Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Preferential ice growth on grooved surface for crisscross-aligned graphene aerogel with large negative Poisson’s ratio
Preferential ice growth on grooved surface for crisscross-aligned graphene aerogel with large negative Poisson’s ratio
Ice formation on grooved surfaces is ubiquitous, but controlling orientation is difficult due to lack of mechanistic insight. Here, the authors observed oriented growth using graphene oxide nanosheets as probes, revealing the effect of groove size, and programmed ice growth to fabricate freeze-cast metamaterials.
- Meng Li
- , Nifang Zhao
- & Hao Bai
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-durable cell-free bioactive hydrogel with fast shape memory and on-demand drug release for cartilage regeneration
Ultra-durable cell-free bioactive hydrogel with fast shape memory and on-demand drug release for cartilage regeneration
Achieving successful in vivo cartilage regeneration remains challenging. Here they present a cell-free, multiple hydrogen-bond crosslinked hydrogel loaded with tannic acid and Kartogenin with ultra-durable mechanical properties and stage-dependent drug release behavior to promote cartilage regeneration.
- Yuxuan Yang
- , Xiaodan Zhao
- & Xuesi Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Local H2 release remodels senescence microenvironment for improved repair of injured bone
Local H2 release remodels senescence microenvironment for improved repair of injured bone
Senescence microenvironment inhibits tissue repair in elderly individuals. Here, the authors demonstrate that local H2 supply has anti-inflammation and anti-senescence effects, and develop a H2-releasing scaffold to enhance aging bone defect repair.
- Shengqiang Chen
- , Yuanman Yu
- & Qianjun He
-
Article
| Open Access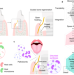 Occlusive membranes for guided regeneration of inflamed tissue defects
Occlusive membranes for guided regeneration of inflamed tissue defects
Symbiosis should be maintained during the oral regeneration period. Herein, authors develop an occlusive membrane that induces symbiosis, thereby improving the performance of guided bone generation therapy.
- Woojin Choi
- , Utkarsh Mangal
- & Jinkee Hong
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoparticles exhibiting virus-mimic surface topology for enhanced oral delivery
Nanoparticles exhibiting virus-mimic surface topology for enhanced oral delivery
The oral delivery of nano-drug delivery systems (Nano-DDS) remains challenging. Here the authors construct core–shell mesoporous silica nanoparticles with virus-like nanospikes and demonstrate the versatility of these nanoparticles as Nano-DDS to achieve efficient oral drug delivery by mimicking structural feature, chiral recognition, and gene encapsulation of viruses.
- Zhentao Sang
- , Lu Xu
- & Heran Li
-
Article
| Open Access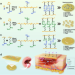 A self-stabilized and water-responsive deliverable coenzyme-based polymer binary elastomer adhesive patch for treating oral ulcer
A self-stabilized and water-responsive deliverable coenzyme-based polymer binary elastomer adhesive patch for treating oral ulcer
The therapeutic benefits of biomaterials-based treatments for oral ulcer have been limited by the materials’ poor adhesion and short-time retention in oral cavity. Here, the authors report a polymer binary elastomer adhesive patch that allows water-responsive sustainable delivery of bioactive small molecules and durable adhesion to oral mucosal wounds to achieve efficient therapy of oral ulcer.
- Chunyan Cui
- , Li Mei
- & Wenguang Liu
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo imaging of mitochondrial DNA mutations using an integrated nano Cas12a sensor
In vivo imaging of mitochondrial DNA mutations using an integrated nano Cas12a sensor
Mutations in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) play critical roles in human diseases. Here, the authors describe an integrated Cas12a sensor for sensing mtDNA mutations in vivo, showing potential for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
- Yanan Li
- , Yonghua Wu
- & Kaixiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access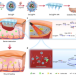 Biofilm microenvironment triggered self-enhancing photodynamic immunomodulatory microneedle for diabetic wound therapy
Biofilm microenvironment triggered self-enhancing photodynamic immunomodulatory microneedle for diabetic wound therapy
The treatment of diabetic wounds tends to be hindered by complex wound environments, and the critical role of the microenvironment in the chronic diabetic wounds has not been explored for therapeutic development. Here, the authors develop a wound microenvironment-responsive microneedle bandage to achieve self-enhanced, catabolic and dynamic therapy of chronic wounds.
