Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Practice and perspectives in the validation of resource management models
Practice and perspectives in the validation of resource management models
Credibility of long-term projection in quantitative models is continuously under debate and they rely on validation to prove projection accuracy. Here the authors investigated the views on the validation approaches and they show that empirical data plays an important role in the validation practice in all main areas of sustainability science.
- Sibel Eker
- , Elena Rovenskaya
- & Simon Langan
-
-
Article
| Open Access Paternal grandfather’s access to food predicts all-cause and cancer mortality in grandsons
Paternal grandfather’s access to food predicts all-cause and cancer mortality in grandsons
Nutritional experience can have phenotypic consequences in subsequent generations, as is evident from studies in animals and plants. Here, Vågerö et al. find in a large three-generation cohort that access to food in the paternal grandfather associates with all-cause and cancer mortality in male grandchildren.
- Denny Vågerö
- , Pia R. Pinger
- & Gerard J. van den Berg
-
Article
| Open Access Degrading permafrost puts Arctic infrastructure at risk by mid-century
Degrading permafrost puts Arctic infrastructure at risk by mid-century
Permafrost thaw poses a serious threat to the sustainable development of Arctic communities. Here the authors show that most fundamental Arctic infrastructure and population will be at high hazard risk, even if the Paris Agreement target is achieved.
- Jan Hjort
- , Olli Karjalainen
- & Miska Luoto
-
Article
| Open Access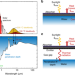 Contactless steam generation and superheating under one sun illumination
Contactless steam generation and superheating under one sun illumination
Solar steam generation is limited by fouling of solar converters, and the steam temperature is usually pinned to 100 °C. Here, both limitations are overcome in a system utilizing a solar absorber and light down-converter to achieve radiative heating, which does not require physical contact between absorber and water.
- Thomas A. Cooper
- , Seyed H. Zandavi
- & Gang Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Why rankings of biomedical image analysis competitions should be interpreted with care
Why rankings of biomedical image analysis competitions should be interpreted with care
Biomedical image analysis challenges have increased in the last ten years, but common practices have not been established yet. Here the authors analyze 150 recent challenges and demonstrate that outcome varies based on the metrics used and that limited information reporting hampers reproducibility.
- Lena Maier-Hein
- , Matthias Eisenmann
- & Annette Kopp-Schneider
-
Article
| Open Access The preeminence of ethnic diversity in scientific collaboration
The preeminence of ethnic diversity in scientific collaboration
Diversity is believed to raise effectiveness and performance but it contains many aspects. Here the authors studied the relationship between research impact and five classes of diversity and found that ethnic diversity had the strongest correlation with scientific impact.
- Bedoor K. AlShebli
- , Talal Rahwan
- & Wei Lee Woon
-
Article
| Open Access Intellectual synthesis in mentorship determines success in academic careers
Intellectual synthesis in mentorship determines success in academic careers
While successful mentors tend to train successful students in academic career, it’s unclear how mentorship determines chances of a success in a trainee. Here, Liénard and colleagues analyze approximately 20 K mentor/trainee relationships in life sciences, and find that success of trainees is associated with an intellectual synthesis between their mentors’ research.
- Jean F. Liénard
- , Titipat Achakulvisut
- & Stephen V. David
-
Article
| Open Access Air quality co-benefits for human health and agriculture counterbalance costs to meet Paris Agreement pledges
Air quality co-benefits for human health and agriculture counterbalance costs to meet Paris Agreement pledges
Local air quality co-benefits can provide convincing support for climate action. Here the authors revisited air quality co-benefits of climate action in the context of NDCs and found that 71–99 thousand premature deaths can be avoided each year by 2030, offsetting the climate mitigation costs on a global level.
- Toon Vandyck
- , Kimon Keramidas
- & Bert Saveyn
-
Article
| Open Access The spread of low-credibility content by social bots
The spread of low-credibility content by social bots
Online misinformation is a threat to a well-informed electorate and undermines democracy. Here, the authors analyse the spread of articles on Twitter, find that bots play a major role in the spread of low-credibility content and suggest control measures for limiting the spread of misinformation.
- Chengcheng Shao
- , Giovanni Luca Ciampaglia
- & Filippo Menczer
-
Article
| Open Access Early childhood investment impacts social decision-making four decades later
Early childhood investment impacts social decision-making four decades later
Early childhood educational intervention has positive outcomes in adulthood, including higher education attainment, economic status, and overall health. This study shows that adults who underwent such intervention have greater enforcement of equality norm during social decision-making, potentially motivated by future planning.
