Featured
-
-
Article |
 Combinatorial flexibility of cytokine function during human T helper cell differentiation
Combinatorial flexibility of cytokine function during human T helper cell differentiation
Type I interferons (IFNs) have pleiotropic functions in the immune system. Here, the authors evaluate transcriptional signatures generated by type I IFN under distinct T helper cell differentiation programmes and show that, depending on the cytokine context, IFN-α differentially modulates the global cytokine profile of each T helper subset.
- Maxime Touzot
- , Maximilien Grandclaudon
- & Vassili Soumelis
-
Article |
 Parallel T-cell cloning and deep sequencing of human MAIT cells reveal stable oligoclonal TCRβ repertoire
Parallel T-cell cloning and deep sequencing of human MAIT cells reveal stable oligoclonal TCRβ repertoire
Mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells are a subset of innate-like T cells, abundant in mucosal tissues, blood and liver. Here, using T-cell cloning and deep sequencing, Lepore et al. analyse the T-cell receptorβ repertoire of MAIT cells and further characterize function and tissue distribution of two semi-invariant subsets of these cells.
- Marco Lepore
- , Artem Kalinichenko
- & Lucia Mori
-
Article |
 IL-21 induces IL-22 production in CD4+ T cells
IL-21 induces IL-22 production in CD4+ T cells
The cytokine interleukin-22 maintains the integrity of the colonic epithelium during inflammation. Here, the authors show that IL-21 regulates the production of IL-22 in T cells and this mechanism plays a protective role in a mouse model of colitis.
- Ada Yeste
- , Ivan D. Mascanfroni
- & Francisco J Quintana
-
Article |
 Nucleic acid sensing by T cells initiates Th2 cell differentiation
Nucleic acid sensing by T cells initiates Th2 cell differentiation
Nucleic acids modulate T cell responses; however, the physiological significance of this property remains unclear. Here, the authors show that self-DNA complexes with antimicrobial peptides or histones, which mediates T cell costimulation to induce Th2 cell differentiation.
- Takayuki Imanishi
- , Chitose Ishihara
- & Takashi Saito
-
Article
| Open Access The Menin–Bach2 axis is critical for regulating CD4 T-cell senescence and cytokine homeostasis
The Menin–Bach2 axis is critical for regulating CD4 T-cell senescence and cytokine homeostasis
Immunosenescence particularly affects the T-cell compartment and is involved in the age-related decline of immune functions. Here, the authors show that the absence of the tumour suppressor Menin results in premature senescence of CD4 T cells.
- Makoto Kuwahara
- , Junpei Suzuki
- & Masakatsu Yamashita
-
Article
| Open Access Epigenetic plasticity of Cd8a locus during CD8+ T-cell development and effector differentiation and reprogramming
Epigenetic plasticity of Cd8a locus during CD8+ T-cell development and effector differentiation and reprogramming
CD8 expression levels on peripheral CD8+ T cells are regulated during development and effector differentiation. Here, the authors show that methylation patterns at the Cd8a locus, whose product is essential for surface CD8 expression, can change during T-cell development, activation, cytokine polarization and reprogramming.
- Kim L. Harland
- , E. Bridie Day
- & Anne Kelso
-
Article |
 FoxP3+ regulatory T cells promote influenza-specific Tfh responses by controlling IL-2 availability
FoxP3+ regulatory T cells promote influenza-specific Tfh responses by controlling IL-2 availability
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) are mainly known to suppress effector T cell and B-cell responses. Here, the authors demonstrate that Tregs are able to promote T follicular helper and germinal centre B-cell responses to influenza by sequestering IL-2, the negative regulator of T follicular helper cell differentiation.
- Beatriz León
- , John E. Bradley
- & André Ballesteros-Tato
-
Article
| Open Access Self-recognition of the endothelium enables regulatory T-cell trafficking and defines the kinetics of immune regulation
Self-recognition of the endothelium enables regulatory T-cell trafficking and defines the kinetics of immune regulation
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) are important for the maintenance of self-tolerance and this requires their trafficking to the lymph nodes and target tissues. Here, the authors show that the recognition of self-antigens expressed by endothelial cells in target tissue is instrumental for efficient Treg recruitment in vivo.