- Li Yang
- , Dan Zhang
- & Xiaowei Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Four-dimensional hydrogel dressing adaptable to the urethral microenvironment for scarless urethral reconstruction
Four-dimensional hydrogel dressing adaptable to the urethral microenvironment for scarless urethral reconstruction
Urethral repair can be carried out using hydrogels, but the harsh microenvironment hinders the repair. Here, the authors report the development of a 4D hydrogel dressing that can provide an early-vascularised and later-antifibrogenic microenvironment to assist in scarless reconstruction.
- Yujie Hua
- , Kai Wang
- & Kaile Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Biofilm heterogeneity-adaptive photoredox catalysis enables red light-triggered nitric oxide release for combating drug-resistant infections
Biofilm heterogeneity-adaptive photoredox catalysis enables red light-triggered nitric oxide release for combating drug-resistant infections
Biofilms are heterogeneous and difficult to treat. Here, the authors report the preparation of micellar nanoparticles specifically for the treatment of biofilm, that release nitric oxide through two distinct photoredox catalysis mechanisms.
- Jian Cheng
- , Guihai Gan
- & Jinming Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging cellular forces with photonic crystals
Imaging cellular forces with photonic crystals
Current techniques for visualizing cell generated forces suffer from throughput limitations. Here, Gu et al. introduced photonic crystal cellular force microscopy, inspired by chameleons, enabling visualization and quantification of vertically directed cell forces, well-suited for drug screening.
- Qiwei Li
- , Zaozao Chen
- & Zhongze Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Diatomic iron nanozyme with lipoxidase-like activity for efficient inactivation of enveloped virus
Diatomic iron nanozyme with lipoxidase-like activity for efficient inactivation of enveloped virus
Enveloped viruses encased within a lipid bilayer membrane are highly contagious and cause diseases like influenza and COVID-19, so strategies for their prevention and inactivation are needed. Here, the authors develop a diatomic iron nanozyme with lipoxidase-like activity for the inactivation of enveloped viruses, where the diatomic iron sites destroy the viral envelope via lipid peroxidation.
- Beibei Li
- , Ruonan Ma
- & Yadong Li
-
Article
| Open Access Resorbable barrier polymers for flexible bioelectronics
Resorbable barrier polymers for flexible bioelectronics
Resorbable bioelectronic devices have potential as tools for monitoring physiological parameters, but short functional lifetimes have slowed translation. Here, the authors report succinate-based copolyesters with barrier properties able to extend the functional lifetime of devices.
- Samantha M. McDonald
- , Quansan Yang
- & Matthew L. Becker
-
Article
| Open Access Site-selected in situ polymerization for living cell surface engineering
Site-selected in situ polymerization for living cell surface engineering
Constructing polymer-based mimics on the surface of cells has potential to manipulate cell behavior, but precise control of grafting sites is challenging. Here, the authors report a method for site selected radical polymerization on cell surfaces by metabolic labelling.
- Yihong Zhong
- , Lijia Xu
- & Huangxian Ju
-
Article
| Open Access Pathogenesis-adaptive polydopamine nanosystem for sequential therapy of ischemic stroke
Pathogenesis-adaptive polydopamine nanosystem for sequential therapy of ischemic stroke
Reperfusion is a main strategy for restoring blood supply after ischemic stroke, but it induces neuroinflammation that undergoes dynamic progression, hindering the treatment of ischemic stroke. Here, the authors report a pathogenesis-adaptive nanosystem for sequential and on-demand regulation of reperfusion-induced dynamic neuroinflammation for ischemic stroke therapy.
- Di Wu
- , Jing Zhou
- & Zhong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired porous three-coordinated single-atom Fe nanozyme with oxidase-like activity for tumor visual identification via glutathione
Bioinspired porous three-coordinated single-atom Fe nanozyme with oxidase-like activity for tumor visual identification via glutathione
It is needed yet difficult to achieve a strategy for synthesizing single-atom nanozymes that integrate atomic metal dispersion, elevated mass transport and tailorable coordination environment. Here, the authors address this issue by developing a biomimetic synthetic strategy and demonstrate the application of the resultant single-atom Fe nanozymes for tumor visual identification.
- Da Chen
- , Zhaoming Xia
- & Yongquan Qu
-
Article
| Open Access Nanosensitizer-mediated augmentation of sonodynamic therapy efficacy and antitumor immunity
Nanosensitizer-mediated augmentation of sonodynamic therapy efficacy and antitumor immunity
The dense stroma of desmoplastic tumor limits nanotherapeutic penetration and hampers the antitumor immune response. Here the authors use tin monosulfide nanoparticles as nano-sonosensitizers to overcome the stromal barrier in triple negative breast cancer and improve the efficacy of sonodynamic therapy and boost antitumor immunity.
