Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo imaging of mitochondrial DNA mutations using an integrated nano Cas12a sensor
In vivo imaging of mitochondrial DNA mutations using an integrated nano Cas12a sensor
Mutations in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) play critical roles in human diseases. Here, the authors describe an integrated Cas12a sensor for sensing mtDNA mutations in vivo, showing potential for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
- Yanan Li
- , Yonghua Wu
- & Kaixiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access mRNA lipid nanoparticle-mediated pyroptosis sensitizes immunologically cold tumors to checkpoint immunotherapy
mRNA lipid nanoparticle-mediated pyroptosis sensitizes immunologically cold tumors to checkpoint immunotherapy
mRNA nanomedicine-based gene therapy may offer opportunities for cancer treatment. Here the authors show that mRNA lipid nanoparticles encoding the N-terminal domain of gasdermin B trigger pyroptosis and promote anti-tumor immune responses in preclinical cancer models.
- Fengqiao Li
- , Xue-Qing Zhang
- & Xiaoyang Xu
-
Article
| Open Access A massively parallel screening platform for converting aptamers into molecular switches
A massively parallel screening platform for converting aptamers into molecular switches
Efforts to convert aptamers into molecular switches using rational design are often unsuccessful. Here the authors describe a massively parallel screening-based strategy whereby millions of potential aptamer switches are synthesised, sequenced and screened directly on a flow-cell.
- Alex M. Yoshikawa
- , Alexandra E. Rangel
- & H. Tom Soh
-
Article
| Open Access Ligand-tethered lipid nanoparticles for targeted RNA delivery to treat liver fibrosis
Ligand-tethered lipid nanoparticles for targeted RNA delivery to treat liver fibrosis
Gene delivery to fibroblasts for liver fibrosis treatment remains challenging. Here the authors develop a combinatorial library of ligand-tethered lipidoids via a modular synthetic method and adopt a 2-round screening strategy to identify lipidoids for potent and selective gene delivery to fibroblasts.
- Xuexiang Han
- , Ningqiang Gong
- & Michael J. Mitchell
-
Article
| Open Access Long-term whole blood DNA preservation by cost-efficient cryosilicification
Long-term whole blood DNA preservation by cost-efficient cryosilicification
Cost-effective methods for long-term storage of DNA are desired. Here the authors present a method for in situ cryosilicification of whole blood cells, allowing long-term and room temperature preservation of genomic information for only approximately $0.5 per sample.
- Liang Zhou
- , Qi Lei
- & Wei Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular doping of nucleic acids into light emitting crystals driven by multisite-intermolecular interaction
Molecular doping of nucleic acids into light emitting crystals driven by multisite-intermolecular interaction
DNAs exhibit a unique molecular doping structure, unseen in conventional hybrid assemblies, when doped into light-emitting organic materials. Here authors unveil doping mechanism of DNAs into organic semiconducting crystals and tailor their photoluminescence and optical waveguide phenomena.
- Woo Hyuk Jung
- , Jin Hyuk Park
- & Dong June Ahn
-
Article
| Open Access Optical-Tweezers-integrating-Differential-Dynamic-Microscopy maps the spatiotemporal propagation of nonlinear strains in polymer blends and composites
Optical-Tweezers-integrating-Differential-Dynamic-Microscopy maps the spatiotemporal propagation of nonlinear strains in polymer blends and composites
The authors present an approach to connect polymer dynamics to force response by integrating optical tweezers with differential dynamic microscopy. They measure blends of ring and linear DNA and observe a resonant response, which is suppressed by the presence of microtubules.
- Karthik R. Peddireddy
- , Ryan Clairmont
- & Rae M. Robertson-Anderson
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient DNA fluorescence labeling via base excision trapping
Efficient DNA fluorescence labeling via base excision trapping
Methods for fluorescently labelling DNAs are expensive and labour-intensive. Here the authors report an in situ DNA labelling strategy for oligonucleotides as well as dsDNA that makes use of aldehyde-reactive rotor dyes to trap AP sites resulting from excision of deaminated DNA bases.
