Featured
-
-
Letter |
 Histone deacetylase 3 prepares brown adipose tissue for acute thermogenic challenge
Histone deacetylase 3 prepares brown adipose tissue for acute thermogenic challenge
Histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) is required to activate brown adipose tissue enhancers to ensure thermogenic aptitude.
- Matthew J. Emmett
- , Hee-Woong Lim
- & Mitchell A. Lazar
-
Letter |
 Core Mediator structure at 3.4 Å extends model of transcription initiation complex
Core Mediator structure at 3.4 Å extends model of transcription initiation complex
The 3.4 Å crystal structure of the 15-subunit core Mediator complex in yeast.
- Kayo Nozawa
- , Thomas R. Schneider
- & Patrick Cramer
-
Letter |
 Cohesin is positioned in mammalian genomes by transcription, CTCF and Wapl
Cohesin is positioned in mammalian genomes by transcription, CTCF and Wapl
The distribution of cohesin in the mouse genome depends on CTCF, transcription and the cohesin release factor Wapl.
- Georg A. Busslinger
- , Roman R. Stocsits
- & Jan-Michael Peters
-
Article |
 Complex multi-enhancer contacts captured by genome architecture mapping
Complex multi-enhancer contacts captured by genome architecture mapping
A technique called genome architecture mapping (GAM) involves sequencing DNA from a large number of thin nuclear cryosections to develop a map of genome organization without the limitations of existing 3C-based methods.
- Robert A. Beagrie
- , Antonio Scialdone
- & Ana Pombo
-
Article |
 Mediator structure and rearrangements required for holoenzyme formation
Mediator structure and rearrangements required for holoenzyme formation
Cryo-electron microscopy maps of the fission yeast Mediator complex and of a Mediator–RNA polymerase II holoenzyme reveal how changes in the Med14 subunit enable large-scale rearrangements of the Mediator structure that are essential for holoenzyme formation.
- Kuang-Lei Tsai
- , Xiaodi Yu
- & Francisco J. Asturias
-
Letter |
 Inhibition of mTOR induces a paused pluripotent state
Inhibition of mTOR induces a paused pluripotent state
Inhibition of mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) suspends mouse blastocyst development and the cells remain ‘paused’ in a reversible pluripotent state, allowing prolonged culture.
- Aydan Bulut-Karslioglu
- , Steffen Biechele
- & Miguel Ramalho-Santos
-
Letter |
 Local regulation of gene expression by lncRNA promoters, transcription and splicing
Local regulation of gene expression by lncRNA promoters, transcription and splicing
Various cis-regulatory functions of genomic loci that produce long non-coding RNAs are revealed, including instances where their promoters have enhancer-like activity and the lncRNA transcripts themselves are not required for activity.
- Jesse M. Engreitz
- , Jenna E. Haines
- & Eric S. Lander
-
Letter |
 Acetylation-regulated interaction between p53 and SET reveals a widespread regulatory mode
Acetylation-regulated interaction between p53 and SET reveals a widespread regulatory mode
The acidic domain of SET binds and represses unacetylated p53, but this interaction is prevented by cellular-stress-induced p53 CTD acetylation.
- Donglai Wang
- , Ning Kon
- & Wei Gu
-
Letter |
 PionX sites mark the X chromosome for dosage compensation
PionX sites mark the X chromosome for dosage compensation
Recognition of the X chromosome by the dosage compensation complex in Drosophila relies on the sequence and shape of PionX sites.
- Raffaella Villa
- , Tamas Schauer
- & Peter B. Becker
-
Letter |
 The mechanism of RNA 5′ capping with NAD+, NADH and desphospho-CoA
The mechanism of RNA 5′ capping with NAD+, NADH and desphospho-CoA
RNA caps other than the 7-methylguanylate modification are generated by a distinct mechanism in which caps are added during, not after, transcription initiation through the use of non-canonical initiating nucleotides by RNA polymerases, a finding which has functional consequences.
- Jeremy G. Bird
- , Yu Zhang
- & Bryce E. Nickels
-
Letter |
 The nature of mutations induced by replication–transcription collisions
The nature of mutations induced by replication–transcription collisions
When transcription and replication machineries collide on DNA, they can cause mutations to occur in the area near the collision; these mutations are now shown to include two types—duplications/deletions within the transcription unit and base substitutions in the cis-regulatory element of gene expression.