- Hongmei Fu
- , Madhav Kishore
- & Federica M. Marelli-Berg
-
Article
| Open Access MHC-dependent inhibition of uterine NK cells impedes fetal growth and decidual vascular remodelling
MHC-dependent inhibition of uterine NK cells impedes fetal growth and decidual vascular remodelling
NK cells are involved in remodelling of the uterine vasculature during pregnancy and the extent of this process is influenced by the combination of maternal NK cell receptors and MHC-I of the fetus. Here, the authors provide further insights into how the presence of MHC-I from each parent differentially affects NK cell function.
- Jens Kieckbusch
- , Louise M. Gaynor
- & Francesco Colucci
-
Article |
 TNF-α blockade induces IL-10 expression in human CD4+ T cells
TNF-α blockade induces IL-10 expression in human CD4+ T cells
Th17 cells are involved in the pathogenesis of several inflammatory diseases. Here, the authors show that inhibitors of the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF, used in patients undergoing anti-inflammatory treatment, might mediate the acquisition of anti-inflammatory properties by these typically pathogenic cells.
- Hayley G. Evans
- , Urmas Roostalu
- & Leonie S. Taams
-
Article
| Open Access Acquisition of innate-like microbial reactivity in mucosal tissues during human fetal MAIT-cell development
Acquisition of innate-like microbial reactivity in mucosal tissues during human fetal MAIT-cell development
Mucosa-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells are a recently described subset of unconventional, innate-like T cells and their development is not well understood. Here, the authors analyse MAIT cells in fetal human tissues and show that, unlike in mice, the commensal microflora is not necessary for their maturation in humans.
- Edwin Leeansyah
- , Liyen Loh
- & Johan K. Sandberg
-
Article |
 PTPN2 attenuates T-cell lymphopenia-induced proliferation
PTPN2 attenuates T-cell lymphopenia-induced proliferation
Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the gene encoding the protein phosphatase PTPN2 are associated with autoimmunity in humans. Here, Wiede et al. show that PTPN2 suppresses the proliferative capacity of T cells in lymphopenia and prevents the development of autoimmunity resulting from overt homoeostatic proliferation.
- Florian Wiede
- , Nicole L. La Gruta
- & Tony Tiganis
-
Article |
 Transcription factor IRF4 drives dendritic cells to promote Th2 differentiation
Transcription factor IRF4 drives dendritic cells to promote Th2 differentiation
Asthma is often characterized by Th2-mediated inflammatory responses, which are initiated by lung dendritic cells. Here, Williams et al.demonstrate that dendritic cell expression of transcription factor IRF4 drives Th2 differentiation through IL-33 and IL-10 activation.
- Jesse W. Williams
- , Melissa Y. Tjota
- & Anne I. Sperling
-
Article |
 Transdifferentiation of parathyroid cells into cervical thymi promotes atypical T-cell development
Transdifferentiation of parathyroid cells into cervical thymi promotes atypical T-cell development
Cervical thymi are secondary sites of T-cell development in mice. Here, the authors investigate previously unknown origin of cervical thymi and show that they develop as a by-product of the normal separation of thymic and parathyroid tissue.
- Jie Li
- , Zhijie Liu
- & Nancy R. Manley
-
Article |
 A genome-wide regulatory network identifies key transcription factors for memory CD8+ T-cell development
A genome-wide regulatory network identifies key transcription factors for memory CD8+ T-cell development
The establishment of a memory phenotype in T cells requires profound changes in their transcriptional profile, but many components of this profile are still not known. Here, the authors perform a systematic study to identify key transcription factors associated with memory CD8+T-cell development.
- Guangan Hu
- & Jianzhu Chen
-
Article |
 Skin thymic stromal lymphopoietin initiates Th2 responses through an orchestrated immune cascade
Skin thymic stromal lymphopoietin initiates Th2 responses through an orchestrated immune cascade
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin is an important initiator of Th2 responses, but, to date, little is known about how it drives the immune cascade in the tissue microenvironment in vivo. Here, the authors show that skin thymic stromal lymphopoietin orchestrate interactions between immune cells, leading to Th2 priming.
- Juan Manuel Leyva-Castillo
- , Pierre Hener
- & Mei Li
-
Article
| Open Access Protective CD8+ T-cell immunity to human malaria induced by chimpanzee adenovirus-MVA immunisation
Protective CD8+ T-cell immunity to human malaria induced by chimpanzee adenovirus-MVA immunisation
Induction of protective immunity mediated by CD8+ T cells has been a long sought goal in vaccinology. Here, Ewer et al. report induction of protective efficacy against Plasmodium falciparummalaria in a phase IIa prime-boost vaccine trial where efficacy correlates strongly with induced CD8 T-cell responses.
