Featured
-
-
Article |
 Self-powered soft robot in the Mariana Trench
Self-powered soft robot in the Mariana Trench
A free-swimming soft robot inspired by deep-sea creatures, with artificial muscle, power and control electronics spread across a polymer matrix, successfully adapts to high pressure and operates in the deep ocean.
- Guorui Li
- , Xiangping Chen
- & Wei Yang
-
Article |
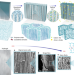 Strong tough hydrogels via the synergy of freeze-casting and salting out
Strong tough hydrogels via the synergy of freeze-casting and salting out
A strategy that combines freeze-casting and salting-out treatments produces strong, tough, stretchable and fatigue-resistant poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels.
- Mutian Hua
- , Shuwang Wu
- & Ximin He
-
Article |
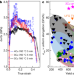 Facile route to bulk ultrafine-grain steels for high strength and ductility
Facile route to bulk ultrafine-grain steels for high strength and ductility
Bulk ultrafine-grained steel is prepared by an approach that involves the rapid production of coherent, disordered nanoprecipitates, which restrict grain growth but do not interfere with twinning or dislocation motion, resulting in high strength and ductility.
- Junheng Gao
- , Suihe Jiang
- & W. Mark Rainforth
-
Perspective |
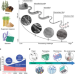 Developing fibrillated cellulose as a sustainable technological material
Developing fibrillated cellulose as a sustainable technological material
Opportunities for the application of fibrillated cellulose materials—which can be extracted from renewable resources—and broader manufacturing issues of scale-up, sustainability and synergy with the paper-making industry are discussed.
- Tian Li
- , Chaoji Chen
- & Liangbing Hu
-
Article |
 A reprogrammable mechanical metamaterial with stable memory
A reprogrammable mechanical metamaterial with stable memory
A reprogrammable mechanical metamaterial constructed of bistable unit cells that can be switched independently and reversibly between two stable states with distinct mechanical properties using magnetic actuation is demonstrated.
- Tian Chen
- , Mark Pauly
- & Pedro M. Reis
-
Article |
 Toughening mechanisms of the elytra of the diabolical ironclad beetle
Toughening mechanisms of the elytra of the diabolical ironclad beetle
A jigsaw-style configuration of interlocking structures identified in the elytra of the remarkably tough diabolical ironclad beetle, Phloeodes diabolicus, is used to inspire crush-resistant multilayer composites for engineering joints.
- Jesus Rivera
- , Maryam Sadat Hosseini
- & David Kisailus
-
Matters Arising |
 Slow compression of crystalline ice at low temperature
Slow compression of crystalline ice at low temperature
- R. Bauer
- , J. S. Tse
- & T. Hattori
-
Article |
 High-strength Damascus steel by additive manufacturing
High-strength Damascus steel by additive manufacturing
A Damascus-like steel consisting of alternating hard and soft layers is created by using a laser additive manufacturing technique and digital control of the processing parameters.
- Philipp Kürnsteiner
- , Markus Benjamin Wilms
- & Dierk Raabe
-
Article |
 Hierarchically structured diamond composite with exceptional toughness
Hierarchically structured diamond composite with exceptional toughness
A diamond composite with a hierarchical microstructure possesses a combination of hardness and toughness surpassing that of all known materials.
- Yonghai Yue
- , Yufei Gao
- & Yongjun Tian
-
Article |
 Short-range order and its impact on the CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy
Short-range order and its impact on the CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy
Metal alloys consisting of three or more major elemental components show enhanced mechanical properties, which are now shown to be correlated with short-range order observed with electron microscopy.
- Ruopeng Zhang
- , Shiteng Zhao
- & Andrew M. Minor
-
Article |
 Layered nanocomposites by shear-flow-induced alignment of nanosheets
Layered nanocomposites by shear-flow-induced alignment of nanosheets
Layered nanocomposites fabricated using a continuous and scalable process achieve properties exceeding those of natural nacre, the result of stiffened matrix polymer chains confined between highly aligned nanosheets.
