Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Structural plasticity for neuromorphic networks with electropolymerized dendritic PEDOT connections
Structural plasticity for neuromorphic networks with electropolymerized dendritic PEDOT connections
Neural networks are powerful tools for solving complex problems, but finding the right network topology for a given task remains an open question. Here, the authors propose a bio-inspired artificial neural network hardware able to self-adapt to solve new complex tasks, by autonomously connecting nodes using electropolymerization.
- Kamila Janzakova
- , Ismael Balafrej
- & Fabien Alibart
-
Article
| Open Access Collaborative and privacy-preserving retired battery sorting for profitable direct recycling via federated machine learning
Collaborative and privacy-preserving retired battery sorting for profitable direct recycling via federated machine learning
Unsorted retired batteries pose recycling challenges due to diverse cathodes. Here, the authors propose a privacy-preserving machine learning system that enables accurate sorting with minimal data, important for a sustainable battery recycling industry.
- Shengyu Tao
- , Haizhou Liu
- & Hongbin Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Early warning signals have limited applicability to empirical lake data
Early warning signals have limited applicability to empirical lake data
Abrupt regime shifts could in theory be predicted from early warning signals. Here, the authors show that true critical transitions are challenging to classify in lake planktonic systems, due to mismatches between trophic levels, and reveal uneven performance of early warning signal detection methods.
- Duncan A. O’Brien
- , Smita Deb
- & Christopher F. Clements
-
Article
| Open Access TransformEHR: transformer-based encoder-decoder generative model to enhance prediction of disease outcomes using electronic health records
TransformEHR: transformer-based encoder-decoder generative model to enhance prediction of disease outcomes using electronic health records
Using AI to predict disease can improve interventions slow down or prevent disease. Here, the authors show that generative AI models built on the framework of Transformer, the model that also empowers ChatGPT, can achieve state-of-the-art performance on disease predictions based on longitudinal electronic records.
- Zhichao Yang
- , Avijit Mitra
- & Hong Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Emulator-based Bayesian inference on non-proportional scintillation models by compton-edge probing
Emulator-based Bayesian inference on non-proportional scintillation models by compton-edge probing
Scintillators are widely used for radiation detection and require proper calibration in such applications. Here the authors discuss a Bayesian inference and machine learning method in combination with the Compton-edge probing that can describe the non-proportional scintillation response of inorganic scintillators.
- David Breitenmoser
- , Francesco Cerutti
- & Sabine Mayer
-
Article
| Open Access Data-driven grading of acute graft-versus-host disease
Data-driven grading of acute graft-versus-host disease
Acute GVHD severity grading is based on target organ assessments. Here, the authors show that data-driven grading can identify 12 distinct grades with specific aGVHD phenotypes, which are associated with clinical outcomes, and that their method outperformed conventional gradings.
- Evren Bayraktar
- , Theresa Graf
- & Amin T. Turki
-
Article
| Open Access Learning few-shot imitation as cultural transmission
Learning few-shot imitation as cultural transmission
The modelling of human-like behaviours is one of the challenges in the field of Artificial Intelligence. Inspired by experimental studies of cultural evolution, the authors propose a reinforcement learning approach to generate agents capable of real-time third-person imitation.
- Avishkar Bhoopchand
- , Bethanie Brownfield
- & Lei M. Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access All electromagnetic scattering bodies are matrix-valued oscillators
All electromagnetic scattering bodies are matrix-valued oscillators
The usual treatment of wave scattering theory relies on a formalism that does not easily allow for probing optimal spectral response. Here, the authors show how an alternative formalism, encoding fundamental principles of causality and passivity, can be used to make sense of complex scattered fields’ structures.
- Lang Zhang
- , Francesco Monticone
- & Owen D. Miller
-
Article
| Open Access The D-Mercator method for the multidimensional hyperbolic embedding of real networks
The D-Mercator method for the multidimensional hyperbolic embedding of real networks
Embedding of complex networks in the latent geometry allows for a better understanding of their features. The authors propose a framework for mapping complex networks into high-dimensional hyperbolic space to capture their intrinsic dimensionality, navigability and community structure.
- Robert Jankowski
- , Antoine Allard
- & M. Ángeles Serrano
-
Article
| Open Access Assessing the value of integrating national longitudinal shopping data into respiratory disease forecasting models
Assessing the value of integrating national longitudinal shopping data into respiratory disease forecasting models
Novel indicators of infectious disease prevalence could improve real-time surveillance and support healthcare planning. Here, the authors show that sales data for non-prescription medications from a UK high street retailer can improve the accuracy of models forecasting mortality from respiratory infections.
