Featured
-
-
Article |
 Spin-mediated shear oscillators in a van der Waals antiferromagnet
Spin-mediated shear oscillators in a van der Waals antiferromagnet
Using several ultrafast diffraction and microscopy techniques, demagnetization-driven interlayer shear of a van der Waals antiferromagnet is visualized at the nanoscale.
- Alfred Zong
- , Qi Zhang
- & Haidan Wen
-
Article |
 Autonomous healing of fatigue cracks via cold welding
Autonomous healing of fatigue cracks via cold welding
We report that fatigue cracks in pure metals can undergo intrinsic self-healing; they were observed to heal by crack flank cold welding induced by local stress state and grain boundary migration.
- Christopher M. Barr
- , Ta Duong
- & Brad L. Boyce
-
Article |
 Heterodimensional superlattice with in-plane anomalous Hall effect
Heterodimensional superlattice with in-plane anomalous Hall effect
A heterodimensional superlattice consisting of an alternating array of a two-dimensional material and a one-dimensional material shows unconventional octahedral stacking and an unexpected room-temperature anomalous Hall effect.
- Jiadong Zhou
- , Wenjie Zhang
- & Zheng Liu
-
Article |
 Dislocation-induced stop-and-go kinetics of interfacial transformations
Dislocation-induced stop-and-go kinetics of interfacial transformations
Environmental transmission electron microscopy is used to reveal that mismatch dislocations modulate the interfacial transformation of copper oxide to copper metal in an intermittent manner.
- Xianhu Sun
- , Dongxiang Wu
- & Guangwen Zhou
-
Article |
 Uniting tensile ductility with ultrahigh strength via composition undulation
Uniting tensile ductility with ultrahigh strength via composition undulation
A nanocrystalline metallic alloy with ultrahigh tensile strength and good ductility is achieved by introducing compositional undulation in a highly concentrated solid solution.
- Heng Li
- , Hongxiang Zong
- & Jun Sun
-
-
Article |
 Intrinsic toughening and stable crack propagation in hexagonal boron nitride
Intrinsic toughening and stable crack propagation in hexagonal boron nitride
Single-crystal monolayer hexagonal boron nitride is unexpectedly tough owing to its asymmetric lattice structure, which facilitates repeated crack deflection, crack branching and edge swapping, enhancing energy dissipation.
- Yingchao Yang
- , Zhigong Song
- & Jun Lou
-
Article |
 Imaging single glycans
Imaging single glycans
An imaging method combining soft-landing electrospray ion beam deposition and low-temperature scanning tunnelling microscopy resolves the structures of glycans at sub-nanometre resolution, revealing the connectivity of glycan chains and the types of linkages.
- X. Wu
- , M. Delbianco
- & K. Kern
-
Article |
 Design and synthesis of multigrain nanocrystals via geometric misfit strain
Design and synthesis of multigrain nanocrystals via geometric misfit strain
Heteroepitaxy is used to precisely control the growth of Mn3O4 shells on the faces of a Co3O4 nanocube crystal, producing uniform grain boundary defects and highly ordered multigrain nanostructures.
- Myoung Hwan Oh
- , Min Gee Cho
- & Taeghwan Hyeon
-
Letter |
 An ultrafast symmetry switch in a Weyl semimetal
An ultrafast symmetry switch in a Weyl semimetal
Terahertz light pulses induce transitions between a topological and a trivial phase in the Weyl semimetal WTe2 through an interlayer shear strain.
- Edbert J. Sie
- , Clara M. Nyby
- & Aaron M. Lindenberg
-
Perspective |
 Structural superlubricity and ultralow friction across the length scales
Structural superlubricity and ultralow friction across the length scales
The phenomenon of ultralow friction between sliding incommensurate crystal surfaces—structural superlubricity—is examined, and the challenges and opportunities involved in its extension to the macroscale are assessed.
- Oded Hod
- , Ernst Meyer
- & Michael Urbakh
-
Letter |
 History-independent cyclic response of nanotwinned metals
History-independent cyclic response of nanotwinned metals
In copper components containing highly oriented nanotwins, correlated ‘necklace’ dislocations moving back and forth offer an unusually fatigue-resistant response to engineering stress.
