Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Resolving the controls of water vapour isotopes in the Atlantic sector
Resolving the controls of water vapour isotopes in the Atlantic sector
Water isotope modelling is an important tool in climate reconstructions, but there remain gaps in our understanding of the effects upon oxygen and hydrogen isotope fractionation, and thus the source of the deposited signal. Here, the authors present a dataset assembled over two years that shows deuterium excess is controlled by humidity and sea surface temperature, and oxygen and hydrogen isotopes as well as deuterium excess are controlled by sublimation of snow in sea-ice regions.
- Jean-Louis Bonne
- , Melanie Behrens
- & Martin Werner
-
Article
| Open Access Benchmark decadal forecast skill for terrestrial water storage estimated by an elasticity framework
Benchmark decadal forecast skill for terrestrial water storage estimated by an elasticity framework
A reliable decadal hydrological prediction is challenging but critical to managing water resources. Here the authors incorporate decadal climate prediction information with an elasticity framework over global river basins, and obtain a new benchmark skill that is significantly higher than before.
- Enda Zhu
- , Xing Yuan
- & Andrew W. Wood
-
Article
| Open Access Forecasting dryland vegetation condition months in advance through satellite data assimilation
Forecasting dryland vegetation condition months in advance through satellite data assimilation
Forecasting drought and its impact on agriculture and ecosystems is challenged by a lack of knowledge of vegetation access to deep moisture. Here the authors show that combining vegetation and water storage remote sensing can be used to infer this knowledge, allowing drought impact forecasts months in advance.
- Siyuan Tian
- , Albert I. J. M. Van Dijk
- & Luigi J. Renzullo
-
Article
| Open Access River channel connectivity shifts metabolite composition and dissolved organic matter chemistry
River channel connectivity shifts metabolite composition and dissolved organic matter chemistry
The underlying mechanisms structuring dissolved organic matter (DOM) composition and reactivity in rivers remain poorly quantified. Here, the authors pair mass spectrometry and fluorescence spectroscopy to show that hydrology and river geomorphology both shape molecular patterns in DOM composition.
- Laurel M. Lynch
- , Nicholas A. Sutfin
- & Matthew D. Wallenstein
-
Article
| Open Access Ocean temperature impact on ice shelf extent in the eastern Antarctic Peninsula
Ocean temperature impact on ice shelf extent in the eastern Antarctic Peninsula
Ocean warming contributes to the thinning of the Antarctic ice shelves, however, lack of observations has prevented a quantification of this contribution. Here the authors use geological records to show that 0.3–1.5 °C ocean warming has played a central role on regional ice shelf instability over the last 9000 years.
- Johan Etourneau
- , Giovanni Sgubin
- & Jung-Hyun Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Large increase in global storm runoff extremes driven by climate and anthropogenic changes
Large increase in global storm runoff extremes driven by climate and anthropogenic changes
Storm runoff extremes dominate flash flood formation and generation, posing a grand threat to ecosystems and communities across the world. Here the authors show that current projected response of these storm runoff extremes to climate and anthropogenic changes are underestimated.
- Jiabo Yin
- , Pierre Gentine
- & Shenglian Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Influence of Tibetan Plateau snow cover on East Asian atmospheric circulation at medium-range time scales
Influence of Tibetan Plateau snow cover on East Asian atmospheric circulation at medium-range time scales
The atmospheric response to subseasonal variability of Tibetan Plateau snow cover has been largely ignored. Here the authors show that the fast subseasonal variability of Tibetan Plateau snow cover is closely related to the subsequent East Asian atmospheric circulation at medium-range time scales.
- Wenkai Li
- , Weidong Guo
- & Jiangfeng Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Seasonal modulation of deep slow-slip and earthquakes on the Main Himalayan Thrust
Seasonal modulation of deep slow-slip and earthquakes on the Main Himalayan Thrust
The interaction between seasonally-induced non-tectonic and tectonic deformation along the Himalayan plate boundary is still debated. Here, the authors propose that seasonal hydrological loading can influence tectonic deformation along this plate boundary using continuous GPS measurements and satellite data.
- Dibyashakti Panda
- , Bhaskar Kundu
- & Amit Kumar Bansal
-
Article
| Open Access Physics-based forecasting of man-made earthquake hazards in Oklahoma and Kansas
Physics-based forecasting of man-made earthquake hazards in Oklahoma and Kansas
Reinjection of saltwater, co-produced with oil, has the potential to trigger damaging earthquakes. Here, using Oklahoma and Kansas as an example, the authors present a new physics-based methodology to forecast future probabilities of potentially damaging induced-earthquakes in space and time.
