News Feature |
Featured
-
-
News & Views Forum |
 Cell parts to complex processes, from the bottom up
Cell parts to complex processes, from the bottom up
Engineering approaches allow biological structures and behaviours to be reconstituted in vitro. A biologist and a physicist discuss the potential and limitations of this bottom-up philosophy in providing insights into complex biological processes.
- Matthew Good
- & Xavier Trepat
-
Letter |
 A separated vortex ring underlies the flight of the dandelion
A separated vortex ring underlies the flight of the dandelion
The flight of dandelion seeds is enabled by an extraordinary vortex ring, which was revealed by the visualization of the flow around the seed.
- Cathal Cummins
- , Madeleine Seale
- & Naomi Nakayama
-
News |
 Peer-reviewed homeopathy study sparks uproar in Italy
Peer-reviewed homeopathy study sparks uproar in Italy
Advocates of homeopathy say that the rat study is evidence of the practice’s efficacy, but some scientists have cast doubt on the paper.
- Giorgia Guglielmi
-
Article |
 The interaction landscape between transcription factors and the nucleosome
The interaction landscape between transcription factors and the nucleosome
A method for systematically exploring interactions between the nucleosome and transcription factors identifies five major interaction patterns.
- Fangjie Zhu
- , Lucas Farnung
- & Jussi Taipale
-
News |
 African and Asian researchers are hampered by visa problems
African and Asian researchers are hampered by visa problems
Researchers from these continents are three to four times more likely to experience visa problems when travelling for work than are Europeans and Americans.
- Maina Waruru
-
Letter |
 An orthogonal proteomic survey uncovers novel Zika virus host factors
An orthogonal proteomic survey uncovers novel Zika virus host factors
Integrative analyses identify host proteins that are modulated by Zika virus at multiple levels and provide a comprehensive framework for the understanding of Zika virus-induced changes to cellular pathways.
- Pietro Scaturro
- , Alexey Stukalov
- & Andreas Pichlmair
-
Letter |
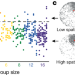 Fitness benefits and emergent division of labour at the onset of group living
Fitness benefits and emergent division of labour at the onset of group living
Experimental data from, and mathematical modelling of, colonies of the clonal raider ant Ooceraea biroi demonstrate that increases in group size generate division of labour among similar individuals, increased homeostasis and higher colony fitness.
- Y. Ulrich
- , J. Saragosti
- & D. J. C. Kronauer
-
Letter |
 Karyotype engineering by chromosome fusion leads to reproductive isolation in yeast
Karyotype engineering by chromosome fusion leads to reproductive isolation in yeast
Yeast chromosomes have been fused to produce viable strains with only two chromosomes that are reproductively isolated from the sixteen-chromosome wild type, but otherwise show high fitness in mitosis and meiosis.
- Jingchuan Luo
- , Xiaoji Sun
- & Jef D. Boeke
-
Letter |
 Species-specific activity of antibacterial drug combinations
Species-specific activity of antibacterial drug combinations
Screening pairwise combinations of antibiotics and other drugs against three bacterial pathogens reveals that antagonistic and synergistic drug–drug interactions are specific to microbial species and strains.
- Ana Rita Brochado
- , Anja Telzerow
- & Athanasios Typas
-
Letter |
 Pairwise and higher-order genetic interactions during the evolution of a tRNA
Pairwise and higher-order genetic interactions during the evolution of a tRNA
Mutagenesis of a yeast tRNA shows that the effects of mutations and how they interact varies both in magnitude and sign between genotypes.
- Júlia Domingo
- , Guillaume Diss
- & Ben Lehner
-
Books & Arts |
 How poets and filmmakers construe complexity at the Crick Institute
How poets and filmmakers construe complexity at the Crick Institute
Philip Ball tours a cross-disciplinary exhibition exploring patterns in bioscience.
- Philip Ball
-
Letter |
 An extracellular network of Arabidopsis leucine-rich repeat receptor kinases
An extracellular network of Arabidopsis leucine-rich repeat receptor kinases
A high-throughput assay is used to analyse 40,000 potential extracellular domain interactions of a large family of plant cell surface receptors (LRR-RKs) and provide a cell surface interaction network for these receptors.
- Elwira Smakowska-Luzan
- , G. Adam Mott
- & Youssef Belkhadir
-
Letter |
 An electric-eel-inspired soft power source from stacked hydrogels
An electric-eel-inspired soft power source from stacked hydrogels
Miniature hydrogel compartments in scalable stacked and folded geometries were used to prepare a contact-activated artificial electric organ.
