Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access EARLY BUD-BREAK 1 and EARLY BUD-BREAK 3 control resumption of poplar growth after winter dormancy
EARLY BUD-BREAK 1 and EARLY BUD-BREAK 3 control resumption of poplar growth after winter dormancy
An AP2/ERF family gene EBB1 and a MADS-box gene SVL encode two regulators of poplar bud break. Here, the authors report another AP2/ERF transcription factor EBB3, which functions together with EBB1, SVL, and cell cycle progression promoter CYCD3.1 to regulate poplar bud break.
- Abdul Azeez
- , Yiru Chen Zhao
- & Victor B. Busov
-
Article
| Open Access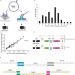 Sequencing of the Arabidopsis NOR2 reveals its distinct organization and tissue-specific rRNA ribosomal variants
Sequencing of the Arabidopsis NOR2 reveals its distinct organization and tissue-specific rRNA ribosomal variants
The nucleolus organizing region (NOR) consists of multiple, highly repetitive rDNA genes. Here Sims et al. use both long- and short-read sequencing to determine the organization and sequence of Arabidopsis NOR2 rDNA and show that different rRNA gene variants are integrated into translating ribosomes in a tissue-specific manner.
- Jason Sims
- , Giovanni Sestini
- & Peter Schlögelhofer
-
Article
| Open Access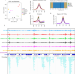 H2AK121ub in Arabidopsis associates with a less accessible chromatin state at transcriptional regulation hotspots
H2AK121ub in Arabidopsis associates with a less accessible chromatin state at transcriptional regulation hotspots
Polycomb Group complexes maintain gene repression through the incorporation of H2AK121ub and H3K27me3. Here, the authors show that H2AK121ub marks less accessible but transcriptionally permissive chromatin, while H3K27me3 enforces a repressed transcriptionally less-permissive state.
- Xiaochang Yin
- , Francisco J. Romero-Campero
- & Yue Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access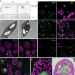 Condensation of Rubisco into a proto-pyrenoid in higher plant chloroplasts
Condensation of Rubisco into a proto-pyrenoid in higher plant chloroplasts
Introducing the pyrenoid-based CO2-concentrating mechanism of green algae into crops could greatly improve photosynthesis. Here, the authors show that expression of the algal linker protein EPYC1 and a plant-algal hybrid Rubisco in Arabidopsis chloroplasts leads to formation of a phase separated algal-like proto-pyrenoid.
- Nicky Atkinson
- , Yuwei Mao
- & Alistair J. McCormick
-
Article
| Open Access Coupling of H3K27me3 recognition with transcriptional repression through the BAH-PHD-CPL2 complex in Arabidopsis
Coupling of H3K27me3 recognition with transcriptional repression through the BAH-PHD-CPL2 complex in Arabidopsis
Histone 3 Lys 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) mediates epigenetic silencing of gene expression. Here, Zhang et al. show that in Arabidopsis, the BAH-domain H3K27me3-reader protein AIPP3 forms a complex with PHD proteins and CPL2, a plant-specific Pol II phosphatase, to inhibit Pol II activity by dephosphorylation.
- Yi-Zhe Zhang
- , Jianlong Yuan
- & Cheng-Guo Duan
-
Article
| Open Access Evidences for a role of two Y-specific genes in sex determination in Populus deltoides
Evidences for a role of two Y-specific genes in sex determination in Populus deltoides
Dioecy has evolved independently from hermaphroditic ancestors in different plant lineages. Here, the authors assemble Populus deltoides male and female genomes, and show the putative roles of a femaleness gene and a maleness gene in sex determination, which suggests independent evolution in different poplar species.
- Liangjiao Xue
- , Huaitong Wu
- & Tongming Yin
-
Article
| Open Access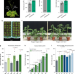 MSH1-induced heritable enhanced growth vigor through grafting is associated with the RdDM pathway in plants
MSH1-induced heritable enhanced growth vigor through grafting is associated with the RdDM pathway in plants
The meiotic transmissibility and progeny phenotypic influence of graft-mediated epigenetic changes remain unclear. Here, the authors use the msh1 mutant in the rootstock to trigger heritable enhanced growth vigor in Arabidopsis and tomato, and show it is associated with the RNA-directed DNA methylation pathway.
