Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal nuclei templated nanostructured membranes prepared by solvent crystallization and polymer migration
Crystal nuclei templated nanostructured membranes prepared by solvent crystallization and polymer migration
Conventionally porous polymeric membranes for filtration are produced by phase-separation techniques, but this process has reached saturation. Here, Li and co-workers developed a manufacturing process involving oriented green solvent crystallization and polymer migration to form high-performance membranes.
- Bo Wang
- , Jing Ji
- & Kang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling the motion of multiple objects on a Chladni plate
Controlling the motion of multiple objects on a Chladni plate
Moving particles on a vibrating plate dates back to 1780s, but it is still challenging to control individual particles in a parallel way. Here, Zhou et al. use a single acoustic actuator and an algorithm to control multiple objects simultaneously and independently for sorting and pattern formation.
- Quan Zhou
- , Veikko Sariola
- & Ville Liimatainen
-
Article
| Open Access Terahertz time-gated spectral imaging for content extraction through layered structures
Terahertz time-gated spectral imaging for content extraction through layered structures
Terahertz radiation may be used to nondestructively detect and study defects and structures within materials. Here the authors use terahertz time-gated spectral imaging to extract occluded text from paper pages with subwavelength spacing.
- Albert Redo-Sanchez
- , Barmak Heshmat
- & Ramesh Raskar
-
Article
| Open Access Non-destructive imaging of buried electronic interfaces using a decelerated scanning electron beam
Non-destructive imaging of buried electronic interfaces using a decelerated scanning electron beam
Imaging buried interfaces is necessary to assess the quality of electronic devices and their degradation mechanisms. Here, Hirohata et al. use energy-filtered scanning electron microscopy to image buried defects in an inorganic lateral spin-valve device, at the nanometre scale and non-destructively.
- Atsufumi Hirohata
- , Yasuaki Yamamoto
- & Andrew J. Vick
-
Article
| Open Access Two-terminal floating-gate memory with van der Waals heterostructures for ultrahigh on/off ratio
Two-terminal floating-gate memory with van der Waals heterostructures for ultrahigh on/off ratio
Traditional non-volatile memories suffer from poor scalability in the vertical direction due to the use of a bulky oxide layer. Here, the authors develop a tunnelling random access memory using a vertical heterostructure composed of atomically thin molybdenum disulfide, boron nitride and graphene.
- Quoc An Vu
- , Yong Seon Shin
- & Woo Jong Yu
-
Review Article
| Open Access Photon management for augmented photosynthesis
Photon management for augmented photosynthesis
Photosynthetic microalgae could provide an ecologically sustainable route to produce solar biofuels and high-value chemicals. Here, the authors review various optical management strategies used to manipulate the incident light in order to increase the efficiency of microalgae biofuel production.
- Matthew D. Ooms
- , Cao Thang Dinh
- & David Sinton
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancing droplet deposition through in-situ precipitation
Enhancing droplet deposition through in-situ precipitation
The extensive use of pesticides in agriculture calls for efficient spraying techniques to reduce pollution of soils and groundwater by toxic chemicals. Damak et al. simultaneously spray liquids containing oppositely charged polyelectrolytes that form defects, pinning droplets on targeted surfaces.
- Maher Damak
- , Md Nasim Hyder
- & Kripa K. Varanasi
-
Article
| Open Access Asymmetric synthesis using chiral-encoded metal
Asymmetric synthesis using chiral-encoded metal
Chiral compounds are extremely important as they can be used in medicine, agriculture and biotechnology. Here, Kuhn and co-workers use a mesoporous metal structure encoded with chiral information in order to induce asymmetry in electrochemical synthesis of mandelic acid.
- Thittaya Yutthalekha
- , Chularat Wattanakit
- & Alexander Kuhn
-
Article
| Open Access Electrolysis of a molten semiconductor
Electrolysis of a molten semiconductor
Conventional metal extraction processes rely on energy intensive pyro- or hydrometallurgical methods which generate pollutants. Here, the authors reveal a high-throughput electro-desulfurization process to convert molten stibnite to pure antimony in a single step, reducing emissions and energy consumption.
