Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access A recently quenched galaxy 700 million years after the Big Bang
A recently quenched galaxy 700 million years after the Big Bang
Analysis of the JWST/NIRSpec spectrum of the recently observed Lyman-break galaxy JADES-GS+53.15508-27.80178 revealed a redshift of z = 7.3, a Balmer break and a complete absence of nebular emission lines, indicating that quenching occurred only 700 million years after the Big Bang.
- Tobias J. Looser
- , Francesco D’Eugenio
- & Jan Scholtz
-
Article |
 Most of the photons that reionized the Universe came from dwarf galaxies
Most of the photons that reionized the Universe came from dwarf galaxies
An analysis of eight ultra-faint galaxies during the epoch of reionization with absolute magnitudes between −17 mag and −15 mag shows that most of the photons that reionized the Universe come from dwarf galaxies.
- Hakim Atek
- , Ivo Labbé
- & Katherine E. Whitaker
-
Article |
 A high black-hole-to-host mass ratio in a lensed AGN in the early Universe
A high black-hole-to-host mass ratio in a lensed AGN in the early Universe
JWST/NIRSpec observations of Abell2744-QSO1 show a high black-hole-to-host mass ratio in the early Universe, which indicates that we are seeing the black hole in a phase of rapid growth, accreting at 30% of the Eddington limit.
- Lukas J. Furtak
- , Ivo Labbé
- & Christina C. Williams
-
Article |
 A massive galaxy that formed its stars at z ≈ 11
A massive galaxy that formed its stars at z ≈ 11
A massive galaxy observed with the JWST indicates that the bulk of its stars formed within the first 500 million years of the Universe.
- Karl Glazebrook
- , Themiya Nanayakkara
- & Angel Chandro-Gomez
-
Article
| Open Access A dynamical measure of the black hole mass in a quasar 11 billion years ago
A dynamical measure of the black hole mass in a quasar 11 billion years ago
Using the GRAVITY+ instrument, dynamical measurement of the black hole mass in a quasar at a redshift of 2.3 (11 billion years ago) shows how the relationship between galaxies and black holes evolves with time.
- R. Abuter
- , F. Allouche
- & G. Zins
-
Article
| Open Access A small and vigorous black hole in the early Universe
A small and vigorous black hole in the early Universe
An extensive analysis of the JWST-NIRSpec spectrum of GN-z11 shows a supermassive black hole of a few million solar masses in a galaxy 440 million years after the Big Bang.
- Roberto Maiolino
- , Jan Scholtz
- & Fengwu Sun
-
Article |
 Ionized gas extends over 40 kpc in an odd radio circle host galaxy
Ionized gas extends over 40 kpc in an odd radio circle host galaxy
We find that the optical emission due to ionized gas that is characteristic of a shock extends 40 kpc in diameter across the host galaxy of an odd radio circle.
- Alison L. Coil
- , Serena Perrotta
- & Kelly E. Whalen
-
Article |
 Bipolar outflows out to 10 kpc for massive galaxies at redshift z ≈ 1
Bipolar outflows out to 10 kpc for massive galaxies at redshift z ≈ 1
An ultra-deep MUSE image of the mean Mg II emission for a sample of galaxies at redshift z ≈ 1 suggests the presence of bipolar outflows on scales of 10 kpc or more.
- Yucheng Guo
- , Roland Bacon
- & Martin Wendt
-
Article
| Open Access A Milky Way-like barred spiral galaxy at a redshift of 3
A Milky Way-like barred spiral galaxy at a redshift of 3
We report observations of ceers-2112 that show that this galaxy, at a redshift of 3, unexpectedly has a barred spiral structure.
- Luca Costantin
- , Pablo G. Pérez-González
- & L. Y. Aaron Yung
-
Article |
 An evolutionary continuum from nucleated dwarf galaxies to star clusters
An evolutionary continuum from nucleated dwarf galaxies to star clusters
In the Virgo galaxy cluster, we identified a continuum of objects that maps the morphological transition between nucleated dwarf galaxies and ultra-compact dwarf galaxies (UCDs), providing evidence for the formation of UCDs through tidal stripping of ancient dwarf galaxies.