- T. Sabari Sankar
- , Brigitta D. Wastuwidyaningtyas
- & Jue D. Wang
-
Article |
 Near-atomic resolution visualization of human transcription promoter opening
Near-atomic resolution visualization of human transcription promoter opening
Cryo-electron microscopy structural models of the human pre-initiation complex at all major steps of transcription initiation at near atomic-level resolution are presented, providing new mechanistic insights into the processes of promoter melting and transcription-bubble formation, as well as an almost complete proposed structural model of all of the pre-initiation complex components and their interactions with DNA.
- Yuan He
- , Chunli Yan
- & Eva Nogales
-
Article |
 Transcription initiation complex structures elucidate DNA opening
Transcription initiation complex structures elucidate DNA opening
The cryo-electron microscopy structures of yeast initiation complexes containing the transcription factors TBP, TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIIE, and TFIIF and containing either closed or open promoter DNA are reported, providing mechanistic insights into DNA opening and template-strand loading.
- C. Plaschka
- , M. Hantsche
- & P. Cramer
-
Article |
 Structure of promoter-bound TFIID and model of human pre-initiation complex assembly
Structure of promoter-bound TFIID and model of human pre-initiation complex assembly
A sub-nanometre resolution cryo-EM structure of human TFIID bound to TFIIA and core promoter DNA and a model of the TFIID-based pre-initiation complex.
- Robert K. Louder
- , Yuan He
- & Eva Nogales
-
Letter |
 Inhibiting fungal multidrug resistance by disrupting an activator–Mediator interaction
Inhibiting fungal multidrug resistance by disrupting an activator–Mediator interaction
A small molecule, inhibitor of a protein–protein interaction between the transcription factor Pdr1 and the Med15 subunit of Mediator in the fungal pathogen Candida glabrata, is identified and characterized here; the compound iKIX1 inhibits Pdr1-mediated gene activation and resensitizes drug-resistant C. glabrata to azole antifungals in vitro and in animal models of disseminated and urinary tract infection.
- Joy L. Nishikawa
- , Andras Boeszoermenyi
- & Haribabu Arthanari
-
Letter |
 Structure of transcribing mammalian RNA polymerase II
Structure of transcribing mammalian RNA polymerase II
The first high-resolution, cryo-electron microscopy structure of mammalian RNA polymerase II, in the form of a transcribing complex comprising DNA template and RNA transcript.
- Carrie Bernecky
- , Franz Herzog
- & Patrick Cramer
-
Article |
 SMN and symmetric arginine dimethylation of RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain control termination
SMN and symmetric arginine dimethylation of RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain control termination
Symmetric dimethylation of the human RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain residue R1810 by the protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) directly recruits the protein survival of motor neuron (SMN) and indirectly recruits the helicase senataxin to resolve R-loops and promote transcription termination.
- Dorothy Yanling Zhao
- , Gerald Gish
- & Jack F. Greenblatt
-
Letter |
 Competition between DNA methylation and transcription factors determines binding of NRF1
Competition between DNA methylation and transcription factors determines binding of NRF1
The relationship between DNA methylation and transcription factor binding was studied across the genome in mouse embryonic stem cells-the study reveals that the transcription factor NRF1 is methylation-sensitive and how physiological binding of NRF1 relies on local removal of DNA methylation.
- Silvia Domcke
- , Anaïs Flore Bardet
- & Dirk Schübeler
-
Article |
 Molecular structures of unbound and transcribing RNA polymerase III
Molecular structures of unbound and transcribing RNA polymerase III
RNA polymerase III (Pol III), the largest eukaryote polymerase yet characterized, transcribes structured small non-coding RNAs; here cryo-electron microscopy structures of budding yeast Pol III allow building of an atomic-level model of the complete 17-subunit complex, both unbound and while elongating RNA.
- Niklas A. Hoffmann
- , Arjen J. Jakobi
- & Christoph W. Müller
-
Letter |
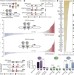 Transcriptional regulators form diverse groups with context-dependent regulatory functions
Transcriptional regulators form diverse groups with context-dependent regulatory functions
A large-scale enhancer complementation assay assessing the activating or repressing contributions of over 800 Drosophila transcription factors and cofactors to combinatorial enhancer control reveals a more complex picture than expected, with many factors having diverse regulatory functions that depend on the enhancer context.
- Gerald Stampfel
- , Tomáš Kazmar
- & Alexander Stark
-
Letter |
 DNA-dependent formation of transcription factor pairs alters their binding specificity
DNA-dependent formation of transcription factor pairs alters their binding specificity
A high-throughput analysis of DNA binding in over 9,000 interacting transcription factor pairs reveals that the interactions are often actively mediated by the DNA itself and the composite DNA sites recognized are different from the individual motifs of each transcription factor.