- Chuangqi Zhao
- , Pengchao Zhang
- & Lei Jiang
-
Article |
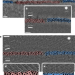 Observations of grain-boundary phase transformations in an elemental metal
Observations of grain-boundary phase transformations in an elemental metal
Atomic-resolution observations combined with simulations show that grain boundaries within elemental copper undergo temperature-induced solid-state phase transformation to different structures; grain boundary phases can also coexist and are kinetically trapped structures.
- Thorsten Meiners
- , Timofey Frolov
- & Christian H. Liebscher
-
Article |
 Strain-hardening and suppression of shear-banding in rejuvenated bulk metallic glass
Strain-hardening and suppression of shear-banding in rejuvenated bulk metallic glass
Bulk metallic glasses can acquire the ability to strain-harden through a mechanical rejuvenation treatment at room temperature that retains their non-crystalline structure.
- J. Pan
- , Yu. P. Ivanov
- & A. L. Greer
-
Article |
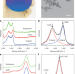 Synthesis and properties of free-standing monolayer amorphous carbon
Synthesis and properties of free-standing monolayer amorphous carbon
The synthesis of surprisingly stable, free-standing single layers of amorphous carbon and their analysis by atomic-resolution imaging could settle a debate about their atomic arrangement and offer unusual electronics applications.
- Chee-Tat Toh
- , Hongji Zhang
- & Barbaros Özyilmaz
-
Article |
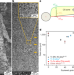 Additive manufacturing of ultrafine-grained high-strength titanium alloys
Additive manufacturing of ultrafine-grained high-strength titanium alloys
Titanium–copper alloys with fully equiaxed grains and a fine microstructure are realized via an additive manufacturing process that exploits high cooling rates and multiple thermal cycles.
- Duyao Zhang
- , Dong Qiu
- & Mark A. Easton
-
Review Article |
 Strategies for improving the sustainability of structural metals
Strategies for improving the sustainability of structural metals
Structural metals enable improved energy efficiency through their reduced mass, higher thermal stability and better mechanical properties; here, methods of improving the sustainability of structural metals, from recycling to contaminant tolerance, are described.
- Dierk Raabe
- , C. Cem Tasan
- & Elsa A. Olivetti
-
Letter |
 Tuning element distribution, structure and properties by composition in high-entropy alloys
Tuning element distribution, structure and properties by composition in high-entropy alloys
In high-entropy alloys, atomic-resolution chemical mapping shows that swapping some of the atoms for larger, more electronegative elements results in atomic-scale modulations that produce higher yield strength, excellent strain hardening and ductility.
- Qingqing Ding
- , Yin Zhang
- & Qian Yu
-
Letter |
 High-temperature bulk metallic glasses developed by combinatorial methods
High-temperature bulk metallic glasses developed by combinatorial methods
Bulk metallic glasses made from alloys of iridium, nickel, tantalum and boron are developed by combinatorial methods, with higher strength at high temperature than those previously produced.
- Ming-Xing Li
- , Shao-Fan Zhao
- & Wei-Hua Wang
-
Article |
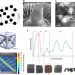 Damage-tolerant architected materials inspired by crystal microstructure
Damage-tolerant architected materials inspired by crystal microstructure
Inspired by the enhanced mechanical strength of microstructured metals, damage-tolerant architected materials are developed in which the internal structure is granular, with different regions having different lattice orientations.
- Minh-Son Pham
- , Chen Liu
- & Jedsada Lertthanasarn
-
Perspective |
 Structural superlubricity and ultralow friction across the length scales
Structural superlubricity and ultralow friction across the length scales
The phenomenon of ultralow friction between sliding incommensurate crystal surfaces—structural superlubricity—is examined, and the challenges and opportunities involved in its extension to the macroscale are assessed.
- Oded Hod
- , Ernst Meyer
- & Michael Urbakh
-
Letter |
 Enhanced strength and ductility in a high-entropy alloy via ordered oxygen complexes
Enhanced strength and ductility in a high-entropy alloy via ordered oxygen complexes
Ordered oxygen complexes in high-entropy alloys enhance both strength and ductility in these compositionally complex solid solutions.
