Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Measuring the mechanical properties of molecular conformers
Measuring the mechanical properties of molecular conformers
Manipulation of single molecules can be achieved using scanning probe microscopy but the influence of molecular conformation on this process has, until now, been unclear. Here, the authors probe two different types of porphyrin conformer on a surface and see strong differences in their mechanochemical response.
- S. P. Jarvis
- , S. Taylor
- & P. Moriarty
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular helices as electron acceptors in high-performance bulk heterojunction solar cells
Molecular helices as electron acceptors in high-performance bulk heterojunction solar cells
In organic photovoltaics, the best-performing devices are often based on fullerene derivatives as the electron acceptor counterpart. Here, the authors present new molecular electron acceptors with a helical structure and achieve 8.3% power conversion efficiency.
- Yu Zhong
- , M. Tuan Trinh
- & Colin Nuckolls
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid glasses from strong and fragile metal-organic framework liquids
Hybrid glasses from strong and fragile metal-organic framework liquids
The fine interface between crystallinity and amorphicity in synthetic hybrid materials has to-date been relatively under-explored. Here, the authors probe the relationship between amorphisation and melting behaviour in zeolitic metal-organic frameworks as a route towards functional glasses.
- Thomas D. Bennett
- , Jin-Chong Tan
- & G. Neville Greaves
-
Article
| Open Access Thermodynamic picture of ultrafast charge transport in graphene
Thermodynamic picture of ultrafast charge transport in graphene
A linear energy–momentum relation of graphene results in a high direct-current electron mobility, but this is not necessarily true at terahertz frequencies. Here, the authors show that its ultrafast conductivity is dependent on a highly nonlinear interplay between heating and cooling of the electron gas.
- Zoltán Mics
- , Klaas-Jan Tielrooij
- & Dmitry Turchinovich
-
Article
| Open Access Local destruction of superconductivity by non-magnetic impurities in mesoscopic iron-based superconductors
Local destruction of superconductivity by non-magnetic impurities in mesoscopic iron-based superconductors
The pairing symmetry of the wavefunction in high-Tciron-based superconductors remains not completely understood. To shed light on this problem, here the authors investigate the local destruction of superconductivity by introducing Zn impurities in the BKZn iron arsenide compound.
- Jun Li
- , Min Ji
- & Victor V. Moshchalkov
-
Article
| Open Access Crystallization of DNA-coated colloids
Crystallization of DNA-coated colloids
DNA-coated colloids have failed to achieve their promise of programmable self-assembly because they stick to each other like Velcro. Here Wang et al.overcome this problem by making clickable smooth colloids that are coated with short single-stranded DNA at high density.
- Yu Wang
- , Yufeng Wang
- & David J. Pine
-
Article
| Open Access Direct characterization of photoinduced lattice dynamics in BaFe2As2
Direct characterization of photoinduced lattice dynamics in BaFe2As2
In BaFe2As2, the lattice couples strongly to the magnetic and electronic degrees of freedom, providing a way to control them. Here, by means of time-resolved X-ray scattering, the authors measure rapid lattice oscillations, which can induce changes in the material’s electronic and magnetic properties.
- S. Gerber
- , K. W. Kim
- & W.-S. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic mineralization of metal-organic frameworks as protective coatings for biomacromolecules
Biomimetic mineralization of metal-organic frameworks as protective coatings for biomacromolecules
Robust biomacromolecules could be used for a wide range of biotechnological applications. Here the authors report a biomimetic mineralization process, in which biomolecules are encapsulated within metal-organic frameworks, and their stability is subsequently increased without significant bioactivity loss.
- Kang Liang
- , Raffaele Ricco
- & Paolo Falcaro
-
Article |
 Predictive modelling-based design and experiments for synthesis and spinning of bioinspired silk fibres
Predictive modelling-based design and experiments for synthesis and spinning of bioinspired silk fibres
Reproducing many naturally occurring silk fibres—such as spider silk—remains a challenge. Here, the authors develop a predictive modelling approach to understand and design the artificial synthesis and fibre-spinning processes, which are tested in the laboratory to create de novobioinspired silk fibres.
