Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Whole-genome doubling drives oncogenic loss of chromatin segregation
Whole-genome doubling drives oncogenic loss of chromatin segregation
Whole-genome doubling induces the loss of segregation of chromatin compartments, and can lead to tumour-promoting epigenetic and transcriptional modifications.
- Ruxandra A. Lambuta
- , Luca Nanni
- & Elisa Oricchio
-
Article |
 Molecular sensing of mechano- and ligand-dependent adhesion GPCR dissociation
Molecular sensing of mechano- and ligand-dependent adhesion GPCR dissociation
A technique to detect the release of N-terminal fragments of Drosophila adhesion G-protein-coupled receptors (aGPCRs) provides insight into the dissociation of aGPCRs, and shows that receptor autoproteolysis enables non-cell-autonomous activity of aGPCRs in the brain.
- Nicole Scholz
- , Anne-Kristin Dahse
- & Tobias Langenhan
-
Article
| Open Access H3K4me3 regulates RNA polymerase II promoter-proximal pause-release
H3K4me3 regulates RNA polymerase II promoter-proximal pause-release
Acute loss of H3K4me3 does not have detectable effects on transcriptional initiation, but leads to a widespread decrease in transcriptional output, an increase in RNA polymerase II pausing and slower elongation
- Hua Wang
- , Zheng Fan
- & Kristian Helin
-
Article |
 Sequence determinant of small RNA production by DICER
Sequence determinant of small RNA production by DICER
Massively parallel assays reveal a highly conserved sequence motif termed the GYM motif, which potentiates RNA interference by directing Dicer-mediated small RNA processing.
- Young-Yoon Lee
- , Haedong Kim
- & V. Narry Kim
-
News & Views |
 MicroRNA uses a gym to get fit for cuts by Dicer enzyme
MicroRNA uses a gym to get fit for cuts by Dicer enzyme
The enzyme Dicer cleaves a type of RNA called a pre-microRNA to make the mature functional RNA. Structural evidence now sheds light on the catalytic mechanism involved and the role of a newly found RNA sequence termed GYM.
- Gunter Meister
-
Article |
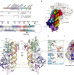 Structure of the human DICER–pre-miRNA complex in a dicing state
Structure of the human DICER–pre-miRNA complex in a dicing state
The active-state structure of human DICER bound to pre-miRNA reveals the structural basis for the specificity of DICER in how it selects substrates in a sequence dependent manner, and sheds light on DICER-related diseases.
- Young-Yoon Lee
- , Hansol Lee
- & Soung-Hun Roh
-
Article |
 mRNA ageing shapes the Cap2 methylome in mammalian mRNA
mRNA ageing shapes the Cap2 methylome in mammalian mRNA
Cap2 methylation increases on transcripts as they age, reducing activation of innate immunity.
- Vladimir Despic
- & Samie R. Jaffrey
-
News & Views |
 Protein structure terminates doubt about how transcription stops
Protein structure terminates doubt about how transcription stops
High-resolution structures of the bacterial Rho protein in complex with an RNA polymerase enzyme and partner proteins provide support for the long-held model of how Rho helps to terminate gene transcription.
- Fahad Rashid
- & James Berger
-
Article |
 Structural basis of Rho-dependent transcription termination
Structural basis of Rho-dependent transcription termination
Structures presented in this study confirm decades of genetic and biochemical evidence for the mechanism of Rho-dependent termination in bacteria.
- Vadim Molodtsov
- , Chengyuan Wang
- & Richard H. Ebright
-
Article
| Open Access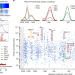 Mitochondrial complexome reveals quality-control pathways of protein import
Mitochondrial complexome reveals quality-control pathways of protein import
An analysis of MitCOM—a comprehensive resource for the identification, organization and interaction of mitochondrial machineries and pathways in yeast—identifies a constitutive pathway for the removal of preproteins.
