Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Episodic transport of discrete magma batches beneath Aso volcano
Episodic transport of discrete magma batches beneath Aso volcano
Repetitive shallow resonances provide a pathway to unravelling episodic magma transport deep in the magma plumbing system. Episodic deformation of ~1 nanoradian over ~100 s beneath Aso volcano potentially provides a link between long-term volcanic output and short-term eruption dynamics.
- Jieming Niu
- & Teh-Ru Alex Song
-
Article
| Open Access Paleocene/Eocene carbon feedbacks triggered by volcanic activity
Paleocene/Eocene carbon feedbacks triggered by volcanic activity
The Paleocene–Eocene boundary coincided with runaway global warming possibly analogous to future climate change, but the sources of greenhouse gasses have remained unresolved. Here, the authors reveal volcanism triggered initial warming, and subsequent carbon was released after crossing a tipping point.
- Sev Kender
- , Kara Bogus
- & Melanie J. Leng
-
Article
| Open Access Climate change modulates the stratospheric volcanic sulfate aerosol lifecycle and radiative forcing from tropical eruptions
Climate change modulates the stratospheric volcanic sulfate aerosol lifecycle and radiative forcing from tropical eruptions
How climate change influences the lifecycle of stratospheric volcanic aerosols and the associated radiative forcing is unknown. Here, the authors present model experiments suggesting that climate change amplifies the forcing of large-magnitude tropical eruptions but reduces the forcing of moderate-magnitude tropical eruptions.
- Thomas J. Aubry
- , John Staunton-Sykes
- & Anja Schmidt
-
Article
| Open Access Uncovering the eruptive patterns of the 2019 double paroxysm eruption crisis of Stromboli volcano
Uncovering the eruptive patterns of the 2019 double paroxysm eruption crisis of Stromboli volcano
Integrated field and laboratory investigations, and numerical simulations of the 2019 paroxysmal explosions at Stromboli volcano revealed that they were anticipated by a week-to-month-long destabilization in the normal volcanic activity, a pattern common to all paroxysms.
- Daniele Andronico
- , Elisabetta Del Bello
- & Federico Valentini
-
Article
| Open Access Out-of-sequence skeletal growth causing oscillatory zoning in arc olivines
Out-of-sequence skeletal growth causing oscillatory zoning in arc olivines
Arc olivines are commonly explained through a paradigm of core-to-rim sequential growth and oscillatory zoning is interpreted to represent magma mixing. Here the authors show Fo–Ni–P oscillatory zoned olivines can grow as out-of-sequence crystal frames and complex zoning can occur in closed systems.
- Pablo Salas
- , Philipp Ruprecht
- & Osvaldo Rabbia
-
Article
| Open Access Sunda arc mantle source δ18O value revealed by intracrystal isotope analysis
Sunda arc mantle source δ18O value revealed by intracrystal isotope analysis
Subduction zone volcanoes are underlain by extensive magma plumbing systems, which can obscure original mantle source signals. Here, the authors show that intra-crystal oxygen isotope analysis of clinopyroxenes from the Sunda arc (Indonesia) reveal the δ18 O value of the sub-arc mantle.
- Frances M. Deegan
- , Martin J. Whitehouse
- & Osvaldo González-Maurel
-
Article
| Open Access Submarine landslide megablocks show half of Anak Krakatau island failed on December 22nd, 2018
Submarine landslide megablocks show half of Anak Krakatau island failed on December 22nd, 2018
The authors here present a detailed reconstruction of the landslide mass following the 2018 eruption of Anak Krakatau. Bathymetry data reports the volume of the collapsed submarine flank to be much larger than previously reported.
- J. E. Hunt
- , D. R. Tappin
- & U. Udrekh
-
Article
| Open Access On the use of plume models to estimate the flux in volcanic gas plumes
On the use of plume models to estimate the flux in volcanic gas plumes
Monitoring the flux of gas from volcanoes is a fundamental component of volcano monitoring programs and is used as a basis for eruption forecasting. Here, the authors present a new method using video images of volcanic gas plumes to measure the speed of convective structures and to estimate volcanic fluxes.
