Featured
-
-
Article |
 A droplet-based electricity generator with high instantaneous power density
A droplet-based electricity generator with high instantaneous power density
A device involving a polytetrafluoroethylene film, an indium tin oxide substrate and an aluminium electrode allows improved electricity generation from water droplets, which bridge the previously disconnected circuit components.
- Wanghuai Xu
- , Huanxi Zheng
- & Zuankai Wang
-
Article |
 Antagonistic cooperativity between crystal growth modifiers
Antagonistic cooperativity between crystal growth modifiers
Inhibitor pairs that suppress the crystallization of haematin, which is a part of malaria parasites’ physiology, show unexpected antagonism due to attenuation of step pinning by kink blockers.
- Wenchuan Ma
- , James F. Lutsko
- & Peter G. Vekilov
-
Article |
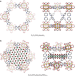 Confinement of atomically defined metal halide sheets in a metal–organic framework
Confinement of atomically defined metal halide sheets in a metal–organic framework
The pore space in the metal–organic framework Zr6O4(OH)4(bpydc)6 can be used as a scaffold to grow precisely defined atomically thick sheets of metal halide materials, taking advantage of multiple binding sites to direct complexation of the metal ions; these metal halide nanosheets fill the size gap between discrete molecular magnets and bulk magnetic materials, with potentially unusual magnetic properties arising from this size regime.
- Miguel I. Gonzalez
- , Ari B. Turkiewicz
- & Jeffrey R. Long
-
Article |
 Voxelated soft matter via multimaterial multinozzle 3D printing
Voxelated soft matter via multimaterial multinozzle 3D printing
Voxelated soft matter is designed and fabricated using multimaterial multinozzle three-dimensional printing, which switches between different viscoelastic inks along the same print filament to print multiple materials simultaneously.
- Mark A. Skylar-Scott
- , Jochen Mueller
- & Jennifer A. Lewis
-
Letter |
 Crosslinking ionic oligomers as conformable precursors to calcium carbonate
Crosslinking ionic oligomers as conformable precursors to calcium carbonate
The crosslinking of oligomeric precursors, controlled by a capping agent, enables the production of moulded crystalline calcium carbonate with continuous structures.
- Zhaoming Liu
- , Changyu Shao
- & Ruikang Tang
-
Article |
 Multivalent anions as universal latent electron donors
Multivalent anions as universal latent electron donors
Multivalent anions are found to be capable of electron-doping polymer semiconductors to realize conductive films with very low work functions, which enable efficient electron injection into materials with low electron affinity.
- Cindy G. Tang
- , Mazlan Nur Syafiqah
- & Peter K. H. Ho
-
Letter |
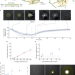 Controlling organization and forces in active matter through optically defined boundaries
Controlling organization and forces in active matter through optically defined boundaries
Light is used to guide the behaviour of an engineered active-matter system, producing structures and properties that can be dynamically manipulated and controlled.
- Tyler D. Ross
- , Heun Jin Lee
- & Matt Thomson
-
Letter |
 Lattice anchoring stabilizes solution-processed semiconductors
Lattice anchoring stabilizes solution-processed semiconductors
The stability of both colloidal quantum dots and perovskites can be improved by combining them into a hybrid material in which matched lattice parameters suppress the formation of undesired phases.
- Mengxia Liu
- , Yuelang Chen
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Letter |
 Chemical control of structure and guest uptake by a conformationally mobile porous material
Chemical control of structure and guest uptake by a conformationally mobile porous material
A new metal–organic framework has several conformational degrees of freedom that can be modified by the external chemical environment to change the structure and trigger the uptake of a guest molecule.
- Alexandros P. Katsoulidis
- , Dmytro Antypov
- & Matthew J. Rosseinsky
-
Review Article |
 Machine learning for molecular and materials science
Machine learning for molecular and materials science
Recent progress in machine learning in the chemical sciences and future directions in this field are discussed.