- Huayi Yin
- , Brice Chung
- & Donald R. Sadoway
-
Article
| Open Access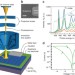 Quantifying redox-induced Schottky barrier variations in memristive devices via in operando spectromicroscopy with graphene electrodes
Quantifying redox-induced Schottky barrier variations in memristive devices via in operando spectromicroscopy with graphene electrodes
Resistive switching in metal oxides is related to the migration of donor defects. Here Baeumer et al. use in operandoX-ray spectromicroscopy to quantify the doping locally and show that small local variations in the donor concentration result in large variations in the device resistance.
- Christoph Baeumer
- , Christoph Schmitz
- & Regina Dittmann
-
Article
| Open Access Ionic imbalance induced self-propulsion of liquid metals
Ionic imbalance induced self-propulsion of liquid metals
The control over the motion and deformation of liquid droplets is essential to many microfluidic and actuation systems. Zavabeti et al. demonstrate that applying a pH or ionic gradient across a droplet of liquid metal alloy of gallium results in its motion due to a breaking of the surface charge symmetry.
- Ali Zavabeti
- , Torben Daeneke
- & Kourosh Kalantar-zadeh
-
Article
| Open Access Mass production of shaped particles through vortex ring freezing
Mass production of shaped particles through vortex ring freezing
The evolution of vortex flow exhibits a rich spectrum of complicated geometries. Here, An et al. utilize these features to control and mass produce inorganic and organic particles via an electrospraying process, whereby the shape of vortex rings translates into particles during a freezing process.
- Duo An
- , Alex Warning
- & Minglin Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Shape-shifting colloids via stimulated dewetting
Shape-shifting colloids via stimulated dewetting
Mimicking the intrinsic adaptability of biological systems in synthetic materials has been a challenge. Here, Sacanna and co-workers have used dewetting forces between an oil phase and solid colloidal substrate to facilitate shape shifting particles that can change geometry by chemical and optical signals.
- Mena Youssef
- , Theodore Hueckel
- & Stefano Sacanna
-
Article
| Open Access Piezoelectric enhancement under negative pressure
Piezoelectric enhancement under negative pressure
Recently, negative pressure has been observed in perovskite nanowires by annealing the wires from a lower-density phase. Here, the authors show that the negative pressure enhances the piezoelectric coefficient of PbTiO3 and Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 nanowires experimentally and by ab initiocalculations.
- Alexander Kvasov
- , Leo J. McGilly
- & Nava Setter
-
Article
| Open Access Rational design of carbon nitride photocatalysts by identification of cyanamide defects as catalytically relevant sites
Rational design of carbon nitride photocatalysts by identification of cyanamide defects as catalytically relevant sites
Graphitic carbon nitride is a promising hydrogen evolution photocatalyst, although there is limited understanding of its mechanistic operation. Here, the authors employ molecular heptazine-based model catalysts to identify catalytically relevant defects and to rationally design a highly active carbon nitride photocatalyst.
- Vincent Wing-hei Lau
- , Igor Moudrakovski
- & Bettina V. Lotsch
-
Article
| Open Access Surface engineering of hierarchical platinum-cobalt nanowires for efficient electrocatalysis
Surface engineering of hierarchical platinum-cobalt nanowires for efficient electrocatalysis
Platinum-based nanowires are promising for fuel cell applications due to their high catalytic activity. Here the authors report on hierarchical platinum-cobalt nanowires with high-index facets showing specific/mass activities for oxygen reduction reaction 39.6/33.7 times higher than commercial Pt/C catalyst.
- Lingzheng Bu
- , Shaojun Guo
- & Xiaoqing Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Loss-tolerant state engineering for quantum-enhanced metrology via the reverse Hong–Ou–Mandel effect
Loss-tolerant state engineering for quantum-enhanced metrology via the reverse Hong–Ou–Mandel effect
N00N states are promising for quantum communications and metrology, but are vulnerable to losses. Here the authors develop a technique for preparing high-fidelity two-photon N00N states in a loss-free fashion, and demonstrate enhanced phase sensitivity without requiring recombination.