- Yong Woong Jun
- , Emily M. Harcourt
- & Eric T. Kool
-
Article
| Open Access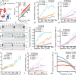 Topological digestion drives time-varying rheology of entangled DNA fluids
Topological digestion drives time-varying rheology of entangled DNA fluids
Understanding and controlling the rheology of polymeric complex fluids is of fundamental importance in both industry and biology. Here, Michieletto et al. show how to achieve time-dependent rheology of DNA solutions via enzymatically-driven architectural alterations by restriction endonucleases.
- D. Michieletto
- , P. Neill
- & R. M. Robertson-Anderson
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-step screening of DNA/lipid nanoparticles and co-delivery with siRNA to enhance and prolong gene expression
Multi-step screening of DNA/lipid nanoparticles and co-delivery with siRNA to enhance and prolong gene expression
Plasmid DNA offers extended transgene expression duration compared to mRNA technologies. Here, using a multi-step screening platform, the authors report the best performing nanoparticle formulations for liver-targeted plasmid DNA expression in vivo.
- Yining Zhu
- , Ruochen Shen
- & Hai-Quan Mao
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding self-assembly at molecular level enables controlled design of DNA G-wires of different properties
Understanding self-assembly at molecular level enables controlled design of DNA G-wires of different properties
G-wire structures have potential applications in bio-nanotechnology, however, this is limited by a lack of understanding about the assembly process and structures formed. Here, the authors use nuclear magnetic resonance and molecular dynamic simulations to understand the guiding principles of G-wire assembly.
- Daša Pavc
- , Nerea Sebastian
- & Primož Šket
-
Article
| Open Access Fast microwave heating-based one-step synthesis of DNA and RNA modified gold nanoparticles
Fast microwave heating-based one-step synthesis of DNA and RNA modified gold nanoparticles
Simple methods for attaching polynucleotides to gold nanoparticles are of interest for simplifying conjugation in a range of applications. Here, the authors report a microwave heating-based method for the fast, one-step attachment of a range of thiolated or non-thiolated DNA and RNA to gold nanoparticles.
- Mengqi Huang
- , Erhu Xiong
- & Xiaoming Zhou
-
Comment
| Open Access An ionizable lipid toolbox for RNA delivery
An ionizable lipid toolbox for RNA delivery
RNA therapeutics have benefited significantly from decades of research on lipid nanoparticles, specifically its key component—the ionizable lipid. This comment discusses the major ionizable lipid types, and provides perspectives for future development.
- Xuexiang Han
- , Hanwen Zhang
- & Michael J. Mitchell
-
Article
| Open Access Self assembling cluster crystals from DNA based dendritic nanostructures
Self assembling cluster crystals from DNA based dendritic nanostructures
Experimental realization of cluster crystals- periodic structures with lattice sites occupied by several, overlapping building blocks, has been elusive. Here, the authors show the existence of well-controlled soft matter cluster crystals composed of a thermosensitive water-soluble polymer and nanometer-scale all-DNA dendrons.
- Emmanuel Stiakakis
- , Niklas Jung
- & Christos N. Likos
-
Article
| Open Access Combination of epigenetic regulation with gene therapy-mediated immune checkpoint blockade induces anti-tumour effects and immune response in vivo
Combination of epigenetic regulation with gene therapy-mediated immune checkpoint blockade induces anti-tumour effects and immune response in vivo
While immunotherapy is a promising cancer treatment option, durable benefits are often rare due to immune escape. Here, the authors combine epigenetic regulation with gene therapy-mediated immune checkpoint blockade and show efficient anti-tumour effects and immune response in vivo.
- Huapan Fang
- , Zhaopei Guo
- & Xuesi Chen
-
Article
| Open Access A smart multiantenna gene theranostic system based on the programmed assembly of hypoxia-related siRNAs
A smart multiantenna gene theranostic system based on the programmed assembly of hypoxia-related siRNAs
The therapeutic application of small interfering RNA (siRNA) is challenging due to its non-specific targeting and delivery issues. Here, the authors report an endogenous micro-RNA guided and hybridisation chain reaction-promoted siRNA delivery system encapsulated in tumour-derived extracellular vesicles, with cancer-specific activation, and achieve silencing of hypoxia-related genes.
