Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 SARS-CoV-2 mimics a host protein to bypass defences
SARS-CoV-2 mimics a host protein to bypass defences
It emerges that the SARS-CoV-2 virus has evolved to mimic one of the histone proteins that package DNA in the cell nucleus. This mimicry leads to disrupted gene transcription and a diminished antiviral response.
- Lisa Thomann
- & Volker Thiel
-
Article |
 SARS-CoV-2 disrupts host epigenetic regulation via histone mimicry
SARS-CoV-2 disrupts host epigenetic regulation via histone mimicry
The SARS-CoV-2 protein ORF8 functions as a mimic of histone H3 to disrupt host cell epigenetic regulation.
- John Kee
- , Samuel Thudium
- & Erica Korb
-
Article |
 Glucose-driven TOR–FIE–PRC2 signalling controls plant development
Glucose-driven TOR–FIE–PRC2 signalling controls plant development
Glucose signalling via TOR controls growth and differentiation through regulation of genome-wide histone methylation via FERTILIZATION-INDEPENDENT ENDOSPERM (FIE).
- Ruiqiang Ye
- , Meiyue Wang
- & Jen Sheen
-
News & Views |
 Two-layer design protects genes from mutations in their enhancers
Two-layer design protects genes from mutations in their enhancers
Gene expression is regulated by clusters of regulatory DNA sequences called enhancers. Basic design principles that protect enhancer networks against the harmful effects of genetic mutations have now been elucidated.
- Ran Elkon
- & Reuven Agami
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo single-molecule analysis reveals COOLAIR RNA structural diversity
In vivo single-molecule analysis reveals COOLAIR RNA structural diversity
The structures of single COOLAIR RNA isoforms change in abundance and shape in response to external conditions; structural mutation of these isoforms altered FLC expression and flowering time, consistent with a regulatory role of the COOLAIR structure in FLC transcription.
- Minglei Yang
- , Pan Zhu
- & Yiliang Ding
-
Review Article |
 Inflammatory memory and tissue adaptation in sickness and in health
Inflammatory memory and tissue adaptation in sickness and in health
A Review on inflammatory memory in non-immune cells of different epithelia and neurons, and the potential mechanisms controlling these epigenetic memories and their implications in human health and disease.
- Shruti Naik
- & Elaine Fuchs
-
Article
| Open Access Cohesin-mediated loop anchors confine the locations of human replication origins
Cohesin-mediated loop anchors confine the locations of human replication origins
A study shows that the three-dimensional conformation of the human genome influences the positioning of DNA replication initiation zones, highlighting cohesin-mediated loop anchors as essential determinants of their precise location.
- Daniel J. Emerson
- , Peiyao A. Zhao
- & Jennifer E. Phillips-Cremins
-
News & Views |
 Maternal enzyme reprograms paternal DNA for healthy offspring
Maternal enzyme reprograms paternal DNA for healthy offspring
It emerges that high blood sugar deregulates the enzyme TET3 in the eggs of female mice, preventing it from properly modifying sperm-derived DNA when eggs are fertilized. This leads to metabolic defects in adult progeny.
- Yumiko K. Kawamura
- & Antoine H. F. M. Peters
-
Article |
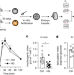 Maternal inheritance of glucose intolerance via oocyte TET3 insufficiency
Maternal inheritance of glucose intolerance via oocyte TET3 insufficiency
Pregestational hyperglycaemia in mothers increases the probability of glucose intolerance in the offspring, an effect controlled by TET3-dependent DNA demethylation of genes involved in insulin secretion.
- Bin Chen
- , Ya-Rui Du
- & Hefeng Huang
-
News & Views |
 An added layer of repression for human genes
An added layer of repression for human genes
A protein complex called the rixosome helps to degrade RNA transcripts that linger after gene expression ceases. This discovery points to distinct roles for the rixosome in regulating chromatin in different species.