- Alexander E. Ulanov
- , Ilya A. Fedorov
- & A. I. Lvovsky
-
Article
| Open Access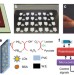 A wearable chemical–electrophysiological hybrid biosensing system for real-time health and fitness monitoring
A wearable chemical–electrophysiological hybrid biosensing system for real-time health and fitness monitoring
Wearable sensors can provide continuous, convenient feedback for users but typically focus on a small number of physiological parameters. Here, the authors report a skin-worn sensing system that combines a biosensor for lactate detection with an electrocardiogram in one patch, with applications for exercise monitoring.
- Somayeh Imani
- , Amay J. Bandodkar
- & Patrick P. Mercier
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering electrocatalytic activity in nanosized perovskite cobaltite through surface spin-state transition
Engineering electrocatalytic activity in nanosized perovskite cobaltite through surface spin-state transition
The activity of electrocatalysts exhibits a strong dependence on their electronic structures. Here, the authors manipulate the eg filling of perovskite cobaltite LaCoO3nanoparticles by changing particle size and show improved oxygen evolution activity with increased numbers of surface high-spin cobalt ions.
- Shiming Zhou
- , Xianbing Miao
- & Jie Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable graphene micro-emitters with fast temporal response and controllable electron emission
Tunable graphene micro-emitters with fast temporal response and controllable electron emission
Controlling the electron emission of microfabricated field emitters can be challenging. Here the authors report controllable and tunable graphene thermionic micro-emitters with well-defined turn-on voltages and switching times in the microsecond range and fabricate uniform micro-emitter arrays.
- Gongtao Wu
- , Xianlong Wei
- & Lianmao Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Viscoelastic lithography for fabricating self-organizing soft micro-honeycomb structures with ultra-high aspect ratios
Viscoelastic lithography for fabricating self-organizing soft micro-honeycomb structures with ultra-high aspect ratios
Tissue engineering applications call for controllable micro-structural units as a platform, but their fabrication remains challenging. Here, Jeong et al. show a method that enables soft materials to self-organize into highly packed micro-honeycomb structures with aspect ratios up to 500, and tunable shapes.
- Gi Seok Jeong
- , Da Yoon No
- & Sang-Hoon Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Mode engineering for realistic quantum-enhanced interferometry
Mode engineering for realistic quantum-enhanced interferometry
Quantum interferometry suffers from residual distinguishability between input photons. Here, the authors show theoretically and experimentally, in a two-photon measurement, how to overcome this by manipulating additional degrees of freedom.
- Michał Jachura
- , Radosław Chrapkiewicz
- & Konrad Banaszek
-
Article
| Open Access Screen-printed flexible MRI receive coils
Screen-printed flexible MRI receive coils
Signal-to-noise ratio is one of the key factors that currently limit the diagnostic image quality and patient conditions of magnetic resonance imaging. Here, Corea et al. use fully printed flexible receive coils, conforming to patient bodies, to improve signals and patient comfort in clinical scanners.
- Joseph R. Corea
- , Anita M. Flynn
- & Ana C. Arias
-
Article
| Open Access Designing high-performance layered thermoelectric materials through orbital engineering
Designing high-performance layered thermoelectric materials through orbital engineering
Thermoelectric materials with enhanced performances need to be identified. Here, the authors use the crystal field splitting energy of orbitals as a descriptor to design thermoelectric materials by solid solution maps and strain engineering in layered CaAl2Si2-type Zintl compounds.
- Jiawei Zhang
- , Lirong Song
- & Bo B. Iversen
-
Article
| Open Access Highly robust crystalsome via directed polymer crystallization at curved liquid/liquid interface
Highly robust crystalsome via directed polymer crystallization at curved liquid/liquid interface
Self-assemblies of polymers to form polymersomes in solution can be used as carriers for drug delivery, but it is challenging to control polymer crystallization to improve their mechanical stability. Here, Wang et al.show the formation of nanosized crystalsomes composed of polymer lamellar single crystals.