- Zhifeng Lei
- , Xiongjun Liu
- & Zhaoping Lu
-
Letter |
 Ceramic–metal composites for heat exchangers in concentrated solar power plants
Ceramic–metal composites for heat exchangers in concentrated solar power plants
A robust ceramic/refractory metal (ZrC/W)-based composite for use in heat exchangers in concentrated solar power plants above 1,023 kelvin is described, having attractive high-temperature thermal, mechanical and chemical properties combined with cost-effective processing.
- M. Caccia
- , M. Tabandeh-Khorshid
- & K. H. Sandhage
-
Letter |
 Multi-step self-guided pathways for shape-changing metamaterials
Multi-step self-guided pathways for shape-changing metamaterials
A scheme for implementing multi-step topological reorganization of a mechanical metamaterial is demonstrated, which proceeds autonomously, without the need for external control.
- Corentin Coulais
- , Alberico Sabbadini
- & Martin van Hecke
-
Letter |
 Three-dimensional printing of hierarchical liquid-crystal-polymer structures
Three-dimensional printing of hierarchical liquid-crystal-polymer structures
3D printing of liquid-crystal polymers can create lightweight hierarchical structures with very high stiffness and toughness.
- Silvan Gantenbein
- , Kunal Masania
- & André R. Studart
-
Letter |
 Topological negative refraction of surface acoustic waves in a Weyl phononic crystal
Topological negative refraction of surface acoustic waves in a Weyl phononic crystal
Sound waves in a specially designed crystal undergo ‘topologically protected’ negative refraction, whereby no reflection is allowed, at certain facets of the crystal and positive refraction at others.
- Hailong He
- , Chunyin Qiu
- & Zhengyou Liu
-
Letter |
 Rapid energy-efficient manufacturing of polymers and composites via frontal polymerization
Rapid energy-efficient manufacturing of polymers and composites via frontal polymerization
Frontal polymerization of dicyclopentadiene is used to generate thermoset polymers and composite materials with much lower energy requirements and cure times than are needed in conventional oven or autoclave curing approaches.
- Ian D. Robertson
- , Mostafa Yourdkhani
- & Scott R. White
-
Letter |
 Processing bulk natural wood into a high-performance structural material
Processing bulk natural wood into a high-performance structural material
A process is described for the transformation of bulk wood into a low-cost, strong, tough, lightweight structural material, by the partial removal of lignin and hemicellulose followed by hot-pressing to densify the natural wood.
- Jianwei Song
- , Chaoji Chen
- & Liangbing Hu
-
Letter |
 Granular materials flow like complex fluids
Granular materials flow like complex fluids
The relaxation dynamics of granular materials is more like that of complex fluids than that of thermal glass-forming systems, owing to the absence of the ‘cage effect’.
- Binquan Kou
- , Yixin Cao
- & Yujie Wang
-
Letter |
 History-independent cyclic response of nanotwinned metals
History-independent cyclic response of nanotwinned metals
In copper components containing highly oriented nanotwins, correlated ‘necklace’ dislocations moving back and forth offer an unusually fatigue-resistant response to engineering stress.
- Qingsong Pan
- , Haofei Zhou
- & Lei Lu
-
Letter |
 Probing the limits of metal plasticity with molecular dynamics simulations
Probing the limits of metal plasticity with molecular dynamics simulations
The limits of dislocation-mediated metal plasticity are studied by using in situ computational microscopy to reduce the enormous amount of data from fully dynamic atomistic simulations into a manageable form.
- Luis A. Zepeda-Ruiz
- , Alexander Stukowski
- & Vasily V. Bulatov
-
Letter |
 3D printing of high-strength aluminium alloys
3D printing of high-strength aluminium alloys
Zirconium nanoparticles introduced into aluminium alloy powders control solidification during 3D printing, enabling the production of crack-free materials with strengths comparable to the corresponding wrought material.
- John H. Martin
- , Brennan D. Yahata
- & Tresa M. Pollock
-
Letter |
 Ultrastrong steel via minimal lattice misfit and high-density nanoprecipitation
Ultrastrong steel via minimal lattice misfit and high-density nanoprecipitation
A method of producing superstrong yet ductile steels using cheaper and lighter alloying elements is described, based on minimization of the lattice misfit to achieve a maximal dispersion of nanoprecipitates, leading to ultimate precipitation strengthening.