- Xue Gong
- , Haizhou Wang
- & Fuan Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Base-pair resolution analysis of the effect of supercoiling on DNA flexibility and major groove recognition by triplex-forming oligonucleotides
Base-pair resolution analysis of the effect of supercoiling on DNA flexibility and major groove recognition by triplex-forming oligonucleotides
In cells, DNA is arranged into topologically-constrained (supercoiled) structures, but how this supercoiling affects the detailed double-helical structure of DNA remains unclear. Here authors use atomic force microscopy and atomistic molecular dynamics simulations, to resolve structures of negatively-supercoiled DNA minicircles at base-pair resolution.
- Alice L. B. Pyne
- , Agnes Noy
- & Sarah A. Harris
-
Article
| Open Access A DNA origami-based aptamer nanoarray for potent and reversible anticoagulation in hemodialysis
A DNA origami-based aptamer nanoarray for potent and reversible anticoagulation in hemodialysis
Safe haemodialysis is essential for patients with acute kidney injury and renal failure. Here the authors present a DNA origami-based approach with high affinity and specificity to thrombin, inhibiting coagulation.
- Shuai Zhao
- , Run Tian
- & Baoquan Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Photon-directed multiplexed enzymatic DNA synthesis for molecular digital data storage
Photon-directed multiplexed enzymatic DNA synthesis for molecular digital data storage
Writing data in DNA is still a bottleneck due to the reliance on chemical synthesis methods. Here the authors report multiplexed enzymatic DNA synthesis using maskless photolithography.
- Howon Lee
- , Daniel J. Wiegand
- & George M. Church
-
Article
| Open Access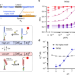 Rational design of aptamer switches with programmable pH response
Rational design of aptamer switches with programmable pH response
Previous design strategies for pH sensitive aptamers were not readily tunable across pH ranges. Here the authors present a general method to convert aptamers into pH-responsive switches using two orthogonal motifs.
- Ian A. P. Thompson
- , Liwei Zheng
- & H. Tom Soh
-
Article
| Open Access Synergistic lipid compositions for albumin receptor mediated delivery of mRNA to the liver
Synergistic lipid compositions for albumin receptor mediated delivery of mRNA to the liver
Lipid-like nanoparticles have applications as non-viral delivery systems for mRNA. Here, the authors develop biodegradable lipids with improved clearance and reduced toxicity.
- Lei Miao
- , Jiaqi Lin
- & Daniel G. Anderson
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum scale organic semiconductors for SERS detection of DNA methylation and gene expression
Quantum scale organic semiconductors for SERS detection of DNA methylation and gene expression
The low detection sensitivity of organic semiconductors has limited their use in biomedical surface-enhanced Raman scattering applications. Here, the authors use quantum scale organic semiconductors and show detection of genomic DNA methylation as well as gene expression.
- Swarna Ganesh
- , Krishnan Venkatakrishnan
- & Bo Tan
-
Article
| Open Access Naturally-occurring cholesterol analogues in lipid nanoparticles induce polymorphic shape and enhance intracellular delivery of mRNA
Naturally-occurring cholesterol analogues in lipid nanoparticles induce polymorphic shape and enhance intracellular delivery of mRNA
Endosomal sequestration of lipid-based nanoparticles is a barrier to delivery of nucleic acids. Here the authors test an array of cholesterol variants and perform in-depth investigation of nanoparticle shape, internal structure and intracellular trafficking.
- Siddharth Patel
- , N. Ashwanikumar
- & Gaurav Sahay
-
Article
| Open Access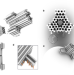 A large size-selective DNA nanopore with sensing applications
A large size-selective DNA nanopore with sensing applications
Artificial nanopores can perform selective gating of molecules analogous to transmembrane proteins. Here, the authors design a DNA origami pore with a controllable lid for size-selective gating and translocation of macromolecules and evaluate its biosensing properties by single particle assay.