- Qingsong Pan
- , Haofei Zhou
- & Lei Lu
-
Letter |
 Deciphering chemical order/disorder and material properties at the single-atom level
Deciphering chemical order/disorder and material properties at the single-atom level
The three-dimensional coordinates of more than 23,000 atoms in an iron-platinum nanoparticle are determined with 22 picometre precision to correlate chemical order/disorder and crystal defects with magnetic properties.
- Yongsoo Yang
- , Chien-Chun Chen
- & Jianwei Miao
-
Letter |
 Extreme creep resistance in a microstructurally stable nanocrystalline alloy
Extreme creep resistance in a microstructurally stable nanocrystalline alloy
A nanocrystalline copper–tantalum alloy with high strength and extremely high-temperature creep resistance is achieved via a processing method that creates clusters of atoms within the alloy that pin grain boundaries.
- K. A. Darling
- , M. Rajagopalan
- & K. N. Solanki
-
Letter |
 Carbon-based tribofilms from lubricating oils
Carbon-based tribofilms from lubricating oils
Moving mechanical interfaces need to be lubricated to ensure long life and easy slippage; here, a new type of coating is described—comprising nitrides of either molybdenum or vanadium, together with a copper or nickel catalyst—that generates protective tribofilms from lubricating oils.
- Ali Erdemir
- , Giovanni Ramirez
- & Subramanian K. R. S. Sankaranarayanan
-
Letter |
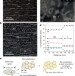 Brittle intermetallic compound makes ultrastrong low-density steel with large ductility
Brittle intermetallic compound makes ultrastrong low-density steel with large ductility
Alloying steel with aluminium improves the material’s strength-to-weight ratio, but the resulting formation of brittle intermetallic compounds within the steel matrix reduces its ductility; here the morphology and distribution of the intermetallic precipitates are controlled to alleviate this problem.
- Sang-Heon Kim
- , Hansoo Kim
- & Nack J. Kim
-
Letter |
 Dislocations in bilayer graphene
Dislocations in bilayer graphene
Basal-plane dislocations, identified as fundamental defects in bilayer graphene by transmission electron microscopy and atomistic simulations, reveal striking size effects, most notably a pronounced buckling of the graphene membrane, which drastically alters the strain state and is of key importance for the material’s mechanical and electronic properties.
- Benjamin Butz
- , Christian Dolle
- & Erdmann Spiecker
-
Letter |
 Ultrahard nanotwinned cubic boron nitride
Ultrahard nanotwinned cubic boron nitride
The hardness, toughness and chemical stability of the well-known superhard material cubic boron nitride have been improved by using a synthesis technique based on specially prepared ‘onion-like’ precursor materials.
- Yongjun Tian
- , Bo Xu
- & Zhongyuan Liu
-
Letter |
 Dodecagonal tiling in mesoporous silica
Dodecagonal tiling in mesoporous silica
The well-established self-assembly of surfactant micelles is used to produce a new mesoporous silica structure, a dodecagonal quasicrystal, which offers larger length scales than intermetallic quasicrystals and improved structural quality compared with soft-matter mesoscale quasicrystals.
- Changhong Xiao
- , Nobuhisa Fujita
- & Osamu Terasaki
-
News |
 Tiny traits cause big headaches
Tiny traits cause big headaches
Nanotech medicines held up by lack of particle characterization.
- Daniel Cressey
-
Research Highlights |
 Organic chemistry: An open and shut case
Organic chemistry: An open and shut case
-
Letter |
 Simultaneous phase and size control of upconversion nanocrystals through lanthanide doping
Simultaneous phase and size control of upconversion nanocrystals through lanthanide doping
Many technological materials are intentionally 'doped' with foreign elements to impart new and desirable properties, a classic example being the doping of semiconductors to tune their electronic behaviour. Here lanthanide doping is used to control the growth of nanocrystals, allowing for simultaneous tuning of the size, crystallographic phase and optical properties of the hybrid material.
- Feng Wang
- , Yu Han
- & Xiaogang Liu

 Structural transition and migration of incoherent twin boundary in diamond
Structural transition and migration of incoherent twin boundary in diamond Perovskite decomposition and missing crystal planes in HRTEM
Perovskite decomposition and missing crystal planes in HRTEM