- Thomas B. H. Schroeder
- , Anirvan Guha
- & Michael Mayer
-
Letter |
 Selective silencing of euchromatic L1s revealed by genome-wide screens for L1 regulators
Selective silencing of euchromatic L1s revealed by genome-wide screens for L1 regulators
The retrotransposition of L1 is controlled by functionally diverse genes at the transcriptional or post-transcriptional levels, and its silencing can lead to the downregulation of host gene expression.
- Nian Liu
- , Cameron H. Lee
- & Joanna Wysocka
-
Letter |
 Maternal age generates phenotypic variation in Caenorhabditis elegans
Maternal age generates phenotypic variation in Caenorhabditis elegans
Maternal age is found to be a major source of phenotypic variation in isogenic C. elegans populations living in a controlled environment, with the progeny of young mothers impaired for multiple fitness traits.
- Marcos Francisco Perez
- , Mirko Francesconi
- & Ben Lehner
-
Article |
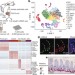 A single-cell survey of the small intestinal epithelium
A single-cell survey of the small intestinal epithelium
Profiling of 53,193 individual epithelial cells from the mouse small intestine identifies previously unknown cell subtypes and corresponding gene markers, providing insight into gut homeostasis and response to pathogens.
- Adam L. Haber
- , Moshe Biton
- & Aviv Regev
-
Letter |
 A global resource allocation strategy governs growth transition kinetics of Escherichia coli
A global resource allocation strategy governs growth transition kinetics of Escherichia coli
A new approach to modelling bacterial growth removes the need to know kinetic parameters for metabolic and regulatory processes and can be used to model adaptive processes such as antibiotic responses and ecological dynamics.
- David W. Erickson
- , Severin J. Schink
- & Terence Hwa
-
Letter |
 Glucose feeds the TCA cycle via circulating lactate
Glucose feeds the TCA cycle via circulating lactate
Metabolic flux analysis in mice reveals that lactate often acts as the primary carbon source for the tricarboxylic acid cycle both in normal tissues and in tumour microenvironments.
- Sheng Hui
- , Jonathan M. Ghergurovich
- & Joshua D. Rabinowitz
-
Letter |
 Proteins evolve on the edge of supramolecular self-assembly
Proteins evolve on the edge of supramolecular self-assembly
Introducing a single ‘sticky’ (hydrophobic) amino acid by point mutation into symmetric protein complexes frequently triggers their association into higher-order assemblies, without affecting their native fold and structure.
- Hector Garcia-Seisdedos
- , Charly Empereur-Mot
- & Emmanuel D. Levy
-
Letter |
 Complex cellular logic computation using ribocomputing devices
Complex cellular logic computation using ribocomputing devices
De-novo-designed RNA molecules are used to construct cellular computing devices that can implement complex logic functions.
- Alexander A. Green
- , Jongmin Kim
- & Peng Yin
-
Letter |
 CRISPR–Cas encoding of a digital movie into the genomes of a population of living bacteria
CRISPR–Cas encoding of a digital movie into the genomes of a population of living bacteria
The authors encode pixel values of a short motion picture into the DNA of a population of Escherichia coli.
- Seth L. Shipman
- , Jeff Nivala
- & George M. Church
-
Letter |
 Identifying specificity groups in the T cell receptor repertoire
Identifying specificity groups in the T cell receptor repertoire
The authors devise an algorithm that can cluster T cell receptor (TCR) sequences sharing the same specificity, predict the HLA restriction of these TCR clusters on the basis of subjects’ genotypes and help to identify specific peptide major histocompatibility complex ligands.
- Jacob Glanville
- , Huang Huang
- & Mark M. Davis
-
Letter |
 Rare cell variability and drug-induced reprogramming as a mode of cancer drug resistance
Rare cell variability and drug-induced reprogramming as a mode of cancer drug resistance
Through drug exposure, a rare, transient transcriptional program characterized by high levels of expression of known resistance drivers can get ‘burned in’, leading to the selection of cells endowed with a transcriptional drug resistance and thus more chemoresistant cancers.