- Rasmus P. Thomsen
- , Mette Galsgaard Malle
- & Jørgen Kjems
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-level patterning nucleic acid photolithography
Multi-level patterning nucleic acid photolithography
Increasing the complexity of engineered nucleic acid constructs and interfacing the microscopic with the macroscopic requires a multifaceted and programmable fabrication approach. Here the authors demonstrate multi-level photolithographic patterning for highly complex patterns at micrometer resolution.
- Kathrin Hölz
- , Erika Schaudy
- & Mark M. Somoza
-
Article
| Open Access Microstructure arrays of DNA using topographic control
Microstructure arrays of DNA using topographic control
DNA is a biological building block which has drawn much attention as a structural material for a range of applications. Here, the authors report that DNA structures can be templated using shear-induced flow and microposts for controllable DNA patterning.
- Yun Jeong Cha
- , Soon Mo Park
- & Dong Ki Yoon
-
Article
| Open Access Label-free detection of conformational changes in switchable DNA nanostructures with microwave microfluidics
Label-free detection of conformational changes in switchable DNA nanostructures with microwave microfluidics
Methods to study conformational changes in biomolecules are limited in resolution and require labelling or other modifications of target analytes. Here the authors present a label-free, microwave microfluidic approach to detect conformational changes of DNA nanostructures based on ionic conductivity.
- Angela C. Stelson
- , Minghui Liu
- & James C. Booth
-
Article
| Open Access Programming molecular topologies from single-stranded nucleic acids
Programming molecular topologies from single-stranded nucleic acids
Designing nucleic acid-based nanostructures with knots remains challenging. Here the authors present a general strategy to design and construct highly knotted 2D and 3D nanostructures from single-stranded DNA or RNA
- Xiaodong Qi
- , Fei Zhang
- & Hao Yan
-
Article
| Open Access A RNA producing DNA hydrogel as a platform for a high performance RNA interference system
A RNA producing DNA hydrogel as a platform for a high performance RNA interference system
Interfering RNA have a range of therapeutic and research based applications, issues with delivery have made systems that make siRNA in situ of interest. Here, the author report on the creation of a DNA hydrogel with improved stability and transcription efficiency over plasmid DNA.
- Jaejung Song
- , Minhyuk Lee
- & Nokyoung Park
-
Article
| Open Access Modular DNA strand-displacement controllers for directing material expansion
Modular DNA strand-displacement controllers for directing material expansion
Materials which change shape in response to a trigger are of interest for soft robotics and targeted therapeutic delivery. Here, the authors report on the development of DNA-crosslinked hydrogels which can expand upon the detection of different biomolecular inputs mediated by DNA strand-displacement.
- Joshua Fern
- & Rebecca Schulman
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping the energy landscapes of supramolecular assembly by thermal hysteresis
Mapping the energy landscapes of supramolecular assembly by thermal hysteresis
Complex assembly pathways often involve transient, partly-formed intermediates that are challenging to characterize. Here, the authors present a simple and rapid spectroscopic thermal hysteresis method for mapping the energy landscapes of supramolecular assembly.
- Robert W. Harkness V
- , Nicole Avakyan
- & Anthony K. Mittermaier
-
Article
| Open Access Topologically frustrated dynamics of crowded charged macromolecules in charged hydrogels
Topologically frustrated dynamics of crowded charged macromolecules in charged hydrogels
Diffusion of molecules in crowded environment is important for various living systems, but the dynamics of charged molecules in charged matrices remains still unexplored. Here the authors report a dynamics of DNA and polyelectrolytes in a charged hydrogel where the guest molecules do not diffuse but experience topologically frustrated dynamics.
- Di Jia
- & Murugappan Muthukumar
-
Article
| Open Access High-resolution AFM structure of DNA G-wires in aqueous solution
High-resolution AFM structure of DNA G-wires in aqueous solution
DNA and RNA G-quadruplexes can stack to form higher-order structures called G-wires. Here the authors report high-resolution AFM images of higher-order DNA G-quadruplexes in aqueous solution that could impact the design of G-wire based nanodevices and the understanding of G-wires in biology.
