Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Decentralized federated learning through proxy model sharing
Decentralized federated learning through proxy model sharing
Federated learning enables multi-institutional collaborations on decentralized data with improved privacy protection. Here, authors propose a new scheme for decentralized federated learning with much less communication overhead and stronger privacy.
- Shivam Kalra
- , Junfeng Wen
- & H. R. Tizhoosh
-
Article
| Open Access Spatially-optimized urban greening for reduction of population exposure to land surface temperature extremes
Spatially-optimized urban greening for reduction of population exposure to land surface temperature extremes
This study uses earth observation data and proposes a method to evaluate and optimize the increment of urban greening to reduce the population exposure to extreme land surface temperatures in cities.
- Emanuele Massaro
- , Rossano Schifanella
- & Gregory Duveiller
-
Article
| Open Access Data-driven prediction of complex crystal structures of dense lithium
Data-driven prediction of complex crystal structures of dense lithium
Recent experiments reveal undetermined crystalline phases near the melting minimum region in lithium. Here, the authors use a crystal structure search method combined with machine learning to explore the energy landscape of lithium and predict complex crystal structures.
- Xiaoyang Wang
- , Zhenyu Wang
- & Yanming Ma
-
Article
| Open Access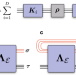 Quantum process tomography with unsupervised learning and tensor networks
Quantum process tomography with unsupervised learning and tensor networks
In quantum technologies, scalable ways to characterise errors in quantum hardware are highly needed. Here, the authors propose an approximate version of quantum process tomography based on tensor network representations of the processes and data-driven optimisation.
- Giacomo Torlai
- , Christopher J. Wood
- & Leandro Aolita
-
Article
| Open Access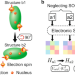 General framework for E(3)-equivariant neural network representation of density functional theory Hamiltonian
General framework for E(3)-equivariant neural network representation of density functional theory Hamiltonian
Fundamental symmetries are crucial to the deep-learning modeling of physical systems. Here the authors use equivariant neural networks preserving the Euclidean symmetries to accelerate electronic structure calculations by orders of magnitude keeping sub-meV accuracy.
- Xiaoxun Gong
- , He Li
- & Yong Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Emergent geometry and duality in the carbon nucleus
Emergent geometry and duality in the carbon nucleus
Carbon (12C) nucleus has interesting characteristics including the existence of the Hoyle state. Here the authors discuss the structure of the nuclear states of 12C by using nuclear lattice effective field theory.
- Shihang Shen
- , Serdar Elhatisari
- & Ulf-G. Meißner
-
Article
| Open Access Optical neural network via loose neuron array and functional learning
Optical neural network via loose neuron array and functional learning
Here the authors have realized a programmable incoherent optical neural network that delivers light-speed, high-bandwidth, and power-efficient neural network inference via processing parallel visible light signals in the free space.
- Yuchi Huo
- , Hujun Bao
- & Sung-Eui Yoon
-
Article
| Open Access Explainable multi-task learning for multi-modality biological data analysis
Explainable multi-task learning for multi-modality biological data analysis
Multimodal biological data is challenging to analyze. Here, the authors develop UnitedNet, an explainable deep neural network for analyzing single-cell multimodal biological data and estimating relationships between gene expression and other modalities with cell-type specificity.
- Xin Tang
- , Jiawei Zhang
- & Jia Liu
-
Article
| Open Access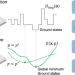 Bifurcation behaviors shape how continuous physical dynamics solves discrete Ising optimization
Bifurcation behaviors shape how continuous physical dynamics solves discrete Ising optimization
Physical and physics-inspired computation is emerging as a new paradigm for tackling hard optimization problems. In this work, the authors establish rigorous mathematical conditions together with new design principles for physical as well as simulated dynamical systems to solve general Ising models.
- Juntao Wang
- , Daniel Ebler
- & Jie Sun
-
Article
| Open Access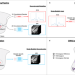 Cross-modal autoencoder framework learns holistic representations of cardiovascular state
Cross-modal autoencoder framework learns holistic representations of cardiovascular state
A challenge in diagnostics is integrating different data modalities to characterize physiological state. Here, the authors show, using the heart as a model system, that cross-modal autoencoders can integrate and translate modalities to improve diagnostics and identify associated genetic variants.
- Adityanarayanan Radhakrishnan
- , Sam F. Friedman
- & Caroline Uhler
-
Article
| Open Access The most at-risk regions in the world for high-impact heatwaves
The most at-risk regions in the world for high-impact heatwaves
The global risk of record-breaking heatwaves is assessed, with the most at-risk regions identified. It is shown that record-smashing events that currently appear implausible could happen anywhere as a result of climate change.
