Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access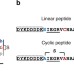 Phage display and selection of lanthipeptides on the carboxy-terminus of the gene-3 minor coat protein
Phage display and selection of lanthipeptides on the carboxy-terminus of the gene-3 minor coat protein
Lanthipeptides are a class of cyclic post-translationally modified peptides with potential drug-like properties. Here the authors develop a phage display system by expressing lanthipeptide precursors as C-terminal fusions to the phage M13 coat protein pIII in E. coli along with the heterologous modifying enzymes.
- Johannes H. Urban
- , Markus A. Moosmeier
- & Josef Prassler
-
Article
| Open Access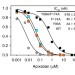 Engineered factor Xa variants retain procoagulant activity independent of direct factor Xa inhibitors
Engineered factor Xa variants retain procoagulant activity independent of direct factor Xa inhibitors
A major drawback in the clinical use of the oral anticoagulants that directly inhibit factor Xa in order to prevent blood clot formation is the potential for life threatening bleeding events. Here the authors describe factor Xa variants that are refractory to inhibition by these anticoagulants and could serve as rescue agents in treated patients.
- Daniël Verhoef
- , Koen M. Visscher
- & Mettine H. A. Bos
-
Article
| Open Access Towards designer organelles by subverting the peroxisomal import pathway
Towards designer organelles by subverting the peroxisomal import pathway
Designer organelles could allow the isolation of synthetic biological pathways from endogenous components of the host cell. Here the authors engineer a peroxisomal protein import pathway orthogonal to the naturally occurring system.
- Laura L. Cross
- , Rupesh Paudyal
- & Stuart L. Warriner
-
Article
| Open Access Improved split fluorescent proteins for endogenous protein labeling
Improved split fluorescent proteins for endogenous protein labeling
Split fluorescent proteins (FPs) have been widely used to visualise proteins in cells. Here the authors develop a screen for engineering new split FPs, and report a yellow-green split-mNeonGreen2 with reduced background, a red split-sfCherry2 for multicolour labeling, and its photoactivatable variant for super-resolution use.
- Siyu Feng
- , Sayaka Sekine
- & Bo Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Construction and in vivo assembly of a catalytically proficient and hyperthermostable de novo enzyme
Construction and in vivo assembly of a catalytically proficient and hyperthermostable de novo enzyme
Catalytic mechanisms of enzymes are well understood, but achieving diverse reaction chemistries in re-engineered proteins can be difficult. Here the authors show a highly efficient and thermostable artificial enzyme that catalyzes a diverse array of substrate oxidations coupled to the reduction of H2O2.
- Daniel W. Watkins
- , Jonathan M. X. Jenkins
- & J. L. Ross Anderson
-
Article
| Open Access De novo active sites for resurrected Precambrian enzymes
De novo active sites for resurrected Precambrian enzymes
The emergence of novel catalytic functions in ancient proteins likely played a role in the evolution of modern enzymes. Here, the authors use protein sequences from Precambrian beta-lactamases and demonstrate that a single hydrophobic-to-ionizable amino acid mutation can lead to substantial Kemp eliminase activity.
- Valeria A. Risso
- , Sergio Martinez-Rodriguez
- & Jose M. Sanchez-Ruiz
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered botulinum neurotoxin B with improved efficacy for targeting human receptors
Engineered botulinum neurotoxin B with improved efficacy for targeting human receptors
Humans are less sensitive to the therapeutic effects of botulinum neurotoxin B (BoNT/B) than the animal models it is tested on due to differences between the human and the mouse receptors. Here, the authors engineer BoNT/B to improve its affinity to human receptors and enhance its therapeutic efficacy.
- Liang Tao
- , Lisheng Peng
- & Min Dong
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient protein production inspired by how spiders make silk
Efficient protein production inspired by how spiders make silk
The properties of many transmembrane or aggregation-prone proteins make them difficult to recombinantly express. Here the authors use a modified N-terminal domain of a spider silk protein to express and purify several difficult to express proteins at levels considerably higher than with conventional tags.