- Katie J. Ewer
- , Geraldine A. O’Hara
- & Adrian V. S. Hill
-
Article |
 Thymic epithelial cell expansion through matricellular protein CYR61 boosts progenitor homing and T-cell output
Thymic epithelial cell expansion through matricellular protein CYR61 boosts progenitor homing and T-cell output
Thymic epithelial cells provide the microenvironment required for the expansion of T cells in the thymus, but their exact function is not well understood. Here, the authors report that thymic epithelial cells are the source of matricellular protein CYR61, which is involved in thymic function and T cell development.
- Yalin Emre
- , Magali Irla
- & Beat A. Imhof
-
Article |
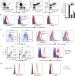 Integrin CD11b negatively regulates BCR signalling to maintain autoreactive B cell tolerance
Integrin CD11b negatively regulates BCR signalling to maintain autoreactive B cell tolerance
Polymorphisms in the integrin gene CD11bare associated with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus, but how this relates to the function of this integrin has not been fully investigated. Here, the authors report that CD11b has a role in the intrinsic maintenance of autoreactive B cell tolerance by regulating BCR signalling.
- Chuanlin Ding
- , Yunfeng Ma
- & Jun Yan
-
Article |
 Acute emergence and reversion of influenza A virus quasispecies within CD8+ T cell antigenic peptides
Acute emergence and reversion of influenza A virus quasispecies within CD8+ T cell antigenic peptides
Cytotoxic CD8+ T cells provide one level of protection against influenza infection. Here, the authors present evidence, in mice and humans, for the emergence and reversion of influenza A virus escape mutants associated with the immune pressure from cytotoxic CD8+ T lymphocytes.
- Sophie A. Valkenburg
- , Sergio Quiñones-Parra
- & Katherine Kedzierska
-
Article
| Open Access Quantal and graded stimulation of B lymphocytes as alternative strategies for regulating adaptive immune responses
Quantal and graded stimulation of B lymphocytes as alternative strategies for regulating adaptive immune responses
B lymphocytes respond to stimulation by proliferating and differentiating. Here the authors quantify and model the responses of B lymphocytes to TLR and CD40-dependent stimulation, and find that the latter induces a more complex response to signals of varying strength.
- E.D. Hawkins
- , M.L. Turner
- & P.D. Hodgkin
-
Article
| Open Access IMGT/HighV QUEST paradigm for T cell receptor IMGT clonotype diversity and next generation repertoire immunoprofiling
IMGT/HighV QUEST paradigm for T cell receptor IMGT clonotype diversity and next generation repertoire immunoprofiling
Dynamic changes in T cell repertoire underlie immune responses during infection, allergy, autoimmunity and cancer. Here, Li et al. present a workflow for high throughput sequencing and analysis of T cell receptor sequences, and use it to monitor the T cell response to influenza vaccination in a human patient.
- Shuo Li
- , Marie-Paule Lefranc
- & Eric J. Gowans
-
Article |
 Highly self-reactive naive CD4 T cells are prone to differentiate into regulatory T cells
Highly self-reactive naive CD4 T cells are prone to differentiate into regulatory T cells
The differentiation of naive CD4 T cells into T-helper-cell subsets is thought to be influenced by factors in the T-cell environment. Martin et al.reveal that cell intrinsic differences also determine lineage commitment and show that cells with the highest avidity for self are most likely to become induced regulatory T cells.
- Bruno Martin
- , Cédric Auffray
- & Bruno Lucas
-
Article |
 Recognition of vitamin B metabolites by mucosal-associated invariant T cells
Recognition of vitamin B metabolites by mucosal-associated invariant T cells
T-cell receptors expressed on mucosal-associated invariant T cells function in a similar manner to innate immune receptors by recognizing small molecules such as microbial metabolites. Here, the authors report structures of this receptor in complex with vitamin B metabolites presented by the MHC-like protein MR1.
- Onisha Patel
- , Lars Kjer-Nielsen
- & Jamie Rossjohn
-
Article |
 The ARNT–STAT3 axis regulates the differentiation of intestinal intraepithelial TCRαβ+CD8αα+ cells
The ARNT–STAT3 axis regulates the differentiation of intestinal intraepithelial TCRαβ+CD8αα+ cells
Intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) defend against pathogens in the gut, and their differentiation depends on both diet and microbiota-derived factors. Nakajima et al. show that signalling through the aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator and STAT3 is required for the development of a subset of IELs.
