Research Briefing |
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Visualization of translation and protein biogenesis at the ER membrane
Visualization of translation and protein biogenesis at the ER membrane
Structural studies of the ribosome-associated endoplasmic reticulum translocon complex based on cryo-electron tomography and molecular modelling reveal multiple intermediate states and interactions between the components of the complex and its cofactors.
- Max Gemmer
- , Marten L. Chaillet
- & Friedrich Förster
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the lysosomal mTORC1–TFEB–Rag–Ragulator megacomplex
Structure of the lysosomal mTORC1–TFEB–Rag–Ragulator megacomplex
Cryogenic-electron microscopy is used to determine the structure of TFEB as presented to mTORC1 for phosphorylation and an explanation is found for the strong dependence of TFEB phosphorylation on FLCN and the RagC GDP state.
- Zhicheng Cui
- , Gennaro Napolitano
- & James H. Hurley
-
Article |
 Structural basis of Rho-dependent transcription termination
Structural basis of Rho-dependent transcription termination
Structures presented in this study confirm decades of genetic and biochemical evidence for the mechanism of Rho-dependent termination in bacteria.
- Vadim Molodtsov
- , Chengyuan Wang
- & Richard H. Ebright
-
Research Briefing |
 A set of factors that silence the protein-making machinery in eggs
A set of factors that silence the protein-making machinery in eggs
In egg cells, the ribosomes — the machinery responsible for protein synthesis — are stored in a dormant state that is released later in the developing embryo. An evolutionarily conserved set of proteins has been shown to bind to ribosomes in the egg cells of vertebrates, stabilizing the ribosomes and suppressing their activity.
-
Article |
 A molecular network of conserved factors keeps ribosomes dormant in the egg
A molecular network of conserved factors keeps ribosomes dormant in the egg
Mass spectrometry and structural studies demonstrate the specific changes in protein composition that accompany the transition of ribosomes in zebrafish and Xenopus eggs from a dormant to an active state during early embryogenesis.
- Friederike Leesch
- , Laura Lorenzo-Orts
- & Andrea Pauli
-
News & Views |
 First full views of a CRISPR-guided system for gene insertion
First full views of a CRISPR-guided system for gene insertion
CRISPR–Cas is a bacterial defence system that can attack invading DNA to protect host cells, or help to insert DNA safely into the genome. Structures of this latter type of CRISPR–Cas system have now been visualized.
- Orsolya Barabas
- & Phoebe A. Rice
-
Article |
 Structural basis for intrinsic transcription termination
Structural basis for intrinsic transcription termination
Structural studies of Escherichia coli transcription intrinsic termination complexes representing distinct intermediates using cryo-electron microscopy provide insights into the steps and mechanism of transcription termination.
- Linlin You
- , Expery O. Omollo
- & Yu Zhang
-
Research Briefing |
 Bacterial receptor crucial for antibiotic resistance imaged in detail
Bacterial receptor crucial for antibiotic resistance imaged in detail
The bacterial protein BlaR1 regulates resistance to β-lactam antibiotics in the multidrug-resistant bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus. Cryo-electron microscopy has revealed the detailed structures of BlaR1 in its resting state and in its β-lactam-bound activated state, illuminating possible routes to combating antibiotic resistance.
-
Article |
 Structures and mechanisms of tRNA methylation by METTL1–WDR4
Structures and mechanisms of tRNA methylation by METTL1–WDR4
Using cryo-electron microscopy, structural and mechanistic insights into how the METTL1–WDR4 complex catalyses methylation of tRNAs are shown.
- Victor M. Ruiz-Arroyo
- , Rishi Raj
- & Yunsun Nam
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of broad-spectrum β-lactam resistance in Staphylococcus aureus
Structural basis of broad-spectrum β-lactam resistance in Staphylococcus aureus
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of Staphylococcus aureus BlaR1 reveal dynamic signalling states regulating broad spectrum β-lactam antibiotic resistance through cleavage of the transcriptional repressor BlaI and induced expression of the β-lactamase blaZ and the β-lactam-resistant cell-wall transpeptidase mecA.
- J. Andrew N. Alexander
- , Liam J. Worrall
- & Natalie C. J. Strynadka
-
Article
| Open Access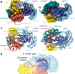 RNA targeting unleashes indiscriminate nuclease activity of CRISPR–Cas12a2
RNA targeting unleashes indiscriminate nuclease activity of CRISPR–Cas12a2
Structural analysis of Cas12a2, a CRISPR-associated nuclease that nonspecifically cleaves ssRNA, ssDNA and dsDNA, reveals a complete activation pathway involved in the abortive infection system protecting cells against invasion.
