Featured
-
-
Q&A
| Open Access A conversation about cultivated meat
A conversation about cultivated meat
Summary: Cultivated or cultured meat is promising to revolutionize the food industry in the coming years to decades, helping to resolve concerns related to the environmental impact and ethical implications linked to conventional meat production. We talked to Dr. Sandhya Sriram, the Group CEO and Co-founder of Shiok Meats Pte. Ltd., Singapore; Prof. Shulamit Levenberg, the former Dean of the Biomedical Engineering Department at the Technion, current Director of the Technion Center for 3D Bioprinting and The Rina & Avner Schneur Center for Diabetes Research, as well as the Co-founder and Chief Scientific Adviser of Aleph Farms, Israel; and Dr. Timothy Olsen, Head of Cultured Meat in the Life Science business at Merck KGaA, Germany; about this relatively new and quickly developing sector. They explain what their teams are working on, including the biggest recent accomplishments, speak about the main challenges facing the field and how they can be resolved, and share their visions about the future of cultivated meat, aiming to provide more equitable and sustainable access to nutritious food for the growing world population.
-
Article
| Open Access Uncertainties in deforestation emission baseline methodologies and implications for carbon markets
Uncertainties in deforestation emission baseline methodologies and implications for carbon markets
This study reveals high variability in deforestation emission baselines typically used to derive carbon credits, with median error at 0.778 times the actual rate. It underscores the need for enhanced methods to improve carbon market accuracy and reliability.
- Hoong Chen Teo
- , Nicole Hui Li Tan
- & Lian Pin Koh
-
Article
| Open Access Projecting future carbon emissions from cement production in developing countries
Projecting future carbon emissions from cement production in developing countries
The rapid deployment of low-carbon measures is urgently needed to reduce cement emissions as cement CO2 emissions from developing countries will almost deplete the remaining cement emissions budget within climate targets.
- Danyang Cheng
- , David M. Reiner
- & Dabo Guan
-
Article
| Open Access Interactions between climate change, urban infrastructure and mobility are driving dengue emergence in Vietnam
Interactions between climate change, urban infrastructure and mobility are driving dengue emergence in Vietnam
The geographic distribution of dengue has been expanding in recent decades, and Vietnam is one of the most severely affected countries. In this study, the authors use Bayesian hierarchical modelling to investigate the socio-environmental and climatic drivers of dengue incidence in Vietnam and how they vary across the country.
- Rory Gibb
- , Felipe J. Colón-González
- & Rachel Lowe
-
Article
| Open Access Deploying green hydrogen to decarbonize China’s coal chemical sector
Deploying green hydrogen to decarbonize China’s coal chemical sector
The coal chemical sector uses coal to produce chemicals and emits substantial greenhouse gases, which are hard to abate by electrification alone. Deploying green H2 for China’s coal chemical plants can reduce ~50% of emissions at a low cost.
- Yang Guo
- , Liqun Peng
- & Denise L. Mauzerall
-
Article
| Open Access Collaborative and privacy-preserving retired battery sorting for profitable direct recycling via federated machine learning
Collaborative and privacy-preserving retired battery sorting for profitable direct recycling via federated machine learning
Unsorted retired batteries pose recycling challenges due to diverse cathodes. Here, the authors propose a privacy-preserving machine learning system that enables accurate sorting with minimal data, important for a sustainable battery recycling industry.
- Shengyu Tao
- , Haizhou Liu
- & Hongbin Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring interactions between socioeconomic context and natural hazards on human population displacement
Exploring interactions between socioeconomic context and natural hazards on human population displacement
Ronco and colleagues analyze disaster-induced movements in the presence of floods, storms, and landslides during 2016–2021, providing empirical evidence that differential vulnerability exists and quantifying its extent. They achieve this by employing explainable machine learning techniques to model and understand internal displacement flows and patterns from observational data.
- Michele Ronco
- , José María Tárraga
- & Gustau Camps-Valls
-
Article
| Open Access Unveiling patterns in human dominated landscapes through mapping the mass of US built structures
Unveiling patterns in human dominated landscapes through mapping the mass of US built structures
Most inhabited areas in the US have more mass in buildings and mobility networks than in plant biomass. Cities are comparably resource efficient, while high material intensity is found in rural areas. Migration reinforces this phenomenon as people leave while built structures remain.
- David Frantz
- , Franz Schug
- & Helmut Haberl
-
Article
| Open Access Feasible supply of steel and cement within a carbon budget is likely to fall short of expected global demand
Feasible supply of steel and cement within a carbon budget is likely to fall short of expected global demand
A new study explores the global feasible supply of steel and cement within Paris-compliant carbon budgets, explicitly considering uncertainties in the deployment of infrastructure and it shows that feasible supply may fall short of expected global demand.