- Shangchao Lin
- , Seunghwa Ryu
- & Markus J. Buehler
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional positioning and control of colloidal objects utilizing engineered liquid crystalline defect networks
Three-dimensional positioning and control of colloidal objects utilizing engineered liquid crystalline defect networks
Topological defects can be used not only to modify the properties of liquid crystals but also as scaffolds to build new structures by trapping particles. Here, Yoshida et al. construct three-dimensional colloidal superstructures in a nematic host, which are reconfigurable in an electric field.
- H. Yoshida
- , K. Asakura
- & M. Ozaki
-
Article |
 Anomalous magnetoresistance in the spinel superconductor LiTi2O4
Anomalous magnetoresistance in the spinel superconductor LiTi2O4
LiTi2O4is the only known spinel oxide superconductor, but systematic investigations of its transport properties have been lacking so far. Here, the authors' analyses detect an unusual magnetoresistance, revealing spin-orbit fluctuations similar to those in high-temperature superconductors.
- K. Jin
- , G. He
- & I. Takeuchi
-
Article
| Open Access Supramolecular gels with high strength by tuning of calix[4]arene-derived networks
Supramolecular gels with high strength by tuning of calix[4]arene-derived networks
The physical properties of gel materials makes them attractive options in various applications, but supramolecular gels typically lack mechanical strength. Here, the authors present a calix[4]arene-based supramoleculer gel tuned to possess high tensile strength.
- Ji Ha Lee
- , Jaehyeon Park
- & Jong Hwa Jung
-
Article
| Open Access Aqueous proton transfer across single-layer graphene
Aqueous proton transfer across single-layer graphene
Proton transfer across graphene is associated with large computed energy barriers and is thought to be generally unfavourable. Here, the authors observe aqueous proton transfer through graphene subjected to pH cycling, suggesting that it is due to transfer through rare, naturally occurring atomic defects.
- Jennifer L. Achtyl
- , Raymond R. Unocic
- & Franz M. Geiger
-
Article
| Open Access Reversed oxygen sensing using colloidal quantum wells towards highly emissive photoresponsive varnishes
Reversed oxygen sensing using colloidal quantum wells towards highly emissive photoresponsive varnishes
Colloidal quantum wells have great potential as solution-processed light sources. Here, Lorenzon et al. demonstrate that such colloidal quantum wells can also be exploited as luminescent-sensing varnishes capable of detecting chemical agents through their reversible emission response.
- Monica Lorenzon
- , Sotirios Christodoulou
- & Sergio Brovelli
-
Article |
 Berry phases and the intrinsic thermal Hall effect in high-temperature cuprate superconductors
Berry phases and the intrinsic thermal Hall effect in high-temperature cuprate superconductors
A fully quantum mechanical description of the thermal Hall effect in high-temperature cuprate superconductors remains elusive. Here, by connecting it to momentum space Berry phases, the authors calculate the dependence of the intrinsic thermal Hall conductivity on temperature, external field and pairing gap.
- Vladimir Cvetkovic
- & Oskar Vafek
-
Article
| Open Access Multiple-length-scale deformation analysis in a thermoplastic polyurethane
Multiple-length-scale deformation analysis in a thermoplastic polyurethane
Thermoplastic polyurethane elastomers are of interest in many applications, but their structure–property relations are not well understood. Here, the authors perform a multiple-length-scale deformation analysis on a thermoplastic polyurethane and shed light on morphological changes during the deformation.
- Tan Sui
- , Nikolaos Baimpas
- & Alexander M. Korsunsky
-
Article
| Open Access Consequences of chirality on the dynamics of a water-soluble supramolecular polymer
Consequences of chirality on the dynamics of a water-soluble supramolecular polymer
Water-soluble supramolecular polymers assemble from individual building blocks, but there is a lack of understanding as to how the properties depend on the components. Here the authors show how the introduction of chiral groups can affect the structural features and dynamic behaviour of the polymer.
