Research Briefing |
Featured
-
-
Article |
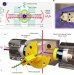 Quantum-enabled millimetre wave to optical transduction using neutral atoms
Quantum-enabled millimetre wave to optical transduction using neutral atoms
We report an ensemble of cold 85Rb atoms strongly coupled to a superconducting resonator and optical cavity, resulting in the demonstration of quantum-enabled transduction of millimetre wave photons to optical photons.
- Aishwarya Kumar
- , Aziza Suleymanzade
- & Jonathan Simon
-
News & Views |
 Bow-tie particles boast a tunable twist
Bow-tie particles boast a tunable twist
Particles that self-assemble from nanoribbons into bow-tie-shaped structures can be tailored to change the degree of their twist. A search for how best to quantify this twist homes in on a measure of how the bow ties respond to light.
- Bart Kahr
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast tunable lasers using lithium niobate integrated photonics
Ultrafast tunable lasers using lithium niobate integrated photonics
A frequency-tunable laser based on a hybrid silicon nitride and lithium niobate integrated photonic platform has a fast tuning rate and could be used for optical ranging applications.
- Viacheslav Snigirev
- , Annina Riedhauser
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
Article |
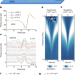 Observation of hydrodynamic plasmons and energy waves in graphene
Observation of hydrodynamic plasmons and energy waves in graphene
By using new on-chip terahertz spectroscopy techniques to measure the absorption spectra of a graphene microribbon as well as the energy waves close to charge neutrality, hydrodynamic collective excitations are observed.
- Wenyu Zhao
- , Shaoxin Wang
- & Feng Wang
-
Technology Feature |
 Smart microscopes spot fleeting biology
Smart microscopes spot fleeting biology
Automated microscopes that adapt to each sample’s quirks can capture elusive biological phenomena at high resolution.
- Jyoti Madhusoodanan
-
Article |
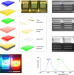 Vertical full-colour micro-LEDs via 2D materials-based layer transfer
Vertical full-colour micro-LEDs via 2D materials-based layer transfer
We report full-colour, vertically stacked µLEDs that achieve exceptionally high array density (5,100 pixels per inch) and small size (4 µm) via a 2D material-based layer transfer technique, allowing the creation of full-colour µLED displays for augmented and virtual reality.
- Jiho Shin
- , Hyunseok Kim
- & Jeehwan Kim
-
Article |
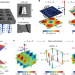 Observation of intrinsic chiral bound states in the continuum
Observation of intrinsic chiral bound states in the continuum
Chiral metasurfaces have been produced, with experimental observation of intrinsic chiral bound states in the continuum, which may lead to applications in chiral light sources and detectors, chiral sensing, valleytronics and asymmetric photocatalysis.
- Yang Chen
- , Huachun Deng
- & Cheng-Wei Qiu
-
Article |
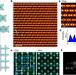 Ultrathin quantum light source with van der Waals NbOCl2 crystal
Ultrathin quantum light source with van der Waals NbOCl2 crystal
A van der Waals crystal, niobium oxide dichloride, with vanishing interlayer electronic coupling and considerable monolayer-like excitonic behaviour in the bulk, as well as strong and scalable second-order optical nonlinearity, is discovered, which enables a high-performance quantum light source.
- Qiangbing Guo
- , Xiao-Zhuo Qi
- & Andrew T. S. Wee
-
Article |
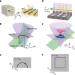 Photonic flatband resonances for free-electron radiation
Photonic flatband resonances for free-electron radiation
A study demonstrates full energy–momentum matching, and enhanced interaction, between free electrons and photons through a continuum of flatband resonances, realized in a silicon-on-insulator photonic crystal slab.
- Yi Yang
- , Charles Roques-Carmes
- & Marin Soljačić
-
Article |
 Synthesis-on-substrate of quantum dot solids
Synthesis-on-substrate of quantum dot solids
Ultrasmall monodisperse perovskite quantum dots are synthesized in situ on a substrate via ligand structure regulation, yielding the highest external quantum efficiency blue perovskite LEDs reported so far.
- Yuanzhi Jiang
- , Changjiu Sun
- & Mingjian Yuan
-
Research Briefing |
 Array of chiral nanoparticles discriminates between enantiomers
Array of chiral nanoparticles discriminates between enantiomers
When circularly polarized light hits an array of chiral gold nanoparticles, it generates polarized electric and magnetic waves across the surface of the nanoparticles. Chiral molecules can alter these resonances, providing a highly sensitive method to determine and quantify molecular chirality, even at very low concentrations.
-
Article |
 Enantioselective sensing by collective circular dichroism
Enantioselective sensing by collective circular dichroism
An array of 2D crystals of isotropic, 432-symmetric chiral gold nanoparticles is shown to exhibit collective resonances with a strong and uniform chiral near field, allowing enantioselective detection by the collective circular dichroism.