- Julia Woitischek
- , Nicola Mingotti
- & Andrew W. Woods
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid heat discharge during deep-sea eruptions generates megaplumes and disperses tephra
Rapid heat discharge during deep-sea eruptions generates megaplumes and disperses tephra
A novel model for submarine tephra dispersal by hydrothermal megaplumes is proposed. The energy flux inferred from our model aligns with megaplume observations, and suggests that the catastrophic release of hot crustal fluids, as opposed to lava heating, is responsible for megaplume generation.
- Samuel S. Pegler
- & David J. Ferguson
-
Article
| Open Access Increased respiratory morbidity associated with exposure to a mature volcanic plume from a large Icelandic fissure eruption
Increased respiratory morbidity associated with exposure to a mature volcanic plume from a large Icelandic fissure eruption
Large fissure eruptions can cause air pollution events when the volcanic plume returns to the same area after the initial advisory has been lifted. Here, the authors show that these events had a significant impact on health care usage in Iceland, and the impact was exacerbated when advisories were not issued successfully.
- Hanne Krage Carlsen
- , Evgenia Ilyinskaya
- & Thorolfur Gudnason
-
Article
| Open Access Nickel isotopes link Siberian Traps aerosol particles to the end-Permian mass extinction
Nickel isotopes link Siberian Traps aerosol particles to the end-Permian mass extinction
The end-Permian mass extinction was the most severe extinction event in the past 540 million years, and the Siberian Traps large igneous province is widely hypothesized to have been the primary trigger for the environmental catastrophe. In this study, Ni isotopes provide the link between Siberian Traps magmatism and early environmental degradation, ultimately leading to the end-Permian extinction.
- Menghan Li
- , Stephen E. Grasby
- & Yanan Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical feedbacks during magma degassing control chlorine partitioning and metal extraction in volcanic arcs
Chemical feedbacks during magma degassing control chlorine partitioning and metal extraction in volcanic arcs
Chlorine behaviour during complex, polybaric arc magma degassing is poorly understood. Here, the authors show that chemical feedbacks during coeval magma differentiation and degassing account for the Cl record at both volcanoes and ore deposits, and quantify the role of Cl in efficient copper extraction during degassing.
- B. Tattitch
- , C. Chelle-Michou
- & R. R. Loucks
-
Article
| Open Access Imagining and constraining ferrovolcanic eruptions and landscapes through large-scale experiments
Imagining and constraining ferrovolcanic eruptions and landscapes through large-scale experiments
Ferrovolcanism is a hypothetical form of planetary volcanism in which the erupted lava is metallic in composition. Here we show that ferrovolcanic lava is denser and less viscous than silicate lava, resulting in fast-moving, thin, braided flows.
- A. Soldati
- , J. A. Farrell
- & J. A. Karson
-
Article
| Open Access Ground deformation reveals the scale-invariant conduit dynamics driving explosive basaltic eruptions
Ground deformation reveals the scale-invariant conduit dynamics driving explosive basaltic eruptions
Here, the authors use 20 years of ground deformation data from Stromboli and correlate this data with eruptive records. They find that duration and amplitude of the inflation trend scales with eruption magnitude, indicating that explosive dynamics obeys the same (scale-invariant) conduit process.
- M. Ripepe
- , G. Lacanna
- & D. Delle Donne
-
Article
| Open Access Caldera resurgence during the 2018 eruption of Sierra Negra volcano, Galápagos Islands
Caldera resurgence during the 2018 eruption of Sierra Negra volcano, Galápagos Islands
The authors here present geodetic and seismic data for a complete eruptive cycle (2005-2018) for Sierra Negra volcano, Galapagos Island. The data shows the largest pre-eruptive inflation (6.5 m) and rates of seismicity ever observed before a basaltic eruption and provides a rare illustration of caldera resurgence mechanisms.
- Andrew F. Bell
- , Peter C. La Femina
- & Michael J. Stock
-
Article
| Open Access The fate of volcanic ash: premature or delayed sedimentation?
The fate of volcanic ash: premature or delayed sedimentation?
Generally it is thought that ash aggregation leads to reduced atmospheric travel distances. Here, the authors show that the rafting effect can increase dispersal range by up to 3.7 times for particles between 300–500 μm, compared to sedimentation of individual clasts.