- Matthew B. Baker
- , Lorenzo Albertazzi
- & E.W. Meijer
-
Article
| Open Access Porous coordination polymers with ubiquitous and biocompatible metals and a neutral bridging ligand
Porous coordination polymers with ubiquitous and biocompatible metals and a neutral bridging ligand
Inexpensive porous materials synthesized from Group II metals may be useful for industrial applications. Here, the authors demonstrate that neutral bridging ligands can be used for the synthesis of magnesium(II) and calcium(II) porous coordination polymers.
- Shin-ichiro Noro
- , Junya Mizutani
- & Takayoshi Nakamura
-
Article
| Open Access A molecular nematic liquid crystalline material for high-performance organic photovoltaics
A molecular nematic liquid crystalline material for high-performance organic photovoltaics
There is a trade-off between increasing thickness of active layers in organic photovoltaic cells to be compatible with modern printing techniques and decreasing it to improve the device performance. Sun et al.report a nematic liquid crystalline molecular electron donor material used in thick layers.
- Kuan Sun
- , Zeyun Xiao
- & David J. Jones
-
Article |
 Ion transport controlled by nanoparticle-functionalized membranes
Ion transport controlled by nanoparticle-functionalized membranes
The regulated passage of ions through a porous membrane is a process applicable to various research disciplines. Here, the authors present a method for the control of porous membrane ion transport, using a deposited layer of ligand-functionalized nanoparticles.
- Edward Barry
- , Sean P. McBride
- & Xiao-Min Lin
-
Article |
 Ultralight nanofibre-assembled cellular aerogels with superelasticity and multifunctionality
Ultralight nanofibre-assembled cellular aerogels with superelasticity and multifunctionality
Materials with ultra-low densities can display a range of useful properties, ranging from compressibility to sound absorption. Here, the authors report the fabrication of ultra-lightweight materials by the assembly of electrospun nanofibres into an aerogel and examine the mechanical properties.
- Yang Si
- , Jianyong Yu
- & Bin Ding
-
Article |
 A trident dithienylethene-perylenemonoimide dyad with super fluorescence switching speed and ratio
A trident dithienylethene-perylenemonoimide dyad with super fluorescence switching speed and ratio
Photoswitchable fluorophores hold promise for organic photonic devices. Here Li et al. report that a trident perylenemonoimide modified by diethienylethenes shows a large on/off ratio and high switching speed, which enables erasable fluorescence patterning, all-optical transistors and optical nanoimaging.
- Chong Li
- , Hui Yan
- & Ming-Qiang Zhu
-
Article |
 High-Tc superconductivity in ultrathin Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+x down to half-unit-cell thickness by protection with graphene
High-Tc superconductivity in ultrathin Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+x down to half-unit-cell thickness by protection with graphene
So-called two-dimensional superconductivity has been reported in several material systems but just how thin a system can be and maintain a superconducting state has been difficult to determine. Da Jiang and colleagues demonstrate that Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+xcontinues to be superconducting even when it is just half a unit cell thick.
- Da Jiang
- , Tao Hu
- & Mianheng Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous critical fields in quantum critical superconductors
Anomalous critical fields in quantum critical superconductors
Superconductivity in the iron pnictides is believed to be related to quantum critical fluctuations. Putzke et al. observe unexpected anomalies in the critical fields of BaFe2(As1−xPx)2that emerge close to its magnetic critical point, which they argue is a generic feature of quantum critical superconductivity.
- C. Putzke
- , P. Walmsley
- & A. Carrington
-
Article |
 Kinetically tuned dimensional augmentation as a versatile synthetic route towards robust metal–organic frameworks
Kinetically tuned dimensional augmentation as a versatile synthetic route towards robust metal–organic frameworks
The synthesis of ultra-stable, single crystalline metal–organic frameworks is challenging. Here, the authors describe a kinetically tuned augmentation synthetic route for the preparation of a range of robust crystalline materials from preformed trimetallic components.
