Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Climbing favours the tripod gait over alternative faster insect gaits
Climbing favours the tripod gait over alternative faster insect gaits
Numerous selective forces shape animal locomotion patterns and as a result, different animals evolved to use different gaits. Here, Ramdyaet al. use live and in silicoDrosophila, as well as an insect-model robot, to gain insights into the conditions that promote the ubiquitous tripod gait observed in most insects.
- Pavan Ramdya
- , Robin Thandiackal
- & Dario Floreano
-
Article
| Open Access Reversed thermo-switchable molecular sieving membranes composed of two-dimensional metal-organic nanosheets for gas separation
Reversed thermo-switchable molecular sieving membranes composed of two-dimensional metal-organic nanosheets for gas separation
Reducing membrane thickness to nanometre scale should increase the throughput of gas separation sieves. Here, the authors report a sieving membrane composed of two-dimensional metal-organic framework nanosheets, exhibiting both high permeation flux and thermally switchable behaviour.
- Xuerui Wang
- , Chenglong Chi
- & Dan Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access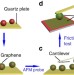 Robust microscale superlubricity under high contact pressure enabled by graphene-coated microsphere
Robust microscale superlubricity under high contact pressure enabled by graphene-coated microsphere
Superlubricity can be unstable in graphene systems, especially under high applied loads. Here the authors use microspheres uniformly coated by graphene to measure friction between 2D materials and show that superlow friction is preserved for long periods of time under high loads and various atmospheres.
- Shu-Wei Liu
- , Hua-Ping Wang
- & Jianbin Luo
-
Article
| Open Access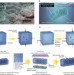 Hydraulic hydrogel actuators and robots optically and sonically camouflaged in water
Hydraulic hydrogel actuators and robots optically and sonically camouflaged in water
Hydrogel actuators have been widely developed to be osmotic-driven but many are in fact only capable of producing low forces. Here, the authors developed high speed and high force hydrogel actuators capable of camouflage optically and sonically with low fatigue over multiple cycles.
- Hyunwoo Yuk
- , Shaoting Lin
- & Xuanhe Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplexed single-mode wavelength-to-time mapping of multimode light
Multiplexed single-mode wavelength-to-time mapping of multimode light
Photonic lanterns are made by merging several single-mode cores into one multimode core. Here, the authors show this type of structure can both perform wavelength-to-time mapping of multimode states of light and couple such light to an array of single-photon avalanche detectors.
- Harikumar K Chandrasekharan
- , Frauke Izdebski
- & Robert R. Thomson
-
Article
| Open Access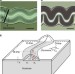 The shape of telephone cord blisters
The shape of telephone cord blisters
Telephone cord blisters constitute a well-known example of patterns generated following buckling in thin films. Here the authors develop an analytical approach that can model the sectional height profiles along the blisters that they measure experimentally and simulate numerically.
- Yong Ni
- , Senjiang Yu
- & Linghui He
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid control and feedback rates enhance neuroprosthetic control
Rapid control and feedback rates enhance neuroprosthetic control
Brain machine interfaces (BMI) enable sensorimotor control of movement yet the parameters that may affect these pathways are not known. Here the authors show systematically that increasing the rate of control from brain as well as feedback rates to the subject results in better performance on a BMI task in monkeys.
- Maryam M. Shanechi
- , Amy L. Orsborn
- & Jose M. Carmena
-
Article
| Open Access A stable lithiated silicon–chalcogen battery via synergetic chemical coupling between silicon and selenium
A stable lithiated silicon–chalcogen battery via synergetic chemical coupling between silicon and selenium
Lithium-based batteries employing silicon anodes and sulfur cathodes are promising for combining low cost and high capacity, but have been limited in terms of cycling stability. Here authors present cycling and characterization data supporting beneficial synergies between a selenium disulfide cathode and a silicon anode.
- KwangSup Eom
- , Jung Tae Lee
- & Thomas F. Fuller
-
Article
| Open Access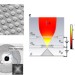 Measurement of transverse emittance and coherence of double-gate field emitter array cathodes
Measurement of transverse emittance and coherence of double-gate field emitter array cathodes
Field emitter arrays are key components for X-ray sources, microwave generators, RF communication and advanced light sources. Tsujinoet al., report double-gate field emitter arrays with competitive beam qualities to the state of the art UV photoexcited cathodes.