- Eduardo Rossi
- , Gholamhossein Bagheri
- & Costanza Bonadonna
-
Comment
| Open Access Land, lava, and disaster create a social dilemma after the 2018 eruption of Kīlauea volcano
Land, lava, and disaster create a social dilemma after the 2018 eruption of Kīlauea volcano
The unprecedented cost of the 2018 eruption in Hawai’i reflects an intersection of disparate physical and social phenomena: widely spaced, highly destructive eruptions, and atypically high population growth. These were linked and the former indirectly drove the latter with unavoidable consequences.
- Bruce F. Houghton
- , Wendy A. Cockshell
- & Eric Yamashita
-
Review Article
| Open Access A review framework of how earthquakes trigger volcanic eruptions
A review framework of how earthquakes trigger volcanic eruptions
This review dives deep into how earthquakes affect volcanoes, specifically into the relation between tectonic seismic activity and subsequent eruptions. Activity may increase in any volcanic setting in the 2–5 years following an earthquake, and especially at volcanic centres featuring vigorous hydrothermal activity.
- Gilles Seropian
- , Ben M. Kennedy
- & Arthur D. Jolly
-
Article
| Open Access Reconciling bubble nucleation in explosive eruptions with geospeedometers
Reconciling bubble nucleation in explosive eruptions with geospeedometers
The authors simulate bubble nucleation in silica-rich magma with conditions appropriate for Plinian eruptions. They demonstrate that the gap between decompression rate estimates from bubble number density and independent geospeedometers can be largely closed if nucleation is heterogenous facilitated by magnetite crystals and decompression rate is calculated as time-averaged values.
- Sahand Hajimirza
- , Helge M. Gonnermann
- & James E. Gardner
-
Perspective
| Open Access The cascading origin of the 2018 Kīlauea eruption and implications for future forecasting
The cascading origin of the 2018 Kīlauea eruption and implications for future forecasting
- M. R. Patrick
- , B. F. Houghton
- & T. Elias
-
Article
| Open Access Determining the current size and state of subvolcanic magma reservoirs
Determining the current size and state of subvolcanic magma reservoirs
This study makes use of the total spread of zircon ages and trace elements to study the thermal evolution of magmatic systems. Applied to Nevado de Toluca, the authors determine the size of its subvolcanic magma reservoir and assess its potential of re-activation.
- Gregor Weber
- , Luca Caricchi
- & Axel K. Schmitt
-
Article
| Open Access Seafloor evidence for pre-shield volcanism above the Tristan da Cunha mantle plume
Seafloor evidence for pre-shield volcanism above the Tristan da Cunha mantle plume
Here, the authors combine bathymetry and sediment echosound data to present a submarine, volcanic map of the Tristan de la Cunha region. They find that the youngest volcanic expression of the Tristan de la Cunha mantle plume is currently located to the (south-) west of the island.
- Wolfram H. Geissler
- , Paul Wintersteller
- & Wilfried Jokat
-
Article
| Open Access Persisting volcanic ash particles impact stratospheric SO2 lifetime and aerosol optical properties
Persisting volcanic ash particles impact stratospheric SO2 lifetime and aerosol optical properties
Volcanic ash is often neglected in climate simulations as it is assumed to have a short atmospheric lifetime. Here, the authors show a persistent super-micron ash layer after the Mt. Kelut eruption in 2014 that impacts the stratospheric sulfur burden and chemistry for over the first months after the eruption.
- Yunqian Zhu
- , Owen B. Toon
- & Sarah Woods
-
Comment
| Open Access How satellite InSAR has grown from opportunistic science to routine monitoring over the last decade
How satellite InSAR has grown from opportunistic science to routine monitoring over the last decade
In the past decade, a new generation of radar satellites have revolutionised our ability to measure Earth’s surface deformation globally and with unprecedented resolution. InSAR is transforming our understanding of faults, volcanoes and ground stability and increasingly influencing hazard management.
- Juliet Biggs
- & Tim J. Wright
-
Article
| Open Access Deep long period volcanic earthquakes generated by degassing of volatile-rich basaltic magmas
Deep long period volcanic earthquakes generated by degassing of volatile-rich basaltic magmas
The origin of deep long-period earthquakes beneath active volcanoes that are sometimes considered as precursors to eruptions remains not fully understood. Here the authors show that these earthquakes can be generated by the rapid degassing in response to the slow decompression of magma over-saturated with H2O and CO2.
