Featured
-
-
Article |
 Structure of PINK1 in complex with its substrate ubiquitin
Structure of PINK1 in complex with its substrate ubiquitin
Stabilization of a transient protein kinase–substrate complex using a nanobody provides molecular details about how the Parkinson’s disease-linked protein kinase PINK1 phosphorylates ubiquitin, and suggests new pharmacological strategies.
- Alexander F. Schubert
- , Christina Gladkova
- & David Komander
-
Letter |
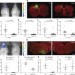 Targeting neuronal activity-regulated neuroligin-3 dependency in high-grade glioma
Targeting neuronal activity-regulated neuroligin-3 dependency in high-grade glioma
The growth of adult and paediatric brain tumours depends on a microenvironmental signalling pathway involving the activity-regulated secretion of neuroligin-3 (NLGN3) from normal neurons and oligodendrocyte precursor cells, highlighting the potential of NLGN3 as a therapeutic target.
- Humsa S. Venkatesh
- , Lydia T. Tam
- & Michelle Monje
-
Letter |
 Cancer progression by reprogrammed BCAA metabolism in myeloid leukaemia
Cancer progression by reprogrammed BCAA metabolism in myeloid leukaemia
BCAT1, a cytosolic aminotransferase for branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), is aberrantly activated and functionally required for disease progression in chronic myeloid leukaemia.
- Ayuna Hattori
- , Makoto Tsunoda
- & Takahiro Ito
-
Letter |
 Intratumoural heterogeneity generated by Notch signalling promotes small-cell lung cancer
Intratumoural heterogeneity generated by Notch signalling promotes small-cell lung cancer
In a mouse model of small-cell lung cancer and in human tumours, activation of the Notch pathway can lead to a cell fate switch of neuroendocrine cells to less proliferative non-neuroendocrine cells, generating intratumoural heterogeneity.
- Jing Shan Lim
- , Alvaro Ibaseta
- & Julien Sage
-
Letter |
 Polyglutamine tracts regulate beclin 1-dependent autophagy
Polyglutamine tracts regulate beclin 1-dependent autophagy
The polyglutamine domain in ataxin 3, which is expanded in spinocerebellar ataxia type 3, allows normal ataxin 3 to interact with and deubiquitinate beclin 1 and thereby to promote autophagy.
- Avraham Ashkenazi
- , Carla F. Bento
- & David C. Rubinsztein
-
Article |
 MC4R-dependent suppression of appetite by bone-derived lipocalin 2
MC4R-dependent suppression of appetite by bone-derived lipocalin 2
Osteoblast-derived LCN2 activates the melanocortin 4 receptor in neurons of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus to suppress appetite, regulates insulin secretion and increases insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance.
- Ioanna Mosialou
- , Steven Shikhel
- & Stavroula Kousteni
-
Letter |
 XRCC1 mutation is associated with PARP1 hyperactivation and cerebellar ataxia
XRCC1 mutation is associated with PARP1 hyperactivation and cerebellar ataxia
Biallelic mutations in human XRCC1 are associated with ocular motor apraxia, axonal neuropathy, and progressive cerebellar ataxia.
- Nicolas C. Hoch
- , Hana Hanzlikova
- & Keith W. Caldecott
-
Letter |
 Mechanism of early dissemination and metastasis in Her2+ mammary cancer
Mechanism of early dissemination and metastasis in Her2+ mammary cancer
Two related papers show that cells disseminated from malignant lesions at early time points during tumorigenesis can contribute to metastases at distant organs and provide insights into the molecular basis of dissemination.
- Kathryn L. Harper
- , Maria Soledad Sosa
- & Julio A. Aguirre-Ghiso
-
Letter |
 Fatty acid synthesis configures the plasma membrane for inflammation in diabetes
Fatty acid synthesis configures the plasma membrane for inflammation in diabetes
Mice with macrophages deficient in fatty acid synthase exhibit lower levels of diabetes-related insulin resistance and inflammation, qualities that are restored on addition of exogenous cholesterol.
- Xiaochao Wei
- , Haowei Song
- & Clay F. Semenkovich
-
Article |
 Frizzled proteins are colonic epithelial receptors for C. difficile toxin B
Frizzled proteins are colonic epithelial receptors for C. difficile toxin B
Here, a genome-wide CRISPR–Cas9 screen is used to identify the Wnt receptors frizzled as physiologically relevant Clostridium difficile toxin B receptors, providing new therapeutic targets for treating C. difficile infections.