- Soichiro Tsujino
- , Prat Das Kanungo
- & R.J. Dwayne Miller
-
Article
| Open Access Bio-inspired self-shaping ceramics
Bio-inspired self-shaping ceramics
Shaping ceramics into complex forms is a formidable goal. Here, the authors present an approach to self-shaping ceramics, inspired by self-folding processes in plants, in which the ceramic microstructure is embedded with aligned platelets that control the orientation of heat-induced shrinkage.
- Fabio L. Bargardi
- , Hortense Le Ferrand
- & André R. Studart
-
Article
| Open Access Grain neighbour effects on twin transmission in hexagonal close-packed materials
Grain neighbour effects on twin transmission in hexagonal close-packed materials
Twin transmission across grain boundaries has important influence on deformation and fracture in hexagonal close-packed metals. Here, experimental and computational statistical analyses show that whether twins cross grain boundaries depends not only on crystal misorientation but also strongly on anisotropy in crystallographic slip.
- M. Arul Kumar
- , I. J. Beyerlein
- & C. N. Tomé
-
Article
| Open Access Improvement of system capacitance via weavable superelastic biscrolled yarn supercapacitors
Improvement of system capacitance via weavable superelastic biscrolled yarn supercapacitors
Carbon nanotube yarns with high loadings of pseudocapacitive material are desirable, e.g., for emerging wearable technologies. Here authors make biscrolled yarns with high loadings of MnO2nanoparticles confined in carbon nanotube galleries, demonstrating very high linear and areal capacitances.
- Changsoon Choi
- , Kang Min Kim
- & Seon Jeong Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Spray printing of organic semiconducting single crystals
Spray printing of organic semiconducting single crystals
The development of organic electronics calls for low-cost printing techniques that can prepare high quality, large-area organic single crystals. Here, Rigaset al. achieve this goal by combining spray printing and antisolvent crystallization and test the method on various materials and substrates.
- Grigorios-Panagiotis Rigas
- , Marcia M. Payne
- & Maxim Shkunov
-
Article
| Open Access Polarization bandgaps and fluid-like elasticity in fully solid elastic metamaterials
Polarization bandgaps and fluid-like elasticity in fully solid elastic metamaterials
Controlling elastic waves in medium is essential to many applications in mechanical to earthquake engineering. Ma et al. demonstrate selective suppression of different vibrational modes in a three-dimensional rod-shape structure, which shows fluid-like elasticity with only longitudinal waves propagating.
- Guancong Ma
- , Caixing Fu
- & Ping Sheng
-
Article
| Open Access A two-dimensional spin field-effect switch
A two-dimensional spin field-effect switch
By forming heterostructures of different layered two-dimensional materials, functional spintronic devices may be built by exploiting the materials’ different spin-orbit coupling and spin transport properties. Here, the authors demonstrate a spin switch in a gated structure of graphene and MoS2.
- Wenjing Yan
- , Oihana Txoperena
- & Fèlix Casanova
-
Article
| Open Access Phosphorene/rhenium disulfide heterojunction-based negative differential resistance device for multi-valued logic
Phosphorene/rhenium disulfide heterojunction-based negative differential resistance device for multi-valued logic
Electronic devices based on negative differential resistance hold promise for multi-valued logic applications. Here, the authors implement such functionalities using an atomically thin phosphorene/rhenium disulfide van der Waals heterostructure, and further demonstrate the implementation of a ternary inverter.
- Jaewoo Shim
- , Seyong Oh
- & Jin-Hong Park
-
Article
| Open Access Photoemission-based microelectronic devices
Photoemission-based microelectronic devices
Most microelectronic devices today exploit the electronic properties of semiconductors. Here, the authors demonstrate a microelectronic device for free-space electrons by using the enhanced fields in a microstructured metal surface to induce effective photoemission.
