Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Affinity-optimizing enhancer variants disrupt development
Affinity-optimizing enhancer variants disrupt development
Low-affinity transcription factor binding sites are prevalent across the genome, and single nucleotide changes that increase binding affinity even slightly can cause gain-of-function gene expression and phenotypes (such as polydactyly).
- Fabian Lim
- , Joe J. Solvason
- & Emma K. Farley
-
News |
 Cloned rhesus monkey lives to adulthood for first time
Cloned rhesus monkey lives to adulthood for first time
A method that provides cloned embryos with a healthy placenta could pave the way for more research involving the primates.
- Miryam Naddaf
-
News |
 Ancient DNA reveals first known case of sex-development disorder
Ancient DNA reveals first known case of sex-development disorder
Researchers identified six ancient humans with chromosomal conditions, including the earliest case of Turner syndrome.
- Carissa Wong
-
News & Views |
 Prehistoric events might explain European multiple sclerosis risk
Prehistoric events might explain European multiple sclerosis risk
An exploration of more than 1,600 ancient Eurasian genomes suggests that genetic changes that increase autoimmune-disease risk in modern Europeans could have protected ancient Europeans from pathogens.
- Samira Asgari
- & Lionel A. Pousaz
-
Research Briefing |
 Deadly mismatch between nuclear and mitochondrial genes in swordtail fish hybrids
Deadly mismatch between nuclear and mitochondrial genes in swordtail fish hybrids
An analysis of the genomes of hybrids of distinct swordtail fish species uncovered a lethal incompatibility between certain combinations of nuclear and mitochondrial genes that encode subunits of complex I — a component of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. The evolutionary history of this incompatibility indicates that the genes involved were transferred between the species through hybridization in the past.
-
News |
 Ancient DNA reveals origins of multiple sclerosis in Europe
Ancient DNA reveals origins of multiple sclerosis in Europe
A huge cache of ancient genomes spanning tens of thousands of years reveals the roots of traits in modern Europeans.
- Sara Reardon
-
Article
| Open Access 100 ancient genomes show repeated population turnovers in Neolithic Denmark
100 ancient genomes show repeated population turnovers in Neolithic Denmark
Integrated data, including 100 human genomes from the Mesolithic, Neolithic and Early Bronze Age periods show that two major population turnovers occurred over just 1,000 years in Neolithic Denmark, resulting in dramatic changes in the genes, diet and physical appearance of the local people, as well as the landscape in which they lived.
- Morten E. Allentoft
- , Martin Sikora
- & Eske Willerslev
-
Article
| Open Access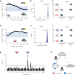 A lethal mitonuclear incompatibility in complex I of natural hybrids
A lethal mitonuclear incompatibility in complex I of natural hybrids
Analysis of naturally hybridizing swordtail fish species reveals a mitonuclear genetic incompatibility among three genes that encode components of mitochondrial respiratory complex I, providing insights into the emergence of hybrid incompatibilities and reproductive barriers.
- Benjamin M. Moran
- , Cheyenne Y. Payne
- & Molly Schumer
-
Article
| Open Access Population genomics of post-glacial western Eurasia
Population genomics of post-glacial western Eurasia
An analysis involving the shotgun sequencing of more than 300 ancient genomes from Eurasia reveals a deep east–west genetic divide from the Black Sea to the Baltic, and provides insight into the distinct effects of the Neolithic transition on either side of this boundary.
- Morten E. Allentoft
- , Martin Sikora
- & Eske Willerslev
-
Article
| Open Access The selection landscape and genetic legacy of ancient Eurasians
The selection landscape and genetic legacy of ancient Eurasians
Analyses of imputed ancient genomes and of samples from the UK Biobank indicate that ancient selection and migration were large contributors to the distribution of phenotypic diversity in present-day Europeans.