- Keith T. Butler
- , Daniel W. Davies
- & Aron Walsh
-
Letter |
 Electrically controlled water permeation through graphene oxide membranes
Electrically controlled water permeation through graphene oxide membranes
The rapid water transport through graphene oxide membranes can be switched off by introducing localized electric fields within the membranes that ionize surrounding water molecules and thus block transport.
- K.-G. Zhou
- , K. S. Vasu
- & R. R. Nair
-
Letter |
 Monolayer atomic crystal molecular superlattices
Monolayer atomic crystal molecular superlattices
Superlattices consisting of alternating monolayer atomic crystals and molecular layers allow access to stable phosphorene monolayers with competitive transistor performance and to bulk monolayer materials with tunable optoelectronic properties.
- Chen Wang
- , Qiyuan He
- & Xiangfeng Duan
-
Letter |
 Sterically controlled mechanochemistry under hydrostatic pressure
Sterically controlled mechanochemistry under hydrostatic pressure
‘Molecular anvil’ molecules consisting of a compressible mechanophore and incompressible ligands react under hydrostatic pressure to produce elemental metal via an unexplored mechanism.
- Hao Yan
- , Fan Yang
- & Nicholas A. Melosh
-
Letter |
 Processing bulk natural wood into a high-performance structural material
Processing bulk natural wood into a high-performance structural material
A process is described for the transformation of bulk wood into a low-cost, strong, tough, lightweight structural material, by the partial removal of lignin and hemicellulose followed by hot-pressing to densify the natural wood.
- Jianwei Song
- , Chaoji Chen
- & Liangbing Hu
-
Letter |
 Perovskite nickelates as electric-field sensors in salt water
Perovskite nickelates as electric-field sensors in salt water
Application of an electric field changes the transport and optical properties of samarium nickelate submerged in water, making it a suitable passive sensor of weak electric fields in salt water.
- Zhen Zhang
- , Derek Schwanz
- & Shriram Ramanathan
-
Letter |
 Organic long persistent luminescence
Organic long persistent luminescence
A blend of two organic molecules excited by a simple LED light source can release the stored excitation energy slowly as ‘long persistent luminescence’ over periods of up to an hour.
- Ryota Kabe
- & Chihaya Adachi
-
Letter |
 Patchy particles made by colloidal fusion
Patchy particles made by colloidal fusion
By exploiting geometric constraints and interfacial forces instead of chemistry, colloidal clusters can be controllably coalesced into particles with uniformly distributed surface patches.
- Zhe Gong
- , Theodore Hueckel
- & Stefano Sacanna
-
Letter |
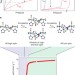 A spin transition mechanism for cooperative adsorption in metal–organic frameworks
A spin transition mechanism for cooperative adsorption in metal–organic frameworks
Metal–organic frameworks that undergo a cooperative spin transition at neighbouring metal centres upon coordination to CO exhibit large CO separation capacities with only small changes in temperature.
- Douglas A. Reed
- , Benjamin K. Keitz
- & Jeffrey R. Long
-
Letter |
 A series of energetic metal pentazolate hydrates
A series of energetic metal pentazolate hydrates
Metal complexes of the pentazole anion exhibit multiple coordination modes, through ionic, covalent and hydrogen-bonding interactions, and good thermal stability with onset decomposition temperatures greater than 100 °C.
- Yuangang Xu
- , Qian Wang
- & Ming Lu
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 Tayi et al. reply
Tayi et al. reply
- Alok S. Tayi
- , Alexander K. Shveyd
- & Samuel I. Stupp
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 Conflicting evidence for ferroelectricity
Conflicting evidence for ferroelectricity
- Gabriele D’Avino
- , Manuel Souto
- & Alberto Girlando
-
Letter |
 A wet-tolerant adhesive patch inspired by protuberances in suction cups of octopi
A wet-tolerant adhesive patch inspired by protuberances in suction cups of octopi
The suction cups found in octopus tentacles are the inspiration for a synthetic adhesive that functions well in dry and wet conditions and is resistant to chemical contamination.