- Uwe Schulte
- , Fabian den Brave
- & Thomas Becker
-
Research Briefing |
 A set of factors that silence the protein-making machinery in eggs
A set of factors that silence the protein-making machinery in eggs
In egg cells, the ribosomes — the machinery responsible for protein synthesis — are stored in a dormant state that is released later in the developing embryo. An evolutionarily conserved set of proteins has been shown to bind to ribosomes in the egg cells of vertebrates, stabilizing the ribosomes and suppressing their activity.
-
News |
 Transgenic ants shed light on insects’ sense of smell
Transgenic ants shed light on insects’ sense of smell
A fluorescent protein helps to pinpoint parts of the brain that help the animals navigate a world of scents.
- Miryam Naddaf
-
Article |
 A molecular network of conserved factors keeps ribosomes dormant in the egg
A molecular network of conserved factors keeps ribosomes dormant in the egg
Mass spectrometry and structural studies demonstrate the specific changes in protein composition that accompany the transition of ribosomes in zebrafish and Xenopus eggs from a dormant to an active state during early embryogenesis.
- Friederike Leesch
- , Laura Lorenzo-Orts
- & Andrea Pauli
-
News & Views |
 First full views of a CRISPR-guided system for gene insertion
First full views of a CRISPR-guided system for gene insertion
CRISPR–Cas is a bacterial defence system that can attack invading DNA to protect host cells, or help to insert DNA safely into the genome. Structures of this latter type of CRISPR–Cas system have now been visualized.
- Orsolya Barabas
- & Phoebe A. Rice
-
News & Views |
 No stopping with a short-stem transfer RNA
No stopping with a short-stem transfer RNA
Messenger RNA has 64 possible triplet sequences, or codons, three of which usually terminate protein synthesis. But some organisms can use all codons to specify amino acids, thanks in part to a surprising feature of a transfer RNA.
- Pavel V. Baranov
- & John F. Atkins
-
Article |
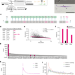 Short tRNA anticodon stem and mutant eRF1 allow stop codon reassignment
Short tRNA anticodon stem and mutant eRF1 allow stop codon reassignment
Analyses of in-frame stop codons in protein-coding genes of Blastocrithidia nonstop with all three stop codons reassigned reveal a mechanism for UGA reassignment in eukaryotes involving shortening of the tRNA anticodon stem and a mutant eRF1 release factor.
- Ambar Kachale
- , Zuzana Pavlíková
- & Julius Lukeš
-
Article |
 Structural basis for intrinsic transcription termination
Structural basis for intrinsic transcription termination
Structural studies of Escherichia coli transcription intrinsic termination complexes representing distinct intermediates using cryo-electron microscopy provide insights into the steps and mechanism of transcription termination.
- Linlin You
- , Expery O. Omollo
- & Yu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Cas12a2 elicits abortive infection through RNA-triggered destruction of dsDNA
Cas12a2 elicits abortive infection through RNA-triggered destruction of dsDNA
RNA targeting by the Sulfuricurvum type V single-effector nuclease SuCas12a2 drives abortive infection through non-specific cleavage of double-stranded DNA—after recognition of an RNA target through an activating protospacer-flanking sequence, SuCas12a2 efficiently degrades ssRNA, ssDNA and dsDNA.
- Oleg Dmytrenko
- , Gina C. Neumann
- & Chase L. Beisel
-
Article |
 Structures and mechanisms of tRNA methylation by METTL1–WDR4
Structures and mechanisms of tRNA methylation by METTL1–WDR4
Using cryo-electron microscopy, structural and mechanistic insights into how the METTL1–WDR4 complex catalyses methylation of tRNAs are shown.
- Victor M. Ruiz-Arroyo
- , Rishi Raj
- & Yunsun Nam
-
Article |
 Structural basis of regulated m7G tRNA modification by METTL1–WDR4
Structural basis of regulated m7G tRNA modification by METTL1–WDR4
Structures of the human METTL1–WDR4 complex are revealed, providing molecular insights into substrate recognition, modification and catalytic regulation by the N7-methylguanosine methyltransferase complex.