- Ebrahim Forati
- , Tyler J. Dill
- & Dan Sievenpiper
-
Article
| Open Access The flux qubit revisited to enhance coherence and reproducibility
The flux qubit revisited to enhance coherence and reproducibility
Scalable quantum information processing requires controllable high-coherence qubits. Here, the authors present superconducting flux qubits with broad frequency tunability, strong anharmonicity and high reproducibility, identifying photon shot noise as the main source of dephasing for further improvements.
- Fei Yan
- , Simon Gustavsson
- & William D. Oliver
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene-coated meshes for electroactive flow control devices utilizing two antagonistic functions of repellency and permeability
Graphene-coated meshes for electroactive flow control devices utilizing two antagonistic functions of repellency and permeability
The wettability properties of graphene hold promise for the realisation of flow control devices. Here, the authors demonstrate that the degree of water penetration through a nickel mesh coated with graphene can be controlled electrically, enabling dynamic locomotion of water droplets.
- Rassoul Tabassian
- , Jung-Hwan Oh
- & Il-Kwon Oh
-
Article
| Open Access Bioengineering of injectable encapsulated aggregates of pluripotent stem cells for therapy of myocardial infarction
Bioengineering of injectable encapsulated aggregates of pluripotent stem cells for therapy of myocardial infarction
Stem cell therapy of myocardial infarction is hampered by poor survival of injected cells. Here the authors develop injectable aggregates of stem cells differentiated to an early cardiac stage and encapsulated in a biodegradable micromatrix, and show their enhanced therapeutic efficacy in a heart infarction mouse model.
- Shuting Zhao
- , Zhaobin Xu
- & Xiaoming He
-
Article
| Open Access Platinum recycling going green via induced surface potential alteration enabling fast and efficient dissolution
Platinum recycling going green via induced surface potential alteration enabling fast and efficient dissolution
Given the scarcity and cost of platinum, it is important to develop sustainable processes for its recycling. Here, the authors report the dissolution of metallic platinum using reductive and oxidative gases to repetitively change its surface oxidation state, in the absence of an external electric current.
- Nejc Hodnik
- , Claudio Baldizzone
- & Karl J. J. Mayrhofer
-
Article
| Open Access Age and structure of a model vapour-deposited glass
Age and structure of a model vapour-deposited glass
Vapour-deposited glasses show high stability compared to that of aged glasses, but a structural understanding remains elusive. Here, Reid et al. find that vapour deposited and liquid-cooled glasses show identical structures, suggesting these two classes of films lie on the same path to equilibrium.
- Daniel R. Reid
- , Ivan Lyubimov
- & Juan J. de Pablo
-
Article
| Open Access Large-scale microfluidics providing high-resolution and high-throughput screening of Caenorhabditis elegans poly-glutamine aggregation model
Large-scale microfluidics providing high-resolution and high-throughput screening of Caenorhabditis elegans poly-glutamine aggregation model
Large-scale screens on whole animals could facilitate drug discovery, but are technically challenging. Here, Mondal et al. develop a microfluidic chip combined with an automated imaging platform that enables high-throughput, high-resolution screening of Caenorhabditis elegansdisease models.
- Sudip Mondal
- , Evan Hegarty
- & Adela Ben-Yakar
-
Article
| Open Access Fabrication of fibrillosomes from droplets stabilized by protein nanofibrils at all-aqueous interfaces
Fabrication of fibrillosomes from droplets stabilized by protein nanofibrils at all-aqueous interfaces
All-aqueous emulsions are useful for delivering and processing biomolecules, but their stability is constrained by low interfacial adsorption energy. Song et al. solve this problem using protein nanofibrils that form a crosslinked network, whose stability is superior to conventional colloidal capsules.
- Yang Song
- , Ulyana Shimanovich
- & Ho Cheung Shum
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning the catalytic CO hydrogenation to straight- and long-chain aldehydes/alcohols and olefins/paraffins
Tuning the catalytic CO hydrogenation to straight- and long-chain aldehydes/alcohols and olefins/paraffins
The catalytic CO hydrogenation traditionally produces mainly methanol and long-chain hydrocarbons. Here, the authors show that the same reaction can be tuned to produce long-chain n-aldehydes, 1-alcohols and olefins, as well as n-paraffins over potassium-promoted CoMn catalysts.