- Yongjiang Li
- , Wei Chen
- & Wei Tao
-
Article
| Open Access Charge-altering releasable transporters enhance mRNA delivery in vitro and exhibit in vivo tropism
Charge-altering releasable transporters enhance mRNA delivery in vitro and exhibit in vivo tropism
Polymers are promising for mRNA delivery, but can have limited efficacy in hard to transfect cells. Here, the authors report charge-altering releasable transporters for improved mRNA transfection in primary T-lymphocytes and enhanced and selective protein expression in vivo.
- Zhijian Li
- , Laura Amaya
- & Paul A. Wender
-
Article
| Open Access An in situ dual-anchoring strategy for enhanced immobilization of PD-L1 to treat autoimmune diseases
An in situ dual-anchoring strategy for enhanced immobilization of PD-L1 to treat autoimmune diseases
Immune checkpoints are critical in maintaining self-tolerance and their therapeutic modulation can be achieved in autoimmune diseases. Here the authors present an in situ dual-anchoring approach that targets PD-L1 and show effects in animal models of autoimmunity.
- Shenqiang Wang
- , Ying Zhang
- & Jicheng Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Self-promoted electroactive biomimetic mineralized scaffolds for bacteria-infected bone regeneration
Self-promoted electroactive biomimetic mineralized scaffolds for bacteria-infected bone regeneration
Infected bone defects are a major challenge in orthopedic treatment. Here, the authors develop an electroactive mineralized scaffold that achieves nearly complete in situ healing of infected bone in rats, rabbits and beagle dogs.
- Zixin Li
- , Danqing He
- & Yan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access An autocatalytic multicomponent DNAzyme nanomachine for tumor-specific photothermal therapy sensitization in pancreatic cancer
An autocatalytic multicomponent DNAzyme nanomachine for tumor-specific photothermal therapy sensitization in pancreatic cancer
Despite delivering gene-specific silencing, the use of deoxyribozymes (DNAzymes) for cancer therapy is limited by toxicity due to off-target effects. Here, the authors develop a multi-component DNAzyme, targeting both miRNA21 and HSP70, to induce tumour-specific sensitisation to photothermal therapy in preclinical models of pancreatic cancer.
- Jiaqi Yan
- , Xiaodong Ma
- & Hongbo Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Near-infrared-II photoacoustic imaging and photo-triggered synergistic treatment of thrombosis via fibrin-specific homopolymer nanoparticles
Near-infrared-II photoacoustic imaging and photo-triggered synergistic treatment of thrombosis via fibrin-specific homopolymer nanoparticles
The near-infrared-II (NIR-II) window has shown great promise for in vivo imaging and therapy. Here, the authors integrate a homopolymer and thermo-sensitive nitric oxide prodrug into nanoparticles for long-wavelength NIR-II photoacoustic imaging and synergistic treatment in preclinical thrombosis models.
- Jianwen Song
- , Xiaoying Kang
- & Ji Qi
-
Article
| Open Access Tandem-biocatalysis reactors constructed by topological evolution of CaCO3 particles into hollow metal hydroxide spheres
Tandem-biocatalysis reactors constructed by topological evolution of CaCO3 particles into hollow metal hydroxide spheres
Hollow inorganic spheres (HISs) hold potential in various technological areas including biocatalysis and biomedicine, but the harsh synthetic conditions have precluded the use of HISs in biological fields. Here, the authors report a biocompatible strategy for synthesizing metal hydroxide HISs that can function as tandem-biocatalytic reactors.
- Sang Yeong Han
- , Nayoung Kim
- & Insung S. Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Single-atom catalysts-based catalytic ROS clearance for efficient psoriasis treatment and relapse prevention via restoring ESR1
Single-atom catalysts-based catalytic ROS clearance for efficient psoriasis treatment and relapse prevention via restoring ESR1
Psoriasis is a common inflammatory disease, and the overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in skin lesions plays a critical role in the progress of psoriasis. Here, the authors report the use of multienzyme-inspired biomimetic iron single-atom catalysts (FeN4O2-SACs) with broad-spectrum ROS-scavenging capability for psoriasis treatment and relapse prevention via related gene restoration.