- Jiazhi Li
- , Longfei Wang
- & Richard I. Gregory
-
News & Views |
 A mechanism for inheriting radiation-induced DNA damage
A mechanism for inheriting radiation-induced DNA damage
Radiation-damaged paternal DNA has been found to cause embryos of the second generation of nematode worms, but not the first, to die. The proposed mechanisms help to explain the observed lack of such an effect in humans.
- Ronald Cutler
- & Jan Vijg
-
Research Briefing |
 Exploring the rapid evolution of the mammalian testis
Exploring the rapid evolution of the mammalian testis
The mammalian testis is a rapidly evolving organ, in both structural and molecular terms. An investigation of testicular cell nuclei from 11 species has unveiled genes, cell types and evolutionary forces that underlie these changes.
-
Article |
 R-loop-derived cytoplasmic RNA–DNA hybrids activate an immune response
R-loop-derived cytoplasmic RNA–DNA hybrids activate an immune response
RNA–DNA hybrids are immunogenic species that can aberrantly accumulate in the cytoplasm after R-loop processing, linking R-loop accumulation to cell death through the innate immune response.
- Magdalena P. Crossley
- , Chenlin Song
- & Karlene A. Cimprich
-
Article
| Open Access Inheritance of paternal DNA damage by histone-mediated repair restriction
Inheritance of paternal DNA damage by histone-mediated repair restriction
In Caenorhabditis elegans, paternal exposure to ionizing radiation results in HIS-24 and HPL-1-dependent genome instability phenotypes, causing embryonic lethality in the offspring.
- Siyao Wang
- , David H. Meyer
- & Björn Schumacher
-
Article |
 BRD8 maintains glioblastoma by epigenetic reprogramming of the p53 network
BRD8 maintains glioblastoma by epigenetic reprogramming of the p53 network
BRD8 is identified as a specific epigenetic vulnerability for glioblastomas that harbour wild-type p53.
- Xueqin Sun
- , Olaf Klingbeil
- & Alea A. Mills
-
Article
| Open Access The molecular evolution of spermatogenesis across mammals
The molecular evolution of spermatogenesis across mammals
Evolutionary analyses of single-nucleus transcriptome data for testes from 11 species are reported, illuminating the molecular evolution of spermatogenesis and associated forces, and providing a resource for investigating the testis across mammals.
- Florent Murat
- , Noe Mbengue
- & Henrik Kaessmann
-
Article |
 A male germ-cell-specific ribosome controls male fertility
A male germ-cell-specific ribosome controls male fertility
RibosomeST—a ribosome with a specialized nascent polypeptide exit tunnel—cotranslationally regulates the folding of a subset of male germ-cell-specific proteins that are essential for the formation of sperm.
- Huiling Li
- , Yangao Huo
- & Jiahao Sha
-
Article |
 Structural variants drive context-dependent oncogene activation in cancer
Structural variants drive context-dependent oncogene activation in cancer
Results are presented that indicate that alterations to gene regulatory three-dimensional architecture are a critical mechanism that enables structural variant-based oncogene activation in cancer genomes and sheds light on the essential elements for such gene activation events.
- Zhichao Xu
- , Dong-Sung Lee
- & Jesse R. Dixon
-
Article
| Open Access A transcriptional switch controls sex determination in Plasmodium falciparum
A transcriptional switch controls sex determination in Plasmodium falciparum
A non-genetic mechanism of sex determination in the human malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum, is described, and the male development 1 gene is identified as a potential target for interventions that block malaria transmission.
- A. R. Gomes
- , A. Marin-Menendez
- & A. M. Talman
-
Article |
 Microbial predators form a new supergroup of eukaryotes
Microbial predators form a new supergroup of eukaryotes
Provora is an ancient supergroup of microbial predators that are genetically, morphologically and behaviourally distinct from other eukaryotes, and comprise two divergent clades of predators—Nebulidia and Nibbleridia—that differ fundamentally in ultrastructure, behaviour and gene content.
- Denis V. Tikhonenkov
- , Kirill V. Mikhailov
- & Patrick J. Keeling
-
Article |
 Genomic signature of Fanconi anaemia DNA repair pathway deficiency in cancer
Genomic signature of Fanconi anaemia DNA repair pathway deficiency in cancer
Defective DNA interstrand crosslink repair in Fanconi anaemia drives extensive genomic rearrangements, thereby substantially increasing the risk of cancer development.