- Yizhi Xiang
- & Norbert Kruse
-
Article
| Open Access Microfluidic cantilever detects bacteria and measures their susceptibility to antibiotics in small confined volumes
Microfluidic cantilever detects bacteria and measures their susceptibility to antibiotics in small confined volumes
Analysis of bacteria and their response to antibiotics in real time is challenging. Here the authors report a microcantilever based system that can detect and discriminate between bacteria species and, due to the ability to discriminate between alive and dead samples, measure response to antibiotics.
- Hashem Etayash
- , M. F. Khan
- & Thomas Thundat
-
Article
| Open Access A 17 GHz molecular rectifier
A 17 GHz molecular rectifier
Molecular electronics holds promise to overcome scaling limits of conventional technologies, but is currently limited to low frequency operation. Here, Trasobares et al. show radio frequencies of up to 17.8 GHz in a molecular diode based on ferrocenyl undecanethiol self-assembled monolayers on gold nanodots.
- J. Trasobares
- , D. Vuillaume
- & N. Clément
-
Article
| Open Access Interplay between hydrophilicity and surface barriers on water transport in zeolite membranes
Interplay between hydrophilicity and surface barriers on water transport in zeolite membranes
Zeolite crystal with porous structure is predicted to be a good membrane material for water purification, but experiments show water uptake orders of magnitude smaller than the theory. Here, Fasano et al. attribute this disagreement to the additional diffusion resistance induced by surface defects.
- Matteo Fasano
- , Thomas Humplik
- & Pietro Asinari
-
Article
| Open Access Intercalated water layers promote thermal dissipation at bio–nano interfaces
Intercalated water layers promote thermal dissipation at bio–nano interfaces
Thermal management is important for designing bio-nano interfaces for biosensing and thermotherapic applications. Here the authors perform simulations showing that nm-thick water layers between graphene and cell membranes display layered ordering, promoting interfacial thermal coupling and thermal dissipation.
- Yanlei Wang
- , Zhao Qin
- & Zhiping Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal nuclei templated nanostructured membranes prepared by solvent crystallization and polymer migration
Crystal nuclei templated nanostructured membranes prepared by solvent crystallization and polymer migration
Conventionally porous polymeric membranes for filtration are produced by phase-separation techniques, but this process has reached saturation. Here, Li and co-workers developed a manufacturing process involving oriented green solvent crystallization and polymer migration to form high-performance membranes.
- Bo Wang
- , Jing Ji
- & Kang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling the motion of multiple objects on a Chladni plate
Controlling the motion of multiple objects on a Chladni plate
Moving particles on a vibrating plate dates back to 1780s, but it is still challenging to control individual particles in a parallel way. Here, Zhou et al. use a single acoustic actuator and an algorithm to control multiple objects simultaneously and independently for sorting and pattern formation.
- Quan Zhou
- , Veikko Sariola
- & Ville Liimatainen
-
Article
| Open Access Terahertz time-gated spectral imaging for content extraction through layered structures
Terahertz time-gated spectral imaging for content extraction through layered structures
Terahertz radiation may be used to nondestructively detect and study defects and structures within materials. Here the authors use terahertz time-gated spectral imaging to extract occluded text from paper pages with subwavelength spacing.
- Albert Redo-Sanchez
- , Barmak Heshmat
- & Ramesh Raskar
-
Article
| Open Access Non-destructive imaging of buried electronic interfaces using a decelerated scanning electron beam
Non-destructive imaging of buried electronic interfaces using a decelerated scanning electron beam
Imaging buried interfaces is necessary to assess the quality of electronic devices and their degradation mechanisms. Here, Hirohata et al. use energy-filtered scanning electron microscopy to image buried defects in an inorganic lateral spin-valve device, at the nanometre scale and non-destructively.
