Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible interlocked porous frameworks allow quantitative photoisomerization in a crystalline solid
Flexible interlocked porous frameworks allow quantitative photoisomerization in a crystalline solid
Organizing photochromic molecules into 3D networks is a key strategy to access photoresponsive materials, but framework rigidity typically limits conversion efficiency. Here, the authors exploit a flexible metal-organic framework to achieve quantitative and reversible photoisomerization in a porous crystalline solid.
- Yongtai Zheng
- , Hiroshi Sato
- & Susumu Kitagawa
-
Article
| Open Access Achieving ultrahigh triboelectric charge density for efficient energy harvesting
Achieving ultrahigh triboelectric charge density for efficient energy harvesting
Triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) harvest ambient mechanical energy and convert it into electrical energy. Here, the authors couple surface polarization from contact electrification with dielectric polarization from a ferroelectric material in vacuum to dramatically enhance the TENG output power.
- Jie Wang
- , Changsheng Wu
- & Zhong Lin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Impact of interfacial molecular orientation on radiative recombination and charge generation efficiency
Impact of interfacial molecular orientation on radiative recombination and charge generation efficiency
Molecular orientation profoundly affects the performance of donor-acceptor heterojunctions, whilst it has remained challenging to investigate the detail. Using a controllable interface, Ran et al. show that the edge-on geometries improve charge generation at the cost of non-radiative recombination loss.
- Niva A. Ran
- , Steffen Roland
- & Thuc-Quyen Nguyen
-
Article
| Open Access Damage tolerance of nuclear graphite at elevated temperatures
Damage tolerance of nuclear graphite at elevated temperatures
Nuclear-grade graphite is an important high-temperature structural material for fission reactors. Here, the authors perform simultaneous X-ray tomography and mechanical testing on a nuclear-grade graphite, finding simultaneous improvement of strength and toughness at elevated temperatures which they attribute primarily to reduction of residual tensile stresses in the as-made material.
- Dong Liu
- , Bernd Gludovatz
- & Robert O. Ritchie
-
Article
| Open Access Electronic metal-support interaction enhanced oxygen reduction activity and stability of boron carbide supported platinum
Electronic metal-support interaction enhanced oxygen reduction activity and stability of boron carbide supported platinum
D-band engineering via alloying platinum is a leading design principle for advanced oxygen reduction electrocatalysts, but stability remains a concern. Here the authors make Pt nanoparticles supported on graphite-rich boron carbide for enhanced activity and stability, isolating and optimizing the electronic metal-support interactions.
- Colleen Jackson
- , Graham T. Smith
- & Denis Kramer
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental study of thermal rectification in suspended monolayer graphene
Experimental study of thermal rectification in suspended monolayer graphene
Thermal rectification is instrumental to achieving active heat flow control and energy harvesting in nanoscale devices. Here, the authors demonstrate thermal rectification in asymmetric graphene nanostructures, achieving a large rectification factor up to 26%.
- Haidong Wang
- , Shiqian Hu
- & Jie Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Diffusion engineering of ions and charge carriers for stable efficient perovskite solar cells
Diffusion engineering of ions and charge carriers for stable efficient perovskite solar cells
Ion migration in perovskite solar cells are known to cause hysteresis and instability. Biet al., report a charge extraction layer based on graphene, fullerenes and carbon quantum dots which suppresses ion diffusion and enhances charge carrier diffusion leading to efficient devices with improved stability.
- Enbing Bi
- , Han Chen
- & Liyuan Han
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical porous carbons with layer-by-layer motif architectures from confined soft-template self-assembly in layered materials
Hierarchical porous carbons with layer-by-layer motif architectures from confined soft-template self-assembly in layered materials
2D nanomaterials are promising capacitive energy storage materials, but their tendency to restack hinders electrolyte transport. Here, Yamauchi and colleagues introduce 2D ordered mesoporous carbons in between MXene layers, and metal removal affords all-carbon porous 2D–2D heterostructures in which restacking is prevented.
- Jie Wang
- , Jing Tang
- & Yusuke Yamauchi
-
Article
| Open Access Temperature-regulated guest admission and release in microporous materials
Temperature-regulated guest admission and release in microporous materials
Regulating guest access and release in porous materials remains an important goal. Here, May and colleagues elucidate the mechanism by which guest admission can be temperature-regulated in typical microporous materials, and experimentally exploit this process to achieve appreciable and reversible hydrogen storage.
- Gang (Kevin) Li
- , Jin Shang
- & Eric F. May
-
Article
| Open Access 11% efficiency solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells with copper(II/I) hole transport materials
11% efficiency solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells with copper(II/I) hole transport materials
Inadequate pore infiltration and low conductivity of hole transporter materials limit the performance of solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells. Using fast charge-exchange Cu(II/I) complexes as part of the hole transporting material, Caoet al. overcome these issues to achieve a record photoconversion efficiency of 11%.
- Yiming Cao
- , Yasemin Saygili
- & Michael Grätzel
-
Article
| Open Access Biogenic non-crystalline U(IV) revealed as major component in uranium ore deposits
Biogenic non-crystalline U(IV) revealed as major component in uranium ore deposits
Crystalline uraninite is believed to be the dominant form in uranium deposits. Here, the authors find that non-crystalline U(IV) generated through biologically mediated U(VI) reduction is the predominant U(IV)species in ore deposits, implying that biogenic processes are more important than previously thought.