- Arttu Jolma
- , Yimeng Yin
- & Jussi Taipale
-
Article |
 Structural basis for gene regulation by a B12-dependent photoreceptor
Structural basis for gene regulation by a B12-dependent photoreceptor
Crystal structures are presented of Thermus thermophilus CarH, a photoreceptor that uses a vitamin B12 derivative, in all three relevant states: in the dark, both free and bound to operator DNA, and after light exposure.
- Marco Jost
- , Jésus Fernández-Zapata
- & Catherine L. Drennan
-
Article |
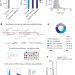 BCL11A enhancer dissection by Cas9-mediated in situ saturating mutagenesis
BCL11A enhancer dissection by Cas9-mediated in situ saturating mutagenesis
A CRISPR-Cas9 approach is used to perform saturating mutagenesis of the human and mouse BCL11A enhancers, producing a map that reveals critical regions and specific vulnerabilities; BCL11A enhancer disruption is validated by CRISPR-Cas9 as a therapeutic strategy for inducing fetal haemoglobin by applying it in both mice and primary human erythroblast cells.
- Matthew C. Canver
- , Elenoe C. Smith
- & Daniel E. Bauer
-
Article |
 Gain-of-function p53 mutants co-opt chromatin pathways to drive cancer growth
Gain-of-function p53 mutants co-opt chromatin pathways to drive cancer growth
A ChIP-seq analysis of the DNA-binding properties of mutant gain-of-function p53 protein compared to wild-type p53 reveals the gain-of-function proteins bind to and activate a distinct set of genes including chromatin modifying enzymes such as the histone methyltransferase MLL; small molecular inhibitors of MLL function may represent a new target for cancers with mutant p53.
- Jiajun Zhu
- , Morgan A. Sammons
- & Shelley L. Berger
-
Letter |
 Real-time observation of the initiation of RNA polymerase II transcription
Real-time observation of the initiation of RNA polymerase II transcription
A single-molecule optical tweezer assay is developed to monitor transcription initiation in eukaryotic RNA polymerase II in real-time, making use of a highly purified preinitiation complex (PIC) from yeast; observations show that a large bubble is opened up in the DNA template during initiation, driven by the TFIIH helicase that forms part of the PIC, along with synthesis of an extended transcript before the transition from transcription initiation into elongation.
- Furqan M. Fazal
- , Cong A. Meng
- & Steven M. Block
-
Letter |
 Intersecting transcription networks constrain gene regulatory evolution
Intersecting transcription networks constrain gene regulatory evolution
Epistatic interactions, whereby a mutation's effect is contingent on another mutation, have been shown to constrain evolution within single proteins, and how such interactions arise in gene regulatory networks has remained unclear; here the appearance of pheromone-response regulator binding sites in the regulatory DNA of the a-specific genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae are shown to have required specific changes in a second pathway during the evolution from its common ancestor with Candida albicans.
- Trevor R. Sorrells
- , Lauren N. Booth
- & Alexander D. Johnson
-
Letter |
 Molecular basis for 5-carboxycytosine recognition by RNA polymerase II elongation complex
Molecular basis for 5-carboxycytosine recognition by RNA polymerase II elongation complex
Structural and biochemical studies of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) assembled on DNA containing 5-carboxycytosine reveals that Pol II can sense the oxidized methylation state of DNA and transiently slows down during transcription.
- Lanfeng Wang
- , Yu Zhou
- & Dong Wang
-
Article |
 The core spliceosome as target and effector of non-canonical ATM signalling
The core spliceosome as target and effector of non-canonical ATM signalling
Transcription-blocking DNA lesions result in chromatin displacement of core spliceosomes containing U2 and U5 snRNPs; consequently, R-loops containing the nascent transcript are formed, which activate ATM in a feed-forward fashion to influence spliceosome dynamics and alternative splicing.
- Maria Tresini
- , Daniël O. Warmerdam
- & Jurgen A. Marteijn
-
Article |
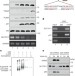 Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression
Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression
p53 suppresses expression of SLC7A11, a key component of the cystine/glutamate amino acid transport machinery, leading to inhibition of cystine uptake and promoting ferroptosis, an iron-dependent form of cell death.
- Le Jiang
- , Ning Kon
- & Wei Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Transcription factor binding dynamics during human ES cell differentiation
Transcription factor binding dynamics during human ES cell differentiation
Lineage-specific transcription factors and signalling pathways cooperate with pluripotency regulators to control the transcriptional networks that drive cell specification and exit from an embryonic stem cell state; here, we report genome-wide binding data for 38 transcription factors combined with analysis of epigenomic and gene expression data during the differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into the three germ layers.