- Andrew L. H. Webster
- , Mathijs A. Sanders
- & Agata Smogorzewska
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of the holo CRISPR RNA-guided transposon integration complex
Structures of the holo CRISPR RNA-guided transposon integration complex
Structural studies of the CRISPR-associated transposon comprising Cas12k, TnsC, TnsB and TniQ from Scytonema hofmannii using cryo-electron microscopy reveal insights into the architecture and mechanism of RNA-guided DNA transposition.
- Jung-Un Park
- , Amy Wei-Lun Tsai
- & Elizabeth H. Kellogg
-
Research Briefing |
 How flowering plants compact their sperm DNA
How flowering plants compact their sperm DNA
It has not been clear how sperm DNA is compacted in the pollen of flowering plants. Research has now revealed that sperm chromatin, which is a complex of DNA and proteins, is packaged by a special histone protein that spontaneously aggregates in a phenomenon known as phase separation.
-
Article
| Open Access Histone H2B.8 compacts flowering plant sperm through chromatin phase separation
Histone H2B.8 compacts flowering plant sperm through chromatin phase separation
H2B.8 is identified as a histone variant that mediates a newly described mechanism of transcription-compatible chromatin condensation in flowering plant sperm cells.
- Toby Buttress
- , Shengbo He
- & Xiaoqi Feng
-
News & Views |
 Catching actin proteins in action
Catching actin proteins in action
Two groups have visualized actin — the protein polymer that gives cells their shape — at high resolution. The structures provide in-depth views of the polymer as it adopts fleeting states and undergoes conformational changes.
- Pilar Cossio
- & Glen M. Hocky
-
Article
| Open Access Semi-automated assembly of high-quality diploid human reference genomes
Semi-automated assembly of high-quality diploid human reference genomes
Which combination of current genome sequencing and assembly approaches results in high-quality, complete diploid genome assemblies is determined.
- Erich D. Jarvis
- , Giulio Formenti
- & Karen H. Miga
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the OMEGA nickase IsrB in complex with ωRNA and target DNA
Structure of the OMEGA nickase IsrB in complex with ωRNA and target DNA
The cryogenic-electron microscopy structure of the D. thermocuniculi IsrB protein in complex with its cognate ωRNA and a target DNA shows that the RNA-dominant IsrB effector complex shares a common scaffold with the protein-dominant Cas9 effector complex.
- Seiichi Hirano
- , Kalli Kappel
- & Feng Zhang
-
Article |
 Programmable RNA sensing for cell monitoring and manipulation
Programmable RNA sensing for cell monitoring and manipulation
RNA sensing-mediated payload expression provides a specific, versatile, simple and generalizable means of detecting and manipulating animal cells with broad potential applications.
- Yongjun Qian
- , Jiayun Li
- & Z. Josh Huang
-
Article |
 Structure of the NuA4 acetyltransferase complex bound to the nucleosome
Structure of the NuA4 acetyltransferase complex bound to the nucleosome
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of NuA4 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae bound to the nucleosome illustrates how NuA4 is assembled and provides mechanistic insights into nucleosome recognition and transcription co-activation by a histone acetyltransferase.
- Keke Qu
- , Kangjing Chen
- & Zhucheng Chen
-
Article |
 A mechanism for oxidative damage repair at gene regulatory elements
A mechanism for oxidative damage repair at gene regulatory elements
The nuclear mitotic apparatus protein NuMA helps to protect genes from oxidative damage by occupying regions around transcription start sites, binding DNA repair factors and promoting transcription following damage.
- Swagat Ray
- , Arwa A. Abugable
- & Sherif F. El-Khamisy
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing translation dynamics at atomic detail inside a bacterial cell
Visualizing translation dynamics at atomic detail inside a bacterial cell
Cryo-electron tomography is used to reveal the structural dynamics and functional diversity of translating ribosomes in Mycoplasma pneumoniae, providing insight into the translation elongation cycle inside cells and how it is reshaped by antibiotics.