- Ryeong Myeong Kim
- , Ji-Hyeok Huh
- & Ki Tae Nam
-
Research Highlight |
 Sharp laser beam reveals internal organs in stunning 3D
Sharp laser beam reveals internal organs in stunning 3D
Scientists refine a technology that peers through bone to image sub-surface body parts.
-
Article |
 A photonic integrated continuous-travelling-wave parametric amplifier
A photonic integrated continuous-travelling-wave parametric amplifier
By using Si3N4 photonic integrated circuits on a silicon chip, a continuous-travelling-wave parametric amplifier is shown to yield a parametric gain exceeding both on-chip propagation loss as well as fibre–chip–fibre coupling losses.
- Johann Riemensberger
- , Nikolai Kuznetsov
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
Article |
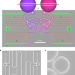 Spin–orbit microlaser emitting in a four-dimensional Hilbert space
Spin–orbit microlaser emitting in a four-dimensional Hilbert space
A fully integrated semiconductor microlaser that exploits spin–orbit coupling of light emits in a four-dimensional Hilbert space, with flexible control of up to six degrees of freedom.
- Zhifeng Zhang
- , Haoqi Zhao
- & Liang Feng
-
Article |
 Integrated femtosecond pulse generator on thin-film lithium niobate
Integrated femtosecond pulse generator on thin-film lithium niobate
A femtosecond pulse generator is realized using an electro-optic time-lens system integrated on a lithium niobate photonic chip, capable of tunable repetition rates and wavelengths.
- Mengjie Yu
- , David Barton III
- & Marko Lončar
-
Article |
 A hybrid optical–wireless network for decimetre-level terrestrial positioning
A hybrid optical–wireless network for decimetre-level terrestrial positioning
A terrestrial networked positioning system based on a hybrid optical–wireless telecommunication infrastructure and that is independent of global navigation satellite systems is demonstrated for urban environments with decimetre-level accuracy.
- Jeroen C. J. Koelemeij
- , Han Dun
- & Christian C. J. M. Tiberius
-
Research Highlight |
 Light does a Möbius strip twist
Light does a Möbius strip twist
Photons trapped inside a special ring must travel two laps before reaching their starting state.
-
Research Briefing |
 Bright, efficient and stable LEDs made using nanocrystals of perovskite material
Bright, efficient and stable LEDs made using nanocrystals of perovskite material
Perovskites are promising candidates for use in next-generation light-emitting diode (LED) displays that are vivid and have high colour quality. LEDs made from particles with a perovskite nanocrystal core and an acidic shell are efficient and bright, and have a long operational half-life.
-
Article |
 Ultra-bright, efficient and stable perovskite light-emitting diodes
Ultra-bright, efficient and stable perovskite light-emitting diodes
The authors develop a method for the production of ultra-bright, efficient and stable perovskite light-emitting diodes, achieved with a simple in situ reaction process.
- Joo Sung Kim
- , Jung-Min Heo
- & Tae-Woo Lee
-
News & Views |
 Electrons turn a piece of wire into a laser-like light source
Electrons turn a piece of wire into a laser-like light source
Shining a laser on an iron wire generates fast-moving electrons that boost the electromagnetic waves created by the light interacting with the wire. This way of making laser-like light could surpass existing methods that use electrons.
- Nicholas Rivera
-
Article |
 Coherent surface plasmon polariton amplification via free-electron pumping
Coherent surface plasmon polariton amplification via free-electron pumping
Stimulated emission by free electrons is used to amplify terahertz surface plasmon polaritons in a manner resembles that of light amplification in a high-gain free-electron laser.
- Dongdong Zhang
- , Yushan Zeng
- & Ruxin Li
-
Article
| Open Access An integrated imaging sensor for aberration-corrected 3D photography
An integrated imaging sensor for aberration-corrected 3D photography
A meta-imaging sensor detects an extra-fine 4D light field distribution using a vibrating microlens array, enabling high-resolution 3D photography up to a gigapixel with fast aberration correction, demonstrated on a telescope aimed at the Moon.
- Jiamin Wu
- , Yuduo Guo
- & Qionghai Dai
-
News & Views Forum |
 Skin colour affects the accuracy of medical oxygen sensors
Skin colour affects the accuracy of medical oxygen sensors
COVID-19 broadened the use of pulse oximeters for rapid blood-oxygen readings, but it also highlighted the fact that skin pigmentation alters measurements. Two groups of researchers analyse this issue, and its effects on people with dark skin.