- Wenda Wang
- , Hao Qi
- & Christopher Y. Li
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering of frustration in colloidal artificial ices realized on microfeatured grooved lattices
Engineering of frustration in colloidal artificial ices realized on microfeatured grooved lattices
Visualizing the dynamics of electron spins in frustrated systems is a challenging task, which may require an alternative way at the microscale. Here, the authors realize an artificial system composed of interacting colloidal particles to mimick frustrated spins, which is potentially helpful in information storage.
- Antonio Ortiz-Ambriz
- & Pietro Tierno
-
Article
| Open Access Aqueous multiphoton lithography with multifunctional silk-centred bio-resists
Aqueous multiphoton lithography with multifunctional silk-centred bio-resists
Scientists are increasingly realising the potential for natural materials in micro- and nanofabrication. Here, the authors employ silk-based resists for aqueous multiphoton lithography towards generating intricate structures by femtosecond direct writing.
- Yun-Lu Sun
- , Qi Li
- & Hong-Bo Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible lithium–oxygen battery based on a recoverable cathode
Flexible lithium–oxygen battery based on a recoverable cathode
Flexible energy storage systems usually have limited energy densities. Here the authors report a flexible lithium–oxygen battery with the cathode consisting of titanium dioxide nanowire arrays grown on carbon textiles, which displays high mechanical strength as well as promising electrochemical performance.
- Qing-Chao Liu
- , Ji-Jing Xu
- & Xin-Bo Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance n-type black phosphorus transistors with type control via thickness and contact-metal engineering
High-performance n-type black phosphorus transistors with type control via thickness and contact-metal engineering
Black phosphorus p-type field-effect switching was previously demonstrated, but type control has proven difficult. Here, the authors create n-type black phosphorus Schottky field-effect transistors in which the polarity is controlled via contact-metal engineering and changing the flake thickness.
- David J. Perello
- , Sang Hoon Chae
- & Young Hee Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Band structure engineering via piezoelectric fields in strained anisotropic CdSe/CdS nanocrystals
Band structure engineering via piezoelectric fields in strained anisotropic CdSe/CdS nanocrystals
Quantum dots confine electrons to a nanometre length scale, and this gives rise to numerous quantum effects. Here, the authors directly control the excitonic structure of nanocrystal quantum dots by manipulating intra-particle piezoelectric fields.
- Sotirios Christodoulou
- , Fernando Rajadell
- & Iwan Moreels
-
Article |
 Engineering near-infrared single-photon emitters with optically active spins in ultrapure silicon carbide
Engineering near-infrared single-photon emitters with optically active spins in ultrapure silicon carbide
Single-photon quantum emitters with optically active spins are desirable for quantum information processing, secure networks and nanosensing, but engineering of these spin centres has been challenging. Here, Fuch et al. demonstrate the control of spin centre density in silicon carbide over eight orders of magnitude.
- F. Fuchs
- , B. Stender
- & G. V. Astakhov
-
Article
| Open Access Large Seebeck effect by charge-mobility engineering
Large Seebeck effect by charge-mobility engineering
The Seebeck effect causes an electrical potential across a temperature gradient in a material, and is therefore useful for generating useful current from waste heat. Here, the authors show that the Seebeck effect can arise due to charge-carrier relaxation in addition to the conventional mechanism.
- Peijie Sun
- , Beipei Wei
- & Frank Steglich
-
Article
| Open Access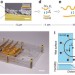 Scaling up nanoscale water-driven energy conversion into evaporation-driven engines and generators
Scaling up nanoscale water-driven energy conversion into evaporation-driven engines and generators
Harvesting energy from evaporation is constrained by the limited transport kinetics of materials and the slowly changing humidity of the environment. Chen et al. follow hierarchical design strategies to overcome these problems and create engines that start and run when placed at air-water interfaces.