- Liang Xue
- , Swantje Lenz
- & Julia Mahamid
-
News |
 AlphaFold developers win US$3-million Breakthrough Prize
AlphaFold developers win US$3-million Breakthrough Prize
DeepMind’s system for predicting the 3D structure of proteins is among five recipients of science’s most lucrative awards.
- Zeeya Merali
-
Article |
 CDK11 regulates pre-mRNA splicing by phosphorylation of SF3B1
CDK11 regulates pre-mRNA splicing by phosphorylation of SF3B1
CDK11 associates with SF3B1 and phosphorylates threonine residues at the N terminus of SF3B1 during spliceosome activation, and the inhibition of CDK11 blocks the activation and leads to widespread intron retention and the accumulation of non-functional spliceosomes on pre-mRNAs and chromatin.
- Milan Hluchý
- , Pavla Gajdušková
- & Dalibor Blazek
-
Article |
 Glucose-driven TOR–FIE–PRC2 signalling controls plant development
Glucose-driven TOR–FIE–PRC2 signalling controls plant development
Glucose signalling via TOR controls growth and differentiation through regulation of genome-wide histone methylation via FERTILIZATION-INDEPENDENT ENDOSPERM (FIE).
- Ruiqiang Ye
- , Meiyue Wang
- & Jen Sheen
-
Article |
 Columnar structure of human telomeric chromatin
Columnar structure of human telomeric chromatin
Cryogenic electron microscopy analyses reveal a new, compact structure of telomeric chromatin, providing mechanistic insight into telomere maintenance and function.
- Aghil Soman
- , Sook Yi Wong
- & Lars Nordenskiöld
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of AAA+ ATPase-mediated RuvAB–Holliday junction branch migration
Mechanism of AAA+ ATPase-mediated RuvAB–Holliday junction branch migration
Structures of the ATP-hydrolysing RuvAB complex captured in multiple conformations provide mechanistic insights into coordinated ATPase and motor activity during DNA recombination.
- Jiri Wald
- , Dirk Fahrenkamp
- & Thomas C. Marlovits
-
Article |
 Selective TnsC recruitment enhances the fidelity of RNA-guided transposition
Selective TnsC recruitment enhances the fidelity of RNA-guided transposition
CRISPR-associated transposons exploit a proofreading checkpoint to ensure high-fidelity selection of genomic sites for DNA insertion through specific recruitment of TnsC oligomers by the Cascade complex.
- Florian T. Hoffmann
- , Minjoo Kim
- & Samuel H. Sternberg
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo single-molecule analysis reveals COOLAIR RNA structural diversity
In vivo single-molecule analysis reveals COOLAIR RNA structural diversity
The structures of single COOLAIR RNA isoforms change in abundance and shape in response to external conditions; structural mutation of these isoforms altered FLC expression and flowering time, consistent with a regulatory role of the COOLAIR structure in FLC transcription.
- Minglei Yang
- , Pan Zhu
- & Yiliang Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Live-seq enables temporal transcriptomic recording of single cells
Live-seq enables temporal transcriptomic recording of single cells
Live-seq, a single-cell transcriptome profiling approach that preserves cell viability during RNA extraction using fluidic force microscopy, can address a range of biological questions by transforming scRNA-seq from an end-point to a temporal analysis approach.
- Wanze Chen
- , Orane Guillaume-Gentil
- & Bart Deplancke
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Cell division
- Chromatin
- Chromosomes
- CRISPR-Cas systems
- DNA damage and repair
- DNA metabolism
- DNA recombination
- DNA replication
- Epigenetics
- Non-coding RNAs
- Nuclear organization
- Post-translational modifications
- Protein folding
- Proteolysis
- Proteomics
- Riboswitches
- Ribozymes
- RNA metabolism
- RNAi
- Single-molecule biophysics
- Transcription
- Transcriptomics
- Translation
- Transposition

 A swapped genetic code prevents viral infections and gene transfer
A swapped genetic code prevents viral infections and gene transfer