- Hardik Kundariya
- , Xiaodong Yang
- & Sally A. Mackenzie
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of key sequence features required for microRNA biogenesis in plants
Identification of key sequence features required for microRNA biogenesis in plants
The secondary structure of miRNA precursor sequences is known to affect processing by DICER-like proteins. Here Rojas et al. show that additional sequence features also play a regulatory role in plants with nucleotide identity at unpaired positions substantially impacting processing efficiency.
- Arantxa M. L. Rojas
- , Salvador I. Drusin
- & Javier F. Palatnik
-
Article
| Open Access Specific features and assembly of the plant mitochondrial complex I revealed by cryo-EM
Specific features and assembly of the plant mitochondrial complex I revealed by cryo-EM
Electrons enter the mitochondrial respiratory chain via complex I. Here, the authors report high-resolution structures of mature plant complex I and one of its assembly intermediates, highlighting plant-specific features including an ancestral carbonic anhydrase domain.
- Heddy Soufari
- , Camila Parrot
- & Yaser Hashem
-
Article
| Open Access Reconstructing the maize leaf regulatory network using ChIP-seq data of 104 transcription factors
Reconstructing the maize leaf regulatory network using ChIP-seq data of 104 transcription factors
Transcriptional factors (TFs) bind in a combinatorial fashion to specify the on-and-off states of genes in a complex and redundant regulatory network. Here, the authors construct the transcription regulatory network in maize leaf using 104 TFs ChIP-seq data and train machine learning models to predict TF binding and colocalization.
- Xiaoyu Tu
- , María Katherine Mejía-Guerra
- & Silin Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access A trimeric CrRLK1L-LLG1 complex genetically modulates SUMM2-mediated autoimmunity
A trimeric CrRLK1L-LLG1 complex genetically modulates SUMM2-mediated autoimmunity
MAPK signaling suppresses autoimmunity mediated by the SUMM2 receptor in Arabidopsis. Here Huang et al. show that a trimeric complex consisting of the GPI anchored protein LLG1, and the two receptor-like proteins LET1 and LET2, promotes activation of SUMM2 according to MAPK signaling status.
- Yanyan Huang
- , Chuanchun Yin
- & Ping He
-
Article
| Open Access A moonlighting role for enzymes of glycolysis in the co-localization of mitochondria and chloroplasts
A moonlighting role for enzymes of glycolysis in the co-localization of mitochondria and chloroplasts
Protein-protein interactions are thought to channel substrates between consecutive enzymes during glycolysis. Here the authors show that Arabidopsis phosphoglycerate mutase and enolase can form a substrate-channelling metabolon and also play a moonlighting role in promoting colocalization of chloroplasts and mitochondria.
- Youjun Zhang
- , Arun Sampathkumar
- & Alisdair R. Fernie
-
Article
| Open Access Changing local recombination patterns in Arabidopsis by CRISPR/Cas mediated chromosome engineering
Changing local recombination patterns in Arabidopsis by CRISPR/Cas mediated chromosome engineering
The heterochromatic knob (hk4S) on Arabidopsis chromosome 4 prevents the recombination between accessions with and without hk4S. Here, via egg-cell specific expression of the Cas9 nuclease, the authors demonstrate targeted reversal of the 1.1 Mb long hk4S-inversion in Col-0 and restore the crossovers with Ler-1.
- Carla Schmidt
- , Paul Fransz
- & Holger Puchta
-
Article
| Open Access KIN10 promotes stomatal development through stabilization of the SPEECHLESS transcription factor
KIN10 promotes stomatal development through stabilization of the SPEECHLESS transcription factor
Stomata development in plants is tightly regulated by developmental and environmental cues. Here the authors show that the energy-sensing SnRK1 complex promotes stomatal development by phosphorylating the SPEECHLESS transcription factor thereby connecting energy signalling and stomatal development.