- Amrita Bhattacharyya
- , Kate M. Campbell
- & Thomas Borch
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental discrimination of ion stopping models near the Bragg peak in highly ionized matter
Experimental discrimination of ion stopping models near the Bragg peak in highly ionized matter
The energy loss of ions in plasma is a challenging issue in inertial confinement fusion and many theoretical models exist on ion-stopping power. Here, the authors use laser-generated plasma probed by accelerator-produced ions in experiments to discriminate various ion stopping models near the Bragg peak.
- W. Cayzac
- , A. Frank
- & M. Roth
-
Article
| Open Access One-Year stable perovskite solar cells by 2D/3D interface engineering
One-Year stable perovskite solar cells by 2D/3D interface engineering
Up-scaling represents a key challenge for photovoltaics based on metal halide perovskites. Using a composite of 2D and 3D perovskites in combination with a printable carbon black/graphite counter electrode; Granciniet al., report 11.2% efficient modules stable over 10,000 hours.
- G. Grancini
- , C. Roldán-Carmona
- & Mohammad Khaja Nazeeruddin
-
Article
| Open Access Designing lead-free antiferroelectrics for energy storage
Designing lead-free antiferroelectrics for energy storage
Antiferroelectric capacitors hold great promise for high-power energy storage. Here, through a first-principles-based computational approach, authors find high theoretical energy densities in rare earth substituted bismuth ferrite, and propose a simple model to assess the storage properties of a general antiferroelectric material.
- Bin Xu
- , Jorge Íñiguez
- & L. Bellaiche
-
Article
| Open Access Visualization of lithium-ion transport and phase evolution within and between manganese oxide nanorods
Visualization of lithium-ion transport and phase evolution within and between manganese oxide nanorods
Hollandite structured materials are potentially useful for battery technologies. Here the authors report the unusual lateral transport of lithium ions between lithiated silver manages oxide nanorods where the reaction fronts and kinetics are maintained within the neighbouring nanorods.
- Feng Xu
- , Lijun Wu
- & Yimei Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Structural water engaged disordered vanadium oxide nanosheets for high capacity aqueous potassium-ion storage
Structural water engaged disordered vanadium oxide nanosheets for high capacity aqueous potassium-ion storage
The authors report that the interplay between structural water and highly disordered vanadium oxide can stabilize the layered metal oxides and enhanced their performance for aqueous potassium-ion storage based on neutron scattering measurements and electrochemical characterizations.
- Daniel Scott Charles
- , Mikhail Feygenson
- & Xiaowei Teng
-
Article
| Open Access Electricity from methane by reversing methanogenesis
Electricity from methane by reversing methanogenesis
Microbial fuel cells generate electricity from a variety of sources, however from methane only negligible electrical power has been reported so far. Here the authors convert methane into electricity using a synthetic consortium consisting of an engineered archaeal strain, microorganisms from methane-acclimated sludge, andGeobacter sulfurreducens.
- Michael J. McAnulty
- , Venkata G. Poosarla
- & Thomas K. Wood
-
Article
| Open Access Nanogenerator-based dual-functional and self-powered thin patch loudspeaker or microphone for flexible electronics
Nanogenerator-based dual-functional and self-powered thin patch loudspeaker or microphone for flexible electronics
Self-powered nanogenerators by harvesting energy from the environment are desirable for future portable and wearable electronics. Liet al. show the use of ferroelectret nanogenerators to build microphone or loudspeaker, which convert electrical signals to mechanical motions in a reversible manner.
- Wei Li
- , David Torres
- & Nelson Sepúlveda
-
Article
| Open Access Energy efficiency to reduce residential electricity and natural gas use under climate change
Energy efficiency to reduce residential electricity and natural gas use under climate change
Climate change may alter building energy demand. Here, the authors quantify changes in residential electricity and natural gas demand in Los Angeles County and find that rising temperatures may increase electricity demand by 41–87% between 2020 and 2060, but improved efficiency could lower this increase to 28%.
- Janet L. Reyna
- & Mikhail V. Chester
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable and efficient separation of hydrogen isotopes using graphene-based electrochemical pumping
Scalable and efficient separation of hydrogen isotopes using graphene-based electrochemical pumping
Thousands of tons of water are processed every year for hydrogen isotope separation, using extremely costly technology. Here the authors demonstrate a fully-scalable graphene electrochemical pump, which promises to dramatically reduce the energy and capital costs.
- M. Lozada-Hidalgo
- , S. Zhang
- & A. K. Geim
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic-level energy storage mechanism of cobalt hydroxide electrode for pseudocapacitors
Atomic-level energy storage mechanism of cobalt hydroxide electrode for pseudocapacitors
Developing high-performance hybrid energy storage devices requires improved understanding of the mechanism that governs the electrochemical reactions. Here, the authors show the atomic-level working process of cobalt hydroxide electrode for pseudocapacitors.
- Ting Deng
- , Wei Zhang
- & Teófilo Rojo
-
Article
| Open Access Directly converting CO2 into a gasoline fuel
Directly converting CO2 into a gasoline fuel
Direct hydrogenation of CO2 into liquid fuels can mitigate CO2 emissions and reduce the rapid depletion of fossil fuels. Here, the authors show an iron-based multifunctional catalyst that converts CO2to gasoline with high selectivity due to synergistic cooperation of multiple catalytic active sites.
- Jian Wei
- , Qingjie Ge
- & Jian Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic behaviour of interphases and its implication on high-energy-density cathode materials in lithium-ion batteries
Dynamic behaviour of interphases and its implication on high-energy-density cathode materials in lithium-ion batteries
In lithium-ion batteries the interactions between the electrode and electrolyte represent a complex but critical process. Here the authors reveal the dynamic behaviour of interphases driven by conductive carbon through chemical and imaging analyses of a model transition-metