Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Mutation bias and GC content shape antimutator invasions
Mutation bias and GC content shape antimutator invasions
Mutators are expected to re-evolve low mutation rates to reduce deleterious load, but empirical evidence is mixed. Here, the authors show that load can vary across mutators and genetic backgrounds, which their simulations suggest can substantially alter antimutator dynamics.
- Alejandro Couce
- & Olivier Tenaillon
-
Article
| Open Access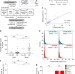 Brain somatic mutations observed in Alzheimer’s disease associated with aging and dysregulation of tau phosphorylation
Brain somatic mutations observed in Alzheimer’s disease associated with aging and dysregulation of tau phosphorylation
The role of brain somatic mutations in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is not well understood. Here the authors carry out high-depth exome sequencing ~500× on brain tissue from patients with AD and controls, and identify mutations in a number of genes that are known to contribute to phosphorylation and aggregation of tau, including PIN1.
- Jun Sung Park
- , Junehawk Lee
- & Jeong Ho Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Myoglobinopathy is an adult-onset autosomal dominant myopathy with characteristic sarcoplasmic inclusions
Myoglobinopathy is an adult-onset autosomal dominant myopathy with characteristic sarcoplasmic inclusions
Myoglobin is a hemeprotein that reversibly binds oxygen and gives muscle its red color. Here, the authors report a genetic variant in the MB gene that associates with myoglobinopathy, an autosomal dominant progressive myopathy, and altered oxygen binding properties of the mutant protein.
- Montse Olivé
- , Martin Engvall
- & Nigel G. Laing
-
Article
| Open Access The use of technical replication for detection of low-level somatic mutations in next-generation sequencing
The use of technical replication for detection of low-level somatic mutations in next-generation sequencing
Somatic mutations of low allele frequencies are often difficult to detect. Here, the authors develop RePlow, a computational method that leverages technical replication for detecting low-level somatic mutations using next-generation sequencing.
- Junho Kim
- , Dachan Kim
- & Sangwoo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access A recurrent cancer-associated substitution in DNA polymerase ε produces a hyperactive enzyme
A recurrent cancer-associated substitution in DNA polymerase ε produces a hyperactive enzyme
Somatic alterations in the exonuclease domain of DNA polymerase ɛ have been linked to the development of highly mutated cancers. Here, the authors report that a major consequence of the most common cancer-associated Polɛ variant is a dramatically increased DNA polymerase activity.
- Xuanxuan Xing
- , Daniel P. Kane
- & Polina V. Shcherbakova
-
Article
| Open Access Capturing variation impact on molecular interactions in the IMEx Consortium mutations data set
Capturing variation impact on molecular interactions in the IMEx Consortium mutations data set
Genetic variants might exert their functional effects via influencing molecular interaction. Here, the authors present a resource featuring almost 28,000 annotations describing the effect of small sequence changes on physical protein interactions, curated by IMEx Consortium curators.
- J. Khadake
- , B. Meldal
- & P. Porras
-
Article
| Open Access CRISPR-FRT targets shared sites in a knock-out collection for off-the-shelf genome editing
CRISPR-FRT targets shared sites in a knock-out collection for off-the-shelf genome editing
Genome editing requires precise targeting of loci with specific gRNAs. Here the authors introduce CRISPR-FRT, which targets flippase recognition sites, common in bacterial genetic collections, for fast off-the-shelf genome engineering.
- Toon Swings
- , David C. Marciano
- & Jan Michiels
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of rare de novo epigenetic variations in congenital disorders
Identification of rare de novo epigenetic variations in congenital disorders
A proportion of neurodevelopmental disorder and congenital anomaly cases remain without a genetic diagnosis. Here, the authors study aberrations of DNA methylation in such cases and find that epivariations might provide an explanation for some of these undiagnosed patients.
- Mafalda Barbosa
- , Ricky S. Joshi
- & Andrew J. Sharp
-
Article
| Open Access Validating the concept of mutational signatures with isogenic cell models
Validating the concept of mutational signatures with isogenic cell models
As cells evolve towards malignancy, somatic mutations arise from defects in DNA damage and repair processes which are each associated with individual mutation signatures. Here the authors show it is possible to recreate cancer mutational signatures in vitro using gene editing experiments in an isogenic human-cell system.
- Xueqing Zou
- , Michel Owusu
- & Serena Nik-Zainal
-
Article
| Open Access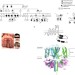 Two missense mutations in KCNQ1 cause pituitary hormone deficiency and maternally inherited gingival fibromatosis
Two missense mutations in KCNQ1 cause pituitary hormone deficiency and maternally inherited gingival fibromatosis
Growth retardation is most commonly caused by genetic defects in the growth hormone pathway. Here, in families with growth retardation and gingival fibromatosis, the authors identify mutations in the potassium channel gene KCNQ1 that cause electrophysiological aberrations and altered ACTH secretion in vitro.
- Johanna Tommiska
- , Johanna Känsäkoski
- & Taneli Raivio
-
Article
| Open Access Somatic mutations in clonally expanded cytotoxic T lymphocytes in patients with newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis
Somatic mutations in clonally expanded cytotoxic T lymphocytes in patients with newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis
Accumulation of somatic mutations in lymphocytes is a feature of some cancers. Here the authors show that patients with recent onset of rheumatoid arthritis also accumulate mutations in their expanded CD8+ effector memory T cell pool independent of cancer association.
- P. Savola
- , T. Kelkka
- & S. Mustjoki
-
Article
| Open Access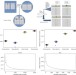 Differences between germline and somatic mutation rates in humans and mice
Differences between germline and somatic mutation rates in humans and mice
Germline mutation rates are known to vary between species but somatic mutation rates are less well understood. Here the authors compare mice and humans, observing that somatic mutation rates were nearly two orders of magnitude higher in both species, with both mutation rates significantly higher in mice.
- Brandon Milholland
- , Xiao Dong
- & Jan Vijg
-
Article
| Open Access Evolutionary interplay between sister cytochrome P450 genes shapes plasticity in plant metabolism
Evolutionary interplay between sister cytochrome P450 genes shapes plasticity in plant metabolism
Genes in the cytochrome P450 family have evolved a wide range of functions. Here, Liu et al. reconstruct the evolution of the P450 genes CYP98A8 and CYP98A9in the Brassicales, revealing a complex history of retrotransposition, tandem duplication and neofunctionalization, followed by subfunctionalization or gene loss in specific lineages.
- Zhenhua Liu
- , Raquel Tavares
- & Hugues Renault
-
Article
| Open Access Breast cancer genome and transcriptome integration implicates specific mutational signatures with immune cell infiltration
Breast cancer genome and transcriptome integration implicates specific mutational signatures with immune cell infiltration
Recent studies using in depth DNA sequencing techniques led to the identification of cancer driver genes but mainly focused on the effect on their expression. Here, the authors analyse 266 cases of breast cancer and report gene expression signatures associated with the number and character of signature mutations.
- Marcel Smid
- , F. Germán Rodríguez-González
- & John W. M. Martens
-
Article
| Open Access The DNA cytosine deaminase APOBEC3H haplotype I likely contributes to breast and lung cancer mutagenesis
The DNA cytosine deaminase APOBEC3H haplotype I likely contributes to breast and lung cancer mutagenesis
The APOBEC family of enzymes are cytidine deaminases with APOBEC3A and APOBEC3B thought to contribute to DNA damage signatures detected in cancer genomes. Here, the authors demonstrate an unappreciated role for APOBEC3H haplotype I in the generation of DNA damage in breast cancer.
- Gabriel J. Starrett
- , Elizabeth M. Luengas
- & Reuben S Harris
-
Article
| Open Access Germline MC1R status influences somatic mutation burden in melanoma
Germline MC1R status influences somatic mutation burden in melanoma
Deleterious germline variants in the MC1Rgene are associated with red hair and freckles, and with an increased risk of developing melanoma. Here, the authors investigate melanoma samples from patients with and without these variants and find that their presence is predictive of a higher overall mutation prevalence.
- Carla Daniela Robles-Espinoza
- , Nicola D. Roberts
- & David J. Adams
-
Article
| Open Access MBTPS2 mutations cause defective regulated intramembrane proteolysis in X-linked osteogenesis imperfecta
MBTPS2 mutations cause defective regulated intramembrane proteolysis in X-linked osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is genetically linked to autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive mutations. Here, Marini et al. describe two families with X-chromosome-linked OI with mutations in MBTPS2 that alter regulated intramembrane proteolysis and subsequent defects in collagen crosslinking and osteoblast function.