- Alexander M. Tsankov
- , Hongcang Gu
- & Alexander Meissner
-
Article |
 Architecture of the RNA polymerase II–Mediator core initiation complex
Architecture of the RNA polymerase II–Mediator core initiation complex
Mediator is the key transcription co-activator complex that enables basal and regulated transcription initiation by RNA polymerase (Pol) II; here a 15-subunit yeast core Mediator bound to a core Pol II initiation complex is reconstituted and its structure determined by cryo-electron microscopy at subnanometre resolution.
- C. Plaschka
- , L. Larivière
- & P. Cramer
-
Article |
 Genome-scale transcriptional activation by an engineered CRISPR-Cas9 complex
Genome-scale transcriptional activation by an engineered CRISPR-Cas9 complex
The CRISPR-Cas9 system, a powerful tool for genome editing, has been engineered to activate endogenous gene transcription specifically and potently on a genome-wide scale and applied to a large-scale gain-of-function screen for studying melanoma drug resistance.
- Silvana Konermann
- , Mark D. Brigham
- & Feng Zhang
-
Letter |
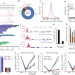 RNA helicase DDX21 coordinates transcription and ribosomal RNA processing
RNA helicase DDX21 coordinates transcription and ribosomal RNA processing
DEAD-box RNA helicase DDX21 is involved in both the transcription and RNA processing of ribosomal genes in human cells, sensing the transcriptional status of both RNA polymerase I and RNA polymerase II and associating with non-coding RNAs involved in ribonucleoprotein formation, possibly allowing for coordinated regulation of protein synthesis.
- Eliezer Calo
- , Ryan A. Flynn
- & Joanna Wysocka
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 POLRMT does not transcribe nuclear genes
POLRMT does not transcribe nuclear genes
- Inge Kühl
- , Christian Kukat
- & Nils-Göran Larsson
-
Letter |
 R-loops induce repressive chromatin marks over mammalian gene terminators
R-loops induce repressive chromatin marks over mammalian gene terminators
R-loops, which have been considered to be rare and potentially harmful transcriptional by-products, are now shown to be needed for antisense transcription and to induce repressive chromatin marks that reinforce pausing of transcription and thereby enhance its termination.
- Konstantina Skourti-Stathaki
- , Kinga Kamieniarz-Gdula
- & Nicholas J. Proudfoot
-
Letter |
 Tyrosine phosphorylation of histone H2A by CK2 regulates transcriptional elongation
Tyrosine phosphorylation of histone H2A by CK2 regulates transcriptional elongation
A conserved tyrosine residue, Tyr 57, of histone H2A is phosphorylated by an unsuspected tyrosine kinase activity of casein kinase 2, influencing a series of histone marks associated with active transcription and regulating transcription elongation.
- Harihar Basnet
- , Xue B. Su
- & Michael G. Rosenfeld
-
Letter |
 Regulation of RNA polymerase II activation by histone acetylation in single living cells
Regulation of RNA polymerase II activation by histone acetylation in single living cells
The interplay of histone acetylation and RNA polymerase II activity is investigated using fluorescence microscopy; acetylation of H3 at Lys 27 enhances the recruitment of a transcriptional activator and accelerates the transition of RNA polymerase II from initiation to elongation, thus indicating that histone acetylation has a causal effect on two distinct steps in transcription activation.
- Timothy J. Stasevich
- , Yoko Hayashi-Takanaka
- & Hiroshi Kimura
-
Letter |
 Transcriptional interference by antisense RNA is required for circadian clock function
Transcriptional interference by antisense RNA is required for circadian clock function
The transcriptions of frq sense and antisense RNAs are mutually inhibitory and form a double negative feedback loop required for robust and sustained circadian rhythmicity: antisense transcription inhibits sense expression by causing chromatin modifications and premature transcription termination.
- Zhihong Xue
- , Qiaohong Ye
- & Yi Liu
-
Letter |
 Noncoding RNA transcription targets AID to divergently transcribed loci in B cells
Noncoding RNA transcription targets AID to divergently transcribed loci in B cells
The 11-subunit RNA exosome is thought to regulate the mammalian noncoding transcriptome; here, a mouse model is generated in which the essential Exosc3 subunit of the RNA exosome in B cells is conditionally deleted, revealing a link between sites of genomic RNA exosome function and AID-mediated chromosomal translocations.
- Evangelos Pefanis
- , Jiguang Wang
- & Uttiya Basu
-
Letter |
 Required enhancer–matrin-3 network interactions for a homeodomain transcription program
Required enhancer–matrin-3 network interactions for a homeodomain transcription program
The POU homeodomain transcription factor Pit1 is required for pituitary development; here Pit1-occupied enhancers are shown to interact with the nuclear architecture components matrin-3 and Satb1, and this association is required for activation of Pit1-regulated enhancers and coding target genes.