- Xiangyu Lu
- , Le Kuai
- & Jianlin Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical assembly of tryptophan zipper peptides into stress-relaxing bioactive hydrogels
Hierarchical assembly of tryptophan zipper peptides into stress-relaxing bioactive hydrogels
Rational design has endowed self-assembling peptides with structural similarities to natural materials, but recreating the dynamic functional properties inherent to natural systems remains challenging. Here the authors report the discovery of a short peptide based on the tryptophan zipper motif, that shows multiscale hierarchical ordering into hydrogels that display emergent dynamic properties.
- Ashley K. Nguyen
- , Thomas G. Molley
- & Kristopher A. Kilian
-
Article
| Open Access Nanomechanical action opens endo-lysosomal compartments
Nanomechanical action opens endo-lysosomal compartments
Endo-lysosomal escape is a highly inefficient process. Here the authors present a lipid-based nanoscale molecular machine that achieves efficient cytosolic transport of biologics by destabilizing endo-lysosomal compartments through nanomechanical action upon light irradiation.
- Yu Zhao
- , Zhongfeng Ye
- & Qiaobing Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Aromatized liposomes for sustained drug delivery
Aromatized liposomes for sustained drug delivery
The development of liposome-based drug delivery systems has been hindered by the systemic toxicity and limited duration of effect due to insufficient drug loading and leakage of payload. Here the authors address these issues by designing aromatized liposomes that feature increased drug loading and slowed release compared to conventional liposomes.
- Yang Li
- , Tianjiao Ji
- & Daniel S. Kohane
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning-enabled constrained multi-objective design of architected materials
Machine learning-enabled constrained multi-objective design of architected materials
Architected materials can have enhanced properties compared to bulk but are difficult to design. Here the authors propose a machine-learning-based pipeline to design architected materials with predetermined elastic modulus and enhanced yield strength and test it in additive manufacturing.
- Bo Peng
- , Ye Wei
- & Peng Wen
-
Article
| Open Access Stretchable piezoelectric biocrystal thin films
Stretchable piezoelectric biocrystal thin films
Developing piezoelectric biocrystals that are stretchable while maintaining structure and stable piezoelectricity is challenging. Here, Li et al. report an amino acid-based piezoelectric biocrystal with omnidirectional stretchability enabled by a truss-like network, for wearable and implantable devices.
- Jun Li
- , Corey Carlos
- & Xudong Wang
-
Article
| Open Access NIR-dye bridged human serum albumin reassemblies for effective photothermal therapy of tumor
NIR-dye bridged human serum albumin reassemblies for effective photothermal therapy of tumor
Human serum albumin (HSA) can be used as a drug delivery material for cancer therapy. Here, the authors report an HSA-based photothermal platform that improves drug loading and photothermal therapeutic performance in breast cancer mouse models.
- Zhaoqing Shi
- , Miaomiao Luo
- & Hongzhong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Deposition and water repelling of temperature-responsive nanopesticides on leaves
Deposition and water repelling of temperature-responsive nanopesticides on leaves
Weak adhesion is a common hindrance to efficient utilization of pesticides in agricultural applications. Here, authors demonstrate leaf-adhesive tebuconazole nanopesticides which can be water-dispersed via flash nanoprecipitation using temperature-responsive copolymers PDMAEMA-b-PCL as the carrier.
- Jie Tang
- , Xiaojing Tong
- & Yisheng Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Injectable and biodegradable piezoelectric hydrogel for osteoarthritis treatment
Injectable and biodegradable piezoelectric hydrogel for osteoarthritis treatment
The use of biomaterial scaffolds-based cartilage grafts could potentially innovate the Osteoarthritis (OA) treatment, but has been limited by toxicity concerns and invasive surgical procedures. Here, the authors report an injectable and biodegradable piezoelectric hydrogel with ultrasound activation to offer a minimally invasive approach for OA treatment.
- Tra Vinikoor
- , Godwin K. Dzidotor
- & Thanh D. Nguyen
-
Article
| Open Access Chronological adhesive cardiac patch for synchronous mechanophysiological monitoring and electrocoupling therapy
Chronological adhesive cardiac patch for synchronous mechanophysiological monitoring and electrocoupling therapy
Flexible electronic hydrogels that allow conformal tissue integration, online precision diagnosis, and simultaneous tissue regeneration are desired for advancing the treatment of myocardial infarction. Here, the authors report a chronological adhesive hydrogel patch integrating diagnostic and therapeutic functions through mechanophysiological monitoring and electrocoupling therapy.
