Featured
-
-
Letter |
 Vowel recognition with four coupled spin-torque nano-oscillators
Vowel recognition with four coupled spin-torque nano-oscillators
A network of four spin-torque nano-oscillators can be trained in real time to recognize spoken vowels, in a simple and scalable approach that could be exploited for large-scale neural networks.
- Miguel Romera
- , Philippe Talatchian
- & Julie Grollier
-
Letter |
 Electronic noise due to temperature differences in atomic-scale junctions
Electronic noise due to temperature differences in atomic-scale junctions
A fundamental electronic noise—beyond electronic thermal noise and voltage-activated shot noise—that is generated by temperature differences across nanoscale conductors is demonstrated, with possible implications for thermometry and electronics.
- Ofir Shein Lumbroso
- , Lena Simine
- & Oren Tal
-
Letter |
 Tunable long-distance spin transport in a crystalline antiferromagnetic iron oxide
Tunable long-distance spin transport in a crystalline antiferromagnetic iron oxide
Tunable spin transport over long distances is demonstrated through the antiferromagnetic insulator haematite, paving the way to the development of spin-logic devices based on antiferromagnetic insulators.
- R. Lebrun
- , A. Ross
- & M. Kläui
-
Letter |
 Hundred-fold enhancement in far-field radiative heat transfer over the blackbody limit
Hundred-fold enhancement in far-field radiative heat transfer over the blackbody limit
Rates of radiative heat transfer between sub-wavelength planar membranes are experimentally and theoretically shown to exceed the blackbody limit in the far field by more than two orders of magnitude.
- Dakotah Thompson
- , Linxiao Zhu
- & Edgar Meyhofer
-
Letter |
 Topological negative refraction of surface acoustic waves in a Weyl phononic crystal
Topological negative refraction of surface acoustic waves in a Weyl phononic crystal
Sound waves in a specially designed crystal undergo ‘topologically protected’ negative refraction, whereby no reflection is allowed, at certain facets of the crystal and positive refraction at others.
- Hailong He
- , Chunyin Qiu
- & Zhengyou Liu
-
Letter |
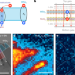 Room-temperature electrical control of exciton flux in a van der Waals heterostructure
Room-temperature electrical control of exciton flux in a van der Waals heterostructure
Heterobilayer excitonic devices consisting of two different van der Waals materials, in which excitons are shared between the layers, exhibit electrically controlled switching actions at room temperature.
- Dmitrii Unuchek
- , Alberto Ciarrocchi
- & Andras Kis
-
Article |
 Coherent spin–photon coupling using a resonant exchange qubit
Coherent spin–photon coupling using a resonant exchange qubit
Coherent coupling between a three-electron spin qubit and single photons in a microwave resonator is demonstrated, which, unlike previous demonstrations, does not require ferromagnetic components near the qubit.
- A. J. Landig
- , J. V. Koski
- & T. Ihn
-
Letter |
 Metallic nanoparticle contacts for high-yield, ambient-stable molecular-monolayer devices
Metallic nanoparticle contacts for high-yield, ambient-stable molecular-monolayer devices
A top-contacting method for the fabrication of molecular devices uses metallic nanoparticles to electrically contact self-assembled monolayers, enabling the preparation of thousands of identical, ambient-stable metal–molecule–metal devices.
- Gabriel Puebla-Hellmann
- , Koushik Venkatesan
- & Emanuel Lörtscher
-
Letter |
 Flying couplers above spinning resonators generate irreversible refraction
Flying couplers above spinning resonators generate irreversible refraction
One-way propagation of light through a standard telecommunications fibre is demonstrated by coupling the fibre to a rapidly rotating silica-glass sphere.
- Shai Maayani
- , Raphael Dahan
- & Tal Carmon
-
Letter |
 A standing molecule as a single-electron field emitter
A standing molecule as a single-electron field emitter
Precision control over matter at the atomic scale enables a planar dye molecule to be lifted up and placed on its edge—a configuration that is surprisingly stable.