- Takuma Watari
- , André Cabrera Serrenho
- & Julian Allwood
-
Article
| Open Access The social costs of tropical cyclones
The social costs of tropical cyclones
The estimates of the societal costs of carbon currently used for policy evaluations may be too low due to an insufficient representation of tropical cyclone damage. Accounting for them substantially increases the estimated benefits of climate change mitigation measures.
- Hazem Krichene
- , Thomas Vogt
- & Christian Otto
-
Article
| Open Access Flood insurance is a driver of population growth in European floodplains
Flood insurance is a driver of population growth in European floodplains
This study finds that flood insurance policy design affects economic development in floodplains and, consequently, flood risk in Europe. Therefore, the authors advocate for flood insurance design to be integrated in climate change adaptation policy.
- Max Tesselaar
- , W. J. Wouter Botzen
- & Jeroen C. J. H. Aerts
-
Article
| Open Access A fish cartel for Africa
A fish cartel for Africa
Englander and Costello note that African coastal waters are among the world’s most biologically rich, but African countries earn much less than their peers from selling access to foreign fishers. They find forming a “fish cartel" would increase African fish biomass by 16% and profits by 23%.
- Gabriel Englander
- & Christopher Costello
-
Article
| Open Access Climate change beliefs and their correlates in Latin America
Climate change beliefs and their correlates in Latin America
The authors map beliefs in climate change and their correlates in Latin America. The study shows skepticism over the existence and anthropogenic origins of climate change to be limited, but identifies a high number of skeptics around the severity of its consequences. Results also show individualistic worldviews to be the most powerful driver of climate change beliefs in the region.
- Matias Spektor
- , Guilherme N. Fasolin
- & Juliana Camargo
-
Article
| Open Access Message framing to promote solar panels
Message framing to promote solar panels
Green technologies foster the use of green energy; however, large investment costs hinder adoption. In a large-scale field experiment, the authors show that message framing can promote a serious commitment to solar panels among the broader public.
- Dominik Bär
- , Stefan Feuerriegel
- & Markus Weinmann
-
Article
| Open Access Decarbonization potential of electrifying 50% of U.S. light-duty vehicle sales by 2030
Decarbonization potential of electrifying 50% of U.S. light-duty vehicle sales by 2030
Electric vehicle sales goals alone will not achieve light duty vehicle emissions targets. Other actions including decarbonizing the electric grid, mode shifting, vehicle downsizing, reducing travel demand, and accelerating fleet turnover, are needed.
- Maxwell Woody
- , Gregory A. Keoleian
- & Parth Vaishnav
-
Article
| Open Access Cumulative effect of PM2.5 components is larger than the effect of PM2.5 mass on child health in India
Cumulative effect of PM2.5 components is larger than the effect of PM2.5 mass on child health in India
Health impact of air pollution is estimated using PM2.5 mass as exposure metric. Here authors show that the impacts on child health is underestimated in India using this metric relative to the cumulative impact of the various PM2.5 components.
- Ekta Chaudhary
- , Franciosalgeo George
- & Unnati Mehta
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring decarbonization pathways for USA passenger and freight mobility
Exploring decarbonization pathways for USA passenger and freight mobility
Rapid adoption of zero-emission vehicles with a concurrent transition to clean electricity is essential to achieve U.S. transportation decarbonization goals. Managing travel demand can ease this transition by reducing the need for clean electricity supply. @cghoehne, @nrel, #NRELMobility
- Christopher Hoehne
- , Matteo Muratori
- & Ookie Ma
-
Article
| Open Access A super liquid-repellent hierarchical porous membrane for enhanced membrane distillation
A super liquid-repellent hierarchical porous membrane for enhanced membrane distillation
Membrane distillation is an emerging desalination technology to obtain freshwater from saline based on low-grade energy. Here the authors report on novel superhydrophobic hierarchical porous membranes with enhanced distillation flux suitable for desalination or wastewater treatment.
- Youmin Hou
- , Prexa Shah
- & Hans-Jürgen Butt
-
Article
| Open Access Urban land patterns can moderate population exposures to climate extremes over the 21st century
Urban land patterns can moderate population exposures to climate extremes over the 21st century
Considering changes in urban land extent, population, and climate over the 21st century, the authors find spatial urban land patterns can reduce rather than increase population exposures to climate extremes, even heat extremes, at regional scales.