- Kohei Nakajima
- , Yoichi Maekawa
- & Koji Yasutomo
-
Article |
 B7-H5 costimulates human T cells via CD28H
B7-H5 costimulates human T cells via CD28H
The end-result of stimulation of T-cell receptors by antigen is in part determined by co-signalling pathways such as the B7/CD28 axis. Zhu et al.identify a novel costimulatory CD28-like receptor and ligand pathway in human T cells.
- Yuwen Zhu
- , Sheng Yao
- & Lieping Chen
-
Article |
 The basis for limited specificity and MHC restriction in a T cell receptor interface
The basis for limited specificity and MHC restriction in a T cell receptor interface
Although structural insights into antigen recognition by T cell receptors are increasingly available, the thermodynamic underpinnings are less well understood. Here the authors deconstruct the energetics of a representative interface and discover that peptide specificity, cross-reactivity and MHC restriction can be inextricably linked.
- Kurt H. Piepenbrink
- , Sydney J. Blevins
- & Brian M. Baker
-
Article |
 Sam68 modulates the promoter specificity of NF-κB and mediates expression of CD25 in activated T cells
Sam68 modulates the promoter specificity of NF-κB and mediates expression of CD25 in activated T cells
The NF-κB complex is a core regulator of inflammatory gene expression and activates transcription of many different target genes. Fu et al. show that NF-κB promoter specificity can be tuned by Sam68, which is required for targeting NF-κB to the CD25 promoter during T cell activation.
- Kai Fu
- , Xin Sun
- & Fengyi Wan
-
Article
| Open Access Microbe-dependent CD11b+ IgA+ plasma cells mediate robust early-phase intestinal IgA responses in mice
Microbe-dependent CD11b+ IgA+ plasma cells mediate robust early-phase intestinal IgA responses in mice
Intestinal plasma cells contribute to the delicate balance between immunity against pathogens and tolerance of intestinal microflora. Kunisawa et al. identify a subpopulation of plasma cells whose proliferation depends on stimulation by microbes and IL-10, and which mediate early-phase responses to oral antigens.
- Jun Kunisawa
- , Masashi Gohda
- & Hiroshi Kiyono
-
Article
| Open Access Basophils are required for the induction of Th2 immunity to haptens and peptide antigens
Basophils are required for the induction of Th2 immunity to haptens and peptide antigens
Both dendritic cells and basophils have been shown to influence T helper 2 cell induction, however the relative importance of their roles remains unclear. Otsuka et al. find that basophils present hapten and peptide antigens to T cells, but are unable to present protein antigens in the absence of dendritic cells.
- Atsushi Otsuka
- , Saeko Nakajima
- & Kenji Kabashima
-
Article
| Open Access Mutually exclusive regulation of T cell survival by IL-7R and antigen receptor-induced signals
Mutually exclusive regulation of T cell survival by IL-7R and antigen receptor-induced signals
Before antigen exposure, T cell survival is dependent on signalling stimulated by IL-7. Koenen et al. show that upon encountering specific antigen, T cell receptor signalling initiates a different set of survival pathways, which actively suppress those that sustain naive T cells.
- Paul Koenen
- , Susanne Heinzel
- & Philip D. Hodgkin
-
Article
| Open Access Prostaglandin E2 promotes Th1 differentiation via synergistic amplification of IL-12 signalling by cAMP and PI3-kinase
Prostaglandin E2 promotes Th1 differentiation via synergistic amplification of IL-12 signalling by cAMP and PI3-kinase
Activation of cAMP signalling by prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) has long been thought to suppress Tcell receptor activation and Th1 cell differentiation. Yao et al. reveal that dual stimulation of both cAMP and PI 3-kinase pathways by PGE2 synergistically promotes Th1 differentiation by amplifying IL-12 and IFN-γsignalling.
- Chengcan Yao
- , Takako Hirata
- & Shuh Narumiya
-
Article
| Open Access The transcriptional repressor NKAP is required for the development of iNKT cells
The transcriptional repressor NKAP is required for the development of iNKT cells
The transcriptional repressor NKAP is required at an early stage of T cell development for the differentiation of αβ T cells. Thapa et al.now show that at a later stage, NKAP has a specific role in positive selection of double positive thymocytes into the iNKT cell lineage.
- Puspa Thapa
- , Joy Das
- & Virginia Smith Shapiro
-
Article
| Open Access IGF-1 promotes the development and cytotoxic activity of human NK cells
IGF-1 promotes the development and cytotoxic activity of human NK cells
Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1 regulates many physiological functions including growth and metabolism. Ni et al.show that human natural killer cells secrete IGF-1 and that IGF-1 enhances the development and cytotoxicity of these cells.