- Taner Esat
- , Niklas Friedrich
- & Ruslan Temirov
-
Letter |
 Ballistic molecular transport through two-dimensional channels
Ballistic molecular transport through two-dimensional channels
Specular scattering of atoms of helium gas flowing through atomically flat, two-dimensional channels results in frictionless gas flow, which is much faster than expected assuming purely diffusive scattering.
- A. Keerthi
- , A. K. Geim
- & B. Radha
-
Letter |
 Comprehensive suppression of single-molecule conductance using destructive σ-interference
Comprehensive suppression of single-molecule conductance using destructive σ-interference
Highly insulating silicon-based molecules, engineered so that conduction is fully suppressed by σ quantum interference even for molecules less than a nanometre long, could prove useful in molecular-scale electronic circuitry.
- Marc H. Garner
- , Haixing Li
- & Gemma C. Solomon
-
Letter |
 Approaching the Schottky–Mott limit in van der Waals metal–semiconductor junctions
Approaching the Schottky–Mott limit in van der Waals metal–semiconductor junctions
In metal–semiconductor junctions, interfacial bonding and disorder cause deviations from theoretical predictions for the energy barrier, but delicately transferring pre-fabricated metal films onto two-dimensional semiconductors can overcome this challenge.
- Yuan Liu
- , Jian Guo
- & Xiangfeng Duan
-
Letter |
 Stabilized entanglement of massive mechanical oscillators
Stabilized entanglement of massive mechanical oscillators
Quantum entanglement is demonstrated in a system of massive micromechanical oscillators coupled to a microwave-frequency electromagnetic cavity by driving the devices into a steady state that is entangled.
- C. F. Ockeloen-Korppi
- , E. Damskägg
- & M. A. Sillanpää
-
Letter |
 Low-loss plasmon-assisted electro-optic modulator
Low-loss plasmon-assisted electro-optic modulator
Ohmic losses in plasmonic devices can be reduced by exploiting ‘resonant switching’, in which light couples to surface plasmon polaritons only when in resonance and bypasses them otherwise.
- Christian Haffner
- , Daniel Chelladurai
- & Juerg Leuthold
-
Letter |
 High-resolution magnetic resonance spectroscopy using a solid-state spin sensor
High-resolution magnetic resonance spectroscopy using a solid-state spin sensor
High-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy at the scale of single cells is achieved by combining a magnetometer consisting of an ensemble of nitrogen–vacancy centres with a narrowband synchronized readout protocol.
- David R. Glenn
- , Dominik B. Bucher
- & Ronald L. Walsworth
-
Article |
 GaN/NbN epitaxial semiconductor/superconductor heterostructures
GaN/NbN epitaxial semiconductor/superconductor heterostructures
Group III/nitride semiconductors have been grown epitaxially on the superconductor niobium nitride, allowing the superconductor’s macroscopic quantum effects to be combined with the semiconductors’ electronic, photonic and piezoelectric properties.
- Rusen Yan
- , Guru Khalsa
- & Debdeep Jena
-
Article |
 Unconventional superconductivity in magic-angle graphene superlattices
Unconventional superconductivity in magic-angle graphene superlattices
A superlattice consisting of two graphene sheets twisted relative to each other by a specific amount exhibits superconductivity when doped electrostatically, with a relatively high critical temperature.
- Yuan Cao
- , Valla Fatemi
- & Pablo Jarillo-Herrero
-
Letter |
 Multi-terminal memtransistors from polycrystalline monolayer molybdenum disulfide
Multi-terminal memtransistors from polycrystalline monolayer molybdenum disulfide
Polycrystalline monolayer molybdenum disulfide is used to fabricate a multi-terminal device combining a memristor and a transistor, which can mimic biological neurons with multiple synapses for neuromorphic computing applications.
- Vinod K. Sangwan
- , Hong-Sub Lee
- & Mark C. Hersam
-
Letter |
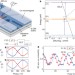 A programmable two-qubit quantum processor in silicon
A programmable two-qubit quantum processor in silicon
A two-qubit quantum processor in a silicon device is demonstrated, which can perform the Deutsch–Josza algorithm and the Grover search algorithm.