- Chao Han
- , Yue Liu
- & Ming-Yi Bai
-
Article
| Open Access Proximity labeling proteomics reveals critical regulators for inner nuclear membrane protein degradation in plants
Proximity labeling proteomics reveals critical regulators for inner nuclear membrane protein degradation in plants
Maintaining protein integrity at the inner nuclear membrane (INM) is critical for eukaryotic cellular function. Here, using proximity-labeling proteomics, Huang et al. profile the INM in Arabidopsis and identify the CDC48 complex and PUX proteins as components of an INM protein degradation pathway.
- Aobo Huang
- , Yu Tang
- & Yangnan Gu
-
Article
| Open Access miR2118-dependent U-rich phasiRNA production in rice anther wall development
miR2118-dependent U-rich phasiRNA production in rice anther wall development
MicroRNA2118 induces the production of phased small interfering RNAs (phaisRNAs) in plants. Here the authors show that rice miR2118 is required for both male and female fertility and supports the production of atypical U-rich 21 nt phasiRNAs that are abundant in anther walls.
- Saori Araki
- , Ngoc Tu Le
- & Reina Komiya
-
Article
| Open Access The characterization of Mediator 12 and 13 as conditional positive gene regulators in Arabidopsis
The characterization of Mediator 12 and 13 as conditional positive gene regulators in Arabidopsis
Mediator is a multiprotein complex required to activate gene transcription by RNAPII. Here, the authors report that MED12 and MED13 are conditional positive regulators that facilitate the expression of genes depleted in active chromatin marks and the induction of gene expression in response to environmental stimuli in Arabidopsis.
- Qikun Liu
- , Sylvain Bischof
- & Steven E. Jacobsen
-
Article
| Open Access Transcript isoform sequencing reveals widespread promoter-proximal transcriptional termination in Arabidopsis
Transcript isoform sequencing reveals widespread promoter-proximal transcriptional termination in Arabidopsis
Gene isoforms result from variable transcription start sites (TSSs) and polyadenylation sites (PASs) at the end of transcripts. Here, the authors perform transcript isoform sequencing and find widespread promoter- proximal transcriptional termination in Arabidopsis, suggesting this may represent a checkpoint that regulates plant gene expression.
- Quentin Angelo Thomas
- , Ryan Ard
- & Sebastian Marquardt
-
Article
| Open Access A common allosteric mechanism regulates homeostatic inactivation of auxin and gibberellin
A common allosteric mechanism regulates homeostatic inactivation of auxin and gibberellin
Enzymatic inactivation of gibberellins and auxin, via GA2ox3 and DAO respectively, contributes to hormone homeostasis in plants. Here Takehara et al. show that both enzymes multimerize in a substrate-concentration-dependent manner, and that this multimerization leads to increased enzyme activity.
- Sayaka Takehara
- , Shun Sakuraba
- & Miyako Ueguchi-Tanaka
-
Article
| Open Access Repressive chromatin modification underpins the long-term expression trend of a perennial flowering gene in nature
Repressive chromatin modification underpins the long-term expression trend of a perennial flowering gene in nature
The flowering regulator FLC shows upregulation and downregulation phases along with long-term past temperature in Arabidopsis halleri. Here, the authors reveal that H3K27me3-mediated chromatin regulation at AhgFLC provides the ability to respond to both the seasonal temperature trends and the perennial life cycle.
- Haruki Nishio
- , Diana M. Buzas
- & Hiroshi Kudoh
-
Article
| Open Access Plant Raf-like kinases regulate the mRNA population upstream of ABA-unresponsive SnRK2 kinases under drought stress
Plant Raf-like kinases regulate the mRNA population upstream of ABA-unresponsive SnRK2 kinases under drought stress
SnRK2 protein kinases play key roles in signaling during plant responses to abiotic stress. Here Soma et al. report three Arabidopsis Raf-like MAP kinase kinase kinases phosphorylate and activate a subclass of SnRK2s that rapidly respond to osmotic stress independently of ABA signaling.