- Michael Uckelmann
- & Chen Davidovich
-
Article
| Open Access Rixosomal RNA degradation contributes to silencing of Polycomb target genes
Rixosomal RNA degradation contributes to silencing of Polycomb target genes
The rixosome associates with Polycomb repressive complexes and chromatin and has a role in silencing of Polycomb target gene expression in human cells via degradation of nascent RNA transcripts.
- Haining Zhou
- , Chad B. Stein
- & Danesh Moazed
-
Technology Feature |
 Revealing chromosome contours, one dot at a time
Revealing chromosome contours, one dot at a time
Methods that meld imaging with sequencing are uncovering the organizational principles of the genome — and how it influences cell fates.
- Amber Dance
-
Outlook |
 Turning back time with epigenetic clocks
Turning back time with epigenetic clocks
If biological ageing can be slowed, halted or rewound, are the machine-learning algorithms the best way to measure it? Some experts are unconvinced.
- Liam Drew
-
News & Views |
 Important genomic regions mutate less often than do other regions
Important genomic regions mutate less often than do other regions
Genomic regions that are crucial for the viability and reproduction of the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana are enriched with molecular features that are associated with a reduced rate of mutation.
- Jianzhi Zhang
-
Article |
 Sex-specific chromatin remodelling safeguards transcription in germ cells
Sex-specific chromatin remodelling safeguards transcription in germ cells
Following global DNA demethylation, mouse gonadal primordial germ cells undergo remodelling of repressive chromatin modifications, resulting in a sex-specific signature that is required to safeguard the transcriptional program.
- Tien-Chi Huang
- , Yi-Fang Wang
- & Petra Hajkova
-
Article
| Open Access Genome surveillance by HUSH-mediated silencing of intronless mobile elements
Genome surveillance by HUSH-mediated silencing of intronless mobile elements
The human silencing hub (HUSH) complex uses introns to distinguish intronless foreign DNA from intron-containing host DNA and modifies chromatin to silence transcription of retrotransposons and retroviruses.
- Marta Seczynska
- , Stuart Bloor
- & Paul J. Lehner
-
Article
| Open Access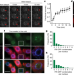 Cold-induced Arabidopsis FRIGIDA nuclear condensates for FLC repression
Cold-induced Arabidopsis FRIGIDA nuclear condensates for FLC repression
In Arabidopsis thaliana, downregulation of the floral repressor FLC in response to cold occurs through a mechanism in which the FLC activator FRIGIDA is sequestered into biomolecular condensates away from the FLC promoter.
- Pan Zhu
- , Clare Lister
- & Caroline Dean
-
Article |
 KDM5B promotes immune evasion by recruiting SETDB1 to silence retroelements
KDM5B promotes immune evasion by recruiting SETDB1 to silence retroelements
KDM5B recruits SETDB1 to repress endogenous retroelements such as MMVL30, suppressing anti-tumour immunity, and the depletion of KDM5B induces a robust adaptive immune response and enhances the response to immune checkpoint blockade.
- Shang-Min Zhang
- , Wesley L. Cai
- & Qin Yan
-
Article
| Open Access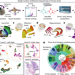 DNA methylation atlas of the mouse brain at single-cell resolution
DNA methylation atlas of the mouse brain at single-cell resolution
A comprehensive survey of the epigenome from 45 regions of the mouse cortex, hippocampus, striatum, pallidum and olfactory areas using single-nucleus DNA methylation sequencing enables identification of 161 cell clusters with distinct locations and projection targets and provides insights into the regulatory landscape underlying neuronal diversity and spatial regulation.
- Hanqing Liu
- , Jingtian Zhou
- & Joseph R. Ecker
-
News & Views |
 Protein condensates provide a platform for controlling chromatin
Protein condensates provide a platform for controlling chromatin
The protein UTX regulates the DNA–protein complex chromatin to suppress tumour growth. Data suggest that the ability of UTX to condense into liquid-like droplets underlies its chromatin-regulating ability.