- Xi Chen
- , Davis Goodnight
- & Ozgur Sahin
-
Article
| Open Access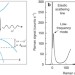 Electronic Raman scattering as an ultra-sensitive probe of strain effects in semiconductors
Electronic Raman scattering as an ultra-sensitive probe of strain effects in semiconductors
Engineering strain in semiconductor structures provides additional control over the optical and electronic properties, which is promising for device applications. Fluegel et al. show that electronic Raman scattering provides a route to sensitively measure the degree of strain in thin semiconductor layers.
- Brian Fluegel
- , Aleksej V. Mialitsin
- & Angelo Mascarenhas
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring the quantum critical behaviour in a driven Tavis–Cummings circuit
Exploring the quantum critical behaviour in a driven Tavis–Cummings circuit
Quantum phase transitions are a discontinuous change in a property of the ground state or the structure of the excited states as a system parameter traverses a critical point. Here, the authors recreate analogous effects with laboratory-achievable light-matter coupling in an on-chip superconducting circuit
- M. Feng
- , Y.P. Zhong
- & H. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Perovskite–fullerene hybrid materials suppress hysteresis in planar diodes
Perovskite–fullerene hybrid materials suppress hysteresis in planar diodes
Metal halide perovskites are promising for solar energy harvesting, but currently prone to a large hysteresis and current instability. Here, Xu et al. show improvements in a hybrid material in which the fullerene is distributed at perovskite grain boundaries and thus passivates defects effectively.
- Jixian Xu
- , Andrei Buin
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article
| Open Access Soft network composite materials with deterministic and bio-inspired designs
Soft network composite materials with deterministic and bio-inspired designs
Soft biological composites have great potential in areas such as artificial tissue constructs and bio-integrated devices, but receive little attention. Here, the authors design soft biomimetic materials that can precisely reproduce the non-linear mechanics of relevant biological materials.
- Kyung-In Jang
- , Ha Uk Chung
- & John A. Rogers
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-nanosecond signal propagation in anisotropy-engineered nanomagnetic logic chains
Sub-nanosecond signal propagation in anisotropy-engineered nanomagnetic logic chains
Closely-spaced anisotropically-engineered single-domain nanomagnets may be exploited to encode and transmit binary information. Here, Gu et al. use time-resolved X-ray microscopy to image signal propagation at the intrinsic nanomagnetic switching limit in permalloy nanomagnet chains.
- Zheng Gu
- , Mark E. Nowakowski
- & Jeffrey Bokor
-
Article |
 Long-living terahertz magnons in ultrathin metallic ferromagnets
Long-living terahertz magnons in ultrathin metallic ferromagnets
The technological application of ultrafast terahertz magnons in itinerant ferromagnetic nanostructures is currently limited by magnon relaxation due to Landau damping. Here, Qin et al. demonstrate suppressed Landau damping and enhanced magnon lifetimes in ultrathin films of Fe–Pd alloy.
- H. J. Qin
- , Kh. Zakeri
- & J. Kirschner
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering two-dimensional superconductivity and Rashba spin–orbit coupling in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 quantum wells by selective orbital occupancy
Engineering two-dimensional superconductivity and Rashba spin–orbit coupling in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 quantum wells by selective orbital occupancy
Two-dimensional electron gases at oxide interfaces induce exotic behaviours. By studying samples with different crystal orientation, Herranz et al.show that the extension and anisotropy of the oxide quantum well properties can be controlled through selective sub-band filling via orientational tuning.
- Gervasi Herranz
- , Gyanendra Singh
- & Josep Fontcuberta
-
Article |
 Optical focusing deep inside dynamic scattering media with near-infrared time-reversed ultrasonically encoded (TRUE) light
Optical focusing deep inside dynamic scattering media with near-infrared time-reversed ultrasonically encoded (TRUE) light
Shaping the incident wavefront allows optical focusing deep inside scattering media, but its application in dynamic media is hindered by its low speed. Here, Liu et al. improve the speed by two orders of magnitude and demonstrate in vivolight focusing inside dynamic scattering media.