- Suihe Jiang
- , Hui Wang
- & Zhaoping Lu
-
Letter |
 Dual-phase nanostructuring as a route to high-strength magnesium alloys
Dual-phase nanostructuring as a route to high-strength magnesium alloys
Combining the benefits of nanocrystals with those of amorphous metallic glasses leads to a dual-phase material—comprising sub-10-nanometre-sized nanocrystalline grains embedded in amorphous glassy shells—that exhibits a strength approaching the ideal theoretical limit.
- Ge Wu
- , Ka-Cheung Chan
- & Jian Lu
-
Letter |
 Enzymatic mineralization generates ultrastiff and tough hydrogels with tunable mechanics
Enzymatic mineralization generates ultrastiff and tough hydrogels with tunable mechanics
Synthetic hydrogels are here created by enzyme-induced mineralization of hydrogel networks, yielding materials that are tough yet impressively stiff, with calcium phosphate particles distributed homogeneously throughout the network.
- Nicolas Rauner
- , Monika Meuris
- & Joerg C. Tiller
-
Letter |
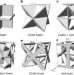 Mechanical metamaterials at the theoretical limit of isotropic elastic stiffness
Mechanical metamaterials at the theoretical limit of isotropic elastic stiffness
Finite-element models are used to identify a material geometry that achieves the theoretical bounds on isotropic elastic stiffness—a combination closed-cell cubic and octet foam.
- J. B. Berger
- , H. N. G. Wadley
- & R. M. McMeeking
-
Letter |
 Static non-reciprocity in mechanical metamaterials
Static non-reciprocity in mechanical metamaterials
Suitably engineered mechanical metamaterials show static non-reciprocity—that is, the transmission of motion from one side to the other depends on the direction of that motion.
- Corentin Coulais
- , Dimitrios Sounas
- & Andrea Alù
-
Article |
 Rational design of reconfigurable prismatic architected materials
Rational design of reconfigurable prismatic architected materials
A robust and scale-independent strategy for the design of reconfigurable architected materials (in which properties are adjusted by altering structure rather than composition) is described, based on space-filling assemblies of polyhedra.
- Johannes T. B. Overvelde
- , James C. Weaver
- & Katia Bertoldi
-
Letter |
 Extreme creep resistance in a microstructurally stable nanocrystalline alloy
Extreme creep resistance in a microstructurally stable nanocrystalline alloy
A nanocrystalline copper–tantalum alloy with high strength and extremely high-temperature creep resistance is achieved via a processing method that creates clusters of atoms within the alloy that pin grain boundaries.
- K. A. Darling
- , M. Rajagopalan
- & K. N. Solanki
-
Letter |
 Carbon-based tribofilms from lubricating oils
Carbon-based tribofilms from lubricating oils
Moving mechanical interfaces need to be lubricated to ensure long life and easy slippage; here, a new type of coating is described—comprising nitrides of either molybdenum or vanadium, together with a copper or nickel catalyst—that generates protective tribofilms from lubricating oils.
- Ali Erdemir
- , Giovanni Ramirez
- & Subramanian K. R. S. Sankaranarayanan
-
Letter |
 Combinatorial design of textured mechanical metamaterials
Combinatorial design of textured mechanical metamaterials
Lattices of cubic building blocks that deform anisotropically and that are designed to fit together like a three-dimensional jigsaw puzzle are 3D printed to create aperiodic, frustration-free, mechanical metamaterials; these metamaterials act as programmable shape-shifters and are able to perform pattern analysis.
- Corentin Coulais
- , Eial Teomy
- & Martin van Hecke
-
Letter |
 Intrinsic ferroelectric switching from first principles
Intrinsic ferroelectric switching from first principles
Molecular dynamics simulations of 90° domain walls in PbTiO3 are used to construct a nucleation-and-growth-based analytical model that quantifies the dynamics of many types of domain walls in various ferroelectrics, suggesting intrinsic domain-wall motion as a universal mechanism for ferroelectric switching.