- David Lara-Astiaso
- & Brian J. P. Huntly
-
Article |
 UTX condensation underlies its tumour-suppressive activity
UTX condensation underlies its tumour-suppressive activity
Phase separation properties are a major determinant of UTX activity in chromatin regulation in tumour suppression, and are dependent on a core intrinsically disordered region of the protein.
- Bi Shi
- , Wei Li
- & Hao Jiang
-
News & Views |
 Deranged chromatin drives uterine fibroid tumours
Deranged chromatin drives uterine fibroid tumours
A previously unknown subgroup of uterine fibroid tumours is driven by mutations that result in disruption of the DNA–protein complex chromatin. The findings could inform the management of this common condition.
- Zehra Ordulu
-
Technology Feature |
 Single-cell analysis enters the multiomics age
Single-cell analysis enters the multiomics age
A rapidly growing collection of software tools is helping researchers to analyse multiple huge ‘-omics’ data sets.
- Jeffrey M. Perkel
-
Article |
 BANP opens chromatin and activates CpG-island-regulated genes
BANP opens chromatin and activates CpG-island-regulated genes
BANP is identified as the transcription factor that binds the CGCG element in a DNA-methylation-dependent manner, opens chromatin and activates a class of essential CpG-island-regulated genes.
- Ralph S. Grand
- , Lukas Burger
- & Dirk Schübeler
-
Article |
 Shape of promoter antisense RNAs regulates ligand-induced transcription activation
Shape of promoter antisense RNAs regulates ligand-induced transcription activation
The authors describe a role for the non-coding antisense transcripts produced at promoters in regulating ligand-induced activation of gene transcription.
- Fan Yang
- , Bogdan Tanasa
- & Michael G. Rosenfeld
-
Research Summary |
 Protein architecture of the yeast genome
Protein architecture of the yeast genome
Use of chromatin immunoprecipitation with exonuclease treatment (ChIP–exo) determines the positional organization of hundreds of chromosomal proteins throughout the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. The resulting ultra-high-resolution map provides insight into the regulation of genes, enhancers, replication origins, centromeres, subtelomeres and transposons.
- B. Franklin Pugh
-
Article
| Open Access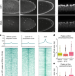 HP1 drives de novo 3D genome reorganization in early Drosophila embryos
HP1 drives de novo 3D genome reorganization in early Drosophila embryos
The heterochromatin protein HP1 has an essential role in establishing several features of the 3D nuclear organization of the genome during early embryonic development in Drosophila.
- Fides Zenk
- , Yinxiu Zhan
- & Nicola Iovino
-
Article |
 The RNA m6A reader YTHDC1 silences retrotransposons and guards ES cell identity
The RNA m6A reader YTHDC1 silences retrotransposons and guards ES cell identity
N6-methyladenosine RNA and its reader YTHDC1 serve as a bridge to silencing retrotransposons through the RNA derived from these retrotransposons in mouse ES cells.
- Jiadong Liu
- , Mingwei Gao
- & Jiekai Chen
-
News & Views |
 Mutation alters chromatin changes during injury response to drive cancer
Mutation alters chromatin changes during injury response to drive cancer
Cancer-associated mutations promote the formation of pancreatic tumours after tissue injury, but how this occurs is unclear. Changes to chromatin in injured cells with such mutations explain this predisposition to malignancy.
- Dane Vassiliadis
- & Mark A. Dawson
-
News & Views |
 An epigenetic tipping point in cancer comes under the microscope
An epigenetic tipping point in cancer comes under the microscope
Two studies show that some cancers are driven by genetic changes in the NSD3 protein that alter its enzymatic activity. Biochemical and structural characterization hints at a route to pharmacological reversal.