- Kaixiang Wang
- , Eric W. Peng
- & Mingcheng Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Polarized thermal emission from dust in a galaxy at redshift 2.6
Polarized thermal emission from dust in a galaxy at redshift 2.6
Linearly polarized thermal emission from dust grains in a strongly lensed, intrinsically luminous galaxy forming stars at a rate more than 1,000 times that of the Milky Way is detected.
- J. E. Geach
- , E. Lopez-Rodriguez
- & K. E. K. Coppin
-
Article |
 Confirmation and refutation of very luminous galaxies in the early Universe
Confirmation and refutation of very luminous galaxies in the early Universe
JWST spectroscopy confirms redshifts for two very luminous galaxies with z > 11, and also demonstrates that another candidate with suggested z ≈ 16 instead has z = 4.9.
- Pablo Arrabal Haro
- , Mark Dickinson
- & Jorge A. Zavala
-
Article |
 Galaxies in voids assemble their stars slowly
Galaxies in voids assemble their stars slowly
We show that void galaxies have had slower star formation histories than galaxies in denser large-scale environments and find two main types of star formation history in all environments.
- Jesús Domínguez-Gómez
- , Isabel Pérez
- & Almudena Zurita
-
Article |
 Detection of stellar light from quasar host galaxies at redshifts above 6
Detection of stellar light from quasar host galaxies at redshifts above 6
Images and spectroscopy obtained by the JWST from two HSC-SSP quasars show massive, compact and disc-like galaxies, indicating that the relation between black holes and their host galaxies was in place less than a billion years after the Big Bang.
- Xuheng Ding
- , Masafusa Onoue
- & Jinyi Yang
-
Article |
 X-ray polarization evidence for a 200-year-old flare of Sgr A*
X-ray polarization evidence for a 200-year-old flare of Sgr A*
A study reports the measurement of the polarization degree and angle of X-rays from Sagittarius A* reflected off a nearby cloud, indicating an X-ray flare about 200 years ago.
- Frédéric Marin
- , Eugene Churazov
- & Silvia Zane
-
Article |
 Spatial variations in aromatic hydrocarbon emission in a dust-rich galaxy
Spatial variations in aromatic hydrocarbon emission in a dust-rich galaxy
We present James Webb Space Telescope observations that detect the 3.3 μm polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon feature in a galaxy observed less than 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang.
- Justin S. Spilker
- , Kedar A. Phadke
- & Katherine E. Whitaker
-
Article
| Open Access A massive quiescent galaxy at redshift 4.658
A massive quiescent galaxy at redshift 4.658
GS-9209 is spectroscopically confirmed as a massive quiescent galaxy at a redshift of 4.658, showing that massive galaxy formation and quenching were already well underway within the first billion years of cosmic history.
- Adam C. Carnall
- , Ross J. McLure
- & Sam Walker
-
Article |
 Temperature inhomogeneities cause the abundance discrepancy in H ii regions
Temperature inhomogeneities cause the abundance discrepancy in H ii regions
The authors report observational evidence that, within interstellar gas, there are temperature inhomogeneities affecting only highly ionized gas and causing the abundance discrepancy problem, and provide new empirical relations for estimation of temperature and metallicity.
- J. Eduardo Méndez-Delgado
- , César Esteban
- & Manuel Peimbert
-
Article |
 The nature of an ultra-faint galaxy in the cosmic dark ages seen with JWST
The nature of an ultra-faint galaxy in the cosmic dark ages seen with JWST
The JWST, with the aid of gravitational lensing, confirms the extreme distance of an ultra-faint galaxy at a redshift of 9.79, showing it to have a luminosity typical of the sources responsible for cosmic reionization and highly compact and complex morphology.
- Guido Roberts-Borsani
- , Tommaso Treu
- & Rogier A. Windhorst
-
Article |
 Compact [C ii] emitters around a C iv absorption complex at redshift 5.7
Compact [C ii] emitters around a C iv absorption complex at redshift 5.7
Investigation of the physical conditions of the circumgalactic medium led to detection of two compact [C ii]-emitting galaxies with narrow linewidths at a redshift of 5.7, associated with a complex, high-ionization C iv absorption system.