- Liang Tao
- , Jie Zhang
- & Min Dong
-
Letter |
 The prion protein is an agonistic ligand of the G protein-coupled receptor Adgrg6
The prion protein is an agonistic ligand of the G protein-coupled receptor Adgrg6
The cellular prion protein PrPC promotes peripheral myelin homeostasis by acting on a G protein-coupled receptor to increase levels of cyclic AMP in Schwann cells.
- Alexander Küffer
- , Asvin K. K. Lakkaraju
- & Adriano Aguzzi
-
Letter |
 CD47-blocking antibodies restore phagocytosis and prevent atherosclerosis
CD47-blocking antibodies restore phagocytosis and prevent atherosclerosis
Atherosclerotic lesions in mice and humans switch on a ‘don’t eat me’ signal—expression of CD47—that prevents effective removal of diseased tissue; anti-CD47 antibody therapy can normalize this defective efferocytosis, with beneficial results in several mouse models of atherosclerosis.
- Yoko Kojima
- , Jens-Peter Volkmer
- & Nicholas J. Leeper
-
Letter |
 Identification of proliferative and mature β-cells in the islets of Langerhans
Identification of proliferative and mature β-cells in the islets of Langerhans
Mature pancreatic β-cells can be distinguished from proliferating ones by expression of the Fltp reporter gene, which is triggered by Wnt signalling and β-cell polarization and islet compaction.
- Erik Bader
- , Adriana Migliorini
- & Heiko Lickert
-
Letter |
 Mitochondrial ROS regulate thermogenic energy expenditure and sulfenylation of UCP1
Mitochondrial ROS regulate thermogenic energy expenditure and sulfenylation of UCP1
Uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1)-dependent thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue is supported by a burst of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species upon cold exposure.
- Edward T. Chouchani
- , Lawrence Kazak
- & Bruce M. Spiegelman
-
Letter |
 PGC1α drives NAD biosynthesis linking oxidative metabolism to renal protection
PGC1α drives NAD biosynthesis linking oxidative metabolism to renal protection
PGC1α protects against kidney injury by upregulating enzymes that enhance nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and driving local accumulation of the fatty acid breakdown product β-hydroxybutyrate, which leads to increased production of the renoprotective prostaglandin E2.
- Mei T. Tran
- , Zsuzsanna K. Zsengeller
- & Samir M. Parikh
-
Letter |
 A phosphoinositide conversion mechanism for exit from endosomes
A phosphoinositide conversion mechanism for exit from endosomes
A mechanism for phosphoinositide conversion at endosomes to enable exit from the endosomal system, suggesting that defective phosphoinositide conversion at endosomes underlies X-linked centronuclear myopathy.
- Katharina Ketel
- , Michael Krauss
- & Volker Haucke
-
Letter |
 Intestinal epithelial tuft cells initiate type 2 mucosal immunity to helminth parasites
Intestinal epithelial tuft cells initiate type 2 mucosal immunity to helminth parasites
Epithelial tuft cells secretion of IL-25 is shown to regulate type 2 epithelial responses to helminth parasite infection via an IL-13/IL-4Rα-dependent feedback loop.
- François Gerbe
- , Emmanuelle Sidot
- & Philippe Jay
-
Article |
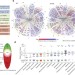 ∆F508 CFTR interactome remodelling promotes rescue of cystic fibrosis
∆F508 CFTR interactome remodelling promotes rescue of cystic fibrosis
A new deep proteomic analysis method is used to identify proteins that interact with wild-type cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) and its mutant version that is the major cause of cystic fibrosis.
- Sandra Pankow
- , Casimir Bamberger
- & John R. Yates III
-
Article |
 Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis
Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis
Exosomes originating from lung-, liver- and brain-tropic tumour cells are preferentially incorporated by specific resident cells of the target organs, thus preparing the site for metastasis; the expression of distinct combinations of exosomal integrin proteins determines the exosomal targeting to each of the three organs, and blocking these integrins reduces organotropic exosome uptake by the target organs, thereby reducing the likelihood of organotropic metastasis.
- Ayuko Hoshino
- , Bruno Costa-Silva
- & David Lyden
-
Letter |
 CMT2D neuropathy is linked to the neomorphic binding activity of glycyl-tRNA synthetase
CMT2D neuropathy is linked to the neomorphic binding activity of glycyl-tRNA synthetase
Charcot–Marie–Tooth diseases are hereditary peripheral neuropathies for which there are currently no effective therapies; here the type 2D subtype of these diseases is shown to be caused by mutations impeding a signalling pathway necessary for motor neuron survival.