- Cornelius Langenbruch
- , Matthew Weingarten
- & Mark D. Zoback
-
Article
| Open Access The shape of watersheds
The shape of watersheds
River networks worldwide follow the emblematic Hack’s Law, which expresses the length of a stream as a function of its watershed area. Here the authors show this law does not depend on lithology or rainfall, but on the shape of watersheds and confirms the self-similarity of river networks.
- Timothée Sassolas-Serrayet
- , Rodolphe Cattin
- & Matthieu Ferry
-
Article
| Open Access Abrupt drainage basin reorganization following a Pleistocene river capture
Abrupt drainage basin reorganization following a Pleistocene river capture
River capture acts as one river steals the neighboring headwaters, which is a dramatic natural process for mountain landscapes evolution. Here the authors show a stream piracy reversed flow in a major river resulting in waterfall formation, bedrock gorge incision, and widespread topographic disequilibrium.
- Niannian Fan
- , Zhongxin Chu
- & Xingnian Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Drought reduces blue-water fluxes more strongly than green-water fluxes in Europe
Drought reduces blue-water fluxes more strongly than green-water fluxes in Europe
The partitioning of drought-induced water deficits into blue-water runoff and green-water evapotranspiration is critical, as the respective anomalies threaten different societal sectors. Here the authors show that drought reduces runoff much faster and stronger than it reduces evapotranspiration across European climates.
- René Orth
- & Georgia Destouni
-
Article
| Open Access Reduced exposure to extreme precipitation from 0.5 °C less warming in global land monsoon regions
Reduced exposure to extreme precipitation from 0.5 °C less warming in global land monsoon regions
The populous global land monsoon region has been suffering from extreme precipitation. Here, the authors show that limiting global warming to 1.5 °C instead of 2 °C could reduce areal and population exposures to baseline once-in-20-year rainfall extremes by 25% (18–41%) and 36% (22–46%), respectively.
- Wenxia Zhang
- , Tianjun Zhou
- & Xiaolong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access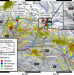 Persistent CO2 emissions and hydrothermal unrest following the 2015 earthquake in Nepal
Persistent CO2 emissions and hydrothermal unrest following the 2015 earthquake in Nepal
Earthquakes rarely affect hydrothermal systems in non-magmatic context. Here the authors report outbursts of CO2 and hydrothermal disturbances triggered by the 2015 Nepal earthquake, revealing high sensitivity of Himalayan hydrothermal systems to co-, post- and possibly pre- seismic deformation.
- Frédéric Girault
- , Lok Bijaya Adhikari
- & Frédéric Perrier
-
Article
| Open Access Thermal sensitivity of CO2 and CH4 emissions varies with streambed sediment properties
Thermal sensitivity of CO2 and CH4 emissions varies with streambed sediment properties
Rivers and streams are important sources of carbon dioxide and methane; however, the drivers of these streambed gas fluxes are poorly understood. Here, the authors show that temperature sensitivity of streambed greenhouse gas emissions varies with substrate, organic matter content and geological origin.
- Sophie A. Comer-Warner
- , Paul Romeijn
- & Stefan Krause
-
Article
| Open Access Thresholds of lake and reservoir connectivity in river networks control nitrogen removal
Thresholds of lake and reservoir connectivity in river networks control nitrogen removal
Lakes, reservoirs, and other ponded waters are common in large river basins yet their influence on nitrogen budgets is often indistinct. Here, the authors show how a ponded waters’ relative size, shape, and degree of connectivity to the river network control nitrogen removal.
- Noah M. Schmadel
- , Judson W. Harvey
- & Durelle Scott
-
-
Article
| Open Access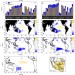 A new interhemispheric teleconnection increases predictability of winter precipitation in southwestern US
A new interhemispheric teleconnection increases predictability of winter precipitation in southwestern US
ENSO is losing predictive power of west US coast precipitation. Here the authors identify a new inter-hemispheric teleconnection that promises earlier and more accurate prediction.
- Antonios Mamalakis
- , Jin-Yi Yu
- & Efi Foufoula-Georgiou
-
Article
| Open Access Overpumping leads to California groundwater arsenic threat
Overpumping leads to California groundwater arsenic threat
Groundwater resources are coming under increasing pressure leading to water quality loss. Here, the authors find that recent groundwater pumping has led to increasing arsenic concentrations in the San Joaquin Valley, California aquifers from arsenic residing in the pore water of clay strata released by overpumping.
