Featured
-
-
News |
 Experimental cancer drug resurfaces
Experimental cancer drug resurfaces
Small clinical trial yields promising results for controversial molecule.
- Heidi Ledford
-
Research Highlights |
Genomics: Rat sequencing redux
-
-
Letter |
 MicroRNA-mediated integration of haemodynamics and Vegf signalling during angiogenesis
MicroRNA-mediated integration of haemodynamics and Vegf signalling during angiogenesis
During embryonic development, blood vessels remodel in response to blood flow. Here, a genetic pathway is described through which this mechanosensory stimulus is integrated with early developmental signals to remodel vessels of the aortic arch in zebrafish. It is found that the flow-induced transcription factor klf2a is required to induce the expression of an endothelial-specific microRNA, activating signalling through the growth factor Vegf.
- Stefania Nicoli
- , Clive Standley
- & Nathan D. Lawson
-
Research Highlights |
 Wildlife biology: Fussy eaters
Wildlife biology: Fussy eaters
-
-
-
Letter |
 Curvature in metabolic scaling
Curvature in metabolic scaling
It has been thought that the basal metabolic rate of organisms increases as body mass is raised to some power, p. But the value of p has proved controversial, with both 2/3 and 3/4 being proposed. It is found here that the relationship between mass and metabolic rate does not follow a pure power law at all, and requires a quadratic term to account for curvature. Taking temperature and phylogeny into account, this explains why different data sets have produced different exponents when a power law has been fitted.
- Tom Kolokotrones
- , Van Savage
- & Walter Fontana
-
Research Highlights |
Metabolism: Fat from fructose
-
News & Views |
 There is no single p
There is no single p
Why metabolic rates do not vary in direct proportion to body mass has long been the subject of debate. Progress has been made with the realization that no universal scaling exponent can be applied to them.
- Craig R. White
-
-
Letter |
 Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase/phosphatase may be an ancestral gluconeogenic enzyme
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase/phosphatase may be an ancestral gluconeogenic enzyme
Thermophilic bacteria and archaea use carbon dioxide or carbon monoxide as a starting material for making the organic substances used in cellular molecules. A central enzyme in this pathway has now been discovered, namely fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase/phosphatase. This enzyme might represent the ancestral gluconeogenic enzyme.
- Rafael F. Say
- & Georg Fuchs
-
Letter |
 Primary contribution to zebrafish heart regeneration by gata4+ cardiomyocytes
Primary contribution to zebrafish heart regeneration by gata4+ cardiomyocytes
Zebrafish are able to replace lost heart muscle efficiently, and are used as a model to understand why natural heart regeneration — after a heart attack, for instance — is blocked in mammals. Here, and in an accompanying paper, genetic fate-mapping approaches reveal which cell population contributes prominently to cardiac muscle regeneration after an injury approximating myocardial infarction. The results show that cardiac muscle regenerates through activation and expansion of existing cardiomyocytes, without involving a stem-cell population.
- Kazu Kikuchi
- , Jennifer E. Holdway
- & Kenneth D. Poss
-
Article |
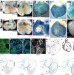 Coronary arteries form by developmental reprogramming of venous cells
Coronary arteries form by developmental reprogramming of venous cells
Prevailing models propose that coronary arteries in the developing heart are formed from progenitor cells originating in the proepicardium. It is found here, however, that these arteries arise from angiogenic sprouts of the major vein that returns circulating blood to the embryonic heart. Thus some differentiated venous cells retain developmental plasticity and respond to local signals to convert to coronary arteries, capillaries and veins.
- Kristy Red-Horse
- , Hiroo Ueno
- & Mark A. Krasnow
-
Article |
 Nitrite-driven anaerobic methane oxidation by oxygenic bacteria
Nitrite-driven anaerobic methane oxidation by oxygenic bacteria
In certain microbes, the anaerobic oxidation of methane can be linked to the reduction of nitrates and nitrites. Here it is shown that this occurs through the intermediate production of oxygen. This brings the number of known biological pathways for oxygen production to four, with implications for our understanding of life on the early Earth.
- Katharina F. Ettwig
- , Margaret K. Butler
- & Marc Strous
-
Letter |
 Zebrafish heart regeneration occurs by cardiomyocyte dedifferentiation and proliferation
Zebrafish heart regeneration occurs by cardiomyocyte dedifferentiation and proliferation
Zebrafish are able to replace lost heart muscle efficiently, and are used as a model to understand why natural heart regeneration — after a heart attack, for instance — is blocked in mammals. Here, and in an accompanying paper, genetic fate-mapping approaches reveal which cell population contributes prominently to cardiac muscle regeneration after an injury approximating myocardial infarction. The results show that cardiac muscle regenerates through activation and expansion of existing cardiomyocytes, without involving a stem-cell population.