- Sydney M. Shaffer
- , Margaret C. Dunagin
- & Arjun Raj
-
News & Views |
 An intracellular dance visualized
An intracellular dance visualized
The development of a microscopy technique that enables observation of the interactions between six types of organelle, in 3D and over time, holds promise for improving our understanding of intracellular processes. See Letter p.162
- Sang-Hee Shim
-
Letter |
 Applying systems-level spectral imaging and analysis to reveal the organelle interactome
Applying systems-level spectral imaging and analysis to reveal the organelle interactome
Using confocal and lattice light sheet microscopy, the authors perform systems-level analysis of the organelle interactome in live cells, allowing them to visualize the frequency and locality of up to five-way interactions between different organelles.
- Alex M. Valm
- , Sarah Cohen
- & Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
-
Article |
 Selectivity determinants of GPCR–G-protein binding
Selectivity determinants of GPCR–G-protein binding
The identification of the positions and patterns of amino acids that form the selectivity determinants for the entire human G-protein and G-protein-coupled receptor signalling system.
- Tilman Flock
- , Alexander S. Hauser
- & M. Madan Babu
-
News |
 Mini reproductive system on a chip mimics human menstrual cycle
Mini reproductive system on a chip mimics human menstrual cycle
Researchers create models of organs such as a uterus and cervix in the laboratory.
- Sara Reardon
-
News & Views |
 Diversity in sight
Diversity in sight
A systematic analysis of bipolar cells, which act as a central signalling conduit in the retina, reveals that the neurons' diverse responses to light are generated largely by feedback from neighbouring amacrine cells. See Article p.439
- Richard H. Masland
-
Letter |
 Single-cell spatial reconstruction reveals global division of labour in the mammalian liver
Single-cell spatial reconstruction reveals global division of labour in the mammalian liver
Single-molecule fluorescence in situ hybridization is performed to identify several landmark genes in the liver and their level of expression in single-cell RNA sequencing is used to spatially reconstruct the zonation of all liver genes.
- Keren Bahar Halpern
- , Rom Shenhav
- & Shalev Itzkovitz
-
Letter |
 Weak synchronization and large-scale collective oscillation in dense bacterial suspensions
Weak synchronization and large-scale collective oscillation in dense bacterial suspensions
Cells in dense bacterial suspensions can self-organize into highly robust collective oscillatory motion, while individual cells move in an erratic manner; their interaction is modelled to reveal a weak synchronization mechanism.
- Chong Chen
- , Song Liu
- & Yilin Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated genomic and molecular characterization of cervical cancer
Integrated genomic and molecular characterization of cervical cancer
This paper describes molecular subtypes of cervical cancers, including squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma clusters defined by HPV status and molecular features, and distinct molecular pathways that are activated in cervical carcinomas caused by different somatic alterations and HPV types.
- Robert D. Burk
- , Zigui Chen
- & David Mutch
-
Review Article |
 Scaling single-cell genomics from phenomenology to mechanism
Scaling single-cell genomics from phenomenology to mechanism
- Amos Tanay
- & Aviv Regev
-
News & Views |
 Molecular memoirs of a cellular family
Molecular memoirs of a cellular family
A system that introduces random modifications to barcode sequences embedded in cells' DNA allows lineage relationships between cells to be discerned, while preserving the cells' spatial relationships. See Letter p.107
- Lauren E. Beck
- & Arjun Raj
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 Drug response consistency in CCLE and CGP
Drug response consistency in CCLE and CGP
- Mehdi Bouhaddou
- , Matthew S. DiStefano
- & Marc R. Birtwistle
-
Brief Communications Arising |
Safikhani et al. reply
- Zhaleh Safikhani
- , Nehme El-Hachem
- & Benjamin Haibe-Kains
-
News & Views |
 Precision timing in a cell
Precision timing in a cell
A 16-year-old synthetic genetic circuit that produces gene-expression oscillations in bacterial cells has been given an upgrade, making it an exceptionally precise biological clock. See Letter p.514
- Xiaojing J. Gao
- & Michael B. Elowitz
-
Letter |
 Synchronous long-term oscillations in a synthetic gene circuit
Synchronous long-term oscillations in a synthetic gene circuit
The first synthetic genetic oscillator or ‘repressilator’ is simplified using insights from stochastic theory, thus achieving remarkably precise and robust oscillations and informing current debates about the next generation of synthetic circuits and their potential applications in cell-based therapies.
- Laurent Potvin-Trottier
- , Nathan D. Lord
- & Johan Paulsson
-
Review Article |
 Mass-spectrometric exploration of proteome structure and function
Mass-spectrometric exploration of proteome structure and function
- Ruedi Aebersold
- & Matthias Mann
-
Letter |
 Insights from biochemical reconstitution into the architecture of human kinetochores
Insights from biochemical reconstitution into the architecture of human kinetochores
Biochemical reconstitution of a synthetic human kinetochore with 21 protein subunits and centromeric nucleosomal DNA unveils fundamental principles of kinetochore organization and function.