- Weiwei He
- , Ge Bai
- & Xiang-Lei Yang
-
Letter |
 Lanosterol reverses protein aggregation in cataracts
Lanosterol reverses protein aggregation in cataracts
Exploring the genetic basis of congenital cataracts in two families identifies a molecule, lanosterol, which prevents intracellular protein aggregation of various cataract-causing mutant crystallins, and which can reduce cataract severity and increase lens transparency in vivo in dogs.
- Ling Zhao
- , Xiang-Jun Chen
- & Kang Zhang
-
Letter |
 The CREB coactivator CRTC2 controls hepatic lipid metabolism by regulating SREBP1
The CREB coactivator CRTC2 controls hepatic lipid metabolism by regulating SREBP1
Studies in mice reveal that CREB regulated transcription coactivator 2 (CRTC2) acts as a mediator of mTOR signalling in the liver to regulate SREBP1-controlled lipid homeostasis during feeding and diabetes; overexpression of a CRTC2 mutant defective for mTOR regulation improves the lipogenic program and insulin sensitivity in obese mice.
- Jinbo Han
- , Erwei Li
- & Yiguo Wang
-
Letter |
 A molecular mechanism of artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria
A molecular mechanism of artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria
Artemisinins are key anti-malarial drugs, but artemisinin resistance has been increasing; this study identifies the molecular target of artemisinins as phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase and increase of the lipid product phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate induces resistance in Plasmodium falciparum.
- Alassane Mbengue
- , Souvik Bhattacharjee
- & Kasturi Haldar
-
Letter |
 The Drosophila TNF receptor Grindelwald couples loss of cell polarity and neoplastic growth
The Drosophila TNF receptor Grindelwald couples loss of cell polarity and neoplastic growth
Cell polarity is an important feature of many tissues and is often disrupted in cancer; the TNF receptor Grindelwald is now shown to have an important role in coordinating cell polarity and neoplastic growth in a Drosophila model.
- Ditte S. Andersen
- , Julien Colombani
- & Pierre Léopold
-
Letter |
 Phosphodiesterase 9A controls nitric-oxide-independent cGMP and hypertrophic heart disease
Phosphodiesterase 9A controls nitric-oxide-independent cGMP and hypertrophic heart disease
The inhibition, in mice, of the phosphodiesterase PDE9A, which specifically regulates natriuretic-peptide-coupled cGMP signalling, is independent of nitric oxide and is upregulated in failing human hearts, and can reverse pre-established stress-induced heart disease.
- Dong I. Lee
- , Guangshuo Zhu
- & David A. Kass
-
Letter |
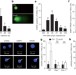 Exit from dormancy provokes DNA-damage-induced attrition in haematopoietic stem cells
Exit from dormancy provokes DNA-damage-induced attrition in haematopoietic stem cells
Here, DNA damage is shown to occur as a direct consequence of inducing haematopoietic stem cells to exit quiescence in response to conditions of stress; in mice with mutations modelling those seen in Fanconi anaemia, this leads to a complete collapse of the haematopoietic system.
- Dagmar Walter
- , Amelie Lier
- & Michael D. Milsom
-
Article |
 Pulmonary macrophage transplantation therapy
Pulmonary macrophage transplantation therapy
This study reports the correction of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) in Csf2rb–/– mice by a single transfer of either wild-type or gene-corrected macrophages directly to the lungs — the transplanted macrophages persisted for at least 1 year; this transplantation strategy obviated the need for myeloablation and immunosuppression and should be a feasible therapy for humans with hereditary PAP.
- Takuji Suzuki
- , Paritha Arumugam
- & Bruce C. Trapnell
-
Letter |
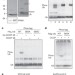 Ubiquitin is phosphorylated by PINK1 to activate parkin
Ubiquitin is phosphorylated by PINK1 to activate parkin
Ubiquitin, known for its role in post-translational modification of other proteins, undergoes post-translational modification itself; after a decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential, the kinase enzyme PINK1 phosphorylates ubiquitin at Ser 65, and the phosphorylated ubiquitin then interacts with ubiquitin ligase (E3) enzyme parkin, which is also phosphorylated by PINK1, and this process is sufficient for full activation of parkin enzymatic activity.
- Fumika Koyano
- , Kei Okatsu
- & Noriyuki Matsuda
-
Article |
 miR-34/449 miRNAs are required for motile ciliogenesis by repressing cp110
miR-34/449 miRNAs are required for motile ciliogenesis by repressing cp110
Loss-of-function studies of the miR-34/449 microRNA family in mouse and Xenopus reveal their evolutionarily conserved role in ciliogenesis by repressing expression of the centriolar protein Cp110.