- Atsufumi Hirohata
- , Yasuaki Yamamoto
- & Andrew J. Vick
-
Article
| Open Access Two-terminal floating-gate memory with van der Waals heterostructures for ultrahigh on/off ratio
Two-terminal floating-gate memory with van der Waals heterostructures for ultrahigh on/off ratio
Traditional non-volatile memories suffer from poor scalability in the vertical direction due to the use of a bulky oxide layer. Here, the authors develop a tunnelling random access memory using a vertical heterostructure composed of atomically thin molybdenum disulfide, boron nitride and graphene.
- Quoc An Vu
- , Yong Seon Shin
- & Woo Jong Yu
-
Review Article
| Open Access Photon management for augmented photosynthesis
Photon management for augmented photosynthesis
Photosynthetic microalgae could provide an ecologically sustainable route to produce solar biofuels and high-value chemicals. Here, the authors review various optical management strategies used to manipulate the incident light in order to increase the efficiency of microalgae biofuel production.
- Matthew D. Ooms
- , Cao Thang Dinh
- & David Sinton
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancing droplet deposition through in-situ precipitation
Enhancing droplet deposition through in-situ precipitation
The extensive use of pesticides in agriculture calls for efficient spraying techniques to reduce pollution of soils and groundwater by toxic chemicals. Damak et al. simultaneously spray liquids containing oppositely charged polyelectrolytes that form defects, pinning droplets on targeted surfaces.
- Maher Damak
- , Md Nasim Hyder
- & Kripa K. Varanasi
-
Article
| Open Access Asymmetric synthesis using chiral-encoded metal
Asymmetric synthesis using chiral-encoded metal
Chiral compounds are extremely important as they can be used in medicine, agriculture and biotechnology. Here, Kuhn and co-workers use a mesoporous metal structure encoded with chiral information in order to induce asymmetry in electrochemical synthesis of mandelic acid.
- Thittaya Yutthalekha
- , Chularat Wattanakit
- & Alexander Kuhn
-
Article
| Open Access Electrolysis of a molten semiconductor
Electrolysis of a molten semiconductor
Conventional metal extraction processes rely on energy intensive pyro- or hydrometallurgical methods which generate pollutants. Here, the authors reveal a high-throughput electro-desulfurization process to convert molten stibnite to pure antimony in a single step, reducing emissions and energy consumption.
- Huayi Yin
- , Brice Chung
- & Donald R. Sadoway
-
Article
| Open Access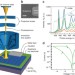 Quantifying redox-induced Schottky barrier variations in memristive devices via in operando spectromicroscopy with graphene electrodes
Quantifying redox-induced Schottky barrier variations in memristive devices via in operando spectromicroscopy with graphene electrodes
Resistive switching in metal oxides is related to the migration of donor defects. Here Baeumer et al. use in operandoX-ray spectromicroscopy to quantify the doping locally and show that small local variations in the donor concentration result in large variations in the device resistance.
- Christoph Baeumer
- , Christoph Schmitz
- & Regina Dittmann
-
Article
| Open Access Ionic imbalance induced self-propulsion of liquid metals
Ionic imbalance induced self-propulsion of liquid metals
The control over the motion and deformation of liquid droplets is essential to many microfluidic and actuation systems. Zavabeti et al. demonstrate that applying a pH or ionic gradient across a droplet of liquid metal alloy of gallium results in its motion due to a breaking of the surface charge symmetry.
- Ali Zavabeti
- , Torben Daeneke
- & Kourosh Kalantar-zadeh
-
Article
| Open Access Mass production of shaped particles through vortex ring freezing
Mass production of shaped particles through vortex ring freezing
The evolution of vortex flow exhibits a rich spectrum of complicated geometries. Here, An et al. utilize these features to control and mass produce inorganic and organic particles via an electrospraying process, whereby the shape of vortex rings translates into particles during a freezing process.
- Duo An
- , Alex Warning
- & Minglin Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Shape-shifting colloids via stimulated dewetting
Shape-shifting colloids via stimulated dewetting
Mimicking the intrinsic adaptability of biological systems in synthetic materials has been a challenge. Here, Sacanna and co-workers have used dewetting forces between an oil phase and solid colloidal substrate to facilitate shape shifting particles that can change geometry by chemical and optical signals.