- Fumiyuki Soma
- , Fuminori Takahashi
- & Kazuko Yamaguchi-Shinozaki
-
Article
| Open Access Transposon age and non-CG methylation
Transposon age and non-CG methylation
RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM) is thought to silence newly inserted transposable elements (TEs) with RNA-independent mechanisms becoming more prominent as TEs age. Here, the authors show that RdDM continues to silence the oldest intact distal TEs in tomato and Arabidopsis suggesting a second, later phase of RdDM.
- Zhengming Wang
- & David C. Baulcombe
-
Article
| Open Access Marker-free carotenoid-enriched rice generated through targeted gene insertion using CRISPR-Cas9
Marker-free carotenoid-enriched rice generated through targeted gene insertion using CRISPR-Cas9
Existing examples of targeted gene insertion in plants either rely on a selectable marker gene or result in short DNA inserts. Here, the authors use an optimized CRISPR-Cas9 method to insert a 5.2 kb carotenoid biosynthesis cassette into genomic safe harbors in rice, and obtain marker-free lines with high carotenoid content.
- Oliver Xiaoou Dong
- , Shu Yu
- & Pamela C. Ronald
-
Article
| Open Access Transient genome-wide interactions of the master transcription factor NLP7 initiate a rapid nitrogen-response cascade
Transient genome-wide interactions of the master transcription factor NLP7 initiate a rapid nitrogen-response cascade
Conventional methods cannot reveal transient transcription factors (TFs) and targets interactions. Here, Alvarez et al. capture both stable and transient TF-target interactions by time-series ChIP-seq and/or DamID-seq in a cell-based TF perturbation system and show NLP7 as a master TF to initiate a rapid nitrogen-response cascade.
- José M. Alvarez
- , Anna-Lena Schinke
- & Gloria M. Coruzzi
-
Article
| Open Access The receptor-like kinase NIK1 targets FLS2/BAK1 immune complex and inversely modulates antiviral and antibacterial immunity
The receptor-like kinase NIK1 targets FLS2/BAK1 immune complex and inversely modulates antiviral and antibacterial immunity
Plants deploy numerous receptor-like kinases (RLKs) to respond to pathogens. Here the authors show that NIK1, an RLK that positively regulates antiviral immunity, negatively regulates the response to bacteria by modulating FLS2/BAK1 complex formation, suggesting crosstalk between bacterial and viral immunity.
- Bo Li
- , Marco Aurélio Ferreira
- & Elizabeth P. B. Fontes
-
Article
| Open Access FIERY1 promotes microRNA accumulation by suppressing rRNA-derived small interfering RNAs in Arabidopsis
FIERY1 promotes microRNA accumulation by suppressing rRNA-derived small interfering RNAs in Arabidopsis
Arabidopsis AGO1 binds both microRNA (miRNA) and endogenous small interfering RNA (siRNA). Here the authors show that 5′−3′ RNA degradation suppresses siRNA biogenesis from ribosomal RNA to prevent overloading of AGO1 with ribosomal siRNA and maintain miRNA-directed post translational gene silencing.
- Chenjiang You
- , Wenrong He
- & Beixin Mo
-
Article
| Open Access Ethylene-mediated nitric oxide depletion pre-adapts plants to hypoxia stress
Ethylene-mediated nitric oxide depletion pre-adapts plants to hypoxia stress
Plant hypoxia responses are controlled by oxygen and nitric oxide (NO)-dependent proteolysis of ERFVII transcription factors. Here Hartman et al. show that passive ethylene entrapment during root submergence enhances NO-scavenger PHYTOGLOBIN1, ERFVII stability and promotes subsequent hypoxia tolerance.
- Sjon Hartman
- , Zeguang Liu
- & Laurentius A. C. J. Voesenek
-
Article
| Open Access CryoEM structures of Arabidopsis DDR complexes involved in RNA-directed DNA methylation
CryoEM structures of Arabidopsis DDR complexes involved in RNA-directed DNA methylation
RNA polymerase V transcription in plants, which is needed DNA methylation and transcriptional silencing, requires components of the DDR complex. Here the authors show that all components of the DDR complex co-localize with Pol V and report the cryoEM structures of two complexes associated with Pol V recruitment.