- Nina Kronqvist
- , Médoune Sarr
- & Jan Johansson
-
Article
| Open Access Improving 10-deacetylbaccatin III-10-β-O-acetyltransferase catalytic fitness for Taxol production
Improving 10-deacetylbaccatin III-10-β-O-acetyltransferase catalytic fitness for Taxol production
Taxol is a widely used anticancer drug that is found in very low amounts in the bark of Taxus plants. Here, the authors improve the catalytic fitness of DBAT, an enzyme that catalyses the conversion of tree by products into taxol, enabling the design of anin vitrobiochemical systems for taxol production.
- Bing-Juan Li
- , Hao Wang
- & Ping Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Antibody targeting intracellular oncogenic Ras mutants exerts anti-tumour effects after systemic administration
Antibody targeting intracellular oncogenic Ras mutants exerts anti-tumour effects after systemic administration
Oncogenic RAS mutants are key anti-cancer targets as KRas mutations are very frequent in human cancers. Here, the authors engineer a cytosol-penetrating anti-Ras antibody and demonstrate its ability to block RAS-effector protein interactions inhibiting tumour growth of Ras mutant-driven cancers.
- Seung-Min Shin
- , Dong-Ki Choi
- & Yong-Sung Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Long-acting protein drugs for the treatment of ocular diseases
Long-acting protein drugs for the treatment of ocular diseases
Retinal vascular disease treatments involve frequent pharmacological intraocular administrations. Here the authors present a method to increase the half-life of injected drugs by fusing these to a hyaluronan-binding peptide, which might lead to less frequent retinal disease treatments.
- Joy G. Ghosh
- , Andrew A. Nguyen
- & Michael Roguska
-
Article
| Open Access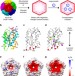 Structure and assembly of scalable porous protein cages
Structure and assembly of scalable porous protein cages
Self-assembling proteins that form capsid-like structures act as molecular containers for diverse cargoes. Here, the authors solve the cryo-EM structures of lumazine synthase shells, and show that supercharged mutants form expanded assemblies, indicating that electrostatics can be exploited to engineer cage architecture.
- Eita Sasaki
- , Daniel Böhringer
- & Donald Hilvert
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering fungal de novo fatty acid synthesis for short chain fatty acid production
Engineering fungal de novo fatty acid synthesis for short chain fatty acid production
The production of short chain fatty acids by microorganisms has numerous industrial and biofuel applications. Here the authors reprogrammeS. cerevisiaefatty acid synthase with five mutations to produce C6- and C8-fatty acids and identify thioesterases responsible for hydrolysis of short chain acyl-CoA hydrolysis.
- Jan Gajewski
- , Renata Pavlovic
- & Martin Grininger
-
Article
| Open Access Correlation of fitness landscapes from three orthologous TIM barrels originates from sequence and structure constraints
Correlation of fitness landscapes from three orthologous TIM barrels originates from sequence and structure constraints
The TIM barrel fold is an evolutionarily conserved motif found in proteins with a variety of enzymatic functions. Here the authors explore the fitness landscape of the TIM barrel protein IGPS and uncover evolutionary constraints on both sequence and structure, accompanied by long range allosteric interactions.
- Yvonne H. Chan
- , Sergey V. Venev
- & C. Robert Matthews
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid construction of metabolite biosensors using domain-insertion profiling
Rapid construction of metabolite biosensors using domain-insertion profiling
In the construction of single fluorescent protein biosensors, selection of the insertion point of a fluorescent protein into a ligand-binding domain is a rate-limiting step. Here, the authors develop an unbiased, high-throughput approach, called domain insertion profiling with DNA sequencing (DIP-seq), to generate a novel trehalose biosensor.
- Dana C. Nadler
- , Stacy-Anne Morgan
- & David F. Savage
-
Article
| Open Access Rational design of a protein that binds integrin αvβ3 outside the ligand binding site
Rational design of a protein that binds integrin αvβ3 outside the ligand binding site
Integrins are transmembrane proteins that have important roles in cell adhesion and signalling. Here the authors design a therapeutic protein that binds integrin αvβ3, has anti-angiogenic activity, and reduces tumour growth in xenograft models, while being seemingly well tolerated.