- Uschi Lindert
- , Wayne A. Cabral
- & Vorasuk Shotelersuk
-
Article
| Open Access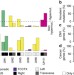 Patients with genetically heterogeneous synchronous colorectal cancer carry rare damaging germline mutations in immune-related genes
Patients with genetically heterogeneous synchronous colorectal cancer carry rare damaging germline mutations in immune-related genes
Some individuals present with multiple synchronous colorectal tumours, but the genetic understanding of this is unclear. Here, the authors use a sequencing strategy to show that the synchronous tumours are genetically independent and the patients harbour rare germline damaging mutations in genes associated with the immune system.
- Matteo Cereda
- , Gennaro Gambardella
- & Francesca D. Ciccarelli
-
Article
| Open Access Rare disruptive mutations and their contribution to the heritable risk of colorectal cancer
Rare disruptive mutations and their contribution to the heritable risk of colorectal cancer
The genetic factors that predispose individuals to familial colorectal cancer are poorly understood. In this study, the authors use whole exome sequencing of 1,006 patients and 1,609 healthy controls and show it is unlikely that further major high-penetrance susceptibility genes exist.
- Daniel Chubb
- , Peter Broderick
- & Richard S. Houlston
-
Article
| Open Access A multigene mutation classification of 468 colorectal cancers reveals a prognostic role for APC
A multigene mutation classification of 468 colorectal cancers reveals a prognostic role for APC
APC is a well-known tumour suppressor that is frequently inactivated in colorectal cancer. Here, the authors sequence more than 1000 cancer genes in 468 colorectal cancers and show that mutation signatures can be used to classify the tumours and that multiple mutations in APCare associated with a poor prognosis.
- Michael J. Schell
- , Mingli Yang
- & Timothy J. Yeatman
-
Article
| Open Access ZBTB7A mutations in acute myeloid leukaemia with t(8;21) translocation
ZBTB7A mutations in acute myeloid leukaemia with t(8;21) translocation
The t(8;21) translocation is often found in acute myeloid leukaemia but is not sufficient for development of the disease. In this study, the authors identify frequent mutations in the transcriptional repressor, ZBTB7A, in these patients and show that the mutations reduce DNA binding activity.
- Luise Hartmann
- , Sayantanee Dutta
- & Philipp A. Greif
-
Article
| Open Access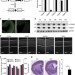 Brain-specific Crmp2 deletion leads to neuronal development deficits and behavioural impairments in mice
Brain-specific Crmp2 deletion leads to neuronal development deficits and behavioural impairments in mice
The in vivo function of CRMP2 is unclear. Zhang et al. generate and characterize brain-specific Crmp2knockout mice. These mice show impairments in hippocampal neurogenesis, neuronal maturation and synaptic transmission, and exhibit schizophrenia-related behavioral deficits.
- Hongsheng Zhang
- , Eunchai Kang
- & Zhiheng Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Mutations in SLC39A14 disrupt manganese homeostasis and cause childhood-onset parkinsonism–dystonia
Mutations in SLC39A14 disrupt manganese homeostasis and cause childhood-onset parkinsonism–dystonia
Karin Tuschl, Philippa Mills and colleagues report mutations in the manganese (Mn) transporter gene SLC39A14in childhood-onset parkinsonism-dystonia. Using functional recapitulation, the authors also show that slc39A14 loss-of-function in zebrafish can lead to Mn dysregulation and locomotor impairment.
- Karin Tuschl
- , Esther Meyer
- & Stephen W. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Epigenetic reprogramming of fallopian tube fimbriae in BRCA mutation carriers defines early ovarian cancer evolution
Epigenetic reprogramming of fallopian tube fimbriae in BRCA mutation carriers defines early ovarian cancer evolution
Women with germline variants in BRCA genes are predisposed to ovarian cancer. In this study, the authors demonstrate that fimbrial tissue from the ovary, the site of ovarian cancer, in BRCAmutant carriers contains marked DNA methylation changes compared with the proximal region of the ovary.
- Thomas E. Bartlett
- , Kantaraja Chindera
- & Martin Widschwendter
-
Article
| Open Access Globally prevalent PfMDR1 mutations modulate Plasmodium falciparum susceptibility to artemisinin-based combination therapies
Globally prevalent PfMDR1 mutations modulate Plasmodium falciparum susceptibility to artemisinin-based combination therapies
Antimalarial chemotherapy relies on combination therapies (ACTs) consisting of an artemisinin derivative and a partner drug. Here, the authors study the effects of globally prevalent mutations in a multidrug resistance transporter (PfMDR1) on the parasite’s susceptibility to ACT drugs.