- Jack P. K. Bravo
- , Thomson Hallmark
- & David W. Taylor
-
Article
| Open Access A quantitative map of nuclear pore assembly reveals two distinct mechanisms
A quantitative map of nuclear pore assembly reveals two distinct mechanisms
Single-molecule calibrated live microscopy and computational modelling have revealed that human nuclear pore complex assembly takes different pathways during the exit from mitosis and during nuclear growth in interphase.
- Shotaro Otsuka
- , Jeremy O. B. Tempkin
- & Jan Ellenberg
-
Article |
 Structural basis of regulated m7G tRNA modification by METTL1–WDR4
Structural basis of regulated m7G tRNA modification by METTL1–WDR4
Structures of the human METTL1–WDR4 complex are revealed, providing molecular insights into substrate recognition, modification and catalytic regulation by the N7-methylguanosine methyltransferase complex.
- Jiazhi Li
- , Longfei Wang
- & Richard I. Gregory
-
Article |
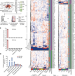 A male germ-cell-specific ribosome controls male fertility
A male germ-cell-specific ribosome controls male fertility
RibosomeST—a ribosome with a specialized nascent polypeptide exit tunnel—cotranslationally regulates the folding of a subset of male germ-cell-specific proteins that are essential for the formation of sperm.
- Huiling Li
- , Yangao Huo
- & Jiahao Sha
-
Article |
 Structural insights into the mechanism of the sodium/iodide symporter
Structural insights into the mechanism of the sodium/iodide symporter
Mutations in the sodium/iodide symporter (NIS) cause congenital hypothyroidism, and our results yield insights into how NIS selects, couples and translocates anions, thereby establishing a framework for understanding NIS function.
- Silvia Ravera
- , Juan Pablo Nicola
- & Nancy Carrasco
-
News |
 After AlphaFold: protein-folding contest seeks next big breakthrough
After AlphaFold: protein-folding contest seeks next big breakthrough
Two years after DeepMind’s revolutionary AI swept a competition for predicting protein structures, researchers are building on AlphaFold’s success.
- Ewen Callaway
-
Article
| Open Access Principles of mitoribosomal small subunit assembly in eukaryotes
Principles of mitoribosomal small subunit assembly in eukaryotes
The structures of both human and yeast mitochondrial ribosomal small subunits undergoing assembly are uncovered.
- Nathan J. Harper
- , Chloe Burnside
- & Sebastian Klinge
-
Article
| Open Access Close relatives of MERS-CoV in bats use ACE2 as their functional receptors
Close relatives of MERS-CoV in bats use ACE2 as their functional receptors
NeoCoV and its close relative, PDF-2180, can efficiently bind to and use specific bat ACE2 orthologues and, less favourably, human ACE2 as entry receptors through their receptor-binding domains on the spike protein.
- Qing Xiong
- , Lei Cao
- & Huan Yan
-
Article |
 Molecular basis for selective activation of DREADD-based chemogenetics
Molecular basis for selective activation of DREADD-based chemogenetics
The mechanism of action of muscarinic receptor-based DREADDs, important chemogenetic tools in neuroscience and cellular signalling research, are described in molecular detail.
- Shicheng Zhang
- , Ryan H. Gumpper
- & Bryan L. Roth
-
Article |
 Cryo-EM structures of the active NLRP3 inflammasome disc
Cryo-EM structures of the active NLRP3 inflammasome disc
We report cryogenic electron microscopy structures of disc-shaped active NLRP3 oligomers in complex with NEK7 and ASC, and propose that the role of NEK7 is to transform NLRP3 into the active NLRP3 inflammasome disc.
- Le Xiao
- , Venkat Giri Magupalli
- & Hao Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of the holo CRISPR RNA-guided transposon integration complex
Structures of the holo CRISPR RNA-guided transposon integration complex
Structural studies of the CRISPR-associated transposon comprising Cas12k, TnsC, TnsB and TniQ from Scytonema hofmannii using cryo-electron microscopy reveal insights into the architecture and mechanism of RNA-guided DNA transposition.
- Jung-Un Park
- , Amy Wei-Lun Tsai
- & Elizabeth H. Kellogg
-
Article |
 Antiviral signalling by a cyclic nucleotide activated CRISPR protease
Antiviral signalling by a cyclic nucleotide activated CRISPR protease
A CalpL–CalpT–CalpS cascade mediated by cyclic oligoadenylates is identified as a mechanism to detect viral RNA and activate subsequent antivirus responses in microorganisms.
- Christophe Rouillon
- , Niels Schneberger
- & Gregor Hagelueken
-
News & Views |
 Folate transporter offers clues for anticancer drugs
Folate transporter offers clues for anticancer drugs
Structural insights into a long-studied folate-transport protein provide evidence that might lead to entirely new targeted anticancer treatments, or boost the success of immunotherapy approaches to tackling tumours.