- Ravi Chakra Turaga
- , Lu Yin
- & Zhi-Ren Liu
-
Article
| Open Access A method to rapidly create protein aggregates in living cells
A method to rapidly create protein aggregates in living cells
Protein aggregates are associated with a wide variety of diseases. Here, in order to address how protein aggregation affects cellular homoeostasis, the authors describe a method to rapidly create protein aggregates in living cells and organisms with precise spatial and temporal control.
- Yusuke Miyazaki
- , Kota Mizumoto
- & Thomas J. Wandless
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for specific single-stranded RNA recognition by designer pentatricopeptide repeat proteins
Structural basis for specific single-stranded RNA recognition by designer pentatricopeptide repeat proteins
Pentatricopeptide repeat (PPR) proteins bind RNA and are involved in the regulation of RNA metabolism in eukaryotes. Here, the authors examine the capability of these proteins as modules for gene manipulation using structural biology methods.
- Cuicui Shen
- , Delin Zhang
- & Ping Yin
-
Article
| Open Access Production of unstable proteins through the formation of stable core complexes
Production of unstable proteins through the formation of stable core complexes
Flexible or disordered domains often hinder the purification of proteins involved in functional interactions. Here the authors describe an approach that enables the production of stable and functional complexes of otherwise unstable proteins in quantities sufficient for structural and functional studies.
- Nicolas Levy
- , Sylvia Eiler
- & Marc Ruff
-
Article
| Open Access Connecting two proteins using a fusion alpha helix stabilized by a chemical cross linker
Connecting two proteins using a fusion alpha helix stabilized by a chemical cross linker
Linking protein components in a controlled manner is crucial for assembling protein nanostructures with pre-determined architecture. Here, the authors use a chemical cross-linker to fuse the terminal helices of two proteins into a single one, forcing the protein domains in a specific orientation.
- Woo Hyeon Jeong
- , Haerim Lee
- & Jie-Oh Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Modulating protein activity using tethered ligands with mutually exclusive binding sites
Modulating protein activity using tethered ligands with mutually exclusive binding sites
Designing proteins whose activities can be switched on and off by effector molecules is a central challenge in protein engineering. Here, the authors use tethered chemical ligands with two mutually exclusive binding sites as a general method to modulate protein activity in response to specific effectors.
- Alberto Schena
- , Rudolf Griss
- & Kai Johnsson
-
Article |
 De novo branching cascades for structural and functional diversity in small molecules
De novo branching cascades for structural and functional diversity in small molecules
Generating diverse structures with a minimum amount of synthetic effort is an important goal for drug discovery. Here, the authors report a two-phase synthesis for the generation of skeletally diverse small molecules—forming molecular scaffolds and subsequently diversifying each into multiple structures.
- Miguel Garcia-Castro
- , Lea Kremer
- & Kamal Kumar
-
Article |
 Protein design with a comprehensive statistical energy function and boosted by experimental selection for foldability
Protein design with a comprehensive statistical energy function and boosted by experimental selection for foldability
Methods to design proteins de novo can give insights into how amino acids fold into particular structures and aid in protein engineering. Here, Xiong et al. compare a novel statistical energy function with established methods and use it to generate four de novoproteins.
- Peng Xiong
- , Meng Wang
- & Haiyan Liu
-
Article |
 Ionic polypeptides with unusual helical stability
Ionic polypeptides with unusual helical stability
Water-soluble peptides with stable α-helical conformations are desirable for a range of applications, but incorporating charged residues to improve solubility usually leads to reduced helical stability. Here, polypeptides produced from amino acids with elongated charged side chains are found to be water soluble and exhibit very high helical stability.
- Hua Lu
- , Jing Wang
- & Jianjun Cheng

 Restoration of patterned vision with an engineered photoactivatable G protein-coupled receptor
Restoration of patterned vision with an engineered photoactivatable G protein-coupled receptor