- T. F. Watson
- , S. G. J. Philips
- & L. M. K. Vandersypen
-
Article |
 A coherent spin–photon interface in silicon
A coherent spin–photon interface in silicon
A single spin in silicon is strongly coupled to a microwave-frequency photon and coherent single-spin dynamics are observed using circuit quantum electrodynamics.
- X. Mi
- , M. Benito
- & J. R. Petta
-
Letter |
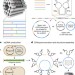 Biotechnological mass production of DNA origami
Biotechnological mass production of DNA origami
All necessary strands for DNA origami can be created in a single scalable process by using bacteriophages to generate single-stranded precursor DNA containing the target sequences interleaved with self-excising DNA enzymes.
- Florian Praetorius
- , Benjamin Kick
- & Hendrik Dietz
-
Letter |
 Inertial picobalance reveals fast mass fluctuations in mammalian cells
Inertial picobalance reveals fast mass fluctuations in mammalian cells
A picobalance consisting of an optically excited microcantilever has been developed and used to measure the masses of individual healthy and virus-infected cells at high temporal and mass resolutions in culture conditions.
- David Martínez-Martín
- , Gotthold Fläschner
- & Daniel J. Müller
-
Letter |
 Ion sieving in graphene oxide membranes via cationic control of interlayer spacing
Ion sieving in graphene oxide membranes via cationic control of interlayer spacing
Cations are used to control the interlayer spacing of graphene oxide membranes, enabling efficient and selective sieving of hydrated cations.
- Liang Chen
- , Guosheng Shi
- & Haiping Fang
-
Letter |
 Molecular machines open cell membranes
Molecular machines open cell membranes
Rotary molecular machines, activated by ultraviolet light, are able to perturb and drill into cell membranes in a controllable manner, and more efficiently than those exhibiting flip-flopping or random motion.
- Víctor García-López
- , Fang Chen
- & James M. Tour
-
Letter |
 Chaotic dynamics in nanoscale NbO2 Mott memristors for analogue computing
Chaotic dynamics in nanoscale NbO2 Mott memristors for analogue computing
A relaxation oscillator incorporating nanoscale niobium dioxide memristors that exhibit both a current- and a temperature-controlled negative differential resistance produces chaotic dynamics that aid biomimetic computing.
- Suhas Kumar
- , John Paul Strachan
- & R. Stanley Williams
-
Letter |
 Quantum simulation of a Fermi–Hubbard model using a semiconductor quantum dot array
Quantum simulation of a Fermi–Hubbard model using a semiconductor quantum dot array
A quantum simulation platform based on quantum dots is reported that can operate at relatively low temperatures, and its utility is shown by simulating a Fermi–Hubbard model.
- T. Hensgens
- , T. Fujita
- & L. M. K. Vandersypen
-
Letter |
 Neuromorphic computing with nanoscale spintronic oscillators
Neuromorphic computing with nanoscale spintronic oscillators
Spoken-digit recognition using a nanoscale spintronic oscillator that mimics the behaviour of neurons demonstrates the potential of such oscillators for realizing large-scale neural networks in future hardware.
- Jacob Torrejon
- , Mathieu Riou
- & Julie Grollier
-
Letter |
 Three-dimensional integration of nanotechnologies for computing and data storage on a single chip
Three-dimensional integration of nanotechnologies for computing and data storage on a single chip
Multiple nanotechnologies are integrated on a single chip to realize a three-dimensional integrated circuit architecture that combines computing and data storage—a potentially transformative advance in computing.
- Max M. Shulaker
- , Gage Hills
- & Subhasish Mitra
-
Letter |
 High-resolution non-destructive three-dimensional imaging of integrated circuits
High-resolution non-destructive three-dimensional imaging of integrated circuits
A recently developed computational imaging technique, X-ray ptychographic tomography, is used to study integrated circuits, and a 3D image of a processor chip with a resolution of 14.6 nm is obtained.
- Mirko Holler
- , Manuel Guizar-Sicairos
- & Gabriel Aeppli
-
Letter |
 Reading and writing single-atom magnets
Reading and writing single-atom magnets
A two-bit magnetic memory is demonstrated, based on the magnetic states of individual holmium atoms, which are read and written in a scanning tunnelling microscope set-up and are stable over many hours.