- Matthew D. Keller
- , Brandon Harrison-Smith
- & Mohammed Shahriar Arefin
-
Research Briefing |
 An optical innovation for metrology at the quantum limit of precision
An optical innovation for metrology at the quantum limit of precision
Frequency-comb lasers are measuring sticks of the optical world and are used in metrology and sensing applications owing to their rigid, comb-like light spectra and metronomic pulsed output. A frequency comb with time-programmable pulses breaks this rigid mould and, in a demonstration of its utility, measures distances at the quantum limit of precision.
-
Article |
 Attosecond clocking of correlations between Bloch electrons
Attosecond clocking of correlations between Bloch electrons
By forcing electron–hole pairs onto closed trajectories attosecond clocking of delocalized Bloch electrons is achieved, enabling greater understanding of unexpected phase transitions and quantum-dynamic phenomena.
- J. Freudenstein
- , M. Borsch
- & R. Huber
-
Article |
 Spontaneous generation and active manipulation of real-space optical vortices
Spontaneous generation and active manipulation of real-space optical vortices
A photonic platform that allows the spontaneous generation and active manipulation of an optical vortex–antivortex pair using an external magnetic field is demonstrated.
- Dongha Kim
- , Arthur Baucour
- & Min-Kyo Seo
-
Article |
 The time-programmable frequency comb and its use in quantum-limited ranging
The time-programmable frequency comb and its use in quantum-limited ranging
A self-referenced optical frequency comb with digital electronics is used for real-time attosecond control of the comb’s pulse train, and can be used in quantum-limited sensing.
- Emily D. Caldwell
- , Laura C. Sinclair
- & Jean-Daniel Deschenes
-
Article |
 Free-space dissemination of time and frequency with 10−19 instability over 113 km
Free-space dissemination of time and frequency with 10−19 instability over 113 km
By using 1 W optical frequency combs and nanowatt-level linear optical sampling modules, a time–frequency dissemination over a free-space link of 113 km is achieved with a stability of less than 4 × 10−19 at 10,000 s.
- Qi Shen
- , Jian-Yu Guan
- & Jian-Wei Pan
-
Article
| Open Access Extending the spectrum of fully integrated photonics to submicrometre wavelengths
Extending the spectrum of fully integrated photonics to submicrometre wavelengths
Fully integrated photonics at submicrometre wavelengths is realized by a heterogeneous integration technology.
- Minh A. Tran
- , Chong Zhang
- & Tin Komljenovic
-
Article |
 Photonic topological insulator induced by a dislocation in three dimensions
Photonic topological insulator induced by a dislocation in three dimensions
By introducing a further modal dimension to transform a two-dimensional photonic waveguide array, a photonic topological insulator with protected topological surface states in three dimensions, enabled by a screw dislocation, is demonstrated.
- Eran Lustig
- , Lukas J. Maczewsky
- & Mordechai Segev
-
News & Views |
 Hybrid laser-trapping technique lights the way for neutral atoms
Hybrid laser-trapping technique lights the way for neutral atoms
An experimental platform that uses two different tools for controlling neutral atoms with laser light combines speed with scalability. The approach provides a crucial step towards realizing innovative quantum algorithms and simulations.
- Giulia Semeghini
-
News & Views |
 Fluorescence limitations overcome by engineering light–matter interactions
Fluorescence limitations overcome by engineering light–matter interactions
The process by which pixels fluoresce in electronic displays uses energy highly inefficiently. The identification of fluorescent molecules with an unusual order of excited states opens up a fresh approach to tackling this issue.
- Juan-Carlos Sancho-García
-
Article |
 Femtosecond laser writing of lithium niobate ferroelectric nanodomains
Femtosecond laser writing of lithium niobate ferroelectric nanodomains
We propose and experimentally demonstrate a non-reciprocal near-infrared femtosecond laser-writing technique for reconfigurable three-dimensional nanoscale ferroelectric domain engineering in LiNbO3 crystals.
- Xiaoyi Xu
- , Tianxin Wang
- & Yong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Delayed fluorescence from inverted singlet and triplet excited states
Delayed fluorescence from inverted singlet and triplet excited states
A fluorescent molecule is described that does not follow Hund’s rule and instead shows singlet and triplet excited states with inverted energy levels, leading to high-efficiency OLEDs with potential implications for optoelectronic devices.
- Naoya Aizawa
- , Yong-Jin Pu
- & Daigo Miyajima
-
News & Views |
 A new phase for the universal growth of interfaces
A new phase for the universal growth of interfaces
Precise optical experiments reveal that quantum excitations in semiconductors share similarities with a host of growing interfaces. The parallels inspire a fresh approach to studying the dynamics of diverse systems in a controllable way.
- Sebastian Diehl
-
Article |
 Kardar–Parisi–Zhang universality in a one-dimensional polariton condensate
Kardar–Parisi–Zhang universality in a one-dimensional polariton condensate
Experiments show that the dynamics of phase fluctuations in a one-dimensional polariton condensate falls in the Kardar–Parisi–Zhang universality class, and theoretical analysis supports this finding revealing the key signatures of this universality class.