- Chaojie Yu
- , Mingyue Shi
- & Junjie Li
-
Article
| Open Access Integration of 3D-printed cerebral cortical tissue into an ex vivo lesioned brain slice
Integration of 3D-printed cerebral cortical tissue into an ex vivo lesioned brain slice
Brain injuries can result in significant damage to the cerebral cortex, and restoring the cellular architecture of the tissue remains challenging. Here, the authors use a droplet printing technique to fabricate a simplified human cerebral cortical column and demonstrate its functionality and potential for future personalized therapy approaches.
- Yongcheng Jin
- , Ellina Mikhailova
- & Hagan Bayley
-
Article
| Open Access Iron oxide nanozymes stabilize stannous fluoride for targeted biofilm killing and synergistic oral disease prevention
Iron oxide nanozymes stabilize stannous fluoride for targeted biofilm killing and synergistic oral disease prevention
Ferumoxytol (Fer) is an FDA-approved iron oxide formulation that disrupts caries-causing biofilms with high specificity but cannot interfere with enamel acid demineralization. Here, Fer is combined with stannous fluoride (SnF2), resulting in enhanced stability of SnF2 and inhibition of both biofilm accumulation and enamel damage more effectively than either alone.
- Yue Huang
- , Yuan Liu
- & Hyun Koo
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic single Al-OH site with high acetylcholinesterase-like activity and self-defense ability for neuroprotection
Biomimetic single Al-OH site with high acetylcholinesterase-like activity and self-defense ability for neuroprotection
The neurotoxicity of organophosphate compounds damages nerve system by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase (AChE) expression, but it is difficult to overcome the deactivation of AChE. Here, the authors report the design of Lewis acid sites in metal-organic frameworks as AChE mimics for effective neuroprotection.
- Weiqing Xu
- , Xiaoli Cai
- & Chengzhou Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable backbone-degradable robust tissue adhesives via in situ radical ring-opening polymerization
Tunable backbone-degradable robust tissue adhesives via in situ radical ring-opening polymerization
Adhesives with both robust adhesion and tunable degradability are clinically and ecologically vital, but their fabrication remains a formidable challenge. Here, the authors report in situ radical ring-opening polymerization-based design and potential biomedical applications of a backbone degradable robust adhesive.
- Ran Yang
- , Xu Zhang
- & Shifang Luan
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of a covalent organic framework with hetero-environmental pores and its medicine co-delivery application
Synthesis of a covalent organic framework with hetero-environmental pores and its medicine co-delivery application
The characteristics of the pores are vital for controlling the performance of covalent organic frameworks, but obtaining different chemical environments in different pores is challenging. Here, the authors report the development of covalent organic frameworks with differing pore environments.
- Wenyan Ji
- , Pai Zhang
- & Bao-Hang Han
-
Article
| Open Access Tracing immune cells around biomaterials with spatial anchors during large-scale wound regeneration
Tracing immune cells around biomaterials with spatial anchors during large-scale wound regeneration
Skin scarring devoid of dermal appendages has unfavorable effects on aesthetic and physiological functions. Here, the authors present a treatment based on extracellular matrix scaffolds and perform multimodal analysis to highlight the role of Tregs recruited by the biomaterial in mitigating tissue fibrous by suppressing excessive inflammation.
- Yang Yang
- , Chenyu Chu
- & Yili Qu
-
Article
| Open Access Pre-activated nanoparticles with persistent luminescence for deep tumor photodynamic therapy in gallbladder cancer
Pre-activated nanoparticles with persistent luminescence for deep tumor photodynamic therapy in gallbladder cancer
Phototherapy of deep tumors suffers from many obstacles, such as limited near-infrared tissue penetration depth and low accumulation efficiency within the target sites. Here, the authors report stimuli sensitive tumor-targeted photodynamic nanoparticles with persistent luminescence for the treatment of deep tumors.
- Sarun Juengpanich
- , Shijie Li
- & Mingyu Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Janus particle-engineered structural lipiodol droplets for arterial embolization
Janus particle-engineered structural lipiodol droplets for arterial embolization
Embolization is one of the most promising strategies for clinical disease treatments, however, the existing embolic materials normally have poor embolization effectiveness. Here, the authors report Janus particle-engineered structural lipiodol droplets by programming the self-assembly of Janus particles at the lipiodol-water interface to achieve highly efficient renal embolization.