- Ryan Smith
- , Rosemary Knight
- & Scott Fendorf
-
-
Article
| Open Access Trends in flood losses in Europe over the past 150 years
Trends in flood losses in Europe over the past 150 years
Flooding may cause loss of life and economic damage, therefore temporal changes need assessment. Here, the authors show that since 1870 there has been an increase in area inundated by floods in Europe, but a reduction in fatalities and economic losses, although caution that smaller floods remain underreported.
- Dominik Paprotny
- , Antonia Sebastian
- & Sebastiaan N. Jonkman
-
Article
| Open Access Persistent multi-scale fluctuations shift European hydroclimate to its millennial boundaries
Persistent multi-scale fluctuations shift European hydroclimate to its millennial boundaries
In recent years, there has been an ongoing discussion about the hydroclimatic changes over Europe. Here, the authors show that since the beginning of the 20th century, hydroclimatic conditions have shifted to their millennial boundaries, remaining at these extreme levels for a period of unprecedented duration.
- Y. Markonis
- , M. Hanel
- & E. R. Cook
-
Article
| Open Access Burned forests impact water supplies
Burned forests impact water supplies
Wildland fire seasons in the United States are getting longer, yet the impacts of fire on water availability at the regional scale are unclear. Here the authors show that fire increased annual river flow throughout the West, while prescribed burns in the subtropical Southeast had limited impact on river flow.
- Dennis W. Hallema
- , Ge Sun
- & Steven G. McNulty
-
Article
| Open Access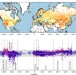 Spatial variation of the rain–snow temperature threshold across the Northern Hemisphere
Spatial variation of the rain–snow temperature threshold across the Northern Hemisphere
Land surface models often use a spatially uniform air temperature threshold when partitioning rain and snow. Here Jennings et al. show that the threshold varies significantly across the Northern Hemisphere and that threshold selection is a large source of uncertainty in snowfall simulations.
- Keith S. Jennings
- , Taylor S. Winchell
- & Noah P. Molotch
-
Article
| Open Access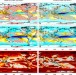 Robustness of anthropogenically forced decadal precipitation changes projected for the 21st century
Robustness of anthropogenically forced decadal precipitation changes projected for the 21st century
Decadal precipitation changes are dominated by random natural variability, posing a challenge for projecting anthropogenic impacts. Here the authors use large suites of model simulations to show that human-induced future decadal shifts in regional precipitation can be distinguished from natural variability.
- Honghai Zhang
- & Thomas L. Delworth
-
Article
| Open Access Wetter summers can intensify departures from natural variability in a warming climate
Wetter summers can intensify departures from natural variability in a warming climate
Climate change can drive local climates outside the range of their historical variability, straining the adaptive capacity of ecological communities. Here the authors show dependencies between climate variables can produce larger and earlier departures from natural variability than is detectable in individual variables.
- Colin R. Mahony
- & Alex J. Cannon
-
Article
| Open Access Similarity of stream width distributions across headwater systems
Similarity of stream width distributions across headwater systems
The morphology and abundance of streams control the rates of hydraulic and biogeochemical exchange between streams, groundwater and the atmosphere. Here, the authors show that stream hydromorphology is predictable within headwater catchments with implications for stream-atmosphere gas exchange estimates.
- George H. Allen
- , Tamlin M. Pavelsky
- & Colin J. Gleason
-
Article
| Open Access Influences of organic carbon speciation on hyporheic corridor biogeochemistry and microbial ecology
Influences of organic carbon speciation on hyporheic corridor biogeochemistry and microbial ecology
The mechanisms responsible for stimulating biogeochemical activity in the hyporheic corridor (HC) are poorly understood. Here, the authors find that previously unrecognized thermodynamic mechanisms regulated by groundwater-river water mixing may strongly influence HC biogeochemical and microbial dynamics.
- James C. Stegen
- , Tim Johnson
- & John Zachara
-
Article
| Open Access Contributions of changes in climatology and perturbation and the resulting nonlinearity to regional climate change
Contributions of changes in climatology and perturbation and the resulting nonlinearity to regional climate change
Changes in climatology and perturbation will lead to different impacts on regional climate change, but their effect remains a subject of debate. Here the authors develop a new downscaling procedure that reveals the importance of both changes on the regional climate and examines their nonlinear effect.
- Sachiho A. Adachi
- , Seiya Nishizawa
- & Hirofumi Tomita
-
Article
| Open Access Designing flows to resolve human and environmental water needs in a dam-regulated river
Designing flows to resolve human and environmental water needs in a dam-regulated river
Human and environmental water needs can come into conflict in dam-regulated river systems. Here, Chen and Olden investigate the potential for the use of fish–flow modeling to make recommendations for the management of native and nonnative fish species whilst providing water for society.