- Larry H. Matherly
- & Zhanjun Hou
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of tankyrase activation by polymerization
Structural basis of tankyrase activation by polymerization
Structural insights into the poly-ADP-ribosyltransferase tankyrase reveal its filamentous architecture and illustrate how assembly controls catalytic and non-catalytic functions.
- Nisha Pillay
- , Laura Mariotti
- & Sebastian Guettler
-
News & Views |
 Uncoordinated protein coordinates cell migration
Uncoordinated protein coordinates cell migration
Mounting evidence suggests that developing neurons and metastatic cancer cells migrate through similar mechanisms. Characterization of a previously unknown complex involved in cell migration confirms this idea.
- Alain Chédotal
-
Research Briefing |
 A bacterial immune system senses a viral protein
A bacterial immune system senses a viral protein
Bacteria have evolved diverse immune systems to defend themselves against viral infection. Many of these systems require specific viral triggers for activation, but these triggers and their activation mechanisms remain mostly unknown. A bacterial immune system that senses a viral structural protein enables an effective immune response against viral infection.
-
News |
 AlphaFold’s new rival? Meta AI predicts shape of 600 million proteins
AlphaFold’s new rival? Meta AI predicts shape of 600 million proteins
Microbial molecules from soil, seawater and human bodies are among the planet’s least understood.
- Ewen Callaway
-
News & Views |
 Catching actin proteins in action
Catching actin proteins in action
Two groups have visualized actin — the protein polymer that gives cells their shape — at high resolution. The structures provide in-depth views of the polymer as it adopts fleeting states and undergoes conformational changes.
- Pilar Cossio
- & Glen M. Hocky
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of the SEA complex
Cryo-EM structure of the SEA complex
The cryo-EM structure of the yeast SEA complex suggests that SEACAT functions as a scaffold for binding TORC1 regulators.
- Lucas Tafur
- , Kerstin Hinterndorfer
- & Robbie Loewith
-
Article |
 Bestrophin-2 and glutamine synthetase form a complex for glutamate release
Bestrophin-2 and glutamine synthetase form a complex for glutamate release
Electrophysiological, structural and biochemical studies on the bestrophin-2 anion channel reveal asymmetric permeability to glutamate and show that it forms a cooperative machinery in complex with glutamine synthetase for glutamate release.
- Aaron P. Owji
- , Kuai Yu
- & Tingting Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of actin filament assembly and aging
Structural basis of actin filament assembly and aging
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of skeletal F-actin show solvent-driven rearrangements governing actin filament assembly and aging with potential application in design of drugs and small molecules for imaging and therapy.
- Wout Oosterheert
- , Björn U. Klink
- & Stefan Raunser
-
Article
| Open Access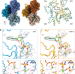 Bending forces and nucleotide state jointly regulate F-actin structure
Bending forces and nucleotide state jointly regulate F-actin structure
The nucleotide state of actin modulates F-actin structural transitions evoked by bending forces.
- Matthew J. Reynolds
- , Carla Hachicho
- & Gregory M. Alushin
-
Article |
 Recognition of cyclic dinucleotides and folates by human SLC19A1
Recognition of cyclic dinucleotides and folates by human SLC19A1
Two cyclic dinucleotide molecules bind within the cavity of human SLC19A1 as a compact dual-molecule unit, whereas folate and antifolate bind to SLC19A1 as a monomer and occupy a distinct pocket of the cavity.
- Qixiang Zhang
- , Xuyuan Zhang
- & Pu Gao
-
News & Views |
 Assembly surprise for membrane proteins
Assembly surprise for membrane proteins
Membrane-spanning proteins have many crucial roles in the cell. New findings challenge our current understanding of the route by which such proteins are inserted into the membranes of animal cells.
- Ben C. Berks
-
Article |
 Mechanism of an intramembrane chaperone for multipass membrane proteins
Mechanism of an intramembrane chaperone for multipass membrane proteins
Biochemical and structural analysis of intermediates during multipass membrane protein biogenesis showed how an intramembrane chaperone guides nascent membrane proteins to a semi-enclosed lipid-filled cavity where they are inserted and folded correctly.
- Luka Smalinskaitė
- , Min Kyung Kim
- & Ramanujan S. Hegde
-
Article |
 Structural principles of B cell antigen receptor assembly
Structural principles of B cell antigen receptor assembly
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the mouse class M immunoglobulin B cell receptor complex provide insight into B cell receptor subunit assembly, domain architecture and signalling mechanism.
- Ying Dong
- , Xiong Pi
- & Hao Wu
-
Research Briefing |
 A look at the protein complex that enables hearing
A look at the protein complex that enables hearing
The molecular basis of how vertebrate animals sense sound and perceive balance has been unclear for decades. The structure of a mechanically sensitive protein complex from nematode worms has been revealed, illuminating the architecture of the machinery that translates mechanical forces into electrical signals.