- Daichi Kashino
- , Simon J. Lilly
- & Anna-Christina Eilers
-
Article
| Open Access Forming intracluster gas in a galaxy protocluster at a redshift of 2.16
Forming intracluster gas in a galaxy protocluster at a redshift of 2.16
Analysis of observations from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array showed evidence of the thermal Sunyaev–Zeldovich effect in the direction of the Spiderweb protocluster at a redshift of 2.156.
- Luca Di Mascolo
- , Alexandro Saro
- & Francesca Rizzo
-
Article |
 A population of red candidate massive galaxies ~600 Myr after the Big Bang
A population of red candidate massive galaxies ~600 Myr after the Big Bang
James Webb Space Telescope early release observations used to search for intrinsically red galaxies from the first 750 million years of cosmic history find six candidate massive galaxies, possibly including one of roughly 1011 solar masses.
- Ivo Labbé
- , Pieter van Dokkum
- & Bingjie Wang
-
Article |
 Intracluster light is already abundant at redshift beyond unity
Intracluster light is already abundant at redshift beyond unity
A study of intracluster light (ICL) in ten high-redshift galaxy clusters finds evidence that gradual stripping may not be the dominant mechanism of ICL formation, but may occur alongside the formation and growth of the brightest cluster galaxies, and/or accretion of preprocessed stars.
- Hyungjin Joo
- & M. James Jee
-
Article |
 Shock cooling of a red-supergiant supernova at redshift 3 in lensed images
Shock cooling of a red-supergiant supernova at redshift 3 in lensed images
The early stages of a lensed supernova at redshift 3 are found in images taken by the Hubble Space Telescope, with observations beginning from around 5.8 hours after the explosion.
- Wenlei Chen
- , Patrick L. Kelly
- & Adi Zitrin
-
Article
| Open Access A 0.6 Mpc H i structure associated with Stephan’s Quintet
A 0.6 Mpc H i structure associated with Stephan’s Quintet
Atomic hydrogen observations in the vicinity of Stephan’s Quintet are reported, showing a large gaseous structure of around 0.6 Mpc in size in the velocity range of 6,550–6,750 km s−1.
- C. K. Xu
- , C. Cheng
- & F. Renaud
-
Article
| Open Access Galaxy clusters enveloped by vast volumes of relativistic electrons
Galaxy clusters enveloped by vast volumes of relativistic electrons
For four galaxy clusters it is shown that the radio halo emission is embedded in a much larger emission that extends over 2–3 Mpc, filling the volume of the clusters.
- V. Cuciti
- , F. de Gasperin
- & C. Tasse
-
Article
| Open Access Observations of a Magellanic Corona
Observations of a Magellanic Corona
By analysing Hubble Space Telescope/Cosmic Origins Spectrograph spectra, evidence is provided for the presence of a Magellanic Corona surrounding the Large Magellanic Cloud, as predicted given its high mass.
- Dhanesh Krishnarao
- , Andrew J. Fox
- & Nicolas Lehner
-
Article |
 Extended far-ultraviolet emission in distant dwarf galaxies
Extended far-ultraviolet emission in distant dwarf galaxies
Observations by the Ultra-Violet Imaging Telescope on AstroSat reveal ten blue compact dwarf galaxies with excess far-ultraviolet emission in their outer region, indicating star formation in accreting disks.
- Anshuman Borgohain
- , Kanak Saha
- & Shyam N. Tandon
-
Article |
 A population of ultraviolet-dim protoclusters detected in absorption
A population of ultraviolet-dim protoclusters detected in absorption
Lyman-α absorption observations from the Las Campanas Observatory are used to find a population of ultraviolet-dim protoclusters that contain few galaxies compared with their analogues in cosmological simulations.