- Evan K. Irving-Pease
- , Alba Refoyo-Martínez
- & Eske Willerslev
-
Article
| Open Access Elevated genetic risk for multiple sclerosis emerged in steppe pastoralist populations
Elevated genetic risk for multiple sclerosis emerged in steppe pastoralist populations
Analysis of a large ancient genome dataset shows that genetic risk for multiple sclerosis rose in steppe pastoralists, providing insight into how genetic ancestry from the Neolithic and Bronze Age has shaped modern immune responses.
- William Barrie
- , Yaoling Yang
- & Eske Willerslev
-
Research Briefing |
 Small numbers of sodium channels on cartilage cells have a large effect on joint damage
Small numbers of sodium channels on cartilage cells have a large effect on joint damage
A type of sodium channel previously thought to be specific to neurons is also present in chondrocytes — cells that are crucial for joint health. Despite having low density, the sodium channels have an outsized role in the progression of osteoarthritis, and their genetic deletion or pharmacological inhibition reduced joint damage in mouse models.
-
Article
| Open Access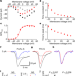 Nav1.7 as a chondrocyte regulator and therapeutic target for osteoarthritis
Nav1.7 as a chondrocyte regulator and therapeutic target for osteoarthritis
The voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.7 has a dual role in osteoarthritis—in chondrocytes, it promotes joint damage, and in dorsal root ganglia neurons, it increases pain transmission.
- Wenyu Fu
- , Dmytro Vasylyev
- & Chuan-ju Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Host genetic regulation of human gut microbial structural variation
Host genetic regulation of human gut microbial structural variation
A meta-analysis of associations between human genetic variation and gut microbial structural variations shows that ABO genotype differentially affects the presence of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii strains containing GalNAc utilization pathway in the gut.
- Daria V. Zhernakova
- , Daoming Wang
- & Jingyuan Fu
-
Book Review |
 The research aiming to keep people healthier for longer
The research aiming to keep people healthier for longer
An exploration of the biological reasons that people age celebrates the role of worms and flies in enabling scientific discovery — and investigates how to age well.
- Linda Partridge
-
Article
| Open Access The energetic and allosteric landscape for KRAS inhibition
The energetic and allosteric landscape for KRAS inhibition
Analysis of the effects of more than 26,000 KRAS mutations on abundance and interactions with six other proteins is used to construct an energy landscape of KRAS and identify allosteric drug target sites.
- Chenchun Weng
- , Andre J. Faure
- & Ben Lehner
-
News & Views |
 Gene expression of single cells mapped in tissue sections
Gene expression of single cells mapped in tissue sections
A tool that tags individual cells in a tissue with a unique barcode means that the gene-expression profile of each cell can be plotted in its original location. This allows spatial information to be captured at single-cell resolution.
- Patrik L. Ståhl
-
News & Views |
 Indigenous diversity in Australia’s DNA tapestry unlocked for genetic equity
Indigenous diversity in Australia’s DNA tapestry unlocked for genetic equity
Diverse genomic sequences might boost equity in areas such as health care. Genomic data from Indigenous Australians, shared through a community-consultation framework, aids efforts to boost genetic representation.
- Katrina G. Claw
- & Amber Nashoba
-
News & Views Forum |
 Cellular atlases of the entire mouse brain
Cellular atlases of the entire mouse brain
In a huge collaborative effort, millions of cells in the mouse brain have been mapped in detail. Two scientists examine the resulting wealth of insights into gene regulation in brain cells, neuronal connections and how our own brains evolved.
- Maria Antonietta Tosches
- & Heather J. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access The landscape of genomic structural variation in Indigenous Australians
The landscape of genomic structural variation in Indigenous Australians
Population-scale whole-genome sequencing across four remote Indigenous Australian communities reveals a large fraction of structural variants that are unique to these populations, emphasizing the genetic distinctiveness of and diversity among Indigenous Australians.
- Andre L. M. Reis
- , Melissa Rapadas
- & Ira W. Deveson
-
Perspective |
 Hold out the genome: a roadmap to solving the cis-regulatory code
Hold out the genome: a roadmap to solving the cis-regulatory code
A roadmap towards solving the cis-regulatory code using a combination of machine learning and massively parallel assays of exogenous DNA is proposed.