- Vikki Thompson
- , Dann Mitchell
- & Julia M. Slingo
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning prediction of the degree of food processing
Machine learning prediction of the degree of food processing
Evidence suggests that increased consumption of ultra-processed food has adverse health implications, however, it remains difficult to classify processed food. Here, the authors introduce FPro, a machine learning-based score predicting the degree of food processing.
- Giulia Menichetti
- , Babak Ravandi
- & Albert-László Barabási
-
Article
| Open Access Active learning-assisted neutron spectroscopy with log-Gaussian processes
Active learning-assisted neutron spectroscopy with log-Gaussian processes
Neutron scattering experiments are important for studying materials properties. Here, the authors present a probabilistic active learning approach for neutron spectroscopy with three-axes spectrometers and demonstrate optimization of beam time use by favoring informative regions of signal.
- Mario Teixeira Parente
- , Georg Brandl
- & Astrid Schneidewind
-
Article
| Open Access Complex computation from developmental priors
Complex computation from developmental priors
Neuroscience has long inspired AI, however the neuroevolutionary search that produces sophisticated behaviors has not been systematized. This paper defines neurodevelopmental ML as a discovery process for structures that promote complex computations.
- Dániel L. Barabási
- , Taliesin Beynon
- & Nicolas Perez-Nieves
-
Article
| Open Access Random fractal-enabled physical unclonable functions with dynamic AI authentication
Random fractal-enabled physical unclonable functions with dynamic AI authentication
In order to be used on a large scale, unclonable tags for anti-counterfeiting should allow mass production at low cost, as well as fast and easy authentication. Here, the authors show how to use one-step annealing of gold films to quickly realize robust tags with high capacity, allowing fast deep-learning based authentication via smartphone readout.
- Ningfei Sun
- , Ziyu Chen
- & Qian Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Combining data and theory for derivable scientific discovery with AI-Descartes
Combining data and theory for derivable scientific discovery with AI-Descartes
Automatic extraction of consistent governing laws from data is a challenging problem. The authors propose a method that takes as input experimental data and background theory and combines symbolic regression with logical reasoning to obtain scientifically meaningful symbolic formulas.
- Cristina Cornelio
- , Sanjeeb Dash
- & Lior Horesh
-
Article
| Open Access Widespread global disparities between modelled and observed mid-depth ocean currents
Widespread global disparities between modelled and observed mid-depth ocean currents
Analysis of big Argo data reveals that model representation of global ocean circulation near 1000-m depth is substantially compromised by inaccuracies. Only 3.8% of the mid-depth ocean circulation can be considered accurately modelled.
- Fenzhen Su
- , Rong Fan
- & Fei Chai
-
Article
| Open Access Automated optimisation of solubility and conformational stability of antibodies and proteins
Automated optimisation of solubility and conformational stability of antibodies and proteins
Antibodies find key applications in research, diagnostics, and therapeutics, but their development can be impeded by poor stability or solubility. Here the authors developed a computational strategy that enables antibody optimisation, without affecting functionality.
- Angelo Rosace
- , Anja Bennett
- & Pietro Sormanni
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic-scale origin of the low grain-boundary resistance in perovskite solid electrolyte Li0.375Sr0.4375Ta0.75Zr0.25O3
Atomic-scale origin of the low grain-boundary resistance in perovskite solid electrolyte Li0.375Sr0.4375Ta0.75Zr0.25O3
Oxide solid electrolytes generally suffer from high grain boundary resistance. Here, the authors use advanced electron microscopy, along with an active learning moment tensor potential, to reveal the atomic-scale origin of low grain-boundary resistance in Li0.375Sr0.4375Ta0.75Zr0.25O3.
- Tom Lee
- , Ji Qi
- & Xiaoqing Pan
-
Article
| Open Access Cellcano: supervised cell type identification for single cell ATAC-seq data
Cellcano: supervised cell type identification for single cell ATAC-seq data
Accurately annotating cell types is a fundamental step in single-cell omics data analysis. Here, the authors develop a computational method called Cellcano based on a two-round supervised learning algorithm to identify cell types for scATAC-seq data and perform benchmarking to demonstrate its accuracy, robustness and computational efficiency.
- Wenjing Ma
- , Jiaying Lu
- & Hao Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Meta-learning biologically plausible plasticity rules with random feedback pathways
Meta-learning biologically plausible plasticity rules with random feedback pathways
The biological plausibility of backpropagation and its relationship with synaptic plasticity remain open questions. The authors propose a meta-learning approach to discover interpretable plasticity rules to train neural networks under biological constraints. The meta-learned rules boost the learning efficiency via bio-inspired synaptic plasticity.