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of the TMC-1 complex illuminate mechanosensory transduction
Structures of the TMC-1 complex illuminate mechanosensory transduction
Structural studies of the native transmembrane channel-like protein 1 (TMC-1) mechanosensory transduction channel complex of Caenorhabditis elegans reveal the subunit composition and the roles of protein–membrane interactions in the conversion of mechanical force to ion channel activity.
- Hanbin Jeong
- , Sarah Clark
- & Eric Gouaux
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the OMEGA nickase IsrB in complex with ωRNA and target DNA
Structure of the OMEGA nickase IsrB in complex with ωRNA and target DNA
The cryogenic-electron microscopy structure of the D. thermocuniculi IsrB protein in complex with its cognate ωRNA and a target DNA shows that the RNA-dominant IsrB effector complex shares a common scaffold with the protein-dominant Cas9 effector complex.
- Seiichi Hirano
- , Kalli Kappel
- & Feng Zhang
-
Article |
 Structure of the NuA4 acetyltransferase complex bound to the nucleosome
Structure of the NuA4 acetyltransferase complex bound to the nucleosome
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of NuA4 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae bound to the nucleosome illustrates how NuA4 is assembled and provides mechanistic insights into nucleosome recognition and transcription co-activation by a histone acetyltransferase.
- Keke Qu
- , Kangjing Chen
- & Zhucheng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing translation dynamics at atomic detail inside a bacterial cell
Visualizing translation dynamics at atomic detail inside a bacterial cell
Cryo-electron tomography is used to reveal the structural dynamics and functional diversity of translating ribosomes in Mycoplasma pneumoniae, providing insight into the translation elongation cycle inside cells and how it is reshaped by antibiotics.
- Liang Xue
- , Swantje Lenz
- & Julia Mahamid
-
Article |
 Structure of the Ebola virus polymerase complex
Structure of the Ebola virus polymerase complex
Structural studies of the Ebola virus polymerase complex provide insights into its function and demonstrate the structural basis of its inhibition by suramin.
- Bin Yuan
- , Qi Peng
- & Yi Shi
-
Research Briefing |
 Structure of wheat immune receptor helps guide design of disease-resistant varieties
Structure of wheat immune receptor helps guide design of disease-resistant varieties
When plants recognize disease-causing organisms, they activate immune responses through mechanisms that are poorly understood. Resolving the structure of a plant receptor-protein complex in wheat that detects fungus-derived molecules reveals that the corresponding receptor family is structurally conserved during evolution.
-
Article
| Open Access A wheat resistosome defines common principles of immune receptor channels
A wheat resistosome defines common principles of immune receptor channels
Evolutionary conservation of plant receptor structure allowed for generation of new variants of wheat and barley nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat receptors (NLRs) that recognize AvrSr35 of the wheat stem rust pathogen, supporting proof of principle for structure-based engineering of NLRs for crop improvement.
- Alexander Förderer
- , Ertong Li
- & Jijie Chai
-
Article |
 Plant receptor-like protein activation by a microbial glycoside hydrolase
Plant receptor-like protein activation by a microbial glycoside hydrolase
A structural analysis focusing on plant immunity reveals how LRR-containing receptor-like proteins recognize pathogenic ligands and consequently become activated, with the data suggesting that these proteins target pathogens through two different mechanisms.
- Yue Sun
- , Yan Wang
- & Jijie Chai
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for directional chitin biosynthesis
Structural basis for directional chitin biosynthesis
Using cryo-electron microscopy, the directional multiple step mechanism of chitin biosynthesis is revealed.
- Wei Chen
- , Peng Cao
- & Qing Yang
-
News |
 Scientists are using AI to dream up revolutionary new proteins
Scientists are using AI to dream up revolutionary new proteins
Huge advances in artificial intelligence mean researchers can design completely original molecules in seconds instead of months.
- Ewen Callaway
-
Article |
 A universal coupling mechanism of respiratory complex I
A universal coupling mechanism of respiratory complex I
Cryo-electron microscopy studies of Escherichia coli complex I suggest a conserved mechanism of coupled proton transfers and electrostatic interactions that result in proton ejection from the complex exclusively at the distal NuoL subunit.
- Vladyslav Kravchuk
- , Olga Petrova
- & Leonid Sazanov
-
Article |
 Columnar structure of human telomeric chromatin
Columnar structure of human telomeric chromatin
Cryogenic electron microscopy analyses reveal a new, compact structure of telomeric chromatin, providing mechanistic insight into telomere maintenance and function.
- Aghil Soman
- , Sook Yi Wong
- & Lars Nordenskiöld

 A transient protein megacomplex that controls degradation of cell components
A transient protein megacomplex that controls degradation of cell components