- Sangyul Baik
- , Da Wan Kim
- & Changhyun Pang
-
Letter |
 Accelerated discovery of two crystal structure types in a complex inorganic phase field
Accelerated discovery of two crystal structure types in a complex inorganic phase field
A computational tool that combines human-like chemical understanding with ab initio methods guides the compositional choice of complex five-component metallic oxides, yielding two new complex crystal structures.
- C. Collins
- , M. S. Dyer
- & M. J. Rosseinsky
-
Letter |
 Predicting crystal growth via a unified kinetic three-dimensional partition model
Predicting crystal growth via a unified kinetic three-dimensional partition model
A general simulation approach that can replicate, and in theory predict, the growth of a wide range of crystal types, including porous, molecular and ionic crystals, is demonstrated.
- Michael W. Anderson
- , James T. Gebbie-Rayet
- & Julian D. Gale
-
Article |
 Functional materials discovery using energy–structure–function maps
Functional materials discovery using energy–structure–function maps
Energy–structure–function maps that describe the possible structures and properties of molecular crystals are developed, and these maps are used to guide the experimental discovery of porous materials with specific functions.
- Angeles Pulido
- , Linjiang Chen
- & Graeme M. Day
-
Letter |
 Abiotic tooth enamel
Abiotic tooth enamel
Nanometre-scale columnar structures in tooth enamel inspire novel nanocomposites containing layers of vertically aligned nanowires, produced by layer-by-layer fabrication and combining high values of both storage modulus and energy dissipation.
- Bongjun Yeom
- , Trisha Sain
- & Nicholas A. Kotov
-
Letter |
 Deciphering chemical order/disorder and material properties at the single-atom level
Deciphering chemical order/disorder and material properties at the single-atom level
The three-dimensional coordinates of more than 23,000 atoms in an iron-platinum nanoparticle are determined with 22 picometre precision to correlate chemical order/disorder and crystal defects with magnetic properties.
- Yongsoo Yang
- , Chien-Chun Chen
- & Jianwei Miao
-
Letter |
 Lanthanum-catalysed synthesis of microporous 3D graphene-like carbons in a zeolite template
Lanthanum-catalysed synthesis of microporous 3D graphene-like carbons in a zeolite template
A long-sought three-dimensional graphene-like carbon structure that resembles periodically networked carbon nanotubes is now readily available through lanthanum-catalysed carbon synthesis using a zeolite template.
- Kyoungsoo Kim
- , Taekyoung Lee
- & Ryong Ryoo
-
Letter |
 Self-assembly of coherently dynamic, auxetic, two-dimensional protein crystals
Self-assembly of coherently dynamic, auxetic, two-dimensional protein crystals
Mutants of the C4-symmetric protein RhuA were designed to self-assemble into two-dimensional crystalline lattices with precise spatial arrangements and patterns; the lattices of one of the variants are auxetic and deform perpendicularly to an applied force in a way that is contrary to what is generally expected in typical materials.
- Yuta Suzuki
- , Giovanni Cardone
- & F. Akif Tezcan
-
Letter |
 Nanocrack-regulated self-humidifying membranes
Nanocrack-regulated self-humidifying membranes
Nanometre-scale cracks in a hydrophobic surface coating applied to hydrocarbon proton-exchange fuel-cell membranes work as tiny valves, delaying water desorption and maintaining ion conductivity in the membrane on dehumidification.
- Chi Hoon Park
- , So Young Lee
- & Young Moo Lee
-
Letter |
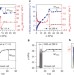 A pressure-amplifying framework material with negative gas adsorption transitions
A pressure-amplifying framework material with negative gas adsorption transitions
For adsorption processes, gas uptake usually increases with increasing pressure; however, here the phenomenon of negative gas adsorption is demonstrated in a metal–organic framework, which undergoes a sudden hysteretic structural deformation and pore contraction, releasing guest molecules.
- Simon Krause
- , Volodymyr Bon
- & Stefan Kaskel
-
Letter |
 Enhancing coherence in molecular spin qubits via atomic clock transitions
Enhancing coherence in molecular spin qubits via atomic clock transitions
Magnetic molecules are candidates for solid-state spin qubits from which a quantum computer might be constructed, but the magnetic interactions between such molecules typically lead to unwanted decoherence; now magnetic molecules have been designed in such a way that their spin dynamics are energetically protected against the decoherence-inducing interactions.