- Martyna W. Sroka
- & Christopher R. Vakoc
-
Nature Video |
 Rewinding the biological clock helps blind mice to see
Rewinding the biological clock helps blind mice to see
Cells in the eye appear to be ‘younger’ after treatment
- Shamini Bundell
-
News & Views |
 Sight restored by turning back the epigenetic clock
Sight restored by turning back the epigenetic clock
Neurons progressively deteriorate with age and lose resilience to injury. It emerges that treatment with three transcription factors can re-endow neurons in the mature eye with youthful characteristics and the capacity to regenerate.
- Andrew D. Huberman
-
News |
 Reversal of biological clock restores vision in old mice
Reversal of biological clock restores vision in old mice
‘Reprogramming’ approach seems to make old cells young again.
- Heidi Ledford
-
Article |
 Reprogramming to recover youthful epigenetic information and restore vision
Reprogramming to recover youthful epigenetic information and restore vision
Expression of three Yamanaka transcription factors in mouse retinal ganglion cells restores youthful DNA methylation patterns, promotes axon regeneration after injury, and reverses vision loss in a mouse model of glaucoma and in aged mice, suggesting that mammalian tissues retain a record of youthful epigenetic information that can be accessed to improve tissue function.
- Yuancheng Lu
- , Benedikt Brommer
- & David A. Sinclair
-
Nature Index |
 Asifa Akhtar is a sign of new things to come at the Max Planck Society
Asifa Akhtar is a sign of new things to come at the Max Planck Society
The molecular biologist hopes to inspire the next generation of scientists.
- Chris Woolston
-
Article |
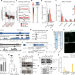 RNA nucleation by MSL2 induces selective X chromosome compartmentalization
RNA nucleation by MSL2 induces selective X chromosome compartmentalization
Dosage compensation in Drosophila involves nucleation of the dosage compensation complex at the X chromosome by MSL2 and the non-coding RNA roX.
- Claudia Isabelle Keller Valsecchi
- , M. Felicia Basilicata
- & Asifa Akhtar
-
Article |
 Epigenetic therapy induces transcription of inverted SINEs and ADAR1 dependency
Epigenetic therapy induces transcription of inverted SINEs and ADAR1 dependency
Inverted-repeat Alu elements are the main source of drug-induced immunogenic double-stranded RNAs, which are destabilized by the RNA deaminase ADAR1, thereby limiting activation of the immune response.
- Parinaz Mehdipour
- , Sajid A. Marhon
- & Daniel D. De Carvalho
-
Article |
 Structure of nucleosome-bound DNA methyltransferases DNMT3A and DNMT3B
Structure of nucleosome-bound DNA methyltransferases DNMT3A and DNMT3B
Catalytically inactive DNMT3B3 is crucial in de novo CpG methylation of DNA, interacting with the nucleosome core to orient catalytically active DNMT3A2 so that it can bind to nearby linker DNA.
- Ting-Hai Xu
- , Minmin Liu
- & Peter A. Jones
-
Article |
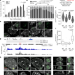 A protein assembly mediates Xist localization and gene silencing
A protein assembly mediates Xist localization and gene silencing
A protein condensate formed by multivalent interactions between the long non-coding RNA Xist and specific RNA-binding proteins drives the compartmentalization required to perpetuate gene silencing on the inactive X chromosome.
- Amy Pandya-Jones
- , Yolanda Markaki
- & Kathrin Plath
-
Article |
 C. elegans interprets bacterial non-coding RNAs to learn pathogenic avoidance
C. elegans interprets bacterial non-coding RNAs to learn pathogenic avoidance
Exposing Caenorhabditis elegans to non-coding small RNAs from pathogenic Pseudomonas aeruginosa induces avoidance behaviours in treated worms and their progeny, which reveals how C. elegans discriminates between bacterial species in its microbial environment.
- Rachel Kaletsky
- , Rebecca S. Moore
- & Coleen T. Murphy
-
Article |
 Epigenetic gene silencing by heterochromatin primes fungal resistance
Epigenetic gene silencing by heterochromatin primes fungal resistance
Fission yeast grown in sublethal levels of caffeine develop heterochromatin-dependent epimutations conferring unstable heritable gene silencing that conveys resistance to caffeine, while remaining genetically wild type.