- Mena Youssef
- , Theodore Hueckel
- & Stefano Sacanna
-
Article
| Open Access Piezoelectric enhancement under negative pressure
Piezoelectric enhancement under negative pressure
Recently, negative pressure has been observed in perovskite nanowires by annealing the wires from a lower-density phase. Here, the authors show that the negative pressure enhances the piezoelectric coefficient of PbTiO3 and Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 nanowires experimentally and by ab initiocalculations.
- Alexander Kvasov
- , Leo J. McGilly
- & Nava Setter
-
Article
| Open Access Rational design of carbon nitride photocatalysts by identification of cyanamide defects as catalytically relevant sites
Rational design of carbon nitride photocatalysts by identification of cyanamide defects as catalytically relevant sites
Graphitic carbon nitride is a promising hydrogen evolution photocatalyst, although there is limited understanding of its mechanistic operation. Here, the authors employ molecular heptazine-based model catalysts to identify catalytically relevant defects and to rationally design a highly active carbon nitride photocatalyst.
- Vincent Wing-hei Lau
- , Igor Moudrakovski
- & Bettina V. Lotsch
-
Article
| Open Access Surface engineering of hierarchical platinum-cobalt nanowires for efficient electrocatalysis
Surface engineering of hierarchical platinum-cobalt nanowires for efficient electrocatalysis
Platinum-based nanowires are promising for fuel cell applications due to their high catalytic activity. Here the authors report on hierarchical platinum-cobalt nanowires with high-index facets showing specific/mass activities for oxygen reduction reaction 39.6/33.7 times higher than commercial Pt/C catalyst.
- Lingzheng Bu
- , Shaojun Guo
- & Xiaoqing Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Loss-tolerant state engineering for quantum-enhanced metrology via the reverse Hong–Ou–Mandel effect
Loss-tolerant state engineering for quantum-enhanced metrology via the reverse Hong–Ou–Mandel effect
N00N states are promising for quantum communications and metrology, but are vulnerable to losses. Here the authors develop a technique for preparing high-fidelity two-photon N00N states in a loss-free fashion, and demonstrate enhanced phase sensitivity without requiring recombination.
- Alexander E. Ulanov
- , Ilya A. Fedorov
- & A. I. Lvovsky
-
Article
| Open Access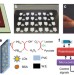 A wearable chemical–electrophysiological hybrid biosensing system for real-time health and fitness monitoring
A wearable chemical–electrophysiological hybrid biosensing system for real-time health and fitness monitoring
Wearable sensors can provide continuous, convenient feedback for users but typically focus on a small number of physiological parameters. Here, the authors report a skin-worn sensing system that combines a biosensor for lactate detection with an electrocardiogram in one patch, with applications for exercise monitoring.
- Somayeh Imani
- , Amay J. Bandodkar
- & Patrick P. Mercier
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering electrocatalytic activity in nanosized perovskite cobaltite through surface spin-state transition
Engineering electrocatalytic activity in nanosized perovskite cobaltite through surface spin-state transition
The activity of electrocatalysts exhibits a strong dependence on their electronic structures. Here, the authors manipulate the eg filling of perovskite cobaltite LaCoO3nanoparticles by changing particle size and show improved oxygen evolution activity with increased numbers of surface high-spin cobalt ions.
- Shiming Zhou
- , Xianbing Miao
- & Jie Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable graphene micro-emitters with fast temporal response and controllable electron emission
Tunable graphene micro-emitters with fast temporal response and controllable electron emission
Controlling the electron emission of microfabricated field emitters can be challenging. Here the authors report controllable and tunable graphene thermionic micro-emitters with well-defined turn-on voltages and switching times in the microsecond range and fabricate uniform micro-emitter arrays.
- Gongtao Wu
- , Xianlong Wei
- & Lianmao Peng

 Harnessing catalytic pumps for directional delivery of microparticles in microchambers
Harnessing catalytic pumps for directional delivery of microparticles in microchambers