- Fang Ni
- , Rui Sun
- & Haiming Wei
-
Article |
 Synaptobrevin2 is the v-SNARE required for cytotoxic T-lymphocyte lytic granule fusion
Synaptobrevin2 is the v-SNARE required for cytotoxic T-lymphocyte lytic granule fusion
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes kill target cells through the fusion of lytic granules at the immunological synapse. Using high-resolution microscopy techniques Matti et al.identify synaptobrevin2 as the vesicular SNARE protein required for this fusion reaction.
- Ulf Matti
- , Varsha Pattu
- & Jens Rettig
-
Article |
 Germinal centre protein HGAL promotes lymphoid hyperplasia and amyloidosis via BCR-mediated Syk activation
Germinal centre protein HGAL promotes lymphoid hyperplasia and amyloidosis via BCR-mediated Syk activation
The human germinal centre-associated lymphoma gene is expressed in germinal centre B-lymphocytes; however, its function is unknown. Here the authors show that human germinal centre-associated lymphoma activates Syk kinase, leading to lymphoid hyperplasia and systemic reactive amyloid A amyloidosis in transgenic mice.
- Isabel Romero-Camarero
- , Xiaoyu Jiang
- & Izidore S Lossos
-
Article
| Open Access T-bet and GATA3 orchestrate Th1 and Th2 differentiation through lineage-specific targeting of distal regulatory elements
T-bet and GATA3 orchestrate Th1 and Th2 differentiation through lineage-specific targeting of distal regulatory elements
T-bet and GATA3 regulate differentiation of T cells into Th1 or Th2 cell fates, but little is known about their functional interaction outside of the IFNγ and Il4 /Il5/Il13 loci. Kanhere et al. map these factors across the genome in human T cells, revealing unappreciated breadth of function and interplay between them.
- Aditi Kanhere
- , Arnulf Hertweck
- & Richard G. Jenner
-
Article |
 Identification and characterization of polyclonal αβ-T cells with dendritic cell properties
Identification and characterization of polyclonal αβ-T cells with dendritic cell properties
The division of the immune system into innate and adaptive arms has become blurred in recent years. Kuka et al.identify a novel population of αβ-T-cell receptor-expressing cells in mice and humans that both presents and responds to antigen and produces interleukin-12, thus exhibiting core properties of both dendritic cells and T cells.
- Mirela Kuka
- , Ivana Munitic
- & Jonathan D. Ashwell
-
Article
| Open Access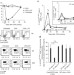 FoxP3+ regulatory CD4 T cells control the generation of functional CD8 memory
FoxP3+ regulatory CD4 T cells control the generation of functional CD8 memory
The role of CD4+ T cells in the generation of memory CD8+ T cells is not fully understood. In this study, the exposure of CD8 memory precursors to interleukin-2 during early antigen priming is shown to be controlled by FoxP3+ regulatory CD4+T cells, resulting in the production of functional memory cells.
- M.G. de Goër de Herve
- , S. Jaafoura
- & Y. Taoufik
-
Article |
 The CD4+ T-cell help signal is transmitted from APC to CD8+ T-cells via CD27–CD70 interactions
The CD4+ T-cell help signal is transmitted from APC to CD8+ T-cells via CD27–CD70 interactions
CD8+ memory cytotoxic T lymphocytes need help from CD4+ T cells to undergo secondary expansion but the mechanisms of help are not fully understood. Here, it is shown that, after activation by CD4+ T cells, antigen-presenting cells activate CD8+T cells via the CD70/CD27 co-stimulatory pathway.
- Sonia Feau
- , Zacarias Garcia
- & Stephen P. Schoenberger
-
Article |
 Host factors dictate control of viral replication in two HIV-1 controller/chronic progressor transmission pairs
Host factors dictate control of viral replication in two HIV-1 controller/chronic progressor transmission pairs
Human immunodeficiency virus patients who maintain low levels of virus or have undetectable levels of virus exist. In this study, the HIV found in two of these patients is shown to replicatein vitro, suggesting that host factors have a role in suppressing virus levels.