- M. Isabel Veiga
- , Satish K. Dhingra
- & David A. Fidock
-
Article
| Open Access Heterogeneity and clinical significance of ESR1 mutations in ER-positive metastatic breast cancer patients receiving fulvestrant
Heterogeneity and clinical significance of ESR1 mutations in ER-positive metastatic breast cancer patients receiving fulvestrant
Fulvestrant degrades the oestrogen receptor. Here, the authors report on a clinical trial using fulvestrant and show that mutations in the oestrogen receptor alpha gene are prevalent in circulating tumour DNA and do not influence the clinical outcome of patients to fulvestrant.
- Jill M. Spoerke
- , Steven Gendreau
- & Mark R. Lackner
-
Article
| Open Access Patient-specific factors influence somatic variation patterns in von Hippel–Lindau disease renal tumours
Patient-specific factors influence somatic variation patterns in von Hippel–Lindau disease renal tumours
Analysing multiple tumours from the same patient permits the study of the germline contribution to cancer. Here, the authors sequence multiple renal tumours from VHL patients and find that intra-patient tumours are clonally distinct but share some genetic features, suggesting that patient-specific factors influence tumour formation.
- Suzanne S. Fei
- , Asia D. Mitchell
- & Paul T. Spellman
-
Article
| Open Access The somatic mutation profiles of 2,433 breast cancers refine their genomic and transcriptomic landscapes
The somatic mutation profiles of 2,433 breast cancers refine their genomic and transcriptomic landscapes
Much effort has recently been devoted to understanding the genomics of breast cancer. In this study, the authors integrate somatic mutation data with previously published copy number aberration and gene expression information for nearly 2,500 breast cancer samples.
- Bernard Pereira
- , Suet-Feung Chin
- & Carlos Caldas
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structure of glycogen debranching enzyme and insights into its catalysis and disease-causing mutations
Crystal structure of glycogen debranching enzyme and insights into its catalysis and disease-causing mutations
Debranching of glycogen is an important step in its use as an energy source. Here, the authors describe the crystal structures of glycogen debranching enzyme alone and in complex with oligosaccharides and provide molecular insights into the function, and into associated diseases.
- Liting Zhai
- , Lingling Feng
- & Song Xiang
-
Article
| Open Access A genetic network that suppresses genome rearrangements in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and contains defects in cancers
A genetic network that suppresses genome rearrangements in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and contains defects in cancers
Here, Richard Kolodner and colleagues use assays in Saccharomyces cerevisiaeto identify 182 genetic modifiers of gross chromosomal rearrangements (GCRs). They also compared these Genome Instability Suppressing (GIS) genes and pathways in human cancer genome, and found many ovarian and colorectal cancer cases have alterations to GIS pathways.
- Christopher D. Putnam
- , Anjana Srivatsan
- & Richard D. Kolodner
-
Article
| Open Access A mutation in the atrial-specific myosin light chain gene (MYL4) causes familial atrial fibrillation
A mutation in the atrial-specific myosin light chain gene (MYL4) causes familial atrial fibrillation
Here, Michael Gollob and colleagues perform a whole exome sequencing study to identify a mutation in the atrial-specific myosin light chain gene MYL4 in a small family with autosomal dominant familial atrial fibrillation. They also test the functionality of this MYL4mutation in zebrafish cardiac function and recapitulate disease-related phenotypes.
- Nathan Orr
- , Rima Arnaout
- & Michael H. Gollob
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial and temporal homogeneity of driver mutations in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma
Spatial and temporal homogeneity of driver mutations in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma
Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Gliomas are diagnosed by sampling a small portion of the tumour. Here, using multiple samples from tumours, the authors analyse the spatial and temporal distribution of driver mutations revealing that H3K27M mutations arise first in tumorigenesis followed by a specific invariable sequence of driver mutations, which are homogeneously distributed across the tumour mass.
- Hamid Nikbakht
- , Eshini Panditharatna
- & Javad Nazarian
-
Article
| Open Access p53 downregulates the Fanconi anaemia DNA repair pathway
p53 downregulates the Fanconi anaemia DNA repair pathway
P53 is regarded as the guardian of the genome, however it is known that mice with increased p53 activity display characteristics of dyskeratosis congenita. Here the authors show that increased p53 activity leads to the repression of telomere maintenance and DNA repair genes.