- Somsakul Pop Wongpalee
- , Shiheng Liu
- & Steven E. Jacobsen
-
Article
| Open Access RST1 and RIPR connect the cytosolic RNA exosome to the Ski complex in Arabidopsis
RST1 and RIPR connect the cytosolic RNA exosome to the Ski complex in Arabidopsis
Cytosolic RNA degradation by the RNA exosome requires the Ski complex. Here the authors show that the proteins RST1 and RIPR assist the RNA exosome and the Ski complex in RNA degradation, thereby preventing the production of secondary siRNAs from endogenous mRNAs.
- Heike Lange
- , Simon Y. A. Ndecky
- & Dominique Gagliardi
-
Article
| Open Access Arabidopsis SWR1-associated protein methyl-CpG-binding domain 9 is required for histone H2A.Z deposition
Arabidopsis SWR1-associated protein methyl-CpG-binding domain 9 is required for histone H2A.Z deposition
The SWI2/SNF2-Related 1 chromatin remodeling complex (SWR1-C) is important for gene regulation, but its composition remains largely uncharacterized in plants. Here, the authors report that methyl-CpG-binding domain 9 (MBD9) is a SWR1-C interacting protein required for histone H2A.Z deposition in Arabidopsis.
- Magdalena E. Potok
- , Yafei Wang
- & Steven E. Jacobsen
-
Article
| Open Access The transcription factor OsSUF4 interacts with SDG725 in promoting H3K36me3 establishment
The transcription factor OsSUF4 interacts with SDG725 in promoting H3K36me3 establishment
The distribution of H3K36me3 varies between species. Here Liu et al. show that the OsSUF4 transcription factor binds its target motif via a zinc finger domain to promote H3K36 methyltransferase targeting close to the transcription start site of genes including the flowering regulators RFT1 and Hd3a.
- Bing Liu
- , Yuhao Liu
- & Aiwu Dong
-
Article
| Open Access The repressive role of Arabidopsis H2A.Z in transcriptional regulation depends on AtBMI1 activity
The repressive role of Arabidopsis H2A.Z in transcriptional regulation depends on AtBMI1 activity
Arabidopsis H2A.Z plays an important role in regulating gene expression in response to stressors; however, the underlying mechanism is still puzzling. Here, the authors show that monoubiquitination of H2A.Z by AtBMI1 is required for H2A.Z-mediated transcriptional repression.
- Ángeles Gómez-Zambrano
- , Wiam Merini
- & Myriam Calonje
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structure of the plant symporter STP10 illuminates sugar uptake mechanism in monosaccharide transporter superfamily
Crystal structure of the plant symporter STP10 illuminates sugar uptake mechanism in monosaccharide transporter superfamily
Plants are dependent on controlled sugar uptake via Monosaccharide Transporters, such as STP10, for correct organ development, sugar accumulation in fruits and microbial defense. Here authors present the crystal structure of STP10 bound to glucose which sheds light on the fundamental principles of sugar transport in the plant-unique MST superfamily.
- Peter Aasted Paulsen
- , Tânia F. Custódio
- & Bjørn Panyella Pedersen
-
Article
| Open Access Proteasomal degradation of BRAHMA promotes Boron tolerance in Arabidopsis
Proteasomal degradation of BRAHMA promotes Boron tolerance in Arabidopsis
Boron is essential for plant survival but high levels can impair growth and cause DNA damage. Here the authors show that Arabidopsis can ameliorate Boron toxicity via proteasomal degradation of BRAHMA to minimize open chromatin and reduce the likelihood of DNA double strand breaks.