- Navid Shervani-Tabar
- & Robert Rosenbaum
-
Perspective
| Open Access Catalyzing next-generation Artificial Intelligence through NeuroAI
Catalyzing next-generation Artificial Intelligence through NeuroAI
One of the ambitions of computational neuroscience is that we will continue to make improvements in the field of artificial intelligence that will be informed by advances in our understanding of how the brains of various species evolved to process information. To that end, here the authors propose an expanded version of the Turing test that involves embodied sensorimotor interactions with the world as a new framework for accelerating progress in artificial intelligence.
- Anthony Zador
- , Sean Escola
- & Doris Tsao
-
Article
| Open Access A comprehensive benchmarking with practical guidelines for cellular deconvolution of spatial transcriptomics
A comprehensive benchmarking with practical guidelines for cellular deconvolution of spatial transcriptomics
This study comprehensively benchmarks 18 state-of-the-art methods for cellular deconvolution of spatial transcriptomics and provide decision-tree-style guidelines and recommendations for method selection.
- Haoyang Li
- , Juexiao Zhou
- & Xin Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Benchmarking integration of single-cell differential expression
Benchmarking integration of single-cell differential expression
Integration of single-cell RNA sequencing data between different samples has been a major challenge for analyzing cell populations. Here the authors benchmark 46 workflows for differential expression analysis of single-cell data with multiple batches and suggest several high-performance methods under different conditions based on simulation and real data analyses.
- Hai C. T. Nguyen
- , Bukyung Baik
- & Dougu Nam
-
Article
| Open Access Accelerating network layouts using graph neural networks
Accelerating network layouts using graph neural networks
Visualization of large complex networks is challenging with limitations for the network size and depicting specific structures. The authors propose a Graph Neural Network based algorithm with improved speed and the quality of graph layouts, which allows for fast and informative visualization of large networks.
- Csaba Both
- , Nima Dehmamy
- & Albert-László Barabási
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial immunization to abate disease spreading in transportation hubs
Spatial immunization to abate disease spreading in transportation hubs
Efficient spatial targeting of interventions could reduce the spread of infections in transportation hubs. Here, the authors assess the optimal locations to target in Heathrow airport using disease transmission models informed by a contact network based on anonymised location data from 200,000 individuals.
- Mattia Mazzoli
- , Riccardo Gallotti
- & José J. Ramasco
-
Article
| Open Access Multistability, intermittency, and hybrid transitions in social contagion models on hypergraphs
Multistability, intermittency, and hybrid transitions in social contagion models on hypergraphs
Social interactions often occur in groups of individuals, which can be mathematically represented as hypergraphs. In this study, the authors analyze the appearance of multistability, intermittency, and hybrid phase transitions in social contagion models on hypergraphs.
- Guilherme Ferraz de Arruda
- , Giovanni Petri
- & Yamir Moreno
-
Article
| Open Access The dynamic nature of percolation on networks with triadic interactions
The dynamic nature of percolation on networks with triadic interactions
Triadic interactions are higher-order interactions relevant to many real complex systems. The authors develop a percolation theory for networks with triadic interactions and identify basic mechanisms for observing dynamical changes of the giant component such as the ones occurring in neuronal and climate networks.
- Hanlin Sun
- , Filippo Radicchi
- & Ginestra Bianconi
-
Article
| Open Access A variational algorithm to detect the clonal copy number substructure of tumors from scRNA-seq data
A variational algorithm to detect the clonal copy number substructure of tumors from scRNA-seq data
The inference of clonal architectures in cancer using single-cell RNA-seq data remains challenging. Here, the authors develop SCEVAN, a variational algorithm for copy number-based clonal structure inference in single-cell RNA-seq data that can characterise evolution and heterogeneity in the tumour and the microenvironment.
- Antonio De Falco
- , Francesca Caruso
- & Michele Ceccarelli
-
Article
| Open Access Complex-tensor theory of simple smectics
Complex-tensor theory of simple smectics
As lamellar materials, smectics exhibit both liquid and solid characteristics, making them difficult to model at the mesoscale. Paget et al. propose a complex tensor order parameter that reflects the smectic symmetries, capable of describing complex defects including dislocations and disclinations.
- Jack Paget
- , Marco G. Mazza
- & Tyler N. Shendruk
-
Article
| Open Access Fundamental limits to learning closed-form mathematical models from data
Fundamental limits to learning closed-form mathematical models from data
Learning analytical models from noisy data remains challenging and depends essentially on the noise level. The authors analyze the transition of the model-learning problem from a low-noise phase to a phase where noise is too high for the underlying model to be learned by any method, and estimate upper bounds for the transition noise.