- Yi Luo
- , Sébastien Hétu
- & Craig Ramey
-
Article
| Open Access Warming assessment of the bottom-up Paris Agreement emissions pledges
Warming assessment of the bottom-up Paris Agreement emissions pledges
The Paris Agreement includes bottom-up pledges and top-down warming threshold. Under this setting where countries effectively choose their own fairness principle, this article assesses the global warming implied by each Nationally Determined Contribution to inform the future ratcheting-up process.
- Yann Robiou du Pont
- & Malte Meinshausen
-
Correspondence
| Open Access Reply to 'Flawed assumptions compromise water yield assessment'
Reply to 'Flawed assumptions compromise water yield assessment'
- Ping Zhou
- , Qiang Li
- & Yongxian Su
-
Article
| Open Access Neural mechanisms for learning self and other ownership
Neural mechanisms for learning self and other ownership
The sense of ownership – of which objects belong to us and which to others - is an important part of our lives, but how the brain keeps track of ownership is poorly understood. Here, the authors show that specific brain areas are involved in ownership acquisition for the self, friends, and strangers.
- Patricia L. Lockwood
- , Marco K. Wittmann
- & Matthew F. S. Rushworth
-
Article
| Open Access An interpretable approach for social network formation among heterogeneous agents
An interpretable approach for social network formation among heterogeneous agents
Complex networks can be a useful tool to investigate problems in social science. Here the authors use game theory to establish a network model and then use a machine learning approach to characterize the role of nodes within a social network.
- Yuan Yuan
- , Ahmad Alabdulkareem
- & Alex ‘Sandy’ Pentland
-
Article
| Open Access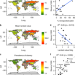 Modern slavery and the race to fish
Modern slavery and the race to fish
There have been growing concerns about the exploitation of workers in the fisheries sectors. Here, Tickler et al. use a country-level metric of slavery to determine the risk of fisheries-level slavery across 20 countries, and find it rises as unreported catch increases and mean value of catch decreases.
- David Tickler
- , Jessica J. Meeuwig
- & Dirk Zeller
-
Article
| Open Access Implicit preference for human trustworthy faces in macaque monkeys
Implicit preference for human trustworthy faces in macaque monkeys
Humans infer the trustworthiness of others based on subtle facial features such as the facial width-to-height ratio, but it is not known whether other primates are sensitive to these cues. Here, the authors show that macaque monkeys prefer to look at human faces which appear trustworthy to humans.
- Manuela Costa
- , Alice Gomez
- & Angela Sirigu
-
Article
| Open Access Inherent potential of steelmaking to contribute to decarbonisation targets via industrial carbon capture and storage
Inherent potential of steelmaking to contribute to decarbonisation targets via industrial carbon capture and storage
Carbon budget is diminishing to comply with the target under 2 °C scenario. Facing the limited capacity to improve energy efficiency, the authors show that steelmaking with inherent decarbonisation process can potentially help achieve 2050 emission reduction targets under 2 °C scenario before 2030.
- Sicong Tian
- , Jianguo Jiang
- & Vasilije Manovic
-
Article
| Open Access Global state and potential scope of investments in watershed services for large cities
Global state and potential scope of investments in watershed services for large cities
Investment in watershed services programs is growing, however the factors that contribute to sustainability of such programs are unclear. Here the authors use a large database of cities around the world to show that payment schemes are more likely to be present in watersheds with more agricultural land and less protected areas.
- Chelsie L. Romulo
- , Stephen Posner
- & Robert I. McDonald
-
Article
| Open Access Closing the gender gap in competitiveness through priming
Closing the gender gap in competitiveness through priming
Men are often more willing to compete compared to women, which may contribute to gender differences in wages and career advancement. Here, the authors show that ‘power priming’ - encouraging people to imagine themselves in a situation of power - can close the gender gap in competitiveness.
- Loukas Balafoutas
- , Helena Fornwagner
- & Matthias Sutter
-
Article
| Open Access Substantiating freedom from parasitic infection by combining transmission model predictions with disease surveys
Substantiating freedom from parasitic infection by combining transmission model predictions with disease surveys
The decision when to stop an intervention is a critical component of parasite elimination programmes, but reliance on surveillance data alone can be inaccurate. Here, Michael et al. combine parasite transmission model predictions with disease survey data to more reliably determine when interventions can be stopped.