- Sito Torres-Garcia
- , Imtiyaz Yaseen
- & Robin C. Allshire
-
Perspective |
 Perspectives on ENCODE
Perspectives on ENCODE
The authors summarize the history of the ENCODE Project, the achievements of ENCODE 1 and ENCODE 2, and how the new data generated and analysed in ENCODE 3 complement the previous phases.
- Federico Abascal
- , Reyes Acosta
- & Richard M. Myers
-
Article
| Open Access Spatiotemporal DNA methylome dynamics of the developing mouse fetus
Spatiotemporal DNA methylome dynamics of the developing mouse fetus
Analysis of 168 methylomes from 12 mouse tissues at 9 developmental stages sheds light on the epigenetic and regulatory landscape during mammalian fetal development.
- Yupeng He
- , Manoj Hariharan
- & Joseph R. Ecker
-
Article |
 MeCP2 links heterochromatin condensates and neurodevelopmental disease
MeCP2 links heterochromatin condensates and neurodevelopmental disease
The chromatin protein MeCP2 is a component of dynamic, liquid-like heterochromatin condensates, and the ability of MeCP2 to form condensates is disrupted by mutations in the MECP2 gene that occur in the neurodevelopmental disorder Rett syndrome.
- Charles H. Li
- , Eliot L. Coffey
- & Richard A. Young
-
Article |
 Histone H3.3 phosphorylation amplifies stimulation-induced transcription
Histone H3.3 phosphorylation amplifies stimulation-induced transcription
The histone variant H3.3 is phosphorylated at Ser31 in induced genes, and this selective mark stimulates the histone methyltransferase SETD2 and ejects the ZMYND11 repressor, thus revealing a role for histone phosphorylation in amplifying de novo transcription.
- Anja Armache
- , Shuang Yang
- & Steven Z. Josefowicz
-
Article |
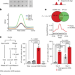 N6-methyladenine in DNA antagonizes SATB1 in early development
N6-methyladenine in DNA antagonizes SATB1 in early development
The DNA modification N6-methyladenine regulates gene expression during mouse trophoblast development by depositing at the boundaries of active chromatin and preventing its spread by antagonizing the chromatin organizer SATB1.
- Zheng Li
- , Shuai Zhao
- & Andrew Z. Xiao
-
Article |
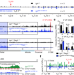 Wapl repression by Pax5 promotes V gene recombination by Igh loop extrusion
Wapl repression by Pax5 promotes V gene recombination by Igh loop extrusion
Pax5 regulates contraction of the immunoglobulin heavy chain (Igh) locus—an essential step in V(D)J recombination—by promoting chromatin loop extrusion via repression of Wapl expression.
- Louisa Hill
- , Anja Ebert
- & Meinrad Busslinger
-
News & Views |
 Genes silenced down the generations, thanks to tails on messenger RNA
Genes silenced down the generations, thanks to tails on messenger RNA
It emerges that strings of nucleotides are added to messenger RNAs that are undergoing silencing in nematode worms. The composition of these nucleotide tails promotes the formation of small RNAs that drive heritable gene regulation.
- Kailee J. Reed
- & Taiowa A. Montgomery
-
Article |
 poly(UG)-tailed RNAs in genome protection and epigenetic inheritance
poly(UG)-tailed RNAs in genome protection and epigenetic inheritance
In Caenorhabditis elegans, the ribonucleotidyltransferase RDE-3 adds alternating uridine and guanosine ribonucleotides to the 3′ termini of RNAs, a key step in RNA interference and thus epigenetic inheritance in the C. elegans germline.
- Aditi Shukla
- , Jenny Yan
- & Scott Kennedy

 Histone H2B.8 compacts flowering plant sperm through chromatin phase separation
Histone H2B.8 compacts flowering plant sperm through chromatin phase separation