Featured
-
-
Article |
 Synthesis of portimines reveals the basis of their anti-cancer activity
Synthesis of portimines reveals the basis of their anti-cancer activity
A scalable total synthesis of portimines enables structural reassignment of portimine B and in-depth functional evaluation of portimine A, revealing that portimine A induces translation inhibition selectively in human cancer cells and is efficacious in vivo tumour-clearance models.
- Junchen Tang
- , Weichao Li
- & Phil S. Baran
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of non-squalene triterpenes
Discovery of non-squalene triterpenes
Chimeric triterpene synthases are identified that catalyse non-squalene-dependent triterpene biosynthesis.
- Hui Tao
- , Lukas Lauterbach
- & Tiangang Liu
-
Article |
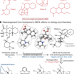 Synthesis and target annotation of the alkaloid GB18
Synthesis and target annotation of the alkaloid GB18
A synthetic route to GB18, an alkaloid from the bark of hallucinogenic Galbulimima sp., is developed, enabling its identification as an antagonist of κ- and μ-opioid receptors.
- Stone Woo
- & Ryan A. Shenvi
-
Article
| Open Access Emergence of methicillin resistance predates the clinical use of antibiotics
Emergence of methicillin resistance predates the clinical use of antibiotics
Methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus appeared in European hedgehogs in the pre-antibiotic era as a co-evolutionary adaptation to antibiotic-producing dermatophytes and have spread within the local hedgehog populations and between hedgehogs and secondary hosts.
- Jesper Larsen
- , Claire L. Raisen
- & Anders R. Larsen
-
Article |
 Computational planning of the synthesis of complex natural products
Computational planning of the synthesis of complex natural products
A synthetic route-planning algorithm, augmented with causal relationships that allow it to strategize over multiple steps, can design complex natural-product syntheses that are indistinguishable from those designed by human experts.
- Barbara Mikulak-Klucznik
- , Patrycja Gołębiowska
- & Bartosz A. Grzybowski
-
Article |
 Synthetic group A streptogramin antibiotics that overcome Vat resistance
Synthetic group A streptogramin antibiotics that overcome Vat resistance
Modular synthesis and structural biology are used to design and characterize group A streptogramin antibiotics, one of which has activity against streptogramin-resistant strains and demonstrates efficacy in a mouse model of bacterial infection.
- Qi Li
- , Jenna Pellegrino
- & Ian B. Seiple
-
Article |
 Concise asymmetric synthesis of (−)-bilobalide
Concise asymmetric synthesis of (−)-bilobalide
A synthetic route to the Ginkgo biloba metabolite (−)-bilobalide is described.
- Meghan A. Baker
- , Robert M. Demoret
- & Ryan A. Shenvi
-
Letter |
 A 16-step synthesis of the isoryanodane diterpene (+)-perseanol
A 16-step synthesis of the isoryanodane diterpene (+)-perseanol
The chemical synthesis of (+)-perseanol, a diterpene with potent insecticidal properties, is reported.
- Arthur Han
- , Yujia Tao
- & Sarah E. Reisman
-
Letter |
 Quaternary-centre-guided synthesis of complex polycyclic terpenes
Quaternary-centre-guided synthesis of complex polycyclic terpenes
An approach in which quaternary centres are leveraged to improve synthetic planning can lead to shorter and optimized syntheses, demonstrated here on a series of polycyclic terpenes.
- Pengfei Hu
- , Hyung Min Chi
- & Scott A. Snyder
-
Letter |
 Discovery of a pathway for terminal-alkyne amino acid biosynthesis
Discovery of a pathway for terminal-alkyne amino acid biosynthesis
Microbial generation of a terminal-alkyne-containing amino acid can be encoded into E. coli and provides the potential for in vivo generation of proteins and natural products for click chemistry.
- J. A. Marchand
- , M. E. Neugebauer
- & M. C. Y. Chang
-
Article |
 Synthesis of E- and Z-trisubstituted alkenes by catalytic cross-metathesis
Synthesis of E- and Z-trisubstituted alkenes by catalytic cross-metathesis
An approach for the synthesis of E- and Z- trisubstituted alkenes in high stereoisomeric purity is developed by merging catalytic cross-metathesis and cross-coupling processes.
- Thach T. Nguyen
- , Ming Joo Koh
- & Amir H. Hoveyda
-
Letter |
 Synergy of synthesis, computation and NMR reveals correct baulamycin structures
Synergy of synthesis, computation and NMR reveals correct baulamycin structures
Experimental and computed nuclear magnetic resonance data and an iterative synthetic strategy have revealed the correct structures of the baulamycins, potentially important antimicrobial compounds, allowing them to be chemically synthesized.