- Sara Jaber
- , Eléonore Toufektchan
- & Franck Toledo
-
Article
| Open Access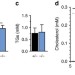 CCC- and WASH-mediated endosomal sorting of LDLR is required for normal clearance of circulating LDL
CCC- and WASH-mediated endosomal sorting of LDLR is required for normal clearance of circulating LDL
Low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) is crucial for cholesterol homeostasis. Here, the authors show that components of the CCC-protein complex, CCDC22 and COMMD1, facilitate the endosomal sorting of LDLR and that mutations in these genes cause hypercholesterolemia in dogs and mice, providing new insights into regulation of cholesterol homeostasis.
- Paulina Bartuzi
- , Daniel D. Billadeau
- & Bart van de Sluis
-
Article
| Open Access Feedback regulation of apical progenitor fate by immature neurons through Wnt7–Celsr3–Fzd3 signalling
Feedback regulation of apical progenitor fate by immature neurons through Wnt7–Celsr3–Fzd3 signalling
The switch from neurogenesis to gliogenesis in cortical development is only partially understood. Here the authors show that Wnt-Planar cell polarity signaling in immature cortical neurons activates Notch in neural progenitor cells, thereby tuning the timing of their fate decisions.
- Wei Wang
- , Yves Jossin
- & Andre M. Goffinet
-
Article
| Open Access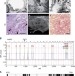 FAT1 mutations cause a glomerulotubular nephropathy
FAT1 mutations cause a glomerulotubular nephropathy
Steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome (SRNS) can cause CKD and necessitate kidney transplant. Here the authors identify FAT1 mutations by homozygosity mapping and whole-exome sequencing in families with SRNS and provide functional mouse and zebrafish evidence that FAT1 is required for normal glomerular and tubular function and that FAT1 mutations can cause SRNS.
- Heon Yung Gee
- , Carolin E. Sadowski
- & Friedhelm Hildebrandt
-
Article
| Open Access Mutations in the nuclear bile acid receptor FXR cause progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis
Mutations in the nuclear bile acid receptor FXR cause progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis
Neonatal cholestasis is a result of elevated bile acid levels, and is associated with mutations in genes regulating bile acid homeostasis. Here the authors identify mutations in the bile acid sensing farnesoid X receptor in four individuals with neonatal cholestasis from two unrelated families.
- Natalia Gomez-Ospina
- , Carol J. Potter
- & David D. Moore
-
Article
| Open Access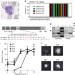 KRAS insertion mutations are oncogenic and exhibit distinct functional properties
KRAS insertion mutations are oncogenic and exhibit distinct functional properties
Amino acid substitutions in K-Ras that constitutively activate the protein are common in cancer. Here, the authors describe mutations in the K-RasSwitch 2 domain and show that the mutant proteins accumulate in the active conformation, exhibit defective binding to PI3 kinase, and are hypersensitive to MEK inhibitors.
- Yasmine White
- , Aditi Bagchi
- & Ari J. Firestone
-
Article
| Open Access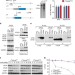 ALS-associated mutant FUS induces selective motor neuron degeneration through toxic gain of function
ALS-associated mutant FUS induces selective motor neuron degeneration through toxic gain of function
The mechanism by which FUS mutations cause familial ALS remains unclear. Here, the authors use mouse transgenic models to show that a toxic gain-of-function underlies motor neuron degeneration, and that the toxicity of mutant FUS does not depend on a loss or excess of FUS activity.
- Aarti Sharma
- , Alexander K. Lyashchenko
- & Neil A. Shneider
-
Article
| Open Access Cancer-associated SF3B1 mutations affect alternative splicing by promoting alternative branchpoint usage
Cancer-associated SF3B1 mutations affect alternative splicing by promoting alternative branchpoint usage
Mutations in the splicing factor SF3B1 are found in uveal melanoma. Here, Alsafadi et al. use RNA-sequencing data from these cancers and experimental models, and show that mutant SF3B1 promotes alternative branchpoints in a specific gene subset and that the mutant protein gains a new function.
- Samar Alsafadi
- , Alexandre Houy
- & Marc-Henri Stern
-
Article
| Open Access Joint mouse–human phenome-wide association to test gene function and disease risk
Joint mouse–human phenome-wide association to test gene function and disease risk
Phenome-wide association is a novel method that links sequence variants to a spectrum of phenotypes and diseases. Here the authors generate detailed mouse genetic and phenome data which links their phenome-wide association study (PheWAS) of mouse to corresponding PheWAS in human.
