Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Activation of coagulation and proinflammatory pathways in thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome and following COVID-19 vaccination
Activation of coagulation and proinflammatory pathways in thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome and following COVID-19 vaccination
Adenovirus-based vaccination for SARS-CoV-2 has a rare chance to cause thrombosis with thrombocytopenia (TTS). Here the authors compare proteomic and transcriptomic data from vaccinated participants with or without TTS to find distinct activations of coagulation and innate immune pathways in patient with TTS, or following initial or boosting vaccination.
- Malika Aid
- , Kathryn E. Stephenson
- & Dan H. Barouch
-
Article
| Open Access MTH1 protects platelet mitochondria from oxidative damage and regulates platelet function and thrombosis
MTH1 protects platelet mitochondria from oxidative damage and regulates platelet function and thrombosis
MTH1 hydrolyzes oxidized nucleotides to prevent their mis-incorporation into DNA under oxidative stress. Here, the authors show that MTH1 is expressed in platelets and its deficiency increases mitochondrial DNA oxidative damage, impairs platelet function and hemostasis.
- Yangyang Ding
- , Xiang Gui
- & Jianlin Qiao
-
Article
| Open Access Molecularly self‐fueled nano-penetrator for nonpharmaceutical treatment of thrombosis and ischemic stroke
Molecularly self‐fueled nano-penetrator for nonpharmaceutical treatment of thrombosis and ischemic stroke
Thrombotic cerebro-cardiovascular diseases are the leading causes of disability and death worldwide but current drug therapeutics show important limitations. Here, the authors exploit a selfpropelling nano-penetrator with high fuel loading and controllable motion which is molecularly co-assembled using a photothermal photosensitizer and a photothermal-activable NO donor.
- Hongyuan Zhang
- , Zhiqiang Zhao
- & Cong Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Thrombosis and thrombocytopenia after vaccination against and infection with SARS-CoV-2 in the United Kingdom
Thrombosis and thrombocytopenia after vaccination against and infection with SARS-CoV-2 in the United Kingdom
Population-based studies can provide information on the safety of COVID-19 vaccines. Here the authors report the rates thrombosis and thrombocytopenia after vaccination against and infection with SARS-CoV-2 in the United Kingdom and compare them with the background (expected) rates in the general population.
- Edward Burn
- , Xintong Li
- & Daniel Prieto-Alhambra
-
Article
| Open Access Functionally integrating nanoparticles alleviate deep vein thrombosis in pregnancy and rescue intrauterine growth restriction
Functionally integrating nanoparticles alleviate deep vein thrombosis in pregnancy and rescue intrauterine growth restriction
There is still an unmet need for effective and safe drugs to treat deep vein thrombosis during pregnancy, a life-threatening condition for the mother and fetus. Here, the authors show that engineered multifunctional nanoparticles can site-specifically dissolve thrombi and reverse deep vein thrombosis-mediated intrauterine growth restriction and delayed development of fetuses in pregnant rats.
- Juan Cheng
- , Siqi Zhang
- & Jianxiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access von Willebrand factor links primary hemostasis to innate immunity
von Willebrand factor links primary hemostasis to innate immunity
von Willebrand factor (VWF) plays a critical role in primary hemostasis following vascular injury by tethering platelets to exposed collagen. Here, VWF binding to macrophages is shown to trigger NF-κB activation and induce pro-inflammatory responses.
- Clive Drakeford
- , Sonia Aguila
- & James S. O’Donnell
-
Article
| Open Access Efficacy and safety of next-generation tick transcriptome-derived direct thrombin inhibitors
Efficacy and safety of next-generation tick transcriptome-derived direct thrombin inhibitors
Bleeding complications limits the use of effective antithrombotics therapeutics. Here, the authors developed next-generation direct thrombin inhibitors with low bleeding risks as safe peri-percutaneous coronary intervention anticoagulants when used in combination with antiplatelets.
- Cho Yeow Koh
- , Norrapat Shih
- & Mark Y. Chan
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of the factor XII contact activation site enables sensitive coagulation diagnostics
Identification of the factor XII contact activation site enables sensitive coagulation diagnostics
Blood coagulation is started by contact to surfaces and this is the principle for a commonly used diagnostic clotting test, aPTT. Here, the authors identify the structure in coagulation factor XII that initiates surface-driven coagulation and use the information to develop improved aPTT assays.
- Marco Heestermans
- , Clément Naudin
- & Thomas Renné
-
Article
| Open Access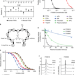 Cyclic peptide FXII inhibitor provides safe anticoagulation in a thrombosis model and in artificial lungs
Cyclic peptide FXII inhibitor provides safe anticoagulation in a thrombosis model and in artificial lungs
Inhibiting thrombosis without inducing bleeding is a major challenge for anticoagulant agents. Here the authors describe a synthetic FXIIa inhibitor able to efficiently prevent thrombosis in mice and suppress coagulation in artificial lungs in rabbits without increasing the risk of bleeding.
- Jonas Wilbs
- , Xu-Dong Kong
- & Christian Heinis
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structure and substrate-induced activation of ADAMTS13
Crystal structure and substrate-induced activation of ADAMTS13
The plasma metalloprotease ADAMTS13 regulates the platelet-tethering function of von Willebrand factor (VWF) in a shear-dependent manner. Here the authors present the ADAMTS13 crystal structure of the 70kDa N-terminal metalloprotease to spacer domains, and using kinetic measurements they identify a substrate binding induced allosteric mechanism for ADAMTS13, where VWF functions both as an activating cofactor and substrate.