- Elizabeth Dolan
- , James Goulding
- & Laila J. Tata
-
Article
| Open Access On-tissue dataset-dependent MALDI-TIMS-MS2 bioimaging
On-tissue dataset-dependent MALDI-TIMS-MS2 bioimaging
There is a need for dataset-dependent MS2 acquisition in trapped ion mobility spectrometry imaging. Here the authors report spatial ion mobility-scheduled exhaustive fragmentation (SIMSEF) which enables on-tissue metabolite and lipid annotation in mass spectrometry bioimaging studies, and use this to visualise the chemical space in rat brains.
- Steffen Heuckeroth
- , Arne Behrens
- & Robin Schmid
-
Article
| Open Access Imitation dynamics on networks with incomplete information
Imitation dynamics on networks with incomplete information
Studies of the evolution of cooperation often assume information use that is inconsistent with empirical observations. Here, the authors’ research on general imitation dynamics reveals that cooperation is fostered by individuals using less personal information and more social information.
- Xiaochen Wang
- , Lei Zhou
- & Aming Li
-
Article
| Open Access Impact of vaccinations, boosters and lockdowns on COVID-19 waves in French Polynesia
Impact of vaccinations, boosters and lockdowns on COVID-19 waves in French Polynesia
In this study, the authors develop a mathematical modelling framework to estimate the impacts of non-pharmaceutical interventions and vaccination on COVID-19 incidence. The model accounts for changes in SARS-CoV-2 variant and population immunity, and here they use it to investigate epidemic dynamics in French Polynesia.
- Lloyd A. C. Chapman
- , Maite Aubry
- & Adam J. Kucharski
-
Article
| Open Access Constructing temporal networks with bursty activity patterns
Constructing temporal networks with bursty activity patterns
Many real-world systems are characterized by bursty dynamics with interchanging periods of intense activity and quiescence. The authors propose a method to construct temporal networks that match a given activity pattern, and apply it to empirical bursty patterns.
- Anzhi Sheng
- , Qi Su
- & Joshua B. Plotkin
-
Article
| Open Access Relational visual representations underlie human social interaction recognition
Relational visual representations underlie human social interaction recognition
Humans are adept at recognizing social interactions in visual scenes. Here, the authors develop a computational model of this ability, and show that humans can make complex social interaction judgments using relational visual representations.
- Manasi Malik
- & Leyla Isik
-
Article
| Open Access A statistical framework for differential pseudotime analysis with multiple single-cell RNA-seq samples
A statistical framework for differential pseudotime analysis with multiple single-cell RNA-seq samples
Pseudotime analysis is prevalent in single-cell RNA-seq, but it remains challenging to perform it across multiple samples and experimental conditions. Here, the authors develop Lamian, a computational framework for multi-sample pseudotime analysis that adjusts for biological and technical variation to detect gene program changes along cell trajectories and across conditions.
- Wenpin Hou
- , Zhicheng Ji
- & Hongkai Ji
-
Article
| Open Access Exploiting redundancy in large materials datasets for efficient machine learning with less data
Exploiting redundancy in large materials datasets for efficient machine learning with less data
Big data is crucial for machine learning, but the redundancies in the datasets are rarely studied. Here the authors reveal significant redundancy in large materials datasets, showing that up to 95% of data can be removed without impacting prediction accuracy.
- Kangming Li
- , Daniel Persaud
- & Jason Hattrick-Simpers
-
Article
| Open Access Reactivity of complex communities can be more important than stability
Reactivity of complex communities can be more important than stability
Ecosystems must be able to bounce back from perturbations to persist without species extinctions. This study uses theoretical modelling to show the importance of reactivity—how species respond in the short term to perturbations—for assessing the health of complex ecosystems, revealing that it can be a better predictor of extinction risk than stability.
- Yuguang Yang
- , Katharine Z. Coyte
- & Aming Li
-
Article
| Open Access Training large-scale optoelectronic neural networks with dual-neuron optical-artificial learning
Training large-scale optoelectronic neural networks with dual-neuron optical-artificial learning
Optoelectronic neural networks are a promising avenue in AI computing for parallelization, power efficiency, and speed. Here, the authors present a dual-neuron optical-artificial learning approach for training large-scale diffractive neural networks, achieving VGG-level performance on ImageNet in simulation with a network that is 10 times larger than existing ones.