- Jing Gao
- & Melissa S. Bukovsky
-
Article
| Open Access A human-machine collaborative approach measures economic development using satellite imagery
A human-machine collaborative approach measures economic development using satellite imagery
A human-AI collaborative computer vision algorithm produces grid-level economic statistics using satellite images and lightweight human annotation, revealing granular development patterns in North Korea and five other least developed Asian countries.
- Donghyun Ahn
- , Jeasurk Yang
- & Sungwon Park
-
Article
| Open Access Circular wood use can accelerate global decarbonisation but requires cross-sectoral coordination
Circular wood use can accelerate global decarbonisation but requires cross-sectoral coordination
Cascading and especially circular wood uses enhance climate-change mitigation achieved by forestry. In combination, these measures could cumulatively mitigate 258.8 million tonnes CO2e by 2050 in the UK but implementation barriers must be overcome.
- Eilidh J. Forster
- , John R. Healey
- & David Styles
-
Article
| Open Access The changing impact of rural electrification on Indian agriculture
The changing impact of rural electrification on Indian agriculture
Electrified groundwater irrigation is a major driver of India’s agricultural growth. India refocussed rural electrification towards household electrification in early 2000s in detriment of groundwater irrigation electrification, the authors find.
- Sudatta Ray
- & Hemant K. Pullabhotla
-
Article
| Open Access Impacts of climate change, population growth, and power sector decarbonization on urban building energy use
Impacts of climate change, population growth, and power sector decarbonization on urban building energy use
This study quantifies mid-21st century hourly building energy use in 277 urban areas in the USA, revealing spatially and temporally heterogeneous changes influenced by future climate, population dynamics, and electric power sector decarbonization.
- Chenghao Wang
- , Jiyun Song
- & Robert B. Jackson
-
Article
| Open Access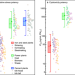 Achieving health-oriented air pollution control requires integrating unequal toxicities of industrial particles
Achieving health-oriented air pollution control requires integrating unequal toxicities of industrial particles
Health-oriented emissions reduction in China focusing on the iron and steel industry can reduce costs by 1.56 billion dollars while lowering the population-weighted toxic potency-adjusted exposure risk.
- Di Wu
- , Haotian Zheng
- & Jiming Hao
-
Article
| Open Access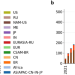 Concentration of asset owners exposed to power sector stranded assets may trigger climate policy resistance
Concentration of asset owners exposed to power sector stranded assets may trigger climate policy resistance
Von Dulong analyzes owners and incidence of asset stranding in the power sector globally. She shows that Asia-Pacific, Europe, and the US are highly exposed to stranded assets, especially coal plants and explores the linkages between asset stranding and climate policy resistance.
- Angelika von Dulong
-
Article
| Open Access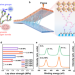 Hyperbranched polymer functionalized flexible perovskite solar cells with mechanical robustness and reduced lead leakage
Hyperbranched polymer functionalized flexible perovskite solar cells with mechanical robustness and reduced lead leakage
The low adhesive fracture energy of electron transport layer/perovskite interface makes it prone to delamination under mechanical stress. Here, authors develop polyamide-amine-based hyperbranched polymer to provide strong adhesion, leading to device efficiency of over 25% for perovskite solar cells.
- Zhihao Li
- , Chunmei Jia
- & Zhen Li
-
Article
| Open Access Improved human greenspace exposure equality during 21st century urbanization
Improved human greenspace exposure equality during 21st century urbanization
A study of 1,028 global cities from 2000-2018 shows increased human exposure to greenspace, reducing greenspace inequality. Notably, cities in the Global South improved nearly four times faster than those in the Global North. These insights can guide city greening strategies.
- Shengbiao Wu
- , Bin Chen
- & Peng Gong
-
Article
| Open Access An early warning signal for grassland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau
An early warning signal for grassland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau
Livestock grazing may drive grassland degradation. Here, the authors use process-based modelling validated with empirical data to define a stocking rate threshold across grassland on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, identify vulnerable areas and predict threshold shifts under future climate scenarios.
- Qiuan Zhu
- , Huai Chen
- & Yanfen Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Achieving decent living standards in emerging economies challenges national mitigation goals for CO2 emissions
Achieving decent living standards in emerging economies challenges national mitigation goals for CO2 emissions
Achieving decent living standards for global emerging economies is estimated to lead to an additional 8.6 Gt of CO2 emission with more than half of emerging economies emitting additional CO2 more than the value of their emission reduction commitments
- Jingwen Huo
- , Jing Meng
- & Dabo Guan
-
Article
| Open Access The global and regional air quality impacts of dietary change
The global and regional air quality impacts of dietary change
Food production, especially of animal products, is a major source of air pollutants. Here, the authors quantify the impacts dietary changes towards more plant-based diets could have for air quality, labour productivity, and human health.