- Fabian D. Natterer
- , Kai Yang
- & Christopher P. Lutz
-
Letter |
 Sideband cooling beyond the quantum backaction limit with squeezed light
Sideband cooling beyond the quantum backaction limit with squeezed light
Squeezed light is used to sideband cool the motion of a macroscopic mechanical object below the limit imposed by quantum fluctuations.
- Jeremy B. Clark
- , Florent Lecocq
- & John D. Teufel
-
Letter |
 Massive radius-dependent flow slippage in carbon nanotubes
Massive radius-dependent flow slippage in carbon nanotubes
The pressure-driven flow rate through individual carbon nanotubes is precisely determined from the hydrodynamics of emerging water jets, revealing unexpectedly large and radius-dependent surface slippage.
- Eleonora Secchi
- , Sophie Marbach
- & Lydéric Bocquet
-
Letter |
 Molecular transport through capillaries made with atomic-scale precision
Molecular transport through capillaries made with atomic-scale precision
Nanometre-scale graphitic capillaries with atomically flat walls are engineered and studied, revealing unexpectedly fast transport of liquid water through channels that accommodate only a few layers of water.
- B. Radha
- , A. Esfandiar
- & A. K. Geim
-
Letter |
 Controlling charge quantization with quantum fluctuations
Controlling charge quantization with quantum fluctuations
A device consisting of a metallic island connected to electrodes via tunable semiconductor-based conduction channels is used to explore the evolution of charge quantization in the presence of quantum fluctuations; the measurements reveal a robust scaling of charge quantization as the square root of the residual electron reflection probability across a quantum channel, consistent with theoretical predictions.
- S. Jezouin
- , Z. Iftikhar
- & F. Pierre
-
Letter |
 Single-layer MoS2 nanopores as nanopower generators
Single-layer MoS2 nanopores as nanopower generators
Blue energy is a desirable renewable resource, involving the osmotic transport of ions through a membrane from seawater to fresh water; here, nanopores have been created in two-dimensional molybdenum-disulfide membranes, and shown to generate a substantial osmotic power output.
- Jiandong Feng
- , Michael Graf
- & Aleksandra Radenovic
-
Letter |
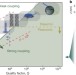 Single-molecule strong coupling at room temperature in plasmonic nanocavities
Single-molecule strong coupling at room temperature in plasmonic nanocavities
Placing a light emitter in an ultra-small optical cavity results in coupling between matter and light, generating new forms of emission that can be exploited in practical or fundamental applications; here, a system is described in which strong light–matter coupling occurs at room temperature and in ambient conditions by aligning single dye molecules in the optical cavities between gold nanoparticles and surfaces.
- Rohit Chikkaraddy
- , Bart de Nijs
- & Jeremy J. Baumberg
-
Letter |
 An autonomous chemically fuelled small-molecule motor
An autonomous chemically fuelled small-molecule motor
A system is described in which a small macrocycle is continuously transported directionally around a cyclic molecular track when powered by irreversible reactions of a chemical fuel; such autonomous chemically fuelled molecular motors should find application as engines in molecular nanotechnology.
- Miriam R. Wilson
- , Jordi Solà
- & David A. Leigh
-
Letter |
 A two-qubit logic gate in silicon
A two-qubit logic gate in silicon
A high-fidelity two-qubit CNOT logic gate is presented, which is realized by combining single- and two-qubit operations with controlled phase operations in a quantum dot system using the exchange interaction.
- M. Veldhorst
- , C. H. Yang
- & A. S. Dzurak
-
Letter |
 A subthermionic tunnel field-effect transistor with an atomically thin channel
A subthermionic tunnel field-effect transistor with an atomically thin channel
A new type of device, the band-to-band tunnel transistor, which has atomically thin molybdenum disulfide as the active channel, operates in a fundamentally different way from a conventional silicon (MOSFET) transistor; it has turn-on characteristics and low-power operation that are better than those of state-of-the-art MOSFETs or any tunnelling transistor reported so far.