- Sijian Tao
- , Bingquan Lin
- & Jun-Bing Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Building block aspect ratio controls assembly, architecture, and mechanics of synthetic and natural protein networks
Building block aspect ratio controls assembly, architecture, and mechanics of synthetic and natural protein networks
Fibrous networks constructed from high aspect ratio protein building blocks are ubiquitous in nature, but the functional advantage of such building blocks over globular proteins is not understood. Here, using shear rheology and small-angle neutron scattering, the authors characterise the mechanical and structural properties of photochemically crosslinked protein L and fibrin networks and show that aspect ratio is a crucial property that defines network architecture and mechanics.
- Matt D. G. Hughes
- , Sophie Cussons
- & Lorna Dougan
-
Article
| Open Access Rescue of dendritic cells from glycolysis inhibition improves cancer immunotherapy in mice
Rescue of dendritic cells from glycolysis inhibition improves cancer immunotherapy in mice
While glycolysis inhibition impairs cancer cell tumourigenic capacities, it also affects immune cells anti-tumour activity. Here, the authors show that rescuing glycolytic inhibition of dendritic cells improves the efficacy of combining immunotherapy with glycolysis inhibition.
- Sahil Inamdar
- , Abhirami P. Suresh
- & Abhinav P. Acharya
-
Article
| Open Access Electrically insulating PBO/MXene film with superior thermal conductivity, mechanical properties, thermal stability, and flame retardancy
Electrically insulating PBO/MXene film with superior thermal conductivity, mechanical properties, thermal stability, and flame retardancy
Constructing thermally conductive but electrically insulating composites remains a challenge. Here, Ti3C2 MXene is combined in a nacre-like structure with the polymer PBO to form such materials, also exhibiting high thermal stability and flame retardancy.
- Yong Liu
- , Weizhi Zou
- & Jian Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Integration of AIEgens into covalent organic frameworks for pyroptosis and ferroptosis primed cancer immunotherapy
Integration of AIEgens into covalent organic frameworks for pyroptosis and ferroptosis primed cancer immunotherapy
Pyroptosis and ferroptosis are typically induced by metal species or chemotherapeutic drugs, and able to boost a robust antitumor immunity, however their therapeutic uses have been hindered by the risks arising from metal species or chemotherapeutic drugs. Here the authors report a pyroptosis and ferroptosis dual-inducer based on non-metallic AIEgen-based covalent organic frameworks.
- Liang Zhang
- , An Song
- & Zhi-Jun Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Protein fibers with self-recoverable mechanical properties via dynamic imine chemistry
Protein fibers with self-recoverable mechanical properties via dynamic imine chemistry
Manipulating the internal interactions within biological fibers to tune macroscopic properties is important but challenging, and can limit applications. Here, the authors report the use of dynamic imine chemistry for engineering molecular interactions and forming strong and tough protein fibers.
- Jing Sun
- , Haonan He
- & Kai Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Targeted mechanical stimulation via magnetic nanoparticles guides in vitro tissue development
Targeted mechanical stimulation via magnetic nanoparticles guides in vitro tissue development
Highly localized mechanical forces that shape in vivo tissue development remain challenging to recapitulate in vitro. Here the authors use magnetically actuated nanoparticles to generate spatially defined forces within organoids, which guide the spatial organization of tissue patterning and growth.
- Abdel Rahman Abdel Fattah
- , Niko Kolaitis
- & Adrian Ranga
-
Article
| Open Access Tricolor visible wavelength-selective photodegradable hydrogel biomaterials
Tricolor visible wavelength-selective photodegradable hydrogel biomaterials
Photodegradable gels are useful for regenerative medicine and tissue engineering, but typically respond to UV light. Here, the authors report a family of 3 photolabile linkers that cleave rapidly and with unique tricolor wavelength-selectivity to visible light.
- Teresa L. Rapp
- & Cole A. DeForest
-
Article
| Open Access A photo-triggered self-accelerated nanoplatform for multifunctional image-guided combination cancer immunotherapy
A photo-triggered self-accelerated nanoplatform for multifunctional image-guided combination cancer immunotherapy
Aggregation-induced emission luminogens (AIEgens) have shown high-performance as photosensitizers. Here the authors combine an AIEgen with paclitaxel-based hypoxia-responsive prodrug into nanoparticles for multifunctional image-guided photodynamic and immunotherapy in preclinical cancer models.
- Xiaoying Kang
- , Yuan Zhang
- & Ben Zhong Tang

 Unlocking the mysterious polytypic features within vaterite CaCO3
Unlocking the mysterious polytypic features within vaterite CaCO3