- Xiaoyun Yuan
- , Yong Wang
- & Lu Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Parallel window decoding enables scalable fault tolerant quantum computation
Parallel window decoding enables scalable fault tolerant quantum computation
In order to be useful for future large-scale quantum computing, quantum error correction needs to allow for fast enough classical decoding time, while at the moment the slowdown is exponential in the size of the code. Here, the authors remove this roadblock, showing how to parallelize decoding and make the slowdown polynomial.
- Luka Skoric
- , Dan E. Browne
- & Earl T. Campbell
-
Article
| Open Access Extracting medicinal chemistry intuition via preference machine learning
Extracting medicinal chemistry intuition via preference machine learning
Over their careers, medicinal chemists develop a gut feeling for what is a promising molecule. Here, the authors use machine learning models to learn this intuition and show that it can be successfully applied in several drug discovery scenarios.
- Oh-Hyeon Choung
- , Riccardo Vianello
- & José Jiménez-Luna
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring decarbonization pathways for USA passenger and freight mobility
Exploring decarbonization pathways for USA passenger and freight mobility
Rapid adoption of zero-emission vehicles with a concurrent transition to clean electricity is essential to achieve U.S. transportation decarbonization goals. Managing travel demand can ease this transition by reducing the need for clean electricity supply. @cghoehne, @nrel, #NRELMobility
- Christopher Hoehne
- , Matteo Muratori
- & Ookie Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical AI enables global interpretation of culture plates in the era of digital microbiology
Hierarchical AI enables global interpretation of culture plates in the era of digital microbiology
DeepColony is a multi-level AI solution for the interpretation of bacterial culturing images in clinical microbiology laboratory automations. Here, the authors show it allows presumptive identification and quantitation of relevant pathogens at both colony- and plate-level.
- Alberto Signoroni
- , Alessandro Ferrari
- & Karissa Culbreath
-
Article
| Open Access A human-machine collaborative approach measures economic development using satellite imagery
A human-machine collaborative approach measures economic development using satellite imagery
A human-AI collaborative computer vision algorithm produces grid-level economic statistics using satellite images and lightweight human annotation, revealing granular development patterns in North Korea and five other least developed Asian countries.
- Donghyun Ahn
- , Jeasurk Yang
- & Sungwon Park
-
Article
| Open Access Knowledge-driven design of solid-electrolyte interphases on lithium metal via multiscale modelling
Knowledge-driven design of solid-electrolyte interphases on lithium metal via multiscale modelling
The application of Li metal electrodes in rechargeable batteries is limited by inherent high reactivity. Here, the authors provide model-based insights into the composition and formation mechanisms of the solid-electrolyte interphase on the µs-scale and suggest design strategies for the interphase.
- Janika Wagner-Henke
- , Dacheng Kuai
- & Ulrike Krewer
-
Article
| Open Access Mutant fixation in the presence of a natural enemy
Mutant fixation in the presence of a natural enemy
Studies on mutant invasion typically assume populations in isolation, rather than part of an ecological community. Here, the authors use computational models to investigate how enemy-victim interactions influence properties of mutant invasion, showing that selection is substantially weakened.
- Dominik Wodarz
- & Natalia L. Komarova
-
Article
| Open Access Automatic correction of performance drift under acquisition shift in medical image classification
Automatic correction of performance drift under acquisition shift in medical image classification
Automatic correction of performance drift caused by changes in image acquisition is key for safe AI deployment. Here, the authors present a solution that restores the expected clinical performance of image classification systems in breast screening and histopathology.
- Mélanie Roschewitz
- , Galvin Khara
- & Ben Glocker
-
Article
| Open Access Remote inspection of adversary-controlled environments
Remote inspection of adversary-controlled environments
Physical unclonable functions (PUFs) normally ensure authentication of small physical objects. Here, instead, the authors observe that also rooms and buildings can serve as PUFs. They apply this insight to monitor the integrity of enclosed environments, such as art galleries, bank vaults, or data centers.
- Johannes Tobisch
- , Sébastien Philippe
- & Ulrich Rührmair
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting discrete-time bifurcations with deep learning
Predicting discrete-time bifurcations with deep learning
Critical transitions and qualitative changes of dynamics in cardiac, ecological, and economical systems, can be characterized by discrete-time bifurcations. The authors propose a deep learning framework that provides early warning signals for critical transitions in discrete-time experimental data.