- Takuya Sakamoto
- , Yayoi Tsujimoto-Inui
- & Toru Fujiwara
-
Article
| Open Access Global identification of Arabidopsis lncRNAs reveals the regulation of MAF4 by a natural antisense RNA
Global identification of Arabidopsis lncRNAs reveals the regulation of MAF4 by a natural antisense RNA
Long non-coding RNAs regulate developmental transitions and stress responses in plants. Here Zhao et al. show that a non-coding antisense transcript MAS transcribed from the Arabidopsis MAF4 locus activates H3K4me3 deposition and MAF4 transcription to suppress precocious flowering.
- Xinyue Zhao
- , Jingrui Li
- & Yijun Qi
-
Article
| Open Access The disease resistance protein SNC1 represses the biogenesis of microRNAs and phased siRNAs
The disease resistance protein SNC1 represses the biogenesis of microRNAs and phased siRNAs
A small RNA-based signaling cascade prevents the induction of plant resistance genes (R-genes) in the absence of pathogen challenge. Here Cai et al. show that nuclear accumulation of the R protein SNC1 can activate immunity by suppressing small RNA production and releasing R-gene repression.
- Qiang Cai
- , Chao Liang
- & Xuemei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Transcriptional read-through of the long non-coding RNA SVALKA governs plant cold acclimation
Transcriptional read-through of the long non-coding RNA SVALKA governs plant cold acclimation
The function of most lncRNA is unknown. Here, the authors show that transcriptional read-through at the Arabidopsis SVALKA locus produces a cryptic lncRNA that overlaps with the neighboring cold-responsive CBF1 gene and limits CBF1 expression via an RNA polymerase II collision-based mechanism.
- Peter Kindgren
- , Ryan Ard
- & Sebastian Marquardt
-
Article
| Open Access Daily humidity oscillation regulates the circadian clock to influence plant physiology
Daily humidity oscillation regulates the circadian clock to influence plant physiology
Humidity has been shown to influence many aspects of plant physiology. Here Mwimba et al. show that oscillating humidity entrains the circadian clock under constant light conditions and enhances clock amplitude in simulated natural environments, while also improving immunity and overall growth.
- Musoki Mwimba
- , Sargis Karapetyan
- & Xinnian Dong
-
Article
| Open Access A genetic network mediating the control of bud break in hybrid aspen
A genetic network mediating the control of bud break in hybrid aspen
Molecular mechanism of how temperature-mediated control of bud break in perennial plants remains unclear. Here, the author show that transcriptional factor SHORT VEGETATIVE PHASE-LIKE and its downstream target TCP18 are negative regulators of hybrid aspen bud break.
- Rajesh Kumar Singh
- , Jay P. Maurya
- & Rishikesh P. Bhalerao
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and biochemical insights into small RNA 3′ end trimming by Arabidopsis SDN1
Structural and biochemical insights into small RNA 3′ end trimming by Arabidopsis SDN1
Small RNA degrading nucleases (SDNs) can degrade short RNAs. Here the authors report the crystal structure of Arabidopsis SDN1 in complex with a single-stranded RNA, and provide new insight into 3′ end trimming mechanism of 3′ to 5′ riboexonucleases in the metabolism of various species of small RNAs.
- Jiayi Chen
- , Li Liu
- & Jinbiao Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Footprints of parasitism in the genome of the parasitic flowering plant Cuscuta campestris
Footprints of parasitism in the genome of the parasitic flowering plant Cuscuta campestris
Parasitic lifestyles leave unique genomic footprints. Here, the authors describe the genome sequence of a parasitic plant, Cuscuta campestris, and find that gene losses and host gene acquisitions reflect the independence from photosynthesis and the ability to retain and express chunks of foreign genomic DNA.
- Alexander Vogel
- , Rainer Schwacke
- & Kirsten Krause
-
Article
| Open Access Dual recognition of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 by a plant histone reader SHL
Dual recognition of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 by a plant histone reader SHL
Histone mark reader proteins bind to particular histone modifications and regulate chromatin state. Here, Qian et al. show that the SHORT LIFE reader has a unique ability to recognize both activating and repressive histone marks and that these interactions enable SHORT LIFE to repress flowering in plants.