- Oscar Fajardo-Fontiveros
- , Ignasi Reichardt
- & Roger Guimerà
-
Article
| Open Access ASGARD is A Single-cell Guided Pipeline to Aid Repurposing of Drugs
ASGARD is A Single-cell Guided Pipeline to Aid Repurposing of Drugs
The full potential of single-cell RNA-sequencing applied to precision medicine has yet to be reached. Here, we propose a drug recommendation system ASGARD, which predicts drugs by considering cell clusters to address the intercellular heterogeneity within each patient.
- Bing He
- , Yao Xiao
- & Lana X. Garmire
-
Article
| Open Access Batch alignment of single-cell transcriptomics data using deep metric learning
Batch alignment of single-cell transcriptomics data using deep metric learning
The increasing scale of single-cell RNA-seq studies presents new challenge for integrating datasets from different batches. Here, the authors develop scDML, a tool that simultaneously removes batch effects, improves clustering performance, recovers true cell types, and scales well to large datasets.
- Xiaokang Yu
- , Xinyi Xu
- & Xiangjie Li
-
Article
| Open Access Diverse behaviors in non-uniform chiral and non-chiral swarmalators
Diverse behaviors in non-uniform chiral and non-chiral swarmalators
Populations of swarming coupled oscillators with inhomogeneous natural frequencies and chirality are relevant for active matter systems and micro-robotics. The authors model and analyze a variety of their self-organized behaviors that mimic natural and artificial micro-scale collective systems.
- Steven Ceron
- , Kevin O’Keeffe
- & Kirstin Petersen
-
Article
| Open Access Universal non-monotonic drainage in large bare viscous bubbles
Universal non-monotonic drainage in large bare viscous bubbles
Bubbles at an air-liquid interface will rupture when their spherical cap becomes sufficiently drained. It is now shown that the film thickness of large bare viscous bubbles is highly non-uniformly distributed, and that a bubble’s thickness profile relates to its drainage velocity.
- Casey Bartlett
- , Alexandros T. Oratis
- & James C. Bird
-
Article
| Open Access A spectral method for assessing and combining multiple data visualizations
A spectral method for assessing and combining multiple data visualizations
Dimension reduction is an indispensable part of modern data science, and many algorithms have been developed. Here, the authors develop a theoretically justified, simple to use and reliable spectral method to assess and combine multiple dimension reduction visualizations of a given dataset from diverse algorithms.
- Rong Ma
- , Eric D. Sun
- & James Zou
-
Article
| Open Access Searching for spin glass ground states through deep reinforcement learning
Searching for spin glass ground states through deep reinforcement learning
Finding the ground states of spin glasses relevant for disordered magnets and many other physical systems is computationally challenging. The authors propose here a deep reinforcement learning framework for calculating the ground states, which can be trained on small-scale spin glass instances and then applied to arbitrarily large ones.
- Changjun Fan
- , Mutian Shen
- & Yang-Yu Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Cartography of Genomic Interactions Enables Deep Analysis of Single-Cell Expression Data
Cartography of Genomic Interactions Enables Deep Analysis of Single-Cell Expression Data
Existing genomic data analysis methods tend to not take full advantage of underlying biological characteristics. Here, the authors leverage the inherent interactions of scRNA-seq data and develop a cartography strategy to contrive the data into a spatially configured genomap for accurate deep pattern discovery.
- Md Tauhidul Islam
- & Lei Xing
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying the direct and indirect protection provided by insecticide treated bed nets against malaria
Quantifying the direct and indirect protection provided by insecticide treated bed nets against malaria
Long lasting insecticide treated mosquito nets (LLINs) provide protection from malaria through both direct effects to the user and indirect community-level effects. Here, the authors use mathematical modelling to assess the relative contributions of these effects under different insecticide resistance and LLIN usage scenarios.
- H. Juliette T. Unwin
- , Ellie Sherrard-Smith
- & Azra C. Ghani
-
Article
| Open Access Learning local equivariant representations for large-scale atomistic dynamics
Learning local equivariant representations for large-scale atomistic dynamics
The paper presents a method that allows scaling machine learning interatomic potentials to extremely large systems, while at the same time retaining the remarkable accuracy and learning efficiency of deep equivariant models. This is obtained with an E(3)- equivariant neural network architecture that combines the high accuracy of equivariant neural networks with the scalability of local methods.