- Thomas M. Bury
- , Daniel Dylewsky
- & Gil Bub
-
Article
| Open Access Hyper-cores promote localization and efficient seeding in higher-order processes
Hyper-cores promote localization and efficient seeding in higher-order processes
Networks with higher-order interactions provide better description of social and biological systems, however tools to analyze their function still need to be developed. The authors introduce here a decomposition of network in hyper-cores, that gives better understanding of spreading processes and can be applied to fingerprint real-world datasets.
- Marco Mancastroppa
- , Iacopo Iacopini
- & Alain Barrat
-
Review Article
| Open AccessThe promise of data science for health research in Africa
In this Review article, the authors discuss emerging efforts to build ethical governance frameworks for data science health research in Africa and the opportunities to advance these through investments by African governments and institutions, international funding organizations and collaborations for research and capacity development.
- Clement A. Adebamowo
- , Shawneequa Callier
- & Sally N. Adebamowo
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient optimization with higher-order Ising machines
Efficient optimization with higher-order Ising machines
Combinatorial optimization problems can be solved on parallel hardware called Ising machines. Most studies have focused on the use of second-order Ising machines. Compared to second-order Ising machines, the authors show that higher-order Ising machines realized with coupled-oscillator networks can be more resource-efficient and provide superior solutions for constraint satisfaction problems.
- Connor Bybee
- , Denis Kleyko
- & Friedrich T. Sommer
-
Article
| Open Access The reaction-diffusion basis of animated patterns in eukaryotic flagella
The reaction-diffusion basis of animated patterns in eukaryotic flagella
In 1952, Turing unlocked the reaction-diffusion basis of natural patterns, such as zebra stripes. The authors propose a reaction-diffusion model that recreates characteristics of the flagellar waveform for bull sperm and Chlamydomonas flagella.
- James F. Cass
- & Hermes Bloomfield-Gadêlha
-
Article
| Open Access A digital twin for DNA data storage based on comprehensive quantification of errors and biases
A digital twin for DNA data storage based on comprehensive quantification of errors and biases
Archiving data in synthetic DNA offers unprecedented storage density and longevity. To understand how experimental choices affect the integrity of digital data stored in DNA, the authors study the evolution of errors and bias and with a digital twin they supply tools for experimental planning and design of error-correcing codes.
- Andreas L. Gimpel
- , Wendelin J. Stark
- & Robert N. Grass
-
Article
| Open Access The complexity of NISQ
The complexity of NISQ
Our current understanding of the computational abilities of near-intermediate scale quantum (NISQ) computing devices is limited, in part due to the absence of a precise definition for this regime. Here, the authors formally define the NISQ realm and provide rigorous evidence that its capabilities are situated between the complexity classes BPP and BQP.
- Sitan Chen
- , Jordan Cotler
- & Jerry Li
-
Article
| Open Access Multimaterial fiber as a physical simulator of a capillary instability
Multimaterial fiber as a physical simulator of a capillary instability
Capillary breakup in multimaterial fibers is explored for the self-assembly of optoelectronic systems. However, its insights primarily stem from numerical simulations, qualitative at best. The authors formulate an analytical model of such breakup, obtaining a window in the governing parameters where the generally chaotic breakup becomes predictable and thus engineerable.
- Camila Faccini de Lima
- , Fan Wang
- & Alexander Gumennik
-
Article
| Open Access On the visual analytic intelligence of neural networks
On the visual analytic intelligence of neural networks
Visual oddity tasks delve into the visual analytic intelligence of humans, which remained challenging for artificial neural networks. The authors propose here a model with biologically inspired neural dynamics and synthetic saccadic eye movements with improved efficiency and accuracy in solving the visual oddity tasks.
- Stanisław Woźniak
- , Hlynur Jónsson
- & Evangelos Eleftheriou
-
Article
| Open Access Realistic fault detection of li-ion battery via dynamical deep learning
Realistic fault detection of li-ion battery via dynamical deep learning
Accurate evaluation of Li-ion battery safety conditions can reduce unexpected cell failures. Here, authors present a large-scale electric vehicle charging dataset for benchmarking existing algorithms, and develop a deep learning algorithm for detecting Li-ion battery faults.
- Jingzhao Zhang
- , Yanan Wang
- & Minggao Ouyang
-
Article
| Open Access Creating speech zones with self-distributing acoustic swarms
Creating speech zones with self-distributing acoustic swarms
Want to mute or focus on speech from a specific region in a crowded room? Here, the authors built an acoustic swarm that, along with neural networks, separates and localizes concurrent speakers in the 2D space with high precision.