- Shi Liu
- , Ilya Grinberg
- & Andrew M. Rappe
-
Letter |
 Controlled fragmentation of multimaterial fibres and films via polymer cold-drawing
Controlled fragmentation of multimaterial fibres and films via polymer cold-drawing
Cold-drawing of multimaterial fibres consisting of a brittle core embedded in a ductile polymer cladding results in controllable fragmentation of the core to produce uniformly sized rods parallel to the drawing direction for cylindrical geometries and narrow, parallel strips perpendicular to the drawing direction for flat geometries.
- Soroush Shabahang
- , Guangming Tao
- & Ayman F. Abouraddy
-
Letter |
 Metastable high-entropy dual-phase alloys overcome the strength–ductility trade-off
Metastable high-entropy dual-phase alloys overcome the strength–ductility trade-off
An alloy design strategy that aims for phase metastability, rather than phase stability, is described that will lead to the development of transformation-induced plasticity-assisted, dual-phase high-entropy alloys, which exhibit a rare combined increase in strength and ductility.
- Zhiming Li
- , Konda Gokuldoss Pradeep
- & Cemal Cem Tasan
-
Article |
 Interface dynamics and crystal phase switching in GaAs nanowires
Interface dynamics and crystal phase switching in GaAs nanowires
Crystal phase switching between zinc-blende and wurtzite phases during the growth of gallium arsenide nanowires is observed experimentally, and explained via changes in the geometry of the catalytic droplet sitting on top of the growing nanowire.
- Daniel Jacobsson
- , Federico Panciera
- & Frances M. Ross
-
Letter |
 Processing and properties of magnesium containing a dense uniform dispersion of nanoparticles
Processing and properties of magnesium containing a dense uniform dispersion of nanoparticles
Magnesium is light but not very strong; here the addition of silicon carbide nanoparticles uniformly dispersed to 14 per cent by volume, achieved through a nanoparticle self-stabilization mechanism in a molten metal alloy, yields improved strength, stiffness, plasticity and high-temperature stability.
- Lian-Yi Chen
- , Jia-Quan Xu
- & Xiao-Chun Li
-
Article |
 The origins of high hardening and low ductility in magnesium
The origins of high hardening and low ductility in magnesium
Practical applications of magnesium as a lightweight structural metal are limited by its high work hardening, low ductility and fracture at very low strains; now molecular dynamics simulations reveal the origins of these problems and offer a route to design magnesium alloys with improved mechanical properties.
- Zhaoxuan Wu
- & W. A. Curtin
-
Letter |
 Rejuvenation of metallic glasses by non-affine thermal strain
Rejuvenation of metallic glasses by non-affine thermal strain
This study shows that metallic glasses can be rejuvenated (taken to higher energy states with more plasticity) by thermally cycling them at relatively low temperatures (well below the glass transition temperature); this is attributed to the effect of intrinsic structural inhomogeneities in the glassy state, which translate into localized internal strains as the temperature is cycled and the different regions expand and contract by different amounts.
- S. V. Ketov
- , Y. H. Sun
- & A. L. Greer
-
Letter |
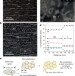 Brittle intermetallic compound makes ultrastrong low-density steel with large ductility
Brittle intermetallic compound makes ultrastrong low-density steel with large ductility
Alloying steel with aluminium improves the material’s strength-to-weight ratio, but the resulting formation of brittle intermetallic compounds within the steel matrix reduces its ductility; here the morphology and distribution of the intermetallic precipitates are controlled to alleviate this problem.
- Sang-Heon Kim
- , Hansoo Kim
- & Nack J. Kim
-
Letter |
 Formation of monatomic metallic glasses through ultrafast liquid quenching
Formation of monatomic metallic glasses through ultrafast liquid quenching
Metallic liquids of single elements have been successfully vitrified to their glassy states by achieving an ultrafast quenching rate in a new experimental design, of which the process has been monitored and studied by a combination of in situ transmission electron microscopy and atoms-to-continuum computer modelling.
- Li Zhong
- , Jiangwei Wang
- & Scott X. Mao

 Determining the three-dimensional atomic structure of an amorphous solid
Determining the three-dimensional atomic structure of an amorphous solid