- Muhandis Shiddiq
- , Dorsa Komijani
- & Stephen Hill
-
Letter |
 Liquids with permanent porosity
Liquids with permanent porosity
Porous materials find use in applications such as gas separation, drug delivery and energy storage, but have hitherto been solid rather than liquid; now a combination of cage molecules and a crown-ether solvent that cannot enter the cage molecules is used to create a porous liquid that can solubilize methane gas better than non-porous liquids.
- Nicola Giri
- , Mario G. Del Pópolo
- & Stuart L. James
-
Letter |
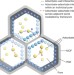 Extra adsorption and adsorbate superlattice formation in metal-organic frameworks
Extra adsorption and adsorbate superlattice formation in metal-organic frameworks
Metal-organic frameworks have a porous structure that has useful applications in gas adsorption; here, small-angle X-ray scattering is used to visualize the process of adsorption as gas pressure increases, revealing that adsorbate molecules interact across pore walls in a way that allows extra adsorbate domains to be created in the framework and to form superlattices, before the adsorbate settles down into a more uniform distribution.
- Hae Sung Cho
- , Hexiang Deng
- & Osamu Terasaki
-
Letter |
 Designing switchable polarization and magnetization at room temperature in an oxide
Designing switchable polarization and magnetization at room temperature in an oxide
Ferroelectricity and ferromagnetism are combined in a bulk perovskite oxide at room temperature by constructing a percolating network of interacting magnetic ions within a complex polar solid.
- P. Mandal
- , M. J. Pitcher
- & M. J. Rosseinsky
-
Letter |
 Computational design of co-assembling protein–DNA nanowires
Computational design of co-assembling protein–DNA nanowires
Computational protein design is used to create a protein–DNA co-assembling nanomaterial; by varying the arrangement of protein-binding sites on the double-stranded DNA, a ‘nanowire’ with single-molecule width can be spontaneously formed by mixing the protein and double-stranded DNA building blocks.
- Yun Mou
- , Jiun-Yann Yu
- & Stephen L. Mayo
-
Letter |
 Beating the Stoner criterion using molecular interfaces
Beating the Stoner criterion using molecular interfaces
By harnessing the charge transfer that takes place at the interface between a metal and a layer of molecules, the usually non-magnetic materials copper and manganese are made magnetic at room temperature.
- Fatma Al Ma’Mari
- , Timothy Moorsom
- & Oscar Cespedes
-
Letter |
 Flexible high-temperature dielectric materials from polymer nanocomposites
Flexible high-temperature dielectric materials from polymer nanocomposites
The addition of boron nitride nanosheets to polymer nanocomposites creates dielectric materials that operate at much higher working temperatures than previous polymer dielectrics, as well as being flexible, lightweight, photopatternable, scalable and robust, which now makes them more attractive for electronic device applications than ceramic dielectrics.
- Qi Li
- , Lei Chen
- & Qing Wang
-
Letter |
 DNA rendering of polyhedral meshes at the nanoscale
DNA rendering of polyhedral meshes at the nanoscale
A general method of folding arbitrary polygonal digital meshes in DNA uses a routeing algorithm based on graph theory and a relaxation simulation that traces scaffold strands through the target structures to produce complex structures with an open conformation that are stable under biological assay conditions.
- Erik Benson
- , Abdulmelik Mohammed
- & Björn Högberg
-
Letter |
 A zeolite family with expanding structural complexity and embedded isoreticular structures
A zeolite family with expanding structural complexity and embedded isoreticular structures
The complex structure of zeolite ZSM-25 is determined and a family of related structures are identified by using electron diffraction to uncover the structural ‘coding’ within them; this enabled the synthesis of two more-complex zeolites in the family.
- Peng Guo
- , Jiho Shin
- & Xiaodong Zou
-
Review Article |
 The crystallography of correlated disorder
The crystallography of correlated disorder
Although classical crystallography is insufficient to determine disordered structure in crystals, correlated disorder does nevertheless contain clear crystallographic signatures that map to the type of disorder, which we are learning to decipher.