- Chris Jopling
- , Eduard Sleep
- & Juan Carlos Izpisúa Belmonte
-
Research Highlights |
Neuroscience: Live-action brain cells
-
News & Views |
 Plumbing the heart
Plumbing the heart
Ever since Leonardo da Vinci sketched the heart vessels in his anatomical notebook in the late fifteenth century, the origin of the coronary vasculature has been in question. We might just have come upon the answer.
- Paul Riley
-
Editorial |
Buyer beware
Lack of US regulation is allowing dubious dietary supplements to be sold as life-enhancing elixirs.
-
Books & Arts |
 Exposing the longevity business
Exposing the longevity business
From caloric restriction to red-grape skins, the anti-ageing industry goes beyond scientific results to market treatments to those who hope to cheat death, cautions S. Jay Olshansky.
- S. Jay Olshansky
-
News & Views |
 NO connection with methane
NO connection with methane
Microorganisms that grow by oxidizing methane come in two basic types, aerobic and anaerobic. Now we have something in between that generates its own supply of molecular oxygen by metabolizing nitric oxide.
- Ronald S. Oremland
-
Review Article |
 Linking functional decline of telomeres, mitochondria and stem cells during ageing
Linking functional decline of telomeres, mitochondria and stem cells during ageing
- Ergün Sahin
- & Ronald A. DePinho
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Neural mechanisms of ageing and cognitive decline
Neural mechanisms of ageing and cognitive decline
- Nicholas A. Bishop
- , Tao Lu
- & Bruce A. Yankner
-
-
News |
 Sperm wars illuminated
Sperm wars illuminated
Insect sperm fight one another with brute force and chemical weapons.
- John Whitfield
-
Letter |
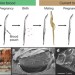 Post-copulatory sexual selection and sexual conflict in the evolution of male pregnancy
Post-copulatory sexual selection and sexual conflict in the evolution of male pregnancy
Male pregnancy is restricted to seahorses, pipefishes and their relatives, in which young are nurtured in the male's brood pouch. It is now clear that the brood pouch has a further function. Studies of Gulf pipefish show that males can selectively abort embryos from females perceived as less attractive, saving resources for more hopeful prospects later. This is the only known example of post-copulatory sexual conflict in a sex-reversed species.
- Kimberly A. Paczolt
- & Adam G. Jones
-
Letter |
 Vascular endothelial growth factor B controls endothelial fatty acid uptake
Vascular endothelial growth factor B controls endothelial fatty acid uptake
VEGF–B is shown to have an unexpected role in targeting lipids to peripheral tissues. VEGF–B controls endothelial uptake of fatty acids via transcriptional regulation of vascular fatty acid transport proteins. Bioinformatic analyses suggest that the uptake of these lipids is tightly coupled with lipid use by mitochondria. Mice that do not have VEGF–B accumulate less lipids in muscle, heart and brown adipose tissue, and instead shunt them to white adipose tissue.
- Carolina E. Hagberg
- , Annelie Falkevall
- & Ulf Eriksson
-
Article |
 Somatic sex identity is cell autonomous in the chicken
Somatic sex identity is cell autonomous in the chicken
In mammals, embryos are considered to be sexually indifferent until the action of a sex-determining gene initiates gonadal differentiation. Here it is demonstrated that this situation is different for birds. Using rare, naturally occurring chimaeric chickens where one side of the animal appears male and the other female, it is shown that avian somatic cells possess an inherent sex identity and that, in birds, sexual differentiation is cell autonomous.
- D. Zhao
- , D. McBride
- & M. Clinton
-
Research Highlights |
Metabolism: Warm milk
-
Letter |
 SIRT3 regulates mitochondrial fatty-acid oxidation by reversible enzyme deacetylation
SIRT3 regulates mitochondrial fatty-acid oxidation by reversible enzyme deacetylation
During fasting SIRT3 is induced in liver and brown adipose tissue. One of SIRT3's substrates is shown to be long–chain acyl co-enzyme A dehydrogenase (LCAD). Without SIRT3 LCAD becomes hyperacetylated, which diminishes its activity, and reduces fatty acid oxidation. Mice without SIRT3 have all the hallmarks of fatty acid oxidation disorders during fasting, including reduced ATP levels and intolerance to cold. Thus, acetylation is a novel regulatory mechanism for fatty acid oxidation.
- Matthew D. Hirschey
- , Tadahiro Shimazu
- & Eric Verdin
-
Research Highlights |
Biology: Stayin' alive
-
News |
 Why the body isn't thirsty at night
Why the body isn't thirsty at night
Body clock is a hormonal dimmer switch that controls water loss.
- Andrew Bennett Hellman
-
Article |
 Orm family proteins mediate sphingolipid homeostasis
Orm family proteins mediate sphingolipid homeostasis
Mutations near the ORMDL3 gene have been associated with childhood asthma. Here, in yeast, Orm proteins are shown to function in sphingolipid homeostasis; alterations in this control result in misregulation of sphingolipid production and accumulation of toxic metabolites. This raises the testable hypothesis that misregulation of sphingolipids may directly contribute to the development of asthma.