- Andrew B. Newman
- , Gwen C. Rudie
- & John S. Mulchaey
-
Article
| Open Access A trail of dark-matter-free galaxies from a bullet-dwarf collision
A trail of dark-matter-free galaxies from a bullet-dwarf collision
The dark-matter-free dwarf galaxies DF2 and DF4 in the NGC 1052 group probably formed together in the aftermath of a single bullet-dwarf collision around eight billion years ago.
- Pieter van Dokkum
- , Zili Shen
- & Aaron Romanowsky
-
Article |
 Resolving the H i in damped Lyman α systems that power star formation
Resolving the H i in damped Lyman α systems that power star formation
Spectroscopy of a gravitationally lensed galaxy at a redshift of 2.7 with spatially resolved maps of two foreground damped Lyman α systems indicates a vast mass of neutral hydrogen gas, consistent with a star-forming region.
- Rongmon Bordoloi
- , John M. O’Meara
- & James D. Neill
-
Article |
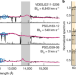 Suppression of black-hole growth by strong outflows at redshifts 5.8–6.6
Suppression of black-hole growth by strong outflows at redshifts 5.8–6.6
A study reporting optical and near-infrared observations of quasars at redshifts 5.8–6.6 shows that about half have strong winds, up to 17% the speed of light, suppressing black-hole growth.
- M. Bischetti
- , C. Feruglio
- & F. Fiore
-
Article |
 A dusty compact object bridging galaxies and quasars at cosmic dawn
A dusty compact object bridging galaxies and quasars at cosmic dawn
An unusual ultraviolet compact object associated with a dusty starburst has been observed at a redshift of about 7.2, with a luminosity that falls between that of quasars and galaxies, possibly in transition between the two.
- S. Fujimoto
- , G. B. Brammer
- & P. A. Oesch
-
Article |
 A highly magnified star at redshift 6.2
A highly magnified star at redshift 6.2
A massive star at a redshift of 6.2, corresponding to 900 million years after the Big Bang, is magnified greatly by lensing of the foreground galaxy cluster WH0137–08.
- Brian Welch
- , Dan Coe
- & Tom Broadhurst
-
Article
| Open Access A time-resolved picture of our Milky Way’s early formation history
A time-resolved picture of our Milky Way’s early formation history
A sample of approximately 250,000 subgiant stars enables an alternative view of the Milky Way’s assembly history, especially the early formation history of the old disk and halo.
- Maosheng Xiang
- & Hans-Walter Rix
-
Article |
 Thermal imaging of dust hiding the black hole in NGC 1068
Thermal imaging of dust hiding the black hole in NGC 1068
Mid-infrared observations of the dusty structures of the galaxy NGC 1068 support the unified model of active galactic nuclei.
- Violeta Gámez Rosas
- , Jacob W. Isbell
- & Gerard Zins
-
Article |
 Black-hole-triggered star formation in the dwarf galaxy Henize 2-10
Black-hole-triggered star formation in the dwarf galaxy Henize 2-10
Optical observations with a linear resolution of a few parsecs show that the outflow from the central black hole in the low-mass galaxy Henize 2-10 triggered a round of star formation.
- Zachary Schutte
- & Amy E. Reines
-
Article |
 A stellar stream remnant of a globular cluster below the metallicity floor
A stellar stream remnant of a globular cluster below the metallicity floor
Observations of a stellar stream below the metallicity floor for a disrupted globular cluster are described.
- Nicolas F. Martin
- , Kim A. Venn
- & Alessio Mucciarelli
-
Article |
 Normal, dust-obscured galaxies in the epoch of reionization
Normal, dust-obscured galaxies in the epoch of reionization
Two serendipitously detected dust-obscured galaxies are reported at z = 6.7 and 7.4, with estimates that such galaxies provide an additional 10–25% contribution to the total star formation rate density at z > 6.
- Y. Fudamoto
- , P. A. Oesch
- & C. White
-
Article |
 Quenching of star formation from a lack of inflowing gas to galaxies
Quenching of star formation from a lack of inflowing gas to galaxies
The authors report 1.3 mm observations of dust emission from strongly lensed galaxies where star formation is quenched, demonstrating that gas depletion is responsible for the cessation of star formation in some high-redshift galaxies.