- Yan Liu
- , Puxiang Lai
- & Lihong V. Wang
-
Article |
 Engineering interlocking DNA rings with weak physical interactions
Engineering interlocking DNA rings with weak physical interactions
Catenanes are structures composed of interlocked supramolecular rings, and they have possible applications as molecular switches and nanomotors. Here, the authors present a catenane formed of interlocked DNA rings, and show how each ring can display independent functionalities.
- Zai-Sheng Wu
- , Zhifa Shen
- & Yingfu Li
-
Article |
 How dead ends undermine power grid stability
How dead ends undermine power grid stability
The cheapest way to add new power stations to a domestic power grid is by tree-like connections to the network. A numerical basin stability analysis of Menck et al.suggests that this undermines a grid’s stability against blackouts but can be fixed with extra transmission lines to these otherwise ‘dead ends’.
- Peter J. Menck
- , Jobst Heitzig
- & Hans Joachim Schellnhuber
-
Article |
 Transforming moiré blisters into geometric graphene nano-bubbles
Transforming moiré blisters into geometric graphene nano-bubbles
Strain engineering has been proposed as a promising strategy for manipulating the electronic properties of graphene. This scanning tunnelling microscopy study demonstrates the feasibility of controlling strain patterns in graphene down to the nanoscale.
- Jiong Lu
- , A.H. Castro Neto
- & Kian Ping Loh
-
Article |
 Low-concentration mechanical biosensor based on a photonic crystal nanowire array
Low-concentration mechanical biosensor based on a photonic crystal nanowire array
Nanomechanical resonators are attractive as ultra-low concentration sensors of biomolecules, as their small scale allows for sensitive mass detection. Here, using a nanowire array as part of a photonic crystal, such a device is presented for light trapping, absorption and low-concentration sensing.
- Yuerui Lu
- , Songming Peng
- & Amit Lal
-
Article
| Open Access Pore surface engineering in covalent organic frameworks
Pore surface engineering in covalent organic frameworks
Covalent organic frameworks form a porous skeleton with a precise pore size and geometry, but control of the pore surface is challenging. Here, a protocol is introduced for pore surface engineering of covalent organic frameworks, allowing the control of composition and density of organic groups in the pores.
- Atsushi Nagai
- , Zhaoqi Guo
- & Donglin Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering modular and orthogonal genetic logic gates for robust digital-like synthetic biology
Engineering modular and orthogonal genetic logic gates for robust digital-like synthetic biology
Biological digital sensors require the fabrication of modular genetic logic gates. Using thePseudomonas syringae hrpsystem, Wang and colleagues generate AND, NOT and NAND gates, demonstrating the ability to engineer a modular system from biological elements.
- Baojun Wang
- , Richard I Kitney
- & Martin Buck
-
Article
| Open Access Mediatorless high-power glucose biofuel cells based on compressed carbon nanotube-enzyme electrodes
Mediatorless high-power glucose biofuel cells based on compressed carbon nanotube-enzyme electrodes
Glucose biofuel cells can be used to produce clean energy from renewable sources, but their use is limited by poor stability and low power output. In this study, bioelectrodes are fabricated using carbon nanotubes and the resulting biofuel cells have improved stability and power.
- Abdelkader Zebda
- , Chantal Gondran
- & Serge Cosnier
-
Article |
 Engineering biosynthetic excitable tissues from unexcitable cells for electrophysiological and cell therapy studies
Engineering biosynthetic excitable tissues from unexcitable cells for electrophysiological and cell therapy studies
Patch-clamp recordings are used to study the function of ion channels, but the method does not allow the assessment of tissue-level function. Kirkton and Bursac introduce a biosynthetic system for the study of channel activity and electrical conduction, facilitating studies of ion channel function.
- Robert D. Kirkton
- & Nenad Bursac

 Intercalated water layers promote thermal dissipation at bio–nano interfaces
Intercalated water layers promote thermal dissipation at bio–nano interfaces