- Robert W. Buckheit III
- , Tracy G. Allen
- & Joel N. Blankson
-
Article
| Open Access Modification of the carboxy-terminal flanking region of a universal influenza epitope alters CD4+ T-cell repertoire selection
Modification of the carboxy-terminal flanking region of a universal influenza epitope alters CD4+ T-cell repertoire selection
Epitopes presented by MHC-II molecules bind to T-cell receptors to activate CD4+ T cells. In this study, changes in the carboxy-terminal region of the influenza hemagglutinin epitope HA305-320alters the strength of binding to the T-cell receptor, thus modulating T-cell receptor usage and activation.
- David K. Cole
- , Kathleen Gallagher
- & Andrew Godkin
-
Article |
 CD91-dependent programming of T-helper cell responses following heat shock protein immunization
CD91-dependent programming of T-helper cell responses following heat shock protein immunization
Heat shock proteins bind to CD91 on antigen presenting cells, resulting in the presentation of chaperoned peptides to T cells. Here, heat shock protein binding is shown to induce phosphorylation of CD91 and stimulate the production of cytokines, thus priming various T-helper cell responses.
- Sudesh Pawaria
- & Robert J. Binder
-
Article |
 In-vitro derived germinal centre B cells differentially generate memory B or plasma cells in vivo
In-vitro derived germinal centre B cells differentially generate memory B or plasma cells in vivo
In response to antigens, B cells proliferate and form germinal centres before differentiating into memory B cells or long-lived plasma cells. Here, a culture method is used to expand B cells in vitro, with the ability to shift the fate of the cells between memory B cells and long-lived plasma cells.
- Takuya Nojima
- , Kei Haniuda
- & Daisuke Kitamura
-
Article
| Open Access Transcription factor IRF8 directs a silencing programme for TH17 cell differentiation
Transcription factor IRF8 directs a silencing programme for TH17 cell differentiation
The molecular mechanisms that regulate TH17 cell diversity are poorly understood. Ouyang et al. show that the transcription factor interferon regulatory factor-8 is required for TH17-cell differentiation and that its absence increases the severity of an experimental model of colitis.
- Xinshou Ouyang
- , Ruihua Zhang
- & Huabao Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access The nuclear orphan receptor Nr4a2 induces Foxp3 and regulates differentiation of CD4+ T cells
The nuclear orphan receptor Nr4a2 induces Foxp3 and regulates differentiation of CD4+ T cells
Regulatory T cells are characterized by the expression of Foxp3, however, how the expression of this protein is controlled is unclear. Here, the authors show that the nuclear orphan receptor, Nr4a2, is a transcriptional activator of Foxp3, and suggest that it is required for the function of regulatory T cells.
- Takashi Sekiya
- , Ikkou Kashiwagi
- & Akihiko Yoshimura
-
Article
| Open Access Inflammation driven by tumour-specific Th1 cells protects against B-cell cancer
Inflammation driven by tumour-specific Th1 cells protects against B-cell cancer
Inflammation can result in the formation of tumours, but the immune system is also involved in the elimination of cancer cells. Here, the authors show that inflammation driven by tumour-specific CD4+T cells results in tumour regression and identify a list of cytokines associated with cancer prevention.
- Ole Audun Werner Haabeth
- , Kristina Berg Lorvik
- & Alexandre Corthay
-
Article |
 The structure of superantigen complexed with TCR and MHC reveals novel insights into superantigenic T cell activation
The structure of superantigen complexed with TCR and MHC reveals novel insights into superantigenic T cell activation
Superantigens are bacterial toxins that interact with host immunoreceptors. Salineet al.report the X-ray structure of staphylococcal enterotoxin H in complex with its human receptors, MHC class II and the T-cell receptor, providing new insights into superantigenic T-cell activation.
- Maria Saline
- , Karin E. J. Rödström
- & Karin Lindkvist-Petersson
-
Article
| Open Access B-cell depletion reveals a role for antibodies in the control of chronic HIV-1 infection
B-cell depletion reveals a role for antibodies in the control of chronic HIV-1 infection
HIV infection can be partially regulated by the host immune system; however whether B cells contribute to this response is unclear. Huanget al. show that transient depletion of B cells can result in an increase in HIV viral load suggesting that these immune cells do participate in the control of HIV infection.
- Kuan-Hsiang G. Huang
- , David Bonsall
- & Paul Klenerman

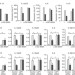 Fucose-specific DC-SIGN signalling directs T helper cell type-2 responses via IKKε- and CYLD-dependent Bcl3 activation
Fucose-specific DC-SIGN signalling directs T helper cell type-2 responses via IKKε- and CYLD-dependent Bcl3 activation