Featured
-
-
Article |
 Flatband λ-Ti3O5 towards extraordinary solar steam generation
Flatband λ-Ti3O5 towards extraordinary solar steam generation
A route to greatly elevate joint densities of states by introducing a flat-band electronic structure is demonstrated, showing metallic λ-Ti3O5 powders have a high solar absorptivity and offering insights into access to cost-effective solar-to-steam generation.
- Bo Yang
- , Zhiming Zhang
- & Liang Zuo
-
Article |
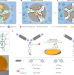 Near-frictionless ion transport within triazine framework membranes
Near-frictionless ion transport within triazine framework membranes
The authors develop a strategy that allows the diffusion limit of ions in water to be approached for large-area, free-standing, synthetic membranes using covalently bonded polymer frameworks with rigidity-confined ion channels.
- Peipei Zuo
- , Chunchun Ye
- & Tongwen Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Aligned macrocycle pores in ultrathin films for accurate molecular sieving
Aligned macrocycle pores in ultrathin films for accurate molecular sieving
Selectively functionalized macrocycles were synthesized with reactivities that preferentially aligned to create well-defined pores across an ultrathin nanofilm offering a strategy to create subnanometre channels in polymer membranes, and demonstrating potential for accurate molecular separations.
- Zhiwei Jiang
- , Ruijiao Dong
- & Andrew G. Livingston
-
Article |
 Atomic imaging of zeolite-confined single molecules by electron microscopy
Atomic imaging of zeolite-confined single molecules by electron microscopy
Using integrated differential phase contrast scanning transmission electron microscopy, the atomic imaging of single pyridine and thiophene molecules identifies host–guest interactions in zeolite ZSM-5 and their adsorption and desorption behaviours can be studied.
- Boyuan Shen
- , Huiqiu Wang
- & Fei Wei
-
Article |
 Asymmetric pore windows in MOF membranes for natural gas valorization
Asymmetric pore windows in MOF membranes for natural gas valorization
A metal–organic framework membrane based on fumarate and mesaconate linkers is shown to have a pore aperture shape that enables efficient and cost-effective removal of nitrogen and carbon dioxide from methane.
- Sheng Zhou
- , Osama Shekhah
- & Mohamed Eddaoudi
-
Article
| Open Access Reconstructed covalent organic frameworks
Reconstructed covalent organic frameworks
A protocol in which monomers are pre-organized using a reversible and removable urea linkage enables the production of covalent organic frameworks with higher crystallinity and porosity than those produced using standard approaches with randomly aligned monomers.
- Weiwei Zhang
- , Linjiang Chen
- & Andrew I. Cooper
-
Article |
 A single-molecule van der Waals compass
A single-molecule van der Waals compass
The orientation of a rotating para-xylene molecule in the nanochannel of a zeolite framework can be visualised by electron microscopy to determine the host–guest van der Waals interaction inside the channel.
- Boyuan Shen
- , Xiao Chen
- & Fei Wei
-
Article |
 Diversity-oriented synthesis of polymer membranes with ion solvation cages
Diversity-oriented synthesis of polymer membranes with ion solvation cages
A diversity-oriented synthesis approach that yields a library of architecturally broad microporous polymers is used to develop structurally diverse polymer membranes with ion specificity and to screen their properties.
- Miranda J. Baran
- , Mark E. Carrington
- & Brett A. Helms
-
Article |
 Additive manufacturing of silica aerogels
Additive manufacturing of silica aerogels
A direct ink writing protocol for silica aerogels enables 3D printing of lightweight, miniaturized objects with complex shapes, with the possibility to easily add functionality by incorporating nanoparticles.
- Shanyu Zhao
- , Gilberto Siqueira
- & Wim J. Malfait
-
Article |
 Functional materials discovery using energy–structure–function maps
Functional materials discovery using energy–structure–function maps
Energy–structure–function maps that describe the possible structures and properties of molecular crystals are developed, and these maps are used to guide the experimental discovery of porous materials with specific functions.