- Krishnashish Bose
- , Christopher J. Lech
- & Anh Tuân Phan
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional structural dynamics of DNA origami Bennett linkages using individual-particle electron tomography
Three-dimensional structural dynamics of DNA origami Bennett linkages using individual-particle electron tomography
Scaffolded DNA origami by folding single-stranded DNA into three-dimensional nanostructures holds promise for building functional nanomachines, yet their dynamic structures remain largely unknown. Here, Lei et al. address this issue using individual-particle electron tomography at 6–14 nm resolution.
- Dongsheng Lei
- , Alexander E. Marras
- & Gang Ren
-
Article
| Open Access DNA multi-bit non-volatile memory and bit-shifting operations using addressable electrode arrays and electric field-induced hybridization
DNA multi-bit non-volatile memory and bit-shifting operations using addressable electrode arrays and electric field-induced hybridization
DNA based technology holds promise for non-volatile memory and computational tasks, yet the relatively slow hybridization kinetics remain a bottleneck. Here, Song et al. have developed an electric field-induced hybridization platform that can speed up multi-bit memory and logic operations.
- Youngjun Song
- , Sejung Kim
- & Xiaohua Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Hyperstretching DNA
Hyperstretching DNA
The mechanics and structural transitions of DNA are important to many essential processes inside living cells. Here the authors combine theory and single-molecule experiments to show that intercalator binding stabilises a new structural state of DNA: hyperstretched DNA.
- Koen Schakenraad
- , Andreas S. Biebricher
- & Paul van der Schoot
-
Article
| Open Access A water-soluble nucleolin aptamer-paclitaxel conjugate for tumor-specific targeting in ovarian cancer
A water-soluble nucleolin aptamer-paclitaxel conjugate for tumor-specific targeting in ovarian cancer
Paclitaxel, a first line chemotherapeutic drug, suffers from poor water solubility and low tissue selectivity. Here, the authors report a water-soluble nucleolin aptamer-paclitaxel conjugate that selectively accumulates in ovarian tumor issues displaying reduced toxicity and improved activity profiles.
- Fangfei Li
- , Jun Lu
- & Ge Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Multifunctional quantum dot DNA hydrogels
Multifunctional quantum dot DNA hydrogels
The development of nanomaterials for imaging and drug delivery has been of great interest to the field. Here, the authors synthesized multifunctional enzyme-responsive hydrogels with self-assembling quantum dots for nucleic acid and drug delivery as well as having imaging capability.
- Libing Zhang
- , Sae Rin Jean
- & Shana O. Kelley
-
Article
| Open Access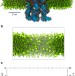 Stability and dynamics of membrane-spanning DNA nanopores
Stability and dynamics of membrane-spanning DNA nanopores
Although DNA nanopores are widely explored as synthetic membrane proteins, it is still unclear how the anionic DNA assemblies stably reside within the hydrophobic core of a lipid bilayer. Here, the authors use molecular dynamics simulations to reveal the key dynamic interactions and energetics stabilizing the nanopore-membrane interaction.
- Vishal Maingi
- , Jonathan R. Burns
- & Mark S. P. Sansom
-
Article
| Open Access Small RNA zippers lock miRNA molecules and block miRNA function in mammalian cells
Small RNA zippers lock miRNA molecules and block miRNA function in mammalian cells
MicroRNAs regulate a wide range of biological processes and being able to inhibit their function could allow the development of therapeutic options. Here the authors describe a ‘small RNA zipper’ that sequesters miRNAs by forming a chain of DNA:RNA duplexes.
- Lingyu Meng
- , Cuicui Liu
- & Zuoren Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Superlattices assembled through shape-induced directional binding
Superlattices assembled through shape-induced directional binding
Controlling self-assembly of nanoparticles into superlattices is an important approach to build functional materials. Here, Lu et al. use directional binding provided by DNA-encoded polyhedral blocks—cubes or octahedrons—to guide spherical nanoparticles into clusters and three-dimensional lattices.
- Fang Lu
- , Kevin G. Yager
- & Oleg Gang

 Dynamic control of DNA condensation
Dynamic control of DNA condensation