- Xusheng Wang
- , Ashutosh K. Pandey
- & Robert W. Williams
-
Article
| Open Access Arrhythmogenesis in Timothy Syndrome is associated with defects in Ca2+-dependent inactivation
Arrhythmogenesis in Timothy Syndrome is associated with defects in Ca2+-dependent inactivation
Timothy Syndrome (TS) is a multisystem disorder caused by two mutations leading to dysfunction of the CaV1.2 channel. Here, Dick et al. uncover a major and mechanistically divergent effect of both mutations on Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent inactivation of CaV1.2 channels, suggesting genetic variant-tailored therapy for TS treatment.
- Ivy E. Dick
- , Rosy Joshi-Mukherjee
- & David T. Yue
-
Article
| Open Access Mutational spectrum of Barrett’s stem cells suggests paths to initiation of a precancerous lesion
Mutational spectrum of Barrett’s stem cells suggests paths to initiation of a precancerous lesion
Barrett’s oesophagus is a precancerous intestinal metaplasia that can progress to oesophageal adenocarcinoma. In this study, the authors isolate and characterize human Barrett’s stem cells and identify a specific genomic pedigree that supports the potential role of these cells as precursors of oesophageal adenocarcinoma.
- Yusuke Yamamoto
- , Xia Wang
- & Wa Xian
-
Article
| Open Access New observations on maternal age effect on germline de novo mutations
New observations on maternal age effect on germline de novo mutations
The study of germline mutations has been greatly enhanced by massive parallel sequencing technologies. Here the authors use deep sequencing data from nearly 700 parent-child trios to show maternal age has a small but significant correlation with the number of de novomutations in the offspring.
- Wendy S. W. Wong
- , Benjamin D. Solomon
- & John E. Niederhuber
-
Article
| Open Access A comprehensive assessment of somatic mutation detection in cancer using whole-genome sequencing
A comprehensive assessment of somatic mutation detection in cancer using whole-genome sequencing
Cancer genetics has benefited from the advent of next generation sequencing, yet a comparison of sequencing and analysis techniques is lacking. Here, the authors sequence a normal-tumour pair and perform data analysis at multiple institutes and highlight some of the pitfalls associated with the different methods.
- Tyler S. Alioto
- , Ivo Buchhalter
- & Ivo G. Gut
-
Article
| Open Access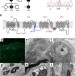 Cold-aggravated pain in humans caused by a hyperactive NaV1.9 channel mutant
Cold-aggravated pain in humans caused by a hyperactive NaV1.9 channel mutant
A mutation in the sodium channel Nav1.9 has been identified in a family and shown to associate with cold-aggravated pain. Here, the authors characterize the electrophysiological consequences of this mutation and propose a mechanism for the pain that the individuals experience.
- Enrico Leipold
- , Andrea Hanson-Kahn
- & Ingo Kurth
-
Article
| Open Access MLLT1 YEATS domain mutations in clinically distinctive Favourable Histology Wilms tumours
MLLT1 YEATS domain mutations in clinically distinctive Favourable Histology Wilms tumours
Wilms tumour is a rare renal neoplasm that primarily affects children but the genomic changes responsible for its development are currently largely unknown. In this study, the authors identify somatic mutations of the MLLT1gene that are potentially involved in the aetiology of a subset of Wilms tumours.
- Elizabeth J. Perlman
- , Samantha Gadd
- & Malcolm A. Smith
-
Article |
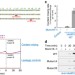 The trans-SNARE-regulating function of Munc18-1 is essential to synaptic exocytosis
The trans-SNARE-regulating function of Munc18-1 is essential to synaptic exocytosis
Munc18-1 binds trans-SNARE complexes and promotes membrane fusion in vitro. Here the authors provide genetic evidence that this trans-SNARE-regulating function plays an essential role in synaptic releases in neurons, and show that this function is disrupted by a disease-causing Munc18-1 mutation.
- Chong Shen
- , Shailendra S. Rathore
- & Jingshi Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Recurrent internal tandem duplications of BCOR in clear cell sarcoma of the kidney
Recurrent internal tandem duplications of BCOR in clear cell sarcoma of the kidney
The genetic basis of clear cell sarcomas of the kidney is not well understood. In this study, Roy et al. perform whole-exome and RNA sequencing of these tumours and identify recurrent internal tandem duplications in BCOR, a key constituent of a variant polycomb repressive complex.
- Angshumoy Roy
- , Vijetha Kumar
- & D. Williams Parsons

 Mitochondrially-targeted APOBEC1 is a potent mtDNA mutator affecting mitochondrial function and organismal fitness in Drosophila
Mitochondrially-targeted APOBEC1 is a potent mtDNA mutator affecting mitochondrial function and organismal fitness in Drosophila