- Albert Musaelian
- , Simon Batzner
- & Boris Kozinsky
-
Article
| Open Access Universal expressiveness of variational quantum classifiers and quantum kernels for support vector machines
Universal expressiveness of variational quantum classifiers and quantum kernels for support vector machines
Rigorous results about the real computational advantages of quantum machine learning are few. Here, the authors prove that a PROMISEBQP-complete problem can be expressed by variational quantum classifiers and quantum support vector machines, meaning that a quantum advantage can be achieved for all ML classification problems that cannot be classically solved in polynomial time.
- Jonas Jäger
- & Roman V. Krems
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum machine learning beyond kernel methods
Quantum machine learning beyond kernel methods
Comparing the capabilities of different quantum machine learning protocols is difficult. Here, the authors show that different learning models based on parametrized quantum circuits can all be seen as quantum linear models, thus driving general conclusions on their resource requirements and capabilities.
- Sofiene Jerbi
- , Lukas J. Fiderer
- & Vedran Dunjko
-
Article
| Open Access Digital circuits and neural networks based on acid-base chemistry implemented by robotic fluid handling
Digital circuits and neural networks based on acid-base chemistry implemented by robotic fluid handling
The complementarity of acids and bases is a fundamental chemical concept. Here, the authors use simple acid-base chemistry to encode binary information and perform information processing including digital circuits and neural networks using robotic fluid handling.
- Ahmed A. Agiza
- , Kady Oakley
- & Sherief Reda
-
Article
| Open Access Topological identification and interpretation for single-cell gene regulation elucidation across multiple platforms using scMGCA
Topological identification and interpretation for single-cell gene regulation elucidation across multiple platforms using scMGCA
A major challenge in analyzing scRNA-seq data arises from challenges related to dimensionality and the prevalence of dropout events. Here the authors develop a deep graph learning method called scMGCA based on a graph-embedding autoencoder that simultaneously learns cell-cell topology representation and cluster assignments, outperforming other state-of-the-art models across multiple platforms.
- Zhuohan Yu
- , Yanchi Su
- & Xiangtao Li
-
Article
| Open Access scMoMaT jointly performs single cell mosaic integration and multi-modal bio-marker detection
scMoMaT jointly performs single cell mosaic integration and multi-modal bio-marker detection
Many methods for single cell data integration have been developed, though mosaic integration remains challenging. Here the authors present scMoMaT, a mosaic integration method for single cell multi-modality data from multiple batches, that jointly learns cell representations and marker features across modalities for different cell clusters, to interpret the cell clusters from different modalities.
- Ziqi Zhang
- , Haoran Sun
- & Xiuwei Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Immune correlates analysis of the PREVENT-19 COVID-19 vaccine efficacy clinical trial
Immune correlates analysis of the PREVENT-19 COVID-19 vaccine efficacy clinical trial
Authors have previously reported on the efficacy and safety of the recombinant spike protein nanoparticle vaccine, NVX-CoV2373, in healthy adults. In this work, they assess anti-spike binding IgG, anti-RBD binding IgG and neutralising antibody titer as correlates of risk and protection against COVID-19.
- Youyi Fong
- , Yunda Huang
- & Peter B. Gilbert
-
Article
| Open Access Impact of the Euro 2020 championship on the spread of COVID-19
Impact of the Euro 2020 championship on the spread of COVID-19
In this Bayesian inference study, the authors aim to quantify the impact of the men’s 2020 UEFA Euro Football Championship on COVID-19 spread in twelve participating countries. They estimate that 0.84 million cases and 1,700 deaths were attributable to the championship, with most impacts in England and Scotland.
- Jonas Dehning
- , Sebastian B. Mohr
- & Viola Priesemann
-
Article
| Open Access Controllable branching of robust response patterns in nonlinear mechanical resonators
Controllable branching of robust response patterns in nonlinear mechanical resonators
Feedback control applied to mechanical resonators can lead to the formation of various complex dynamic behaviors. Here the authors demonstrate flexible and controllable switching between dynamical structures in the response of harmonically driven micro-mechanical resonators.
- Axel M. Eriksson
- , Oriel Shoshani
- & David A. Czaplewski
-
Article
| Open Access Leveraging molecular structure and bioactivity with chemical language models for de novo drug design
Leveraging molecular structure and bioactivity with chemical language models for de novo drug design
Generative Deep Learning holds promise for mining the unexplored “chemical universe” for new drugs. Here, the authors demonstrate the de novo design of phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma (PI3Kγ) inhibitors for the PI3K/Akt pathway in human tumor cells.
- Michael Moret
- , Irene Pachon Angona
- & Gisbert Schneider

 Retrosynthesis prediction using an end-to-end graph generative architecture for molecular graph editing
Retrosynthesis prediction using an end-to-end graph generative architecture for molecular graph editing