- Jingjing Wu
- , Paula Lorenzo
- & Varinder K. Aggarwal
-
Letter |
 Decarboxylative alkenylation
Decarboxylative alkenylation
Starting with alkyl carboxylic acids, a simple olefin synthesis using any substitution pattern or geometry, based on amide-bond synthesis with nickel- or iron-based catalysis, is described.
- Jacob T. Edwards
- , Rohan R. Merchant
- & Phil S. Baran
-
Letter |
 Molybdenum chloride catalysts for Z-selective olefin metathesis reactions
Molybdenum chloride catalysts for Z-selective olefin metathesis reactions
Substitution of a ligand in molybdenum-based complexes enables typically inert hexafluorobutene to participate in Z-selective olefin cross-metathesis reactions.
- Ming Joo Koh
- , Thach T. Nguyen
- & Amir H. Hoveyda
-
Article |
 A platform for the discovery of new macrolide antibiotics
A platform for the discovery of new macrolide antibiotics
A practical, fully synthetic route to macrolide antibiotics via the convergent assembly of simple chemical building blocks is described; more than 300 new macrolide antibiotic candidates have been synthesized using this approach, a number of which are active against bacterial strains that are resistant to currently used antibiotics.
- Ian B. Seiple
- , Ziyang Zhang
- & Andrew G. Myers
-
Letter |
 Nineteen-step total synthesis of (+)-phorbol
Nineteen-step total synthesis of (+)-phorbol
Enantiospecific total synthesis of (+)-phorbol in only 19 steps from the abundant monoterpene (+)-3-carene is demonstrated using a two-phase terpene synthesis strategy.
- Shuhei Kawamura
- , Hang Chu
- & Phil S. Baran
-
Article |
 Network-analysis-guided synthesis of weisaconitine D and liljestrandinine
Network-analysis-guided synthesis of weisaconitine D and liljestrandinine
WebNetwork analysis to determine the maximally bridged ring (or rings) of molecules is used as part of a strategy for the syntheses of architecturally complex natural chemicals; this strategy is demonstrated via the synthesis of the diterpenoid alkaloids weisaconitine D and liljestrandinine.
- C. J. Marth
- , G. M. Gallego
- & R. Sarpong
-
Letter |
 Synthesis of macrocyclic natural products by catalyst-controlled stereoselective ring-closing metathesis
Synthesis of macrocyclic natural products by catalyst-controlled stereoselective ring-closing metathesis
- Miao Yu
- , Chenbo Wang
- & Amir H. Hoveyda
-
News & Views |
 Triumph for unnatural synthesis
Triumph for unnatural synthesis
Nature crafts many molecules from common precursors, but this approach isn't always possible in chemical synthesis. A strategy for synthesizing a family of natural products succeeds by ignoring nature's blueprint. See Article p.461
- Stéphane Quideau
-
News & Views |
 New lead for pain treatment
New lead for pain treatment
The synthesis of conolidine, a scarce, naturally occurring compound, has enabled the first studies of its pharmacological properties to be carried out. Excitingly, conolidine is a painkiller that seems to have an unusual mechanism of action.
- Sarah E. Reisman
-
News |
 Compound offers pain relief without the complications
Compound offers pain relief without the complications
The synthesis of a natural pain reliever could lead to an analgesic without serious side effects.
- Philip Ball
-
Article |
 Catalytic Z-selective olefin cross-metathesis for natural product synthesis
Catalytic Z-selective olefin cross-metathesis for natural product synthesis
There are a large number of chemical transformations in which alkenes act as the reactants and/or the products of the reaction, but methods enabling the facile synthesis of 1,2-disubstituted Z alkenes are scarce. This paper describes catalytic Z-selective cross-metathesis reactions of terminal enol ethers, which have not been reported previously,and allylic amides, used thus far only in E-selective processes. The utility of this methodology is demonstrated by its use in syntheses of anti oxidant C18 (plasm)-16:0 (PC), found in electrically active tissues and implicated in Alzheimer's disease, and the potent immunostimulant KRN7000.
- Simon J. Meek
- , Robert V. O’Brien
- & Amir H. Hoveyda
-
News |
 Chemists crack complex compound
Chemists crack complex compound
Naturalistic approach vindicated as sponge molecule yields to synthesis in the lab.
- Mark Peplow

 Computational prediction of complex cationic rearrangement outcomes
Computational prediction of complex cationic rearrangement outcomes