- Katherine E. Whitaker
- , Christina C. Williams
- & Francesco Valentino
-
Article |
 The diffuse γ-ray background is dominated by star-forming galaxies
The diffuse γ-ray background is dominated by star-forming galaxies
The diffuse, isotropic background of gamma rays comes mainly from star-forming galaxies, according to a physical model of gamma-ray emission.
- Matt A. Roth
- , Mark R. Krumholz
- & Silvia Celli
-
Article |
 Large metallicity variations in the Galactic interstellar medium
Large metallicity variations in the Galactic interstellar medium
The metallicity of the interstellar medium measured towards 25 stars relatively near the Sun shows large variations, suggesting that infalling pristine gas is not efficiently mixed in the interstellar medium.
- Annalisa De Cia
- , Edward B. Jenkins
- & Jens-Kristian Krogager
-
Article |
 Anisotropic satellite galaxy quenching modulated by black hole activity
Anisotropic satellite galaxy quenching modulated by black hole activity
An analysis of archival data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey finds that star-forming satellite galaxies are relatively more common along the minor axis of central galaxies owing to the effect of black hole feedback.
- Ignacio Martín-Navarro
- , Annalisa Pillepich
- & Volker Springel
-
Article |
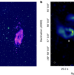 Jets from MRC 0600-399 bent by magnetic fields in the cluster Abell 3376
Jets from MRC 0600-399 bent by magnetic fields in the cluster Abell 3376
Radio observations of the cluster Abell 3376, combined with numerical modelling, attribute the bent jets associated with the second-brightest galaxy in the cluster to an ordered magnetic field at the discontinuity.
- James O. Chibueze
- , Haruka Sakemi
- & Tsutomu T. Takeuchi
-
Article |
 All-sky dynamical response of the Galactic halo to the Large Magellanic Cloud
All-sky dynamical response of the Galactic halo to the Large Magellanic Cloud
The detection of structure in the distribution of giant stars in the outer Galactic halo shows the substantial global impact of the Magellanic clouds on our Galaxy.
- Charlie Conroy
- , Rohan P. Naidu
- & Benjamin D. Johnson
-
Article |
 Detection of large-scale X-ray bubbles in the Milky Way halo
Detection of large-scale X-ray bubbles in the Milky Way halo
Observations from the eROSITA telescope reveal soft-X-ray-emitting bubbles extending above and below the Galactic plane, which arose from energy injected into the Galactic halo from past activity in the Galactic centre.
- P. Predehl
- , R. A. Sunyaev
- & J. Wilms
-
Article |
 Stellar clustering shapes the architecture of planetary systems
Stellar clustering shapes the architecture of planetary systems
The architecture of planetary systems is shown to be strongly affected by stellar clustering in position-velocity phase space; hot Jupiters occur preferentially at high density, suggesting that their extreme orbits originate from environmental perturbations.
- Andrew J. Winter
- , J. M. Diederik Kruijssen
- & Mélanie Chevance
-
Article |
 H i 21-centimetre emission from an ensemble of galaxies at an average redshift of one
H i 21-centimetre emission from an ensemble of galaxies at an average redshift of one
Emission from atomic hydrogen at a wavelength of 21 centimetres had been observed from galaxies at a maximum redshift of 0.4, but is now reported at a redshift of about 1.
- Aditya Chowdhury
- , Nissim Kanekar
- & K. S. Dwarakanath
-
Article |
 Cold gas in the Milky Way’s nuclear wind
Cold gas in the Milky Way’s nuclear wind
Observations of a cold molecular gas associated with the atomic hydrogen outflow from the centre of our Galaxy indicate that this gas has a surprisingly high mass but unclear origin.
- Enrico M. Di Teodoro
- , N. M. McClure-Griffiths
- & Lucia Armillotta

 Star formation shut down by multiphase gas outflow in a galaxy at a redshift of 2.45
Star formation shut down by multiphase gas outflow in a galaxy at a redshift of 2.45