- Quentin Fontaine
- , Davide Squizzato
- & Jacqueline Bloch
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of Rabi dynamics with a short-wavelength free-electron laser
Observation of Rabi dynamics with a short-wavelength free-electron laser
Rabi dynamics between the ground state and an excited state in helium atoms are generated using femtosecond extreme-ultraviolet pulses from a seeded free-electron laser, which may allow ultrafast manipulation of coherent processes at short wavelengths.
- Saikat Nandi
- , Edvin Olofsson
- & Jan Marcus Dahlström
-
Nature Index |
 Four rising stars who are reshaping nanoscience
Four rising stars who are reshaping nanoscience
From nano-filters for tackling water pollution to protein fingerprinting that treats disease, these researchers are making their mark on the field.
- Gemma Conroy
- & Benjamin Plackett
-
Article
| Open Access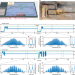 Self-emergence of robust solitons in a microcavity
Self-emergence of robust solitons in a microcavity
Slow nonlinearities of a free-running microresonator-filtered fibre laser are shown to transform temporal cavity solitons into the system’s dominant attractor, leading to reliable self-starting oscillation of microcavity-solitons that are naturally robust to perturbations.
- Maxwell Rowley
- , Pierre-Henry Hanzard
- & Alessia Pasquazi
-
Article
| Open Access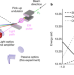 Experimental demonstration of optical stochastic cooling
Experimental demonstration of optical stochastic cooling
Stochastic cooling at optical frequencies is demonstrated in an experiment at the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory’s Integrable Optics Test Accelerator, substantially increasing the bandwidth of stochastic cooling compared with conventional systems.
- J. Jarvis
- , V. Lebedev
- & A. Valishev
-
Research Briefing |
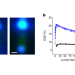 Bright blue nanoscale LEDs for next-generation displays
Bright blue nanoscale LEDs for next-generation displays
Microscopic light-emitting diodes (LEDs) have applications ranging from augmented-reality displays to large-screen products, but their brightness typically decreases as their size is reduced. A solution to this problem has now been found and used to manufacture bright blue nanoscale LEDs.
-
Article |
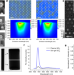 Highly efficient blue InGaN nanoscale light-emitting diodes
Highly efficient blue InGaN nanoscale light-emitting diodes
Using a sol–gel passivation method, the fabrication of blue InGaN nanorod-LEDs with the highest external quantum efficiency value ever reported for LEDs in the nanoscale is demonstrated.
- Mihyang Sheen
- , Yunhyuk Ko
- & Changhee Lee
-
Technology Feature |
 Light-based sensors set to revolutionize on-site testing
Light-based sensors set to revolutionize on-site testing
Nanophotonic biosensors exploit light’s properties to detect molecular interactions in real time at the point of need.
- Diana Kwon
-
Research Briefing |
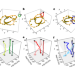 The knotty problem of tuning an instrument
The knotty problem of tuning an instrument
Tuning the resonances of an object is crucial in many settings, from musical instruments to ultrasensitive detectors for electromagnetic and gravitational waves. This task might seem straightforward but its mathematical description has been shown to involve rich topological structures known as knots and braids.
-
Article |
 Anti-reflection structure for perfect transmission through complex media
Anti-reflection structure for perfect transmission through complex media
An anti-reflection structure is used to eliminate all back scattering of light passing through a diffusive medium.
- Michael Horodynski
- , Matthias Kühmayer
- & Matthieu Davy
-
Article |
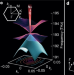 Scalable single-mode surface-emitting laser via open-Dirac singularities
Scalable single-mode surface-emitting laser via open-Dirac singularities
A photonic crystal cavity arranged in a hexagonal pattern shows unconventional losses that allow single-mode lasing operation to be maintained as the cavity is scaled up in size.
- Rushin Contractor
- , Wanwoo Noh
- & Boubacar Kanté
-
Research Highlight |
 These ‘drab’ moths dazzle when the light is right
These ‘drab’ moths dazzle when the light is right
Night-loving insects that look brown by day have bright, species-specific patterns under infrared light.
-
Article |
 Axial Higgs mode detected by quantum pathway interference in RTe3
Axial Higgs mode detected by quantum pathway interference in RTe3
Detection of an axial Higgs mode by quantum pathway interference reveals an unconventional charge density wave phase in RTe3.
- Yiping Wang
- , Ioannis Petrides
- & Kenneth S. Burch

 Laser-cooled atoms bring networks of quantum computers a step closer
Laser-cooled atoms bring networks of quantum computers a step closer