- Carl G. de Boer
- & Jussi Taipale
-
News & Views |
 Nausea and vomiting in pregnancy linked to hormone from fetus
Nausea and vomiting in pregnancy linked to hormone from fetus
Maternal sensitivity to a hormone produced by the fetus might underlie the risk of severe nausea and vomiting in human pregnancy — a finding that could open up strategies for the treatment of this debilitating condition.
- Alice E. Hughes
- & Rachel M. Freathy
-
News |
 Australian Indigenous genomes are highly diverse and unlike those anywhere else
Australian Indigenous genomes are highly diverse and unlike those anywhere else
In collecting genomic data for Indigenous Australians, scientists hope to expand knowledge of human genetic diversity and improve health for this group.
- Bianca Nogrady
-
Article
| Open Access Indigenous Australian genomes show deep structure and rich novel variation
Indigenous Australian genomes show deep structure and rich novel variation
Analysis of the genomes of 159 individuals from four Indigenous communities in Australia shows a high level of genetic variation and demonstrates the need for greater representation of Indigenous Australians in reference panels and clinical databases.
- Matthew Silcocks
- , Ashley Farlow
- & Stephen Leslie
-
Article
| Open Access Conserved and divergent gene regulatory programs of the mammalian neocortex
Conserved and divergent gene regulatory programs of the mammalian neocortex
A single-cell multiomics analysis of over 200,000 cells of the primary motor cortex of human, macaque, marmoset and mouse shows that divergence of transcription factor expression corresponds to species-specific epigenome landscapes, and conserved and divergent gene regulatory features are reflected in the evolution of the three-dimensional genome.
- Nathan R. Zemke
- , Ethan J. Armand
- & Bing Ren
-
Article
| Open Access In vitro production of cat-restricted Toxoplasma pre-sexual stages
In vitro production of cat-restricted Toxoplasma pre-sexual stages
A study describes the molecular basis of sexual development of Toxoplasma gondii entirely in vitro, demonstrating the role and interaction of AP2XII-1 and AP2XI-2 in the developmental program of this protozoan parasite.
- Ana Vera Antunes
- , Martina Shahinas
- & Mohamed-Ali Hakimi
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell analysis of chromatin accessibility in the adult mouse brain
Single-cell analysis of chromatin accessibility in the adult mouse brain
An atlas of candidate cis-regulatory DNA elements (cCREs) in the adult mouse brain unravels the transcriptional regulatory programs that drive the heterogeneity and complexity of brain structure and function.
- Songpeng Zu
- , Yang Eric Li
- & Bing Ren
-
Article
| Open Access GDF15 linked to maternal risk of nausea and vomiting during pregnancy
GDF15 linked to maternal risk of nausea and vomiting during pregnancy
Elevated circulating levels of GDF15 in pregnant women are associated with severe nausea and vomiting, and sensitivity to such symptoms during pregnancy is partly determined by prepregnancy levels of this hormone.
- M. Fejzo
- , N. Rocha
- & S. O’Rahilly
-
Article
| Open Access Brain-wide correspondence of neuronal epigenomics and distant projections
Brain-wide correspondence of neuronal epigenomics and distant projections
This study uses epi-retro-seq to link single-cell epigenomes and cell types to long-distance projections for neurons dissected from different regions projecting to different targets across the whole mouse brain.
- Jingtian Zhou
- , Zhuzhu Zhang
- & Edward M. Callaway
-
Article |
 Base-editing mutagenesis maps alleles to tune human T cell functions
Base-editing mutagenesis maps alleles to tune human T cell functions
Massive-scale mutational screening across 385 genes reveals a wide spectrum of alleles that govern tunable T cell functions, including cytokine production and cytotoxicity.