- John R. Weir
- , Alex C. Faesen
- & Andrea Musacchio
-
Letter |
 Synchronized cycles of bacterial lysis for in vivo delivery
Synchronized cycles of bacterial lysis for in vivo delivery
Clinically relevant bacteria have been engineered to lyse synchronously at a threshold population density and release genetically encoded therapeutics; treatment of mice with these bacteria slowed the growth of tumours.
- M. Omar Din
- , Tal Danino
- & Jeff Hasty
-
Research Highlights |
Genetic switches for long life
-
Outlook |
 Policy: Urban physics
Policy: Urban physics
Cities are complex environments. Planning interventions that borrow principles from theoretical physics could help to improve peoples' lives.
- Kevin Pollock
-
Letter |
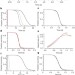 The temporal scaling of Caenorhabditis elegans ageing
The temporal scaling of Caenorhabditis elegans ageing
A diverse range of molecular and genetic manipulations all alter lifespan distributions of Caenorhabditis elegans by an apparent stretching or shrinking of time.
- Nicholas Stroustrup
- , Winston E. Anthony
- & Walter Fontana
-
Books & Arts |
 Books in brief
Books in brief
Barbara Kiser reviews five of the week's best science picks.
- Barbara Kiser
-
News & Views |
 A stretch in time
A stretch in time
Plots of survival against time for nematode worms in different conditions can be superimposed by rescaling the time axis. This observation has far-reaching implications for our understanding of the nature of ageing. See Letter p.103
- Zachary Pincus
-
Article |
 Codon influence on protein expression in E. coli correlates with mRNA levels
Codon influence on protein expression in E. coli correlates with mRNA levels
In-depth analyses of protein expression studies are used to derive a new codon-influence metric that correlates with global protein levels, mRNA levels and mRNA lifetimes in vivo, indicating tight coupling between translation efficiency and mRNA stability; genes redesigned based on these analyses consistently yield high protein expression levels both in vivo and in vitro.
- Grégory Boël
- , Reka Letso
- & John F. Hunt
-
Article |
 Overflow metabolism in Escherichia coli results from efficient proteome allocation
Overflow metabolism in Escherichia coli results from efficient proteome allocation
Using experimental proteomics and modelling in E. coli, the amount of protein needed to run respiration (per ATP produced) is shown to be twice as much as that needed to run fermentation; results demonstrate that overflow metabolism (known as the Warburg effect in cancer cells) is a necessary outcome of optimal bacterial growth, governed by a global resource allocation program, and that the methodology is directly applicable to synthetic biology and cancer research.
- Markus Basan
- , Sheng Hui
- & Terence Hwa
-
Article |
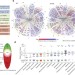 ∆F508 CFTR interactome remodelling promotes rescue of cystic fibrosis
∆F508 CFTR interactome remodelling promotes rescue of cystic fibrosis
A new deep proteomic analysis method is used to identify proteins that interact with wild-type cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) and its mutant version that is the major cause of cystic fibrosis.
- Sandra Pankow
- , Casimir Bamberger
- & John R. Yates III
-
Outlook |
 Deep phenotyping: The details of disease
Deep phenotyping: The details of disease
Precision medicine demands precise matching of deep genomic and phenotypic models — and the deeper you go, the more you know.
- Cathryn M. Delude
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Bayesian inference
- Biobricks
- Biochemical networks
- Bioenergetics
- Cellular noise
- Complexity
- Computer modelling
- Computer science
- Control theory
- Criticality
- Differential equations
- DNA computing and cryptography
- Dynamic networks
- Dynamical systems
- Emergence
- Evolvability
- Genetic circuit engineering
- Genetic interaction
- Genomic engineering
- Information theory
- Logic gates
- Metabolic engineering
- Modularity
- Molecular engineering
- Molecular fluctuations
- Multicellular systems
- Multistability
- Nonlinear dynamics
- Numerical simulations
- Oscillators
- Population dynamics
- Programming language
- Protein engineering
- Regulatory networks
- Reverse engineering
- Robustness
- Signal processing
- Single-cell imaging
- Software
- Standardization
- Stochastic modelling
- Stochastic networks
- Synthetic biology
- Systems analysis
- Time series

 How biologists are creating life-like cells from scratch
How biologists are creating life-like cells from scratch