- Edwin Michael
- , Morgan E. Smith
- & Frank O. Richards
-
Article
| Open Access Diverging importance of drought stress for maize and winter wheat in Europe
Diverging importance of drought stress for maize and winter wheat in Europe
Drivers of crop yield variability require quantification, and historical records can help in improving understanding. Here, Webber et al. report that drought stress will remain a key driver of yield losses in wheat and maize across Europe, and benefits from CO2 will be limited in low-yielding years.
- Heidi Webber
- , Frank Ewert
- & Daniel Wallach
-
Article
| Open Access A global strategy to mitigate the environmental impact of China’s ruminant consumption boom
A global strategy to mitigate the environmental impact of China’s ruminant consumption boom
Rising demand for ruminant meat and dairy products in developing nations drives increasing GHG and ammonia emissions from livestock. Authors show here that only long-term adoption of global best-practice in sustainable intensification buffered by a short-term coping strategy of green-source trading can offer a way forward.
- Yuanyuan Du
- , Ying Ge
- & Raphael K. Didham
-
Article
| Open Access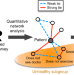 A scalable online tool for quantitative social network assessment reveals potentially modifiable social environmental risks
A scalable online tool for quantitative social network assessment reveals potentially modifiable social environmental risks
An individual’s social network—their friends, family, and acquaintances—is important for their health, but existing tools for assessing social networks have limitations. Here, the authors introduce a quantitative social network assessment tool on a secure open-source web platform and show its utility in a nation-wide study.
- Amar Dhand
- , Charles C. White
- & Philip L. De Jager
-
Article
| Open Access Physics-based forecasting of man-made earthquake hazards in Oklahoma and Kansas
Physics-based forecasting of man-made earthquake hazards in Oklahoma and Kansas
Reinjection of saltwater, co-produced with oil, has the potential to trigger damaging earthquakes. Here, using Oklahoma and Kansas as an example, the authors present a new physics-based methodology to forecast future probabilities of potentially damaging induced-earthquakes in space and time.
- Cornelius Langenbruch
- , Matthew Weingarten
- & Mark D. Zoback
-
Article
| Open Access Gender differences in individual variation in academic grades fail to fit expected patterns for STEM
Gender differences in individual variation in academic grades fail to fit expected patterns for STEM
Men are over-represented in the STEM (science, technology, engineering and mathematics) workforce even though girls outperform boys in these subjects at school. Here, the authors cast doubt on one leading explanation for this paradox, the ‘variability hypothesis’.
- R. E. O’Dea
- , M. Lagisz
- & S. Nakagawa
-
Article
| Open Access Estimating sources and sinks of malaria parasites in Madagascar
Estimating sources and sinks of malaria parasites in Madagascar
Understanding the source of malaria outbreaks in low-transmission areas is important for controlling the disease. Here, the authors use mobile phone data to map malaria transmission in Madagascar, and are able to show that primary sources of infection in the capital city are found along populated coastal areas.
- Felana Angella Ihantamalala
- , Vincent Herbreteau
- & Amy Wesolowski
-
Article
| Open Access Plant neighbor detection and allelochemical response are driven by root-secreted signaling chemicals
Plant neighbor detection and allelochemical response are driven by root-secreted signaling chemicals
Plant growth and physiology respond to the presence of neighboring plants. Here the authors show that the chemicals (-)-loliolide and jasmonic acid, which were present in the root exudates of a range of plant species, can be detected by wheat and induce allelochemical production.
- Chui-Hua Kong
- , Song-Zhu Zhang
- & Peng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding 6th-century barbarian social organization and migration through paleogenomics
Understanding 6th-century barbarian social organization and migration through paleogenomics
The Longobards invaded and conquered much of Italy after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. Here, the authors sequence and analyze ancient genomic DNA from 63 samples from two cemeteries associated with the Longobards and identify kinship networks and two distinct genetic and cultural groups in each.