- David K. Breslow
- , Sean R. Collins
- & Jonathan S. Weissman
-
News & Views |
 A brake on lipid synthesis
A brake on lipid synthesis
Although sphingolipids are vital cellular components, the path to their production is paved with toxic intermediates. Orm proteins allow cells to form these lipids without killing themselves in the process.
- Fikadu G. Tafesse
- & Joost C. M. Holthuis
-
Letter |
 Sister chromosome pairing maintains heterozygosity in parthenogenetic lizards
Sister chromosome pairing maintains heterozygosity in parthenogenetic lizards
The existence of all-female species of whiptail lizard, formed as a hybrid between sexual species, has been known since 1962; however, how the meiotic program is altered to produce diploid eggs while maintaining heterozygosity has remained unclear. Here it is shown in parthenogenetic species that meiosis initiates with twice the number of chromosomes compared to sexual species, and that pairing and recombination takes place between genetically identical sister chromosomes instead of between homologues.
- Aracely A. Lutes
- , William B. Neaves
- & Peter Baumann
-
Article |
 Rfx6 directs islet formation and insulin production in mice and humans
Rfx6 directs islet formation and insulin production in mice and humans
Pancreatic β-cells release insulin, which controls energy homeostasis in vertebrates, and its lack causes diabetes mellitus. The transcription factor neurogenin 3 (Neurog3) initiates differentiation of β-cells and other islet cell types from pancreatic endoderm; here, the transcription factor Rfx6 is shown to direct islet cell differentiation downstream of Neurog3 in mice and humans. This may be useful in efforts to generate β-cells for patients with diabetes.
- Stuart B. Smith
- , Hui-Qi Qu
- & Michael S. German
-
Research Highlights |
Cardiovascular biology: Fatty foam cells
-
-
Research Highlights |
Vascular biology: Hearty hormones
-
News |
 A softer ride for barefoot runners
A softer ride for barefoot runners
People who run long distances without shoes cushion the blow with their gait.
- Lizzie Buchen
-
Letter |
 Hsp70 stabilizes lysosomes and reverts Niemann–Pick disease-associated lysosomal pathology
Hsp70 stabilizes lysosomes and reverts Niemann–Pick disease-associated lysosomal pathology
Heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) is a molecular chaperone which, by inhibiting lysosomal membrane permeabilization, promotes the survival of stressed cells. Hsp70 is now shown to stabilize lysosomes by binding to an anionic phospholipid, BMP, resulting in stimulation of acid sphingomyelinase (ASM) activity. Notably, the decreased ASM activity and lysosomal stability seen in patients with Niemann–Pick disease can be corrected by treatment with recombinant Hsp70.
- Thomas Kirkegaard
- , Anke G. Roth
- & Marja Jäättelä
-
Letter |
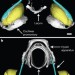 A bony connection signals laryngeal echolocation in bats
A bony connection signals laryngeal echolocation in bats
Echolocation is usually associated with bats. Many echolocating bats produce signals in the larynx, but a few species produce tongue clicks. Here, studies show that in all bats that use larynx-generated clicks, the stylohyal bone is connected to the tympanic bone. Study of the stylohyal and tympanic bones of a primitive fossil bat indicates that this species may have been able to echolocate, despite previous evidence to the contrary, raising the question of when and how echolocation evolved in bats.
- Nina Veselka
- , David D. McErlain
- & M. Brock Fenton
-
Research Highlights |
Evolutionary biology: How girls go solo
-
News |
 Brother sperm train together
Brother sperm train together
Mouse sperm cells team up with their kin in the race to fertilize eggs.
- John Whitfield
-
Letter |
 Competition drives cooperation among closely related sperm of deer mice
Competition drives cooperation among closely related sperm of deer mice
Sperm can increase their swimming velocity and gain a competitive advantage over sperm from another male by forming cooperative groups, such that selection should favour cooperation of the most closely related sperm. Sperm of deer mice are now shown to aggregate more often with conspecific than heterospecific sperm, in accordance with this theory, whereas in a monogamous species lacking sperm competition, sperm indiscriminately group with unrelated conspecific sperm.
- Heidi S. Fisher
- & Hopi E. Hoekstra
-

 The metabolic secrets of good runners
The metabolic secrets of good runners Why twins age differently
Why twins age differently Lost curve hits a nerve
Lost curve hits a nerve Biodemography of human ageing
Biodemography of human ageing Lessons on longevity from budding yeast
Lessons on longevity from budding yeast The genetics of ageing
The genetics of ageing The barefoot professor
The barefoot professor Institutions investigate 'reactome' data
Institutions investigate 'reactome' data