- Dawei Feng
- , Kecheng Wang
- & Hong-Cai Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Polymer collapse in miscible good solvents is a generic phenomenon driven by preferential adsorption
Polymer collapse in miscible good solvents is a generic phenomenon driven by preferential adsorption
Smart polymers exhibit a swelling–collapse–swelling transition in mixed (co)solvents and the underlined mechanism remains a matter of debate. Mukherji et al. explain this transition using a generic model based purely on a thermodynamic treatment of preferential polymer–cosolvent interaction.
- Debashish Mukherji
- , Carlos M. Marques
- & Kurt Kremer
-
Article |
 A general and scalable synthesis approach to porous graphene
A general and scalable synthesis approach to porous graphene
Scalable routes towards porous graphene are useful for developing materials for mass transfer applications. Here, the authors report the fabrication of porous graphene with controllable pore size and nitrogen content via the carbothermal reaction of graphene and (poly)oxometallates.
- Ding Zhou
- , Yi Cui
- & Bao-Hang Han
-
Article |
 Control superstructure of rigid polyelectrolytes in oppositely charged hydrogels via programmed internal stress
Control superstructure of rigid polyelectrolytes in oppositely charged hydrogels via programmed internal stress
Biomaterials composed of macromolecules display complex structures with long range order, but it is difficult to create similarly complex superstructures in hydrogels. Here, the authors control the orientation of polyelectrolytes in hydrogels by introducing programmed swelling patterns and internal stresses.
- Riku Takahashi
- , Zi Liang Wu
- & Jian Ping Gong
-
Article |
 Engineering chiral porous metal-organic frameworks for enantioselective adsorption and separation
Engineering chiral porous metal-organic frameworks for enantioselective adsorption and separation
The separation of chiral molecules is a fundamental and industrially relevant challenge. Here, the authors report a chiral metal-organic framework that functions as a solid-state host capable of absorbing and separating mixtures of a range of chiral amines, with high enatioselectivity.
- Yongwu Peng
- , Tengfei Gong
- & Yong Cui
-
Article |
 Self-assembly of colloid-cholesteric composites provides a possible route to switchable optical materials
Self-assembly of colloid-cholesteric composites provides a possible route to switchable optical materials
Colloidal particles dispersed in liquid crystal hold promise for new functional materials with tunable elastic and electro-optic properties. Through simulations, Stratford et al.predict a new class of colloidal networks in a chiral liquid crystal host, which could guide the design of these materials.
- K. Stratford
- , O. Henrich
- & D. Marenduzzo
-
Article
| Open Access A liquid crystalline chirality balance for vapours
A liquid crystalline chirality balance for vapours
Chiral determination of vapours is possible in biological systems as an important part of the olfactory system. Here, the authors describe a system that is capable of visually detecting and distinguishing the chirality of vapour-phase molecules by structural changes in a liquid crystal confined in open microchannels.
- Takuya Ohzono
- , Takahiro Yamamoto
- & Jun-ichi Fukuda
-
Article |
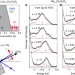 High-energy spin and charge excitations in electron-doped copper oxide superconductors
High-energy spin and charge excitations in electron-doped copper oxide superconductors
Understanding spin dynamics in the cuprates is vital to understanding the origin high-temperature superconductivity. X-ray and neutron spectra obtained by Ishii et al.suggest that the spins in electron-doped cuprates are itinerant, in contrast to recent evidence that in hole-doped cuprates they are localized.
- K. Ishii
- , M. Fujita
- & J. Mizuki
-
Article |
 Spatially and temporally reconfigurable assembly of colloidal crystals
Spatially and temporally reconfigurable assembly of colloidal crystals
Controlling colloidal assemblies without the need of a template or electrode is still a challenging goal. Here Kim et al.use photo-induced ion flow in an indium tin oxide-coated substrate to control this process, allowing reversible assembly of colloidal crystals in a three-dimensional manner.
- Youngri Kim
- , Aayush A. Shah
- & Michael J. Solomon
-
Article |
 Novel polymer-free iridescent lamellar hydrogel for two-dimensional confined growth of ultrathin gold membranes
Novel polymer-free iridescent lamellar hydrogel for two-dimensional confined growth of ultrathin gold membranes
The structure of hydrogels is normally isotropic, but anisotropic hydrogels with a periodic lamellar structure can also be synthesized. Here the confined water layers in a lamellar hydrogel are used to guide the growth of large area, single-crystalline gold membranes with two-dimensional properties.