- Oleg Melnik
- , Vladimir Lyakhovsky
- & Olga Bergal-Kuvikas
-
Article
| Open Access Cryptic evolved melts beneath monotonous basaltic shield volcanoes in the Galápagos Archipelago
Cryptic evolved melts beneath monotonous basaltic shield volcanoes in the Galápagos Archipelago
In this study the authors show that monotonous basaltic volcanoes can host a range of melts in their sub-volcanic systems, extending to rhyolitic compositions. The study implies that volcanoes which have produced monotonous basaltic lavas on long timescales could transition to more explosive, silica-rich eruptions in the future.
- Michael J. Stock
- , Dennis Geist
- & John Maclennan
-
Article
| Open Access Automatic precursor recognition and real-time forecasting of sudden explosive volcanic eruptions at Whakaari, New Zealand
Automatic precursor recognition and real-time forecasting of sudden explosive volcanic eruptions at Whakaari, New Zealand
In this study, the authors investigate the predictability of sudden eruptions, motivated by the 2019 eruption at Whakaari (White Island), New Zealand. The paper proposes a machine learning approach that is able to identify eruption precursors in data streaming from a single seismic station at Whakaari.
- D. E. Dempsey
- , S. J. Cronin
- & A. W. Kempa-Liehr
-
Article
| Open Access Combined ground and aerial measurements resolve vent-specific gas fluxes from a multi-vent volcano
Combined ground and aerial measurements resolve vent-specific gas fluxes from a multi-vent volcano
Combining multiple ultraviolet cameras with synchronous aerial measurements, the authors here present vent-specific gas compositions and fluxes for Stromboli volcano. The results show that gas compositions vary between different vents, mirroring differences in eruptive behavior.
- T. D. Pering
- , E. J. Liu
- & A. J. S. McGonigle
-
Article
| Open Access A bedform phase diagram for dense granular currents
A bedform phase diagram for dense granular currents
In this study, Smith and colleagues employ analogue experiments to show the controlling parameters on sediment bedforms in pyroclastic density current deposits. The findings are applied and validated on natural deposits.
- Gregory Smith
- , Peter Rowley
- & Samuel Capon
-
Article
| Open Access Unexpected large eruptions from buoyant magma bodies within viscoelastic crust
Unexpected large eruptions from buoyant magma bodies within viscoelastic crust
Large-volume volcanic eruptions can occur despite only limited precursory activity. Here the authors show that modelling the combined effects of buoyant magma, viscoelastic earth behaviour, and sustained magma channels can explain such behaviour of volcanoes and gives an estimate of pressure evolution in magma bodies.
- Freysteinn Sigmundsson
- , Virginie Pinel
- & Tadashi Yamasaki
-
Article
| Open Access Deep CO2 in the end-Triassic Central Atlantic Magmatic Province
Deep CO2 in the end-Triassic Central Atlantic Magmatic Province
Many major mass extinction events have been associated with large volcanic eruption events, with the argument that large volumes of volcanic degassing could trigger past global climate changes. Here, the authors find that during the end-Triassic extinction event volcanic pulses emitted large amounts of CO2 comparable to projected anthropogenic emissions for the 21st century in the future 2 °C warming scenario.
- Manfredo Capriolo
- , Andrea Marzoli
- & Csaba Szabó
-
Article
| Open Access Microstructural constraints on magmatic mushes under Kīlauea Volcano, Hawaiʻi
Microstructural constraints on magmatic mushes under Kīlauea Volcano, Hawaiʻi
Olivine crystals with prominent intracrystalline distortions have previously been used to quantify deformational processes within the mantle. Here, the authors show that similar techniques can be applied to deformed volcanic olivine crystals, providing quantitative constraints on the geometry of melt-rich mush piles within magmatic plumbing systems.
- Penny E. Wieser
- , Marie Edmonds
- & John Wheeler
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal scavenging from mush piles recorded by melt inclusions
Crystal scavenging from mush piles recorded by melt inclusions
The increasingly prevalent view of magmatic systems as mush-dominated challenges the common assumption that melt inclusions record the pre-eruptive storage and processing of the melts they were erupted with. Here, the authors show that melt inclusions from Kīlauea Volcano, Hawai'i exhibit extreme compositional diversity, consistent with the accumulation of inclusion-bearing crystals in magmatic mush zones for >170 years before their eventual eruption in unrelated carrier melts.