- William Chen
- & Julian D. Olden
-
Article
| Open Access Observed positive vegetation-rainfall feedbacks in the Sahel dominated by a moisture recycling mechanism
Observed positive vegetation-rainfall feedbacks in the Sahel dominated by a moisture recycling mechanism
Vegetation-rainfall feedbacks in the Sahel are thought to be positive, but the precise mechanisms for this are unclear. Here the authors analyse observations to show that a moisture recycling mechanism drives this feedback.
- Yan Yu
- , Michael Notaro
- & Yaxing Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Intensification of terrestrial carbon cycle related to El Niño–Southern Oscillation under greenhouse warming
Intensification of terrestrial carbon cycle related to El Niño–Southern Oscillation under greenhouse warming
The terrestrial carbon cycle is strongly influenced by El Niño/Southern Oscillation (ENSO), but how this relationship will change in future is not clear. Here the authors use state-of-the-art models to show that the sensitivity of the carbon cycle to ENSO will increase under future climate change.
- Jin-Soo Kim
- , Jong-Seong Kug
- & Su-Jong Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access Global patterns of nitrate storage in the vadose zone
Global patterns of nitrate storage in the vadose zone
Current global-scale nitrogen (N) budgets quantifying anthropogenic impacts on the N cycle do not explicitly consider nitrate storage in the vadose zone. Here, using estimates of depth to groundwater and nitrate leaching between 1900–2000, the authors show that the vadose zone is an important store of nitrate.
- M. J. Ascott
- , D. C. Gooddy
- & A. M. Binley
-
Article
| Open Access Clay mineral formation under oxidized conditions and implications for paleoenvironments and organic preservation on Mars
Clay mineral formation under oxidized conditions and implications for paleoenvironments and organic preservation on Mars
In the Gale Crater on Mars, organic matter has been detected, but in much lower concentrations than expected. Here, the authors conduct clay mineral synthesis experiments which suggest that clay minerals may rapidly form under oxidized conditions and thus explain the low organic concentrations in Gale Crater.
- Seth R. Gainey
- , Elisabeth M. Hausrath
- & Courtney L. Bartlett
-
Article
| Open Access Water induced sediment levitation enhances downslope transport on Mars
Water induced sediment levitation enhances downslope transport on Mars
Downslope sediment transport on Mars is reported, but the transport capacity of unstable water under low pressures is not well understood. Here, the authors present a newly discovered, highly reactive transportation mechanism that is only possible under low pressure environments.
- Jan Raack
- , Susan J. Conway
- & Manish R. Patel
-
Article
| Open Access Water conservation benefits of urban heat mitigation
Water conservation benefits of urban heat mitigation
Cool roofs have been shown to mitigate heat in urban areas, but their impact on water conservation has not been examined. Here the authors conduct simulations with an urban canopy model to show that implementation of cool roofs in California can also reduce outdoor water consumption by up to 9%.
- Pouya Vahmani
- & Andrew D. Jones
-
Article
| Open Access Volcanic suppression of Nile summer flooding triggers revolt and constrains interstate conflict in ancient Egypt
Volcanic suppression of Nile summer flooding triggers revolt and constrains interstate conflict in ancient Egypt
The degree to which human societies have responded to past climatic changes remains unclear. Here, using a novel combination of approaches, the authors show how volcanically-induced suppression of Nile summer flooding led to societal unrest in Ptolemaic Egypt (305–30 BCE).
- Joseph G. Manning
- , Francis Ludlow
- & Jennifer R. Marlon
-
Article
| Open Access Causes of model dry and warm bias over central U.S. and impact on climate projections
Causes of model dry and warm bias over central U.S. and impact on climate projections
Climate models repeatedly show a warm and dry bias over the central United States, but the origin of this bias remains unclear. Here the authors associate this bias to precipitation deficits in models and after applying a correction, projected precipitation in this region shows no significant changes.
- Yanluan Lin
- , Wenhao Dong
- & Yong Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Upstream watershed condition predicts rural children’s health across 35 developing countries
Upstream watershed condition predicts rural children’s health across 35 developing countries
Globally diarrheal disease through contaminated water sources is a major cause of child mortality. Here, the authors compile a database of 293,362 children in 35 countries and find that upstream tree cover is linked to a lower probability of diarrheal disease and that increasing tree cover may lower mortality.
- Diego Herrera
- , Alicia Ellis
- & Taylor H. Ricketts
-
Article
| Open Access A threefold rise in widespread extreme rain events over central India
A threefold rise in widespread extreme rain events over central India
Against the backdrop of a declining monsoon, the number of extreme rain events is on the rise over central India. Here the authors identify a threefold increase in widespread extreme rains over the region during 1950–2015, driven by an increasing variability of the low-level westerlies over the Arabian Sea.