- Jian Niu
- , Dong Wang
- & Jian Jin
-
Article |
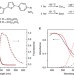 Electrofluorochromism in π-conjugated ionic liquid crystals
Electrofluorochromism in π-conjugated ionic liquid crystals
The ability to easily modulate a material’s photoluminescent properties in response to stimuli is difficult to achieve in liquid crystals. Here the authors report ionic liquid crystals exhibiting high fluorescent quantum yields with redox-dependent photoluminescence.
- Amerigo Beneduci
- , Sante Cospito
- & Giuseppe Chidichimo
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient and tunable white-light emission of metal–organic frameworks by iridium-complex encapsulation
Efficient and tunable white-light emission of metal–organic frameworks by iridium-complex encapsulation
Although many metal–organic frameworks are luminescent, few are capable of white-light emission. Here, the authors incorporate a yellow-emitting guest molecule into the cavities of a blue-emitting metal–organic framework, and tune the composition to emit white light with relatively high quantum yield.
- Chun-Yi Sun
- , Xin-Long Wang
- & Jing Li
-
Article
| Open Access Confinement of pyridinium hemicyanine dye within an anionic metal-organic framework for two-photon-pumped lasing
Confinement of pyridinium hemicyanine dye within an anionic metal-organic framework for two-photon-pumped lasing
Two-photon-pumped dye lasers are useful for applications such as biological imaging; however, loss processes reduce their efficiency. Here, metal-organic frameworks, into which the laser dye is incorporated, demonstrate enhanced laser operation because losses such as dye aggregation-caused quenching are reduced.
- Jiancan Yu
- , Yuanjing Cui
- & Guodong Qian
-
Article
| Open Access Localized cell stimulation by nitric oxide using a photoactive porous coordination polymer platform
Localized cell stimulation by nitric oxide using a photoactive porous coordination polymer platform
Localized cell stimulation is useful in the analysis of biological signalling networks. Here the authors develop a photosensitive porous framework to achieve spatiotemporally controlled cellular delivery of the gaseous biomolecule nitric oxide, using it to regulate intracellular calcium levels.
- Stéphane Diring
- , Dan Ohtan Wang
- & Shuhei Furukawa
-
Article |
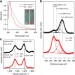 Revealing the ultrafast process behind the photoreduction of graphene oxide
Revealing the ultrafast process behind the photoreduction of graphene oxide
Photoreduction is a promising method for the synthesis of reduced graphene oxide, but the dynamics of the process are unclear. Here, the authors explore the process via a pump–probe technique, revealing its ultrafast nature and the involvement of solvated electrons produced by irradiation of the solvent.
- Régis Y. N. Gengler
- , Daniel S. Badali
- & R. J. Dwayne Miller
-
Article |
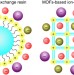 Selective anion exchange with nanogated isoreticular positive metal-organic frameworks
Selective anion exchange with nanogated isoreticular positive metal-organic frameworks
Crystalline porous materials are commonly based around negatively charged frameworks, so ion-exchange is limited to cations. Here, the authors report a series of positive metal-organic frameworks, capable of ion exchange of large organic anions, with potential in separation and purification applications.
- Xiang Zhao
- , Xianhui Bu
- & Pingyun Feng
-
Article |
 Disk-cylinder and disk-sphere nanoparticles via a block copolymer blend solution construction
Disk-cylinder and disk-sphere nanoparticles via a block copolymer blend solution construction
Compositionally and geometrically complex nano-objects are an important goal in medicinal, photonic and electronic materials research. Here, the authors fabricate disk-sphere and disk-cylinder nanoparticles with defined multicompartments from binary mixtures of block copolymers.