- Carlos Eduardo G. Amorim
- , Stefania Vai
- & Krishna R. Veeramah
-
Article
| Open Access A global meta-analysis of yield stability in organic and conservation agriculture
A global meta-analysis of yield stability in organic and conservation agriculture
Yields vary between different cropping systems, though their temporal stability has not been quantified. Here, Knapp and van der Heijden present a meta-analysis showing that yields in organic agriculture have, per unit food produced, a lower temporal stability.
- Samuel Knapp
- & Marcel G. A. van der Heijden
-
Article
| Open Access Biased sequential sampling underlies the effects of time pressure and delay in social decision making
Biased sequential sampling underlies the effects of time pressure and delay in social decision making
It has been proposed that humans make unselfish decisions if constrained to decide quickly, but other research has suggested that time constraint makes us selfish. Here, the authors reconcile these two views showing that pro-social people become more pro-social under time pressure, but selfish subjects do the opposite.
- Fadong Chen
- & Ian Krajbich
-
Article
| Open Access Revisiting the functional significance of binocular cues for perceiving motion-in-depth
Revisiting the functional significance of binocular cues for perceiving motion-in-depth
The presence of opposite horizontal motion in the two eyes is a cue for perceiving motion-in-depth, but also leads to suppressed motion sensitivity. Here, the authors address this paradox and show that spatial and interocular integration mechanisms, distinct from the extraction of motion-in-depth, drive suppression.
- Peter J. Kohler
- , Wesley J. Meredith
- & Anthony M. Norcia
-
Comment
| Open Access Building optimism at the environmental science-policy-practice interface through the study of bright spots
Building optimism at the environmental science-policy-practice interface through the study of bright spots
- Christopher Cvitanovic
- & Alistair J. Hobday
-
Article
| Open Access Sequences of purchases in credit card data reveal lifestyles in urban populations
Sequences of purchases in credit card data reveal lifestyles in urban populations
Digital traces of our lives have the potential to allow insights into collective behaviors. Here, the authors cluster consumers by their credit card purchase sequences and discover five distinct groups, within which individuals also share similar mobility and demographic attributes.
- Riccardo Di Clemente
- , Miguel Luengo-Oroz
- & Marta C. González
-
Article
| Open Access Ancient DNA from Chalcolithic Israel reveals the role of population mixture in cultural transformation
Ancient DNA from Chalcolithic Israel reveals the role of population mixture in cultural transformation
The Late Chalcolithic material culture in the southern Levant has unique attributes that suggest spread of people or culture. Here, the authors use genome-wide ancient DNA data from 22 individuals from a Chalcolithic site and show evidence of complex population movements and turnovers.
- Éadaoin Harney
- , Hila May
- & David Reich
-
Article
| Open Access Carbon losses from deforestation and widespread degradation offset by extensive growth in African woodlands
Carbon losses from deforestation and widespread degradation offset by extensive growth in African woodlands
Degradation—the loss of carbon stored in intact woodland—is very difficult to measure over large areas. Here, the authors show that carbon emissions from degradation in African woodlands greatly exceed those from deforestation, but are happening alongside widespread increases in biomass in remote areas.
- Iain M. McNicol
- , Casey M. Ryan
- & Edward T. A. Mitchard
-
Perspective
| Open Access A framework for enhancing ethical genomic research with Indigenous communities
A framework for enhancing ethical genomic research with Indigenous communities
Indigenous peoples are still underrepresented in genetic research. Here, the authors propose an ethical framework consisting of six major principles that encourages researchers and Indigenous communities to build strong and equal partnerships to increase trust, engagement and diversity in genomic studies.
- Katrina G. Claw
- , Matthew Z. Anderson
- & Joseph M. Yracheta
-
Perspective
| Open AccessDesigning with living systems in the synthetic yeast project
Synthetic biology often views the organism as a chassis into which a circuit can be inserted. Here the authors explore the idea of the organism as a core aspect of design, aiding researchers in navigating the genetic space opened up by SCRaMbLE.
- Erika Szymanski
- & Jane Calvert
-
Article
| Open Access A user-friendly herbicide derived from photo-responsive supramolecular vesicles
A user-friendly herbicide derived from photo-responsive supramolecular vesicles
Paraquat is a widely used herbicide that is highly toxic to humans upon acute ingestion or chronic exposure. Here, the authors generate a photosensitive formulation that releases paraquat upon exposure to UV light or sunlight, which shows an improved safety profile in zebrafish and mouse models, while maintaining substantial herbicidal activity.