- Anastasis Petri
- , Hyo Jung Kim
- & James T. B. Crawley
-
Article
| Open Access Adenosine receptor agonism protects against NETosis and thrombosis in antiphospholipid syndrome
Adenosine receptor agonism protects against NETosis and thrombosis in antiphospholipid syndrome
Antiphospholipid syndrome is characterised by increased neutrophil extracellular trap formation (NETosis) and, consequently, increased thrombotic events. Here Ali et al. show that treatment with adenosine receptor agonists suppresses NETosis and venous thrombosis in mouse models of antiphospholipid syndrome.
- Ramadan A. Ali
- , Alex A. Gandhi
- & Jason S. Knight
-
Article
| Open Access A shear-dependent NO-cGMP-cGKI cascade in platelets acts as an auto-regulatory brake of thrombosis
A shear-dependent NO-cGMP-cGKI cascade in platelets acts as an auto-regulatory brake of thrombosis
Nitric oxide (NO) inhibits thrombosis in part by stimulating cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) production and cGMP-dependent protein kinase I (cGKI) activity in platelets. Here, Wen et al. develop a cGMP sensor mouse to follow cGMP dynamics in platelets, and find that shear stress activates NO-cGMP-cGKI signaling during platelet aggregation to limit thrombosis.
- Lai Wen
- , Susanne Feil
- & Robert Feil
-
Article
| Open Access Apolipoprotein A-IV binds αIIbβ3 integrin and inhibits thrombosis
Apolipoprotein A-IV binds αIIbβ3 integrin and inhibits thrombosis
Activation of integrin αIIbβ3 at the surface of platelets is required for their aggregation and for thrombus formation. Here Xu et al. identify apolipoprotein A-IV as a novel ligand for platelet αIIbβ3 integrin, and find it inhibits platelet aggregation and thrombosis.
- Xiaohong Ruby Xu
- , Yiming Wang
- & Heyu Ni
-
Article
| Open Access Cathelicidins prime platelets to mediate arterial thrombosis and tissue inflammation
Cathelicidins prime platelets to mediate arterial thrombosis and tissue inflammation
Cathelicidins are antimicrobial peptides that eliminate pathogens and contribute to the innate immune response. Here the authors show that neutrophil-derived LL-37/CRAMP induces platelet activation and promotes arterial thrombosis and thrombo-inflammation.
- Joachim Pircher
- , Thomas Czermak
- & Christian Schulz
-
Article
| Open Access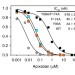 Engineered factor Xa variants retain procoagulant activity independent of direct factor Xa inhibitors
Engineered factor Xa variants retain procoagulant activity independent of direct factor Xa inhibitors
A major drawback in the clinical use of the oral anticoagulants that directly inhibit factor Xa in order to prevent blood clot formation is the potential for life threatening bleeding events. Here the authors describe factor Xa variants that are refractory to inhibition by these anticoagulants and could serve as rescue agents in treated patients.
- Daniël Verhoef
- , Koen M. Visscher
- & Mettine H. A. Bos
-
Article
| Open Access Platelet function is modified by common sequence variation in megakaryocyte super enhancers
Platelet function is modified by common sequence variation in megakaryocyte super enhancers
Numerous genetic variants, including those located in the non-coding regions of the genome, are known to be associated with blood cells traits. Here, Frontini and colleagues investigate their potential regulatory functions using epigenomic data and promoter long-range interactions.
- Romina Petersen
- , John J. Lambourne
- & Mattia Frontini
-
Article
| Open Access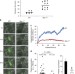 Leukocyte integrin Mac-1 regulates thrombosis via interaction with platelet GPIbα
Leukocyte integrin Mac-1 regulates thrombosis via interaction with platelet GPIbα
The binding of the leukocyte integrin Mac1 to the platelet receptor GPIbα is important for the physiological response to tissue injury. Here the authors show that this interaction also regulates thrombosis, without influencing bleeding time, which may provide clues for the development of new anti-thrombotic drugs.
- Yunmei Wang
- , Huiyun Gao
- & Daniel I. Simon
-
Article
| Open Access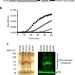 Protein disulfide isomerase secretion following vascular injury initiates a regulatory pathway for thrombus formation
Protein disulfide isomerase secretion following vascular injury initiates a regulatory pathway for thrombus formation
What keeps blood from clotting in homeostasis is a puzzle. Here, the authors suggest that lack of the enzyme disulfide isomerase (PDI) in the blood is key, and show that PDI is secreted only after vascular injury to act on substrates that include vitronectin, affecting its binding to αVβ3 and αIIbβ3 integrins and enabling thrombus formation.
- Sheryl R. Bowley
- , Chao Fang
- & Bruce Furie
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic description of the immune complex involved in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
Atomic description of the immune complex involved in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is an autoimmune thrombotic disease with limited treatment options. Here the authors present crystallographic data on the disease-causing immune complex, providing the structural basis for the development of new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches to HIT.
- Zheng Cai
- , Serge V. Yarovoi
- & Mark I. Greene
-
Article |
 Loss of PIKfyve in platelets causes a lysosomal disease leading to inflammation and thrombosis in mice
Loss of PIKfyve in platelets causes a lysosomal disease leading to inflammation and thrombosis in mice
PIKfyve is a lipid kinase essential for regulation of membrane homeostasis and vesicle trafficking along the endosomal-lysosomal pathway. Here the authors show that mice lacking PIKfyve exclusively in their platelets exhibit a systemic disorder characterized by multi-organ inflammation and thrombosis due to aberrant platelet lysosome function.
- Sang H. Min
- , Aae Suzuki
- & Charles S. Abrams

 Protein disulfide isomerase cleaves allosteric disulfides in histidine-rich glycoprotein to regulate thrombosis
Protein disulfide isomerase cleaves allosteric disulfides in histidine-rich glycoprotein to regulate thrombosis