- Shuiming Qian
- , Xinchen Lv
- & Jiamu Du
-
Article
| Open Access The 3.3 Å structure of a plant geminivirus using cryo-EM
The 3.3 Å structure of a plant geminivirus using cryo-EM
Geminiviruses are an important plant pathogen that causes large food crop losses globally. Here the authors describe a high resolution cryo-EM structure of the Ageratum yellow vein virus and reveal the molecular details of how a single capsid protein sequence can adopt the different conformations needed to build that geminate capsid.
- Emma L. Hesketh
- , Keith Saunders
- & Neil A. Ranson
-
Article
| Open Access TET-mediated epimutagenesis of the Arabidopsis thaliana methylome
TET-mediated epimutagenesis of the Arabidopsis thaliana methylome
In plants, variation in DNA methylation can influence agronomically important traits. Here the authors show that expression of a human Ten-eleven translocation enzyme can generate heritable hypomethylation alleles in Arabidopsis, providing a novel method to manipulate DNA methylation for breeding and research purposes.
- Lexiang Ji
- , William T. Jordan
- & Robert J. Schmitz
-
Article
| Open Access High-resolution spatiotemporal transcriptome mapping of tomato fruit development and ripening
High-resolution spatiotemporal transcriptome mapping of tomato fruit development and ripening
Cell-type transcriptome profiling greatly elucidate organismal development. Here, the authors report a spatiotemporally resolved comprehensive transcriptome analysis of tomato fruit ontogeny and suggest a new model of fruit maturation which initiates in internal tissues then radiates outwards.
- Yoshihito Shinozaki
- , Philippe Nicolas
- & Jocelyn K. C. Rose
-
Article
| Open Access Redox regulation of PEP activity during seedling establishment in Arabidopsis thaliana
Redox regulation of PEP activity during seedling establishment in Arabidopsis thaliana
The plastid-encoded RNA polymerase PEP is regulated according to plastid redox state. Here, the authors show that the redox-regulated PRIN2 protein is reduced to monomeric form in a thiol-dependent manner in response to light and that PRIN2 monomers are required for PEP activity and retrograde signaling.
- Manuel Guinea Díaz
- , Tamara Hernández-Verdeja
- & Åsa Strand
-
Article
| Open Access A hydrophobic anchor mechanism defines a deacetylase family that suppresses host response against YopJ effectors
A hydrophobic anchor mechanism defines a deacetylase family that suppresses host response against YopJ effectors
A subset of α/β hydrolases is known to suppress the pathogen-triggered hypersensitive response (HR) in plants, but their mechanism of action remains unclear. The authors present two crystal structures and functional analyses of these enzymes, showing that HR is suppressed by a previously unknown family of deacetylases.
- Marco Bürger
- , Björn C. Willige
- & Joanne Chory
-
Article
| Open Access RNA degradation by the plant RNA exosome involves both phosphorolytic and hydrolytic activities
RNA degradation by the plant RNA exosome involves both phosphorolytic and hydrolytic activities
The yeast and human RNA exosome is structurally related to prokaryotic phosphorylases but degrades RNA only via associated hydrolytic activities. Here the authors show that the RNA exosome of plants, and likely those of a few basal eukaryotes, combines phosphorolytic and hydrolytic activities to degrade RNA.
- Natalia Sikorska
- , Hélène Zuber
- & Dominique Gagliardi
-
Article
| Open Access An oomycete plant pathogen reprograms host pre-mRNA splicing to subvert immunity
An oomycete plant pathogen reprograms host pre-mRNA splicing to subvert immunity
Various effectors of plant pathogens modulate host cell biology. Here, Huang et al. show PsAvr3c, an avirulence effector from oomycete plant pathogen Phytophthora sojae, can reprogram host pre-mRNA splicing for immune modulation.
- Jie Huang
- , Lianfeng Gu
- & Suomeng Dong

 The TUTase URT1 connects decapping activators and prevents the accumulation of excessively deadenylated mRNAs to avoid siRNA biogenesis
The TUTase URT1 connects decapping activators and prevents the accumulation of excessively deadenylated mRNAs to avoid siRNA biogenesis