- Cheng Gao
- , Qiaoxian Huang
- & Ruibing Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Exploiting a cognitive bias promotes cooperation in social dilemma experiments
Exploiting a cognitive bias promotes cooperation in social dilemma experiments
The decoy effect refers to the fact that the presence of a third option can shift people’s preferences between two other options even though the third option is inferior to both. Here, the authors show how the decoy effect can enhance cooperation in a social dilemma, the repeated prisoner’s dilemma.
- Zhen Wang
- , Marko Jusup
- & Stefano Boccaletti
-
Article
| Open Access Differential temporal salience of earning and saving
Differential temporal salience of earning and saving
Economists have observed that many people seem unwilling to save for the future. Here, the authors show that earning and saving are subject to a basic asymmetry in attentional choice, such that cues that are associated with saving are perceived as occurring later than cues associated with earning.
- Kesong Hu
- , Eve De Rosa
- & Adam K. Anderson
-
Article
| Open Access Assessment of the impact of shared brain imaging data on the scientific literature
Assessment of the impact of shared brain imaging data on the scientific literature
Data sharing is recognized as a way to promote scientific collaboration and reproducibility, but some are concerned over whether research based on shared data can achieve high impact. Here, the authors show that neuroimaging papers using shared data are no less likely to appear in top-ranked journals.
- Michael P. Milham
- , R. Cameron Craddock
- & Arno Klein
-
Article
| Open Access Burden on hydropower units for short-term balancing of renewable power systems
Burden on hydropower units for short-term balancing of renewable power systems
Quantifying burden on hydropower units for balancing variable renewable energy sources has been uncertain and difficult. Herein Yang et al. propose a framework and characterize the burden, performance and compensation of hydropower regulation of renewable power systems.
- Weijia Yang
- , Per Norrlund
- & Urban Lundin
-
Comment
| Open AccessFrom petri dishes to politics – a multi-pronged approach is essential for saving endangered species
- Terri L. Roth
- & William F. Swanson
-
Article
| Open Access Immediate action is the best strategy when facing uncertain climate change
Immediate action is the best strategy when facing uncertain climate change
Reducing the adverse effects of climate change triggered by human activity requires cooperation on a global scale. Modelling this challenge as an evolutionary game shows that the emerging contributions of selfish players depend strongly on the risk scenario at stake.
- Maria Abou Chakra
- , Silke Bumann
- & Arne Traulsen
-
Article
| Open Access Predictive modeling of battery degradation and greenhouse gas emissions from U.S. state-level electric vehicle operation
Predictive modeling of battery degradation and greenhouse gas emissions from U.S. state-level electric vehicle operation
The effects of battery degradation on the energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions from electric vehicles are unknown. Here the authors show that the lifetime of a typical battery is between 5.2 and 13.3 years across the U.S., with an 11.5–16.2% increase in energy consumption and CO2 emissions.
- Fan Yang
- , Yuanyuan Xie
- & Chris Yuan
-
Article
| Open Access Dispositional free riders do not free ride on punishment
Dispositional free riders do not free ride on punishment
Strong positive and strong negative reciprocators reward cooperation and punish defection, respectively, regardless of future benefits. Here, Weber and colleagues demonstrate that dispositions towards strong positive and strong negative reciprocity are not correlated within individuals.
- Till O. Weber
- , Ori Weisel
- & Simon Gächter
-
Article
| Open Access Innovation and cumulative culture through tweaks and leaps in online programming contests
Innovation and cumulative culture through tweaks and leaps in online programming contests
The cumulative development of culture has proven difficult to study in the laboratory. Here, the authors examine entries to a series of large programming contests to show that successful entries are usually ‘tweaks’ of existing solutions, but occasional ‘leaps’ can bring larger benefits.
- Elena Miu
- , Ned Gulley
- & Luke Rendell
-
Article
| Open Access Tolerance to ambiguous uncertainty predicts prosocial behavior
Tolerance to ambiguous uncertainty predicts prosocial behavior
Ambiguous uncertainty refers to situations where the likelihood of specific outcomes are not known. Here, the authors show that people tolerant to ambiguous uncertainty are more likely to make costly decisions to cooperate with or trust others.
- Marc-Lluís Vives
- & Oriel FeldmanHall

 Electrical appliances moderate households’ water demand response to heat
Electrical appliances moderate households’ water demand response to heat