- Angeles Pulido
- , Linjiang Chen
- & Graeme M. Day
-
Letter |
 Ultra-selective high-flux membranes from directly synthesized zeolite nanosheets
Ultra-selective high-flux membranes from directly synthesized zeolite nanosheets
A direct synthesis of high-aspect-ratio microporous zeolite nanosheets and the use of such nanosheets in separation membranes are described.
- Mi Young Jeon
- , Donghun Kim
- & Michael Tsapatsis
-
Letter |
 Lanthanum-catalysed synthesis of microporous 3D graphene-like carbons in a zeolite template
Lanthanum-catalysed synthesis of microporous 3D graphene-like carbons in a zeolite template
A long-sought three-dimensional graphene-like carbon structure that resembles periodically networked carbon nanotubes is now readily available through lanthanum-catalysed carbon synthesis using a zeolite template.
- Kyoungsoo Kim
- , Taekyoung Lee
- & Ryong Ryoo
-
Letter |
 Methane storage in flexible metal–organic frameworks with intrinsic thermal management
Methane storage in flexible metal–organic frameworks with intrinsic thermal management
Two flexible metal-organic frameworks are presented as solid adsorbents for methane that undergo reversible phase transitions at specific methane pressures, enabling greater storage capacities of usable methane than have been achieved previously, while also providing internal heat management of the system.
- Jarad A. Mason
- , Julia Oktawiec
- & Jeffrey R. Long
-
Letter |
 A zeolite family with expanding structural complexity and embedded isoreticular structures
A zeolite family with expanding structural complexity and embedded isoreticular structures
The complex structure of zeolite ZSM-25 is determined and a family of related structures are identified by using electron diffraction to uncover the structural ‘coding’ within them; this enabled the synthesis of two more-complex zeolites in the family.
- Peng Guo
- , Jiho Shin
- & Xiaodong Zou
-
Letter |
 Mesoporous TiO2 single crystals delivering enhanced mobility and optoelectronic device performance
Mesoporous TiO2 single crystals delivering enhanced mobility and optoelectronic device performance
A new low-temperature synthetic method of growing semiconductor mesoporous single crystals of titanium dioxide is described; the resulting films have much higher conductivities and electron mobilities than nanocrystalline titanium dioxide.
- Edward J. W. Crossland
- , Nakita Noel
- & Henry J. Snaith
-
Letter |
 Porous materials with optimal adsorption thermodynamics and kinetics for CO2 separation
Porous materials with optimal adsorption thermodynamics and kinetics for CO2 separation
A series of porous crystalline materials known as metal–organic materials are prepared, and a full sorption study shows that controlled pore size (rather than large surface area) coupled with appropriate chemistry lead to materials exhibiting fast and highly selective CO2 sorption.
- Patrick Nugent
- , Youssef Belmabkhout
- & Michael J. Zaworotko
-
News & Views |
 Thin films with a hidden twist
Thin films with a hidden twist
Many naturally occurring substances have a 'handedness' that enables them to interact highly specifically with matter or light. The helical features responsible for this can now be replicated in solid, porous films. See Letter p.422
- Andreas Stein
-
Letter |
 Free-standing mesoporous silica films with tunable chiral nematic structures
Free-standing mesoporous silica films with tunable chiral nematic structures
Some beetle shells exhibit iridescence owing to the chiral organization of chitin making up the beetle's exoskeleton. Inspired by this, these authors fabricate thin glass films with helical pores introduced using a renewable cellulose template. The chiral structure allows the material, which can be free-standing, to selectively reflect light at a specific wavelength that can be tuned across the visible spectrum by altering the ratio of silica to cellulose during synthesis.
- Kevin E. Shopsowitz
- , Hao Qi
- & Mark J. MacLachlan

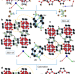 Interchain-expanded extra-large-pore zeolites
Interchain-expanded extra-large-pore zeolites