- Malek Itani
- , Tuochao Chen
- & Shyamnath Gollakota
-
Article
| Open Access epiAneufinder identifies copy number alterations from single-cell ATAC-seq data
epiAneufinder identifies copy number alterations from single-cell ATAC-seq data
'Here the authors present epiAneufinder, an algorithm for the identification of single-cell copy number alterations from scATAC-seq data, and explore the clonal heterogeneity in cell populations.
- Akshaya Ramakrishnan
- , Aikaterini Symeonidi
- & Maria Colomé-Tatché
-
Article
| Open Access Capturing dynamical correlations using implicit neural representations
Capturing dynamical correlations using implicit neural representations
Analysis of experimental data in condensed matter is often challenging due to system complexity and slow character of physical simulations. The authors propose a framework that combines machine learning with theoretical calculations to enable real-time analysis for electron, neutron, and x-ray spectroscopies.
- Sathya R. Chitturi
- , Zhurun Ji
- & Joshua J. Turner
-
Article
| Open Access A robust normalized local filter to estimate compositional heterogeneity directly from cryo-EM maps
A robust normalized local filter to estimate compositional heterogeneity directly from cryo-EM maps
Heterogeneity in structural biology data includes potentially valuable information about binding and dynamics. Here, the authors devise, validate and demonstrate a method to quantify local heterogeneity in 3D reconstructions.
- Björn O. Forsberg
- , Pranav N. M. Shah
- & Alister Burt
-
Article
| Open Access A GPU-based computational framework that bridges neuron simulation and artificial intelligence
A GPU-based computational framework that bridges neuron simulation and artificial intelligence
High computational cost severely limit the applications of biophysically detailed multi-compartment models. Here, the authors present DeepDendrite, a GPU-optimized tool that drastically accelerates detailed neuron simulations for neuroscience and AI, enabling exploration of intricate neuronal processes and dendritic learning mechanisms in these fields.
- Yichen Zhang
- , Gan He
- & Tiejun Huang
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access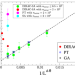 Reply to: Deep reinforced learning heuristic tested on spin-glass ground states: The larger picture
Reply to: Deep reinforced learning heuristic tested on spin-glass ground states: The larger picture
- Changjun Fan
- , Mutian Shen
- & Yang-Yu Liu
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access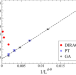 Deep reinforced learning heuristic tested on spin-glass ground states: The larger picture
Deep reinforced learning heuristic tested on spin-glass ground states: The larger picture
- Stefan Boettcher
-
Article
| Open Access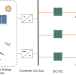 Digital twin based monitoring and control for DC-DC converters
Digital twin based monitoring and control for DC-DC converters
In this work, authors explore DC-DC converter monitoring and control and demonstrate a generalizable digital twin based buck converter system that enables dynamic synchronization even under reference value changes, physical system model variation, and physical controller failure.
- Zhongcheng Lei
- , Hong Zhou
- & Guo-Ping Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Transfer Learning with Kernel Methods
Transfer Learning with Kernel Methods
Transfer learning can be applied in computer vision and natural language processing to utilize knowledge from a source task to improve performance on a target task. The authors propose a framework for transfer learning with kernel methods for improved image classification and virtual drug screening.
- Adityanarayanan Radhakrishnan
- , Max Ruiz Luyten
- & Caroline Uhler
-
Article
| Open Access ADuLT: An efficient and robust time-to-event GWAS
ADuLT: An efficient and robust time-to-event GWAS
Robust genome-wide association study (GWAS) methods that can utilise time-to-event information such as age-of-onset will help increase power in analyses for common health outcomes. Here, the authors propose a computationally efficient time-to-event model for GWAS.
- Emil M. Pedersen
- , Esben Agerbo
- & Bjarni J. Vilhjálmsson
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning the dimension of a Fano variety
Machine learning the dimension of a Fano variety
Fano varieties are mathematical shapes that are basic units in geometry, they are challenging to classify in high dimensions. The authors introduce a machine learning approach that picks out geometric structure from complex mathematical data where rigorous analytical methods are lacking.
- Tom Coates
- , Alexander M. Kasprzyk
- & Sara Veneziale

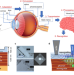 On-chip phonon-magnon reservoir for neuromorphic computing
On-chip phonon-magnon reservoir for neuromorphic computing