- Penny E. Wieser
- , Marie Edmonds
- & Barbara E. Kunz
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of reactivation of a hydrothermal system from seismic anisotropy changes
Evidence of reactivation of a hydrothermal system from seismic anisotropy changes
In this study, the authors monitor a hydrothermal fluid surge through seismic anisotropy changes at the Hakone volcanic field, Japan. The authors find the anisotropy changes to be set off by the seismic waves of the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake, that reactivated the hydrothermal system.
- Maria Saade
- , Kohtaro Araragi
- & Florent Brenguier
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrothermal alteration of andesitic lava domes can lead to explosive volcanic behaviour
Hydrothermal alteration of andesitic lava domes can lead to explosive volcanic behaviour
The permeability of a dome exerts a control on the outgassing efficiency of the underlying magma. The authors investigate the role of hydrothermal alteration on this process in the laboratory and use these data to model whether the overpressures generated are capable of promoting explosive behaviour.
- Michael J. Heap
- , Valentin R. Troll
- & Thomas R. Walter
-
Article
| Open Access Compositional boundary layers trigger liquid unmixing in a basaltic crystal mush
Compositional boundary layers trigger liquid unmixing in a basaltic crystal mush
This study seeks to tackle the question of why intermediate magmatic rock compositions are poorly represented on the Earth’s surface. The authors do so by tracking the evolution of the physical behaviour of immiscible Fe-rich liquids within a sample suite from the lava lake on the Kilauea Iki volcano, Hawaii.
- Victoria C. Honour
- , Marian B. Holness
- & Marlon M. Jean
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Wiggle-match radiocarbon dating of the Taupo eruption
Wiggle-match radiocarbon dating of the Taupo eruption
- Alan G. Hogg
- , Colin J. N. Wilson
- & Fiona Petchey
-
Article
| Open Access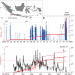 Complex hazard cascade culminating in the Anak Krakatau sector collapse
Complex hazard cascade culminating in the Anak Krakatau sector collapse
On 22 December 2018, the western flank of Anak Krakatau collapsed into the sea of the Sunda Strait triggering a tsunami which killed approximately 430 people and displaced 33,000. Here, the authors show that Anak Krakatau exhibited an elevated state of activity several months prior to the collapse, including precursory thermal anomalies, an increase in the island’s surface area, and a gradual seaward motion of the southwestern flank.
- Thomas R. Walter
- , Mahmud Haghshenas Haghighi
- & Peter Gaebler
-
Article
| Open Access Fluid dynamic induced break-up during volcanic eruptions
Fluid dynamic induced break-up during volcanic eruptions
Determining if a volcanic eruption will behave effusively or explosively is crucial for predicting the potential hazard type and for planning effective mitigation. Here, the authors present a universal, fluid dynamic induced, break-up criterion for low viscosity melts.
- T. J. Jones
- , C. D. Reynolds
- & S. C. Boothroyd
-
Article
| Open Access The mechanism of tidal triggering of earthquakes at mid-ocean ridges
The mechanism of tidal triggering of earthquakes at mid-ocean ridges
Tidal triggering of earthquakes at Axial Volcano on the Juan de Fuca ridge is shown to be driven by tidally induced magma chamber inflation. Fitting the data to theory requires that the frictional parameter A be much smaller than laboratory measurements indicate.
- Christopher H. Scholz
- , Yen Joe Tan
- & Fabien Albino
-
Article
| Open Access The footprint of column collapse regimes on pyroclastic flow temperatures and plume heights
The footprint of column collapse regimes on pyroclastic flow temperatures and plume heights
Pyroclastic density currents (PDCs) are a major threat during explosive volcanic eruptions, hence the possibility to forecast them would be a vital improvement for risk mitigation. Here the authors present a 3D flow model to quantify the thermal patterns leading to volcanic ash plume collapse conditions.
- Matteo Trolese
- , Matteo Cerminara
- & Guido Giordano
-
Article
| Open Access Fluidal pyroclasts reveal the intensity of peralkaline rhyolite pumice cone eruptions
Fluidal pyroclasts reveal the intensity of peralkaline rhyolite pumice cone eruptions
Dynamics of peralkaline rhyolite eruptions remain elusive due to the lack of direct observations. Here the authors provide X-ray Computed Tomography, thermal modelling and field data of fluidal shaped pyroclasts and show that peralkaline rhyolite pumice cones are the product of moderate to intense eruptions.