- Marco Springmann
- , Rita Van Dingenen
- & Adrian Leip
-
Article
| Open Access Sustainably developing global blue carbon for climate change mitigation and economic benefits through international cooperation
Sustainably developing global blue carbon for climate change mitigation and economic benefits through international cooperation
Sustainable development of blue carbon has increased globally over the past two decades. Global cooperation could enable countries to improve blue carbon sustainable development, increase carbon sequestration, and generate up to $136.34 million in 2030 in economic benefits.
- Cuicui Feng
- , Guanqiong Ye
- & Zhenci Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Costs and health benefits of the rural energy transition to carbon neutrality in China
Costs and health benefits of the rural energy transition to carbon neutrality in China
Electric cooking and air-to-air heat pump adoption in China advances carbon neutrality and the rural energy transition, with the transformation costs offset by monetized health benefits in most provinces.
- Teng Ma
- , Silu Zhang
- & Yang Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Reducing risks of antibiotics to crop production requires land system intensification within thresholds
Reducing risks of antibiotics to crop production requires land system intensification within thresholds
Crop intensification has increased agricultural production albeit with an increase in field antibiotic pollution. Here, Chen et al. project how antibiotic pollution undermines production and how intensification needs to be kept below a threshold.
- Fangkai Zhao
- , Lei Yang
- & Liding Chen
-
Article
| Open Access The neglected role of abandoned cropland in supporting both food security and climate change mitigation
The neglected role of abandoned cropland in supporting both food security and climate change mitigation
This work demonstrates how global abandoned cropland is an untapped land resource. If recultivated and reforested strategically, it can provide substantial carbon sequestration and food production potential to support our shared climate and food security goals.
- Qiming Zheng
- , Tim Ha
- & Lian Pin Koh
-
Article
| Open Access Location is a major barrier for transferring US fossil fuel employment to green jobs
Location is a major barrier for transferring US fossil fuel employment to green jobs
This study tests the case for the absorption of current fossil fuel workers in emerging green jobs from the perspective of their skills and location. It finds location to be a barrier in a Just Transition for these workers.
- Junghyun Lim
- , Michaël Aklin
- & Morgan R. Frank
-
Article
| Open Access A net-zero emissions strategy for China’s power sector using carbon-capture utilization and storage
A net-zero emissions strategy for China’s power sector using carbon-capture utilization and storage
This study indicates that allowing up to 20% abated fossil fuel in China’s power generation system could reduce the power shortage rate by up to 9% in 2050, and increase system resilience during weather events relative to a zero fossil fuel system.
- Jing-Li Fan
- , Zezheng Li
- & Bo Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Causal inference from cross-sectional earth system data with geographical convergent cross mapping
Causal inference from cross-sectional earth system data with geographical convergent cross mapping
Temporal causation models perform poorly in causal inference for variables with limited temporal variations. This paper establishes a causal inference model, which can reveal the nonlinear complex casual associations based on cross-sectional Earth System data.
- Bingbo Gao
- , Jianyu Yang
- & Jinfeng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Global fossil fuel reduction pathways under different climate mitigation strategies and ambitions
Global fossil fuel reduction pathways under different climate mitigation strategies and ambitions
An analysis of the IPCC AR6 scenarios database explores how quickly coal, oil, and gas production and use should be reduced in line with net-zero goals, and points to the need to adopt phase-out benchmarks alongside other climate mitigation targets.
- Ploy Achakulwisut
- , Peter Erickson
- & Steve Pye
-
Article
| Open Access Feeding climate and biodiversity goals with novel plant-based meat and milk alternatives
Feeding climate and biodiversity goals with novel plant-based meat and milk alternatives
Meat and dairy alternatives are promoted for diet sustainability. Here, the authors use a modelling approach to show that replacing 50% of pork, chicken, beef and milk globally with plant-based alternatives can reduce GHG emissions by 6.3 Gt CO2eq year-1 and more than half biodiversity loss by 2050.
- Marta Kozicka
- , Petr Havlík
- & Noel Gurwick
-
Article
| Open Access Global land and water limits to electrolytic hydrogen production using wind and solar resources
Global land and water limits to electrolytic hydrogen production using wind and solar resources
This study composes a country-specific analysis of land and water requirements for electrolytic hydrogen production, revealing nations constrained in achieving self-sufficiency in hydrogen supply and nations who can become hydrogen exporters.