- David A. Keen
- & Andrew L. Goodwin
-
Article |
 Cooperative insertion of CO2 in diamine-appended metal-organic frameworks
Cooperative insertion of CO2 in diamine-appended metal-organic frameworks
A cooperative insertion mechanism for CO2 adsorption is shown to generate highly efficient adsorbents for carbon capture applications.
- Thomas M. McDonald
- , Jarad A. Mason
- & Jeffrey R. Long
-
Letter |
 Anomalous dispersions of ‘hedgehog’ particles
Anomalous dispersions of ‘hedgehog’ particles
Micrometre-sized particles covered with stiff, nanoscale spikes are shown to exhibit long-term colloidal stability in both hydrophilic and hydrophobic media, without the need for chemical coating, owing to the effect of the spikes on the contact area and, consequently, the force between the particles.
- Joong Hwan Bahng
- , Bongjun Yeom
- & Nicholas Kotov
-
Letter |
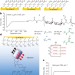 Modulation of hydrophobic interactions by proximally immobilized ions
Modulation of hydrophobic interactions by proximally immobilized ions
Chemical force microscopy measurements show that the immobilization of specific cationic groups near non-polar domains produces pronounced changes in the domains’ hydrophobic interaction strengths: charged ammonium groups double interaction strengths, whereas guanidinium groups eliminate measurable interactions.
- C. Derek Ma
- , Chenxuan Wang
- & Nicholas L. Abbott
-
Letter |
 Compositional engineering of perovskite materials for high-performance solar cells
Compositional engineering of perovskite materials for high-performance solar cells
Inorganic–organic lead halide perovskite could be efficient when used as the light-harvesting component of solar cells; here incorporation of methylammonium lead bromide into formamidinium lead iodide stabilizes the perovskite and improves the power conversion efficiency of the solar cell up to 17.9 per cent.
- Nam Joong Jeon
- , Jun Hong Noh
- & Sang Il Seok
-
Letter |
 An anisotropic hydrogel with electrostatic repulsion between cofacially aligned nanosheets
An anisotropic hydrogel with electrostatic repulsion between cofacially aligned nanosheets
Usually materials design focuses on attractive interactions, but here a hydrogel is described whose properties are dominated by electrostatic repulsion between negatively charged titanate nanosheets embedded within it; the material, inspired by articular cartilage, deforms easily when sheared parallel to the sheets but resists compressive forces applied orthogonally.
- Mingjie Liu
- , Yasuhiro Ishida
- & Takuzo Aida
-
Letter |
 Formation and properties of ice XVI obtained by emptying a type sII clathrate hydrate
Formation and properties of ice XVI obtained by emptying a type sII clathrate hydrate
Gas hydrates are ice-like solids that have guest species encaged within a crystalline water framework, making the empty hydrate a natural — though long assumed to be inaccessible — point of reference; it is now shown that several days of continuous vacuum pumping removes all guests from neon hydrate, and the physical properties of the empty hydrate have been determined.
- Andrzej Falenty
- , Thomas C. Hansen
- & Werner F. Kuhs
-
Letter |
 Vibrational spectroscopy in the electron microscope
Vibrational spectroscopy in the electron microscope
Recent advances in electron microscopy are shown to allow vibrational spectroscopy at high spatial resolution in a scanning transmission electron microscope, and also to enable the direct detection of hydrogen.
- Ondrej L. Krivanek
- , Tracy C. Lovejoy
- & Peter A. Crozier
-
Letter |
 Large, non-saturating magnetoresistance in WTe2
Large, non-saturating magnetoresistance in WTe2
The magnetoresistance effect in WTe2, a layered semimetal, is extremely large: the electrical resistance can be changed by more than 13 million per cent at very high magnetic fields and low temperatures.
- Mazhar N. Ali
- , Jun Xiong
- & R. J. Cava

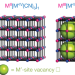 Hidden diversity of vacancy networks in Prussian blue analogues
Hidden diversity of vacancy networks in Prussian blue analogues