- Ralf Schmidt
- , Carl C. Ward
- & Alexander Marson
-
Article
| Open Access Cell-type-directed design of synthetic enhancers
Cell-type-directed design of synthetic enhancers
Deep learning models were used to design synthetic cell-type-specific enhancers that work in fruit fly brains and human cell lines, an approach that also provides insights into these gene regulatory elements.
- Ibrahim I. Taskiran
- , Katina I. Spanier
- & Stein Aerts
-
Article
| Open Access Targeted design of synthetic enhancers for selected tissues in the Drosophila embryo
Targeted design of synthetic enhancers for selected tissues in the Drosophila embryo
Deep learning and transfer learning were used to design tissue-specific enhancers in the Drosophila embryo that were active and specific, validating this approach to achieve tissue-, cell type- and cell state-specific expression control.
- Bernardo P. de Almeida
- , Christoph Schaub
- & Alexander Stark
-
News |
 How CRISPR gene editing could help treat Alzheimer’s
How CRISPR gene editing could help treat Alzheimer’s
Some researchers hoping that gene-editing technology can conquer forms of Alzheimer’s caused by genetic mutations.
- Tosin Thompson
-
News |
 CRISPR 2.0: a new wave of gene editors heads for clinical trials
CRISPR 2.0: a new wave of gene editors heads for clinical trials
Landmark approval of the first CRISPR therapy paves the way for treatments based on more efficient and more precise genome editors.
- Heidi Ledford
-
News & Views |
 An expanded genomic database for identifying disease-related variants
An expanded genomic database for identifying disease-related variants
An expanded version of a human-genome database called gnomAD, containing 76,156 whole-genome sequences, has enabled investigation of how variants in non-protein-coding regions of the genome affect health.
- Ryan S. Dhindsa
- & Slavé Petrovski
-
Article |
 A genomic mutational constraint map using variation in 76,156 human genomes
A genomic mutational constraint map using variation in 76,156 human genomes
A genomic constraint map for the human genome constructed using data from 76,156 human genomes from the Genome Aggregation Database shows that non-coding constrained regions are enriched for regulatory elements and variants associated with complex diseases and traits.
- Siwei Chen
- , Laurent C. Francioli
- & Konrad J. Karczewski
-
Article
| Open Access A human embryonic limb cell atlas resolved in space and time
A human embryonic limb cell atlas resolved in space and time
Using single-cell and spatial transcriptomics, human embryonic limb development across space and time and the diversification and cross-species conservation of cells are demonstrated.
- Bao Zhang
- , Peng He
- & Sarah A. Teichmann
-
Article |
 Genetic risk converges on regulatory networks mediating early type 2 diabetes
Genetic risk converges on regulatory networks mediating early type 2 diabetes
Integration of multiomics data with functional analysis of pancreatic tissues from individuals with early-stage type 2 diabetes indicates that the genetic risk converges on RFX6, which regulates chromatin architecture at multiple risk loci.
- John T. Walker
- , Diane C. Saunders
- & Marcela Brissova
-
Obituary |
 Evelyn Fox Keller (1936–2023), philosopher who questioned gender roles in science
Evelyn Fox Keller (1936–2023), philosopher who questioned gender roles in science
Mathematical biologist, philosopher and historian of science who challenged the vision of science as a masculine activity.
- Marga Vicedo
-
News |
 World’s biggest set of human genome sequences opens to scientists
World’s biggest set of human genome sequences opens to scientists
The whole genomes of 500,000 people in the UK Biobank will help researchers to probe our genetic code for links to disease.
- Ewen Callaway
-
Research Briefing |
 The genetic diversity of Bantu-speaking populations helped to shape African history
The genetic diversity of Bantu-speaking populations helped to shape African history
Analysis of a massive genomic data set reveals the profound effects that the movement of Bantu-speaking peoples had on Africa’s biological, linguistic and cultural landscape. These findings provide valuable insights for a wide range of disciplines and serve as a comprehensive data set of ancient and modern African individuals for comparative studies.