- Davide Tonelli
- , Lorenzo Rosa
- & Francesco Contino
-
Article
| Open Access Sustainable reference points for multispecies coral reef fisheries
Sustainable reference points for multispecies coral reef fisheries
The sustainability of the majority of multispecies reef fisheries around the globe remains unassessed. This study provides context-specific sustainable reference points for coral reef fish using environmental conditions. Using these reference points, they show that most reef fish stocks have failed at least one fisheries sustainability benchmark.
- Jessica Zamborain-Mason
- , Joshua E. Cinner
- & Sean R. Connolly
-
Article
| Open Access Inherent spatiotemporal uncertainty of renewable power in China
Inherent spatiotemporal uncertainty of renewable power in China
Renewable uncertainty analysis is vital for stochastic-aware research. This study generates a benchmark dataset of year-long hourly renewable prediction errors in China, and reveals the law of the spatiotemporal distribution of renewable uncertainty.
- Jianxiao Wang
- , Liudong Chen
- & Guannan He
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid increase in the risk of heat-related mortality
Rapid increase in the risk of heat-related mortality
The risk of heat-mortality is increasing sharply. The authors report that heat-mortality levels of a 1-in-100-year summer in the climate of 2000 can be expected once every ten to twenty years in the current climate and at least once in five years with 2 °C of global warming.
- Samuel Lüthi
- , Christopher Fairless
- & Ana M. Vicedo-Cabrera
-
Article
| Open Access The cost of electrifying all households in 40 Sub-Saharan African countries by 2030
The cost of electrifying all households in 40 Sub-Saharan African countries by 2030
Solar-powered standalone systems drastically lower the cost of electrifying sub-Saharan Africa. Household electrification can be provided at 7c USD per person per day on average. To reflect inter- and intra-country variance, policymakers should consider electrification cost curves.
- Florian Egli
- , Churchill Agutu
- & Tobias S. Schmidt
-
Article
| Open Access Truck platooning reshapes greenhouse gas emissions of the integrated vehicle-road infrastructure system
Truck platooning reshapes greenhouse gas emissions of the integrated vehicle-road infrastructure system
Truck platooning allows for trucks to travel synchronously in close proximity to improve fuel efficiency. Here, authors evaluate the decarbonization effects of platooning on the vehicle-road system at a large-scale road network level revealing a trade-off between emission reduction and cost rise.
- Huailei Cheng
- , Yuhong Wang
- & Tian Jin
-
Article
| Open Access A lignin-derived material improves plant nutrient bioavailability and growth through its metal chelating capacity
A lignin-derived material improves plant nutrient bioavailability and growth through its metal chelating capacity
Biorefinery lignin waste has little value in the market. Here, Liu et al. find that water-soluble lignin, converted from sulfuric acid lignin, improves plant iron bioavailability and growth through a metal chelating capacity comparable to the metal chelator EDTA.
- Qiang Liu
- , Tsubasa Kawai
- & Baohai Li
-
Article
| Open Access How climate policy commitments influence energy systems and the economies of US states
How climate policy commitments influence energy systems and the economies of US states
In the US, states vary in their efforts to address climate change. Stronger state climate policies reduce CO2 emissions without harming the economy, but these reductions are unlikely to meet the goals in the Paris Climate Accord.
- Parrish Bergquist
- & Christopher Warshaw
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery and rational engineering of PET hydrolase with both mesophilic and thermophilic PET hydrolase properties
Discovery and rational engineering of PET hydrolase with both mesophilic and thermophilic PET hydrolase properties
Extensive research efforts have been directed towards the development of PET hydrolases with improved activity, but template enzymes used are limited. Here, the authors report a PET hydrolase from Cryptosporangium aurantiacum (CaPETase) that exhibits high thermostability and PET degradation activity at ambient temperatures and determine its crystal structure.
- Hwaseok Hong
- , Dongwoo Ki
- & Kyung-Jin Kim
-
Article
| Open Access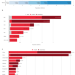 Global air pollution exposure and poverty
Global air pollution exposure and poverty
This study shows that 716 million of the world’s lowest income people live in areas with unsafe levels of air pollution, especially in Sub-Saharan Africa. With limited access to healthcare, they are especially vulnerable.
- Jun Rentschler
- & Nadezda Leonova

 Approaching national climate targets in China considering the challenge of regional inequality
Approaching national climate targets in China considering the challenge of regional inequality