study surveys genome for cause of multiple sclerosis
Twin study surveys genome for cause of multiple sclerosis
Mapping milestone emphasizes complexity of disease.
- Alla Katsnelson
-
News & Views |
 Extreme makeover of pancreatic α-cells
Extreme makeover of pancreatic α-cells
Most insulin-secreting pancreatic β-cells are irreplaceably lost in type 1 diabetes. In a mouse model, pancreatic α-cells seem to sacrifice their identity to replenish the low stock of β-cells
1 . Two experts discuss what this means for understanding the basic cell biology involved and its relevance to treating diabetes.boxed-text - Kenneth S. Zaret
- & Morris F. White
-
News & Views |
 Host and microbes in a pickle
Host and microbes in a pickle
Metabolic disorders such as obesity are characterized by long-term, low-grade inflammation. Under certain conditions, the resident microorganisms of the gut might contribute to this inflammation, resulting in disease.
- Ping Li
- & Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
-
Review Article |
 Genetics, pathogenesis and clinical interventions in type 1 diabetes
Genetics, pathogenesis and clinical interventions in type 1 diabetes
- Jeffrey A. Bluestone
- , Kevan Herold
- & George Eisenbarth
-
News |
 Fat rats skew research results
Fat rats skew research results
Overfed lab animals make poor subjects for experiments.
- Daniel Cressey
-
Authors |
 Constantin Polychronakos & Michael German
Constantin Polychronakos & Michael German
Projects converge on gene central to formation of insulin-producing cells.
-
Letter |
 A new highly penetrant form of obesity due to deletions on chromosome 16p11.2
A new highly penetrant form of obesity due to deletions on chromosome 16p11.2
Recently, numerous single nucleotide polymorphisms have been identified as being associated with obesity, but these loci together account for only a small fraction of the known heritable component. Here, an association is reported between rare deletions of at least 593 kilobases at 16p11.2 and a highly penetrant form of obesity. The strategy used of combining study of extreme phenotypes with targeted follow-up is promising for identifying missing heritability in obesity.
- R. G. Walters
- , S. Jacquemont
- & J. S. Beckmann
-
Research Highlights |
Cancer biology: Weighted cancer risk

 Diabetes in India
Diabetes in India