- Rui Song
- , Peter Walentek
- & Lin He
-
Letter |
 Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase knockdown protects against diet-induced obesity
Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase knockdown protects against diet-induced obesity
Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT) expression is increased in white adipose tissue and liver of obese and diabetic mice, Nnmt knockdown protects against diet-induced obesity by altering the availability of adipose S-adenosylmethionine and NAD+, rendering Nnmt a novel target for treating obesity and type 2 diabetes.
- Daniel Kraus
- , Qin Yang
- & Barbara B. Kahn
-
Article |
 C9orf72 nucleotide repeat structures initiate molecular cascades of disease
C9orf72 nucleotide repeat structures initiate molecular cascades of disease
Structurally polymorphic C9orf72 hexanucleotide repeats cause an impairment in transcriptional processivity and lead to accumulation of truncated repeat-containing transcripts that bind to specific ribonucleoproteins, such as nucleolin, in a conformation-dependent manner resulting in nucleolar stress and C9orf72-linked pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia.
- Aaron R. Haeusler
- , Christopher J. Donnelly
- & Jiou Wang
-
Letter |
 Aprataxin resolves adenylated RNA–DNA junctions to maintain genome integrity
Aprataxin resolves adenylated RNA–DNA junctions to maintain genome integrity
This study shows that aprataxin, encoded by a gene mutated in the neurodegenerative disorder AOA1, can remove the 5′ AMP from RNA–DNA junctions; this RNA–DNA damage response promotes cell survival.
- Percy Tumbale
- , Jessica S. Williams
- & R. Scott Williams
-
Letter |
 Divergent angiocrine signals from vascular niche balance liver regeneration and fibrosis
Divergent angiocrine signals from vascular niche balance liver regeneration and fibrosis
Divergent angiocrine signals from liver sinusoidal endothelial cells elicit regeneration after immediate injury and provoke fibrosis after chronic insult.
- Bi-Sen Ding
- , Zhongwei Cao
- & Shahin Rafii
-
Article |
 A small-molecule AdipoR agonist for type 2 diabetes and short life in obesity
A small-molecule AdipoR agonist for type 2 diabetes and short life in obesity
An orally active small molecule, AdipRon, that binds to and activates both adiponectin receptors (AdipoR1 and AdipoR2) is identified; it ameliorates diabetes in mice on a high-fat diet and in genetically obese db/db mice, and if this can be extrapolated to humans, orally active agonists such as AdipoRon are a promising new approach to treat obesity-related diseases such as type 2 diabetes.
- Miki Okada-Iwabu
- , Toshimasa Yamauchi
- & Takashi Kadowaki
-
Letter |
 Structure of LIMP-2 provides functional insights with implications for SR-BI and CD36
Structure of LIMP-2 provides functional insights with implications for SR-BI and CD36
These results reveal the first high-resolution structural analysis of LIMP-2 and, by homology modelling, the structure of SR-BI and CD36, members of the CD36 superfamily of scavenger receptor proteins.
- Dante Neculai
- , Michael Schwake
- & Sirano Dhe-Paganon
-
Letter |
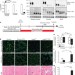 LARGE glycans on dystroglycan function as a tunable matrix scaffold to prevent dystrophy
LARGE glycans on dystroglycan function as a tunable matrix scaffold to prevent dystrophy
This study finds a direct correlation between LARGE-glycan extension on dystroglycan and the protein’s capacity for extracellular matrix ligands; in regenerating mouse muscle, short LARGE-glycan polysaccharides cause various defects, including muscle dysfunction and a predisposition to dystrophy, and in muscular dystrophy patients, increased clinical severity of disease corresponds to shorter LARGE-glycans.
- Matthew M. Goddeeris
- , Biming Wu
- & Kevin P. Campbell
-
Letter |
 EndMT contributes to the onset and progression of cerebral cavernous malformations
EndMT contributes to the onset and progression of cerebral cavernous malformations
Cerebral cavernous malformations associated with loss of function of Ccm1 are shown to be formed by endothelial cells undergoing endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT) induced by TGF-β and BMP signalling; inhibition of TGF-β and BMP signalling prevents EndMT and the appearance of CCM lesions.
- Luigi Maddaluno
- , Noemi Rudini
- & Elisabetta Dejana
-
Letter |
 Lamin A/C and emerin regulate MKL1–SRF activity by modulating actin dynamics
Lamin A/C and emerin regulate MKL1–SRF activity by modulating actin dynamics
Lamin and emerin mutations causing cardiomyopathies are associated with an impairment in actin dynamics, resulting in aberrant nuclear translocation and downstream signalling of the transcription factor MKL1, which is pivotal for cardiac development.