- M. K. Roxy
- , Subimal Ghosh
- & M. Rajeevan
-
Article
| Open Access Potential for natural evaporation as a reliable renewable energy resource
Potential for natural evaporation as a reliable renewable energy resource
The evaporation of water represents an alternative source of renewable energy. Building on previous models of evaporation, Cavusoglu et al. show that the power available from this natural resource is comparable to wind and solar power, yet it does not suffer as much from varying weather conditions.
- Ahmet-Hamdi Cavusoglu
- , Xi Chen
- & Ozgur Sahin
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrologic resilience and Amazon productivity
Hydrologic resilience and Amazon productivity
Earth system model simulations of future climate in the Amazon show little agreement. Here, the authors show that biases in internally generated climate explain most of this uncertainty and that the balance between water-saturated and water-limited evapotranspiration controls the Amazon resilience to climate change.
- Anders Ahlström
- , Josep G. Canadell
- & Robert B. Jackson
-
Article
| Open Access Major agricultural changes required to mitigate phosphorus losses under climate change
Major agricultural changes required to mitigate phosphorus losses under climate change
The impact of climate change on phosphorus (P) loss from land to water is unclear. Here, the authors use P flux data, climate simulations and P transfer models to show that only large scale agricultural change will limit the effect of climate change on average winter P loads in three catchments across the UK.
- M. C. Ockenden
- , M. J. Hollaway
- & P. M. Haygarth
-
Article
| Open Access Recent increases in terrestrial carbon uptake at little cost to the water cycle
Recent increases in terrestrial carbon uptake at little cost to the water cycle
The response of the coupled carbon and water cycles to anthropogenic climate change is unclear. Here, the authors show that terrestrial carbon uptake increased significantly from 1982 to 2011 and that this increase is largely driven by increased water-use efficiency, rather than an increase in water use.
- Lei Cheng
- , Lu Zhang
- & Yongqiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of snow-fed rivers affects flow regimes more than climate change
Regulation of snow-fed rivers affects flow regimes more than climate change
Global warming and hydropower regulations are major threats to future fresh-water availability and biodiversity. Here, the authors show that their impact on flow regime over a large landmass result in similar changes, but hydropower is more critical locally and may have potential for climate adaptation in floodplains.
- B. Arheimer
- , C. Donnelly
- & G. Lindström
-
Article
| Open Access Water scarcity hotspots travel downstream due to human interventions in the 20th and 21st century
Water scarcity hotspots travel downstream due to human interventions in the 20th and 21st century
Water scarcity threatens a growing number of global catchments. Here, the authors examine how human interventions (HI) affected water scarcity between 1971 and 2010 and find that HI caused increases in the average duration and occurrence of water scarcity for 32% and 34% of the global population, respectively.
- T.I.E. Veldkamp
- , Y. Wada
- & P. J. Ward
-
Article
| Open Access Tightening of tropical ascent and high clouds key to precipitation change in a warmer climate
Tightening of tropical ascent and high clouds key to precipitation change in a warmer climate
The sensitivity of global precipitation to warming is largely governed by changes in atmospheric longwave radiation, a function of cloud cover. Here the authors show that tightening of the tropical circulation with warming drives a decrease in high cloud cover, resulting in higher precipitation changes.
- Hui Su
- , Jonathan H. Jiang
- & Yuk L. Yung
-
Article
| Open Access River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans
River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans
Rivers provide a major pathway for ocean plastic waste, but effective mitigation is dependent on a quantification of active sources. Here, the authors present a global model of riverine plastic inputs, and estimate annual plastic waste of almost 2.5 million tonnes, with 86% sourced from Asia.
- Laurent C. M. Lebreton
- , Joost van der Zwet
- & Julia Reisser
-
Article
| Open Access New Martian valley network volume estimate consistent with ancient ocean and warm and wet climate
New Martian valley network volume estimate consistent with ancient ocean and warm and wet climate
To understand the early Martian climate, the volume of the global Martian valley network is required. Here, the authors use a black top hat transformation method and find that the minimum global valley network volume is 1.74 × 1,014 m3 with a minimum cumulative volume of water required of 6.86 × 1,017 m3.
- Wei Luo
- , Xuezhi Cang
- & Alan D. Howard

 Enhanced future changes in wet and dry extremes over Africa at convection-permitting scale
Enhanced future changes in wet and dry extremes over Africa at convection-permitting scale Hydrology and the future of the Greenland Ice Sheet
Hydrology and the future of the Greenland Ice Sheet Effective adaptation to rising flood risk
Effective adaptation to rising flood risk