- Dorota Skowronska-Krawczyk
- , Qi Ma
- & Michael G. Rosenfeld
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 Universality of core promoter elements?
Universality of core promoter elements?
- Matthias Siebert
- & Johannes Söding
-
Letter |
 Selective transcriptional regulation by Myc in cellular growth control and lymphomagenesis
Selective transcriptional regulation by Myc in cellular growth control and lymphomagenesis
Global transcriptional and epigenomic analyses in diverse cell types reveal that the primary action of Myc is to up- and downregulate transcription of distinct groups of genes, rather than to amplify transcription of all active genes; general RNA amplification, when observed, is better explained as an indirect consequence of Myc’s action on cellular physiology.
- Arianna Sabò
- , Theresia R. Kress
- & Bruno Amati
-
Letter |
 Activation and repression by oncogenic MYC shape tumour-specific gene expression profiles
Activation and repression by oncogenic MYC shape tumour-specific gene expression profiles
Inducing changes in the levels of the MYC oncoprotein is shown to activate and repress specific sets of target genes that are characteristic of tumour cells, providing an insight into the mechanism by which MYC can stimulate tumorigenesis in contrast to its physiological role.
- Susanne Walz
- , Francesca Lorenzin
- & Martin Eilers
-
Letter |
 Enhancer loops appear stable during development and are associated with paused polymerase
Enhancer loops appear stable during development and are associated with paused polymerase
A high-resolution map of enhancer three-dimensional contacts during Drosophila embryogenesis shows that although local regulatory interactions are frequent, long-range interactions are also very common; unexpectedly, most interactions appear unchanged between tissues and across development and are formed prior to gene expression, indicating that transcription initiates from preformed enhancer–promoter loops, which are associated with paused polymerase.
- Yad Ghavi-Helm
- , Felix A. Klein
- & Eileen E. M. Furlong
-
Letter |
 Obesity-associated variants within FTO form long-range functional connections with IRX3
Obesity-associated variants within FTO form long-range functional connections with IRX3
Obesity-associated noncoding sequences within FTO are functionally connected with IRX3, and long-range enhancers in this region recapitulate aspects of IRX3 expression, suggesting that the obesity-associated interval is part of IRX3 regulation; Irx3-deficient mice have lower body weight and are resistant to diet-induced obesity, suggesting IRX3 as a novel determinant of body mass and composition.
- Scott Smemo
- , Juan J. Tena
- & Marcelo A. Nóbrega
-
Article |
 C9orf72 nucleotide repeat structures initiate molecular cascades of disease
C9orf72 nucleotide repeat structures initiate molecular cascades of disease
Structurally polymorphic C9orf72 hexanucleotide repeats cause an impairment in transcriptional processivity and lead to accumulation of truncated repeat-containing transcripts that bind to specific ribonucleoproteins, such as nucleolin, in a conformation-dependent manner resulting in nucleolar stress and C9orf72-linked pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia.
- Aaron R. Haeusler
- , Christopher J. Donnelly
- & Jiou Wang
-
Article |
 UvrD facilitates DNA repair by pulling RNA polymerase backwards
UvrD facilitates DNA repair by pulling RNA polymerase backwards
UvrD acts in nucleotide excision repair by using its helicase/translocase activity to induce RNA polymerase backtracking, enabling repair enzymes to access DNA lesions.
- Vitaly Epshtein
- , Venu Kamarthapu
- & Evgeny Nudler
-
Letter |
 Convergent evolution of a fused sexual cycle promotes the haploid lifestyle
Convergent evolution of a fused sexual cycle promotes the haploid lifestyle
In the predominantly diploid yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, regulatory control of mating is separate from meiosis; here the related hemiascomycete yeast Candida lusitaniae is shown to have coordinated regulatory control of mating and meiosis, favouring the formation of haploids.
- Racquel Kim Sherwood
- , Christine M. Scaduto
- & Richard J. Bennett
-
Letter |
 Glutamine methylation in histone H2A is an RNA-polymerase-I-dedicated modification
Glutamine methylation in histone H2A is an RNA-polymerase-I-dedicated modification
A description of a new histone modification, methylation of glutamine, on histone H2A in yeast and human cells.
- Peter Tessarz
- , Helena Santos-Rosa
- & Tony Kouzarides

 In vivo FRET–FLIM reveals cell-type-specific protein interactions in Arabidopsis roots
In vivo FRET–FLIM reveals cell-type-specific protein interactions in Arabidopsis roots