- Chin Yee Ho
- , Diana E. Jaalouk
- & Jan Lammerding
-
Letter |
 Brown-fat paucity due to impaired BMP signalling induces compensatory browning of white fat
Brown-fat paucity due to impaired BMP signalling induces compensatory browning of white fat
A shortage of constitutive brown adipose tissue is shown to result when brown adipogenic progenitor cells lack a type of BMP receptor; however, this leads to an increase in sympathetic input to white adipose tissue and a compensatory browning of white fat depots.
- Tim J. Schulz
- , Ping Huang
- & Yu-Hua Tseng
-
Article |
 Mutations in prion-like domains in hnRNPA2B1 and hnRNPA1 cause multisystem proteinopathy and ALS
Mutations in prion-like domains in hnRNPA2B1 and hnRNPA1 cause multisystem proteinopathy and ALS
The identification of pathogenic mutations within prion-like domains (PrLDs) of the RNA-binding proteins hnRNPA2B1 and hnRNPA1 add to our understanding of how mutations in these proteins lead to degenerative disease, and highlight the potential importance of PrLDs in degenerative diseases of the nervous system, muscle and bone.
- Hong Joo Kim
- , Nam Chul Kim
- & J. Paul Taylor
-
Letter |
 Obesity-induced overexpression of miR-802 impairs glucose metabolism through silencing of Hnf1b
Obesity-induced overexpression of miR-802 impairs glucose metabolism through silencing of Hnf1b
The livers of obese mice and humans show increased levels of miR-802 resulting in impaired glucose tolerance and decreased insulin sensitivity through silencing of Hnf1b, revealing a novel pathway with potential relevance for type 2 diabetes.
- Jan-Wilhelm Kornfeld
- , Catherina Baitzel
- & Jens C. Brüning
-
Letter |
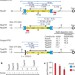 Recombination-restarted replication makes inverted chromosome fusions at inverted repeats
Recombination-restarted replication makes inverted chromosome fusions at inverted repeats
A new mechanism of chromosomal rearrangement is identified through the observation that broken or collapsed DNA replication forks restarted by homologous recombination have a high propensity for U-turns at short inverted repeats; the error-prone nature of this mechanism is suggested to contribute to gross chromosomal rearrangements and copy-number variations present in cancer and other genomic disorders.
- Ken’Ichi Mizuno
- , Izumi Miyabe
- & Johanne M. Murray
-
Research Highlights |
Fat helps tumours to grow
-
Article |
 Small heat-shock proteins protect from heat-stroke-associated neurodegeneration
Small heat-shock proteins protect from heat-stroke-associated neurodegeneration
Heat stroke triggers necrotic cell death and neurodegeneration in Caenorhabditis elegans, but hormetic preconditioning at a mildly elevated temperature strongly protects C. elegans from necrosis induced by several insults, including heat, and shields mammalian neurons from heat cytotoxicity, suggesting that this protective mechanism is conserved.
- Nikos Kourtis
- , Vassiliki Nikoletopoulou
- & Nektarios Tavernarakis
-
Letter |
 Genotoxic consequences of endogenous aldehydes on mouse haematopoietic stem cell function
Genotoxic consequences of endogenous aldehydes on mouse haematopoietic stem cell function
The function of haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells is impaired by damaged DNA; here, endogenously generated aldehydes are found to be one source of such damage, which is repaired by the Fanconi anaemia pathway.
- Juan I. Garaycoechea
- , Gerry P. Crossan
- & Ketan J. Patel
-
Research Highlights |
Multiple malaria mechanisms
-
Letter |
 Transformation by the (R)-enantiomer of 2-hydroxyglutarate linked to EGLN activation
Transformation by the (R)-enantiomer of 2-hydroxyglutarate linked to EGLN activation
The (R)-enantiomer of 2-hydroxyglutarate, which is produced when IDH is mutated in human tumours, is shown to stimulate the activity of the EGLN prolyl 4-hydroxylases, leading to diminished levels of HIF and enhanced human astrocyte proliferation.
- Peppi Koivunen
- , Sungwoo Lee
- & William G. Kaelin Jr
-
-
Research Highlights |
Parkinson's propagator

 Enhancing mitochondrial proteostasis reduces amyloid-β proteotoxicity
Enhancing mitochondrial proteostasis reduces amyloid-β proteotoxicity The DNA damage response and cancer therapy
The DNA damage response and cancer therapy