- Jiahua Zhu
- , Shiyi Zhang
- & Darrin J. Pochan
-
Article |
 Reversible patterning and actuation of hydrogels by electrically assisted ionoprinting
Reversible patterning and actuation of hydrogels by electrically assisted ionoprinting
Techniques for shape-controlling of hydrogels, that is, crosslinked networks of polymers, could make possible various biomimetic applications. Palleau et al.propose a strategy to pattern three-dimensional hydrogels using electric potential, which allows directed bending and fast controllable actuation.
- Etienne Palleau
- , Daniel Morales
- & Orlin D. Velev
-
Article |
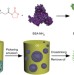 Interfacial assembly of protein–polymer nano-conjugates into stimulus-responsive biomimetic protocells
Interfacial assembly of protein–polymer nano-conjugates into stimulus-responsive biomimetic protocells
Proteins are ideal building blocks for self-assembly of artificial cell-like architectures, but their realization is rare. Huang et al.report an interfacial assembly of protein–polymer conjugates, which exhibit cellular properties such as encapsulating guest molecules and switching enzyme activity.
- Xin Huang
- , Mei Li
- & Stephen Mann
-
Article |
 An influenza virus-inspired polymer system for the timed release of siRNA
An influenza virus-inspired polymer system for the timed release of siRNA
Small interfering RNA is degraded by plasma and can’t cross the cell membrane due to its negative charge. Here, the authors present an influenza inspired polymer carrier, capable of local RNA delivery, which degrades to a non-toxic by-product, and is thus suitable for multiple doses.
- Nghia P Truong
- , Wenyi Gu
- & Michael J Monteiro
-
Article
| Open Access A synthetic route to ultralight hierarchically micro/mesoporous Al(III)-carboxylate metal-organic aerogels
A synthetic route to ultralight hierarchically micro/mesoporous Al(III)-carboxylate metal-organic aerogels
Hierarchically porous metal-organic monoliths are potential materials for mass transfer applications. Here, the authors synthesize metal-organic aerogels via the gelation of metal-organic frameworks, and are able to tune their porosity exploiting the properties of both crystalline and aerogel materials.
- Lei Li
- , Shenglin Xiang
- & Cheng-Yong Su
-
Article |
 New materials for methane capture from dilute and medium-concentration sources
New materials for methane capture from dilute and medium-concentration sources
Methane is an important greenhouse gas but its capture presents a challenge due to its weak interactions with most materials. Here the authors perform a systematic screening of liquid solvents and nanoporous zeolites, and identify zeolite structures with good potential for methane uptake and separation.
- Jihan Kim
- , Amitesh Maiti
- & Roger D. Aines
-
Article |
 Moderate doping leads to high performance of semiconductor/insulator polymer blend transistors
Moderate doping leads to high performance of semiconductor/insulator polymer blend transistors
Blends of different polymer compounds are widely used for organic field-effect transistors. Here, Neher and colleagues show that moderate carrier doping is important to achieve maximum performance in blends of insulating and semiconducting polymers.
- Guanghao Lu
- , James Blakesley
- & Dieter Neher
-
Article |
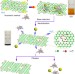 Probing the catalytic activity of porous graphene oxide and the origin of this behaviour
Probing the catalytic activity of porous graphene oxide and the origin of this behaviour
Graphene oxide has been proposed as an alternative to precious metals for the catalysis of aerobic oxidative reactions; however, high catalyst loadings are needed. Here a simple base and acid treatment is shown to enhance its catalytic activity for the oxidative coupling of amines under ambient conditions.
- Chenliang Su
- , Muge Acik
- & Kian Ping Loh
-
Article |
 Biomimetic superelastic graphene-based cellular monoliths
Biomimetic superelastic graphene-based cellular monoliths
The exploitation of the properties of graphene, such as mechanical strength and electrical conductivity, in deformable macroscopic materials is desirable. Here, a combination of graphene chemistry and ice physics is used to fabricate biomimetic, ultralight and superelastic graphene cellular monoliths.
- Ling Qiu
- , Jeffery Z. Liu
- & Dan Li

 Direct observation of ultrafast coherent exciton dynamics in helical π-stacks of self-assembled perylene bisimides
Direct observation of ultrafast coherent exciton dynamics in helical π-stacks of self-assembled perylene bisimides