-
Research Briefing |
 Whole-genome alignment with primates reveals DNA elements conserved in humans
Whole-genome alignment with primates reveals DNA elements conserved in humans
By comparing DNA sequences across hundreds of species of primates and other mammals, an analysis identifies non-coding regulatory elements that are conserved only in primates and that could have important roles in complex traits and diseases in humans.
-
News & Views |
 An immune-cell transcription factor tethers DNA together
An immune-cell transcription factor tethers DNA together
A transcription factor in immune cells forms an unexpectedly ladder-like complex with two DNA molecules, allowing the expression of genes that these cells need to suppress harmful immune responses.
- Zhi Liu
- & Ye Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access MSL2 ensures biallelic gene expression in mammals
MSL2 ensures biallelic gene expression in mammals
After loss of MSL2, a class of dosage-sensitive genes transitions from biallelic to monoallelic expression, whereby one allele remains active, retaining active histone modifications and transcription factor binding, and the other allele is silenced, exhibiting loss of promoter–enhancer contacts and the acquisition of DNA methylation.
- Yidan Sun
- , Meike Wiese
- & Asifa Akhtar
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of constrained sequence elements across 239 primate genomes
Identification of constrained sequence elements across 239 primate genomes
Whole-genome alignment of 239 primate species reveals noncoding regulatory elements that are under selective constraint in primates but not in other placental mammals, that are enriched for variants that affect human gene expression and complex traits in diseases.
- Lukas F. K. Kuderna
- , Jacob C. Ulirsch
- & Kyle Kai-How Farh
-
Article
| Open Access The genetic legacy of the expansion of Bantu-speaking peoples in Africa
The genetic legacy of the expansion of Bantu-speaking peoples in Africa
We gathered genetic data for 1,763 individuals from 147 populations across 14 African countries, and 12 Late Iron Age individuals, to trace the expansion of Bantu-speaking peoples over the past 6,000 years.
- Cesar A. Fortes-Lima
- , Concetta Burgarella
- & Carina M. Schlebusch
-
Nature Podcast |
 Audio long read: Apple revival — how science is bringing historic varieties back to life
Audio long read: Apple revival — how science is bringing historic varieties back to life
Genomic studies of heirloom apples could help safeguard the future of the fruit.
- Christopher Kemp
- & Benjamin Thompson
-
News |
 ‘Treasure trove’ of new CRISPR systems holds promise for genome editing
‘Treasure trove’ of new CRISPR systems holds promise for genome editing
An algorithm that can analyse hundreds of millions of genetic sequences has identified DNA-cutting genes and enzymes that are extremely rare in nature.
- Sara Reardon
-
News & Views |
 Ancient DNA uncovers past migrations in California
Ancient DNA uncovers past migrations in California
Genomic data from ancient humans who lived up to 7,400 years ago, sampled from across California and Mexico, unveil patterns of migration that could explain how some Indigenous languages spread in parts of North America.
- Alan Izarraras-Gomez
- & Diego Ortega-Del Vecchyo
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Agricultural genetics
- Animal breeding
- Behavioural genetics
- Cancer genetics
- Cancer genomics
- Clinical genetics
- Consanguinity
- CRISPR-Cas systems
- Cytogenetics
- Development
- Epigenetics
- Epigenomics
- Eukaryote
- Evolutionary biology
- Functional genomics
- Gene expression
- Gene regulation
- Genetic association study
- Genetic hybridization
- Genetic interaction
- Genetic linkage study
- Genetic markers
- Genome
- Genomic instability
- Genomics
- Genotype
- Haplotypes
- Heritable quantitative trait
- Immunogenetics
- Inbreeding
- Medical genetics
- Microbial genetics
- Mutation
- Neurodevelopmental disorders
- Plant breeding
- Plant genetics
- Polyploidy
- Population genetics
- Prokaryote
- Quantitative trait
- RNA splicing
- RNAi
- Sequencing

 Alternative splicing of latrophilin-3 controls synapse formation
Alternative splicing of latrophilin-3 controls synapse formation