- Ben Clarke
- , Eliza S. Calder
- & Gezahegn Yirgu
-
Article
| Open Access Dyke intrusion between neighbouring arc volcanoes responsible for 2017 pre-eruptive seismic swarm at Agung
Dyke intrusion between neighbouring arc volcanoes responsible for 2017 pre-eruptive seismic swarm at Agung
Using seismic data and numerical modelling, here, the authors characterize the three-month period of unrest occurring prior to the 2017 Agung eruption (Bali, Indonesia). They observe a large uplift signal located at ~5 km from Agung summit corresponding to the emplacement of a 10 km deep magma intrusion between Agung edifice and Batur caldera, suggesting a potential magmatic connection between the two volcanic systems.
- Fabien Albino
- , Juliet Biggs
- & Devy Kamil Syahbana
-
Article
| Open Access Degassing-induced fractionation of multiple sulphur isotopes unveils post-Archaean recycled oceanic crust signal in hotspot lava
Degassing-induced fractionation of multiple sulphur isotopes unveils post-Archaean recycled oceanic crust signal in hotspot lava
Mantle-sourced magmas erupted at hotspot volcanoes can provide clues to the sulphur cycle over geological timescales. In this work, sulphur isotopes were analysed in crystal-hosted inclusions entrapped at depth, and reveal the presence of post-Archaean recycled material in the Canary Island mantle.
- Patrick Beaudry
- , Marc-Antoine Longpré
- & John Stix
-
Article
| Open Access Combined effusive-explosive silicic volcanism straddles the multiphase viscous-to-brittle transition
Combined effusive-explosive silicic volcanism straddles the multiphase viscous-to-brittle transition
Recent observations of silicic eruptions show that they can be both effusive and explosive at the same time. Here the authors use scaled experiments to demonstrate that magma in effusive eruptions will fracture during flow to the Earth’s surface, accommodating mixed eruption styles.
- Fabian B. Wadsworth
- , Taylor Witcher
- & Donald B. Dingwell
-
Article
| Open Access Global-scale control of extensional tectonics on CO2 earth degassing
Global-scale control of extensional tectonics on CO2 earth degassing
Earth degassing of CO2-rich fluids contributes significantly to the global carbon budget but its link to tectonic regimes remains unclear. Here, the authors use global geological datasets to show that there is a positive spatial correlation between CO2 discharges and extensional tectonic regimes.
- Giancarlo Tamburello
- , Silvia Pondrelli
- & Dmitri Rouwet
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for magmatic carbon bias in 14C dating of the Taupo and other major eruptions
Evidence for magmatic carbon bias in 14C dating of the Taupo and other major eruptions
Correlations between prehistoric eruptions and other phenomena depend on accurate dating of the eruption. Here the authors show that magmatic CO2 in groundwater can bias radiocarbon ages for eruptions and that plateaux of carbon isotopic values in tree ring sequences biased by magmatic CO2 foreshadow major eruptions.
- Richard N. Holdaway
- , Brendan Duffy
- & Ben Kennedy
-
Article
| Open Access Post-eruptive mobility of lithium in volcanic rocks
Post-eruptive mobility of lithium in volcanic rocks
Lithium, an increasingly economically important element, is also used to trace the cycling of materials through the Earth system. Here the authors show that post-eruptive processes such as degassing and groundmass crystallisation control the inventory of lithium in volcanic deposits.
- B. S. Ellis
- , D. Szymanowski
- & M. Guillong
-
Review Article
| Open Access Controls on explosive-effusive volcanic eruption styles
Controls on explosive-effusive volcanic eruption styles
Eruptive styles at a single volcano may transition from explosive to effusive behaviour (or vice versa) at any given time. This review examines the underlying controls on eruptive styles such as magma viscosity, degassing and conduit geometry at volcanoes with silicic compositions.
- Mike Cassidy
- , Michael Manga
- & Olivier Bachmann

 Volumetric extrusive rates of silicic supereruptions from the Afro-Arabian large igneous province
Volumetric extrusive rates of silicic supereruptions from the Afro-Arabian large igneous province