- Deblina Sarkar
- , Xuejun Xie
- & Kaustav Banerjee
-
Letter |
 Measurement-based control of a mechanical oscillator at its thermal decoherence rate
Measurement-based control of a mechanical oscillator at its thermal decoherence rate
A position sensor is demonstrated that is capable of resolving the zero-point motion of a nanomechanical oscillator in the timescale of its thermal decoherence; it achieves an imprecision that is four orders of magnitude below that at the standard quantum limit and is used to feedback-cool the oscillator to a mean photon number of five.
- D. J. Wilson
- , V. Sudhir
- & T. J. Kippenberg
-
Letter |
 Graphene kirigami
Graphene kirigami
The ratio of in-plane stiffness to out-of-plane bending stiffness of graphene is shown to be similar to that of a piece of paper, which allows ideas from kirigami (a variation of origami that allows cutting) to be applied to micrometre-scale graphene sheets to build mechanically stretchable yet robust electrodes, springs and hinges.
- Melina K. Blees
- , Arthur W. Barnard
- & Paul L. McEuen
-
Letter |
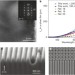 Visible-frequency hyperbolic metasurface
Visible-frequency hyperbolic metasurface
Visible-frequency hyperbolic metasurfaces defined on single-crystal silver exhibit negative refraction and diffraction-free propagation, as well as strong, dispersion-dependent spin–orbit coupling for propagating surface plasmon polaritons, with device performance greatly exceeding those of previous bulk metamaterial demonstrations.
- Alexander A. High
- , Robert C. Devlin
- & Hongkun Park
-
Letter |
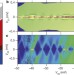 Electron pairing without superconductivity
Electron pairing without superconductivity
Evidence is presented for electron pairing in strontium titanate far above the superconducting transition temperature; such pairs are thought to be the long-sought pre-formed pairs that condense at lower temperatures to give rise to the unconventional superconducting state in this system.
- Guanglei Cheng
- , Michelle Tomczyk
- & Jeremy Levy
-
Letter |
 Training and operation of an integrated neuromorphic network based on metal-oxide memristors
Training and operation of an integrated neuromorphic network based on metal-oxide memristors
A transistor-free metal-oxide memristor crossbar with low device variability is realised and trained to perform a simple classification task, opening the way to integrated neuromorphic networks of a complexity comparable to that of the human brain, with high operational speed and manageable power dissipation.
- M. Prezioso
- , F. Merrikh-Bayat
- & D. B. Strukov
-
Letter |
 Monolayer semiconductor nanocavity lasers with ultralow thresholds
Monolayer semiconductor nanocavity lasers with ultralow thresholds
A miniature laser is reported that uses two-dimensional tungsten diselenide as the active medium, which is placed on a photonic crystal membrane that acts as the laser cavity; the laser emits visible light, with an ultralow pump threshold.
- Sanfeng Wu
- , Sonia Buckley
- & Xiaodong Xu
-
Letter |
 Shape-changing magnetic assemblies as high-sensitivity NMR-readable nanoprobes
Shape-changing magnetic assemblies as high-sensitivity NMR-readable nanoprobes
A shape-changing sensor made of pairs of magnetic disks spaced by swellable hydrogel material removes all need for optical access by operating in the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) radio-frequency spectrum.
- G. Zabow
- , S. J. Dodd
- & A. P. Koretsky
-
Letter |
 Ultrasensitive mechanical crack-based sensor inspired by the spider sensory system
Ultrasensitive mechanical crack-based sensor inspired by the spider sensory system
A mechanical crack-based sensor inspired by the mechanism spiders use to sense minute variations in stress offers ultrahigh sensitivity to pressure and vibration and can easily be mounted on human skin for the purposes of speech recognition and the monitoring of physiological signals.
- Daeshik Kang
- , Peter V. Pikhitsa
- & Mansoo Choi
-
Letter |
 Design and fabrication of memory devices based on nanoscale polyoxometalate clusters
Design and fabrication of memory devices based on nanoscale polyoxometalate clusters
Flash memories are essential for modern electronics; here a selenium-templated polyoxometalate is used to engineer new metal–oxide–semiconductor devices.
- Christoph Busche
- , Laia Vilà-Nadal
- & Leroy Cronin

 Measurement-based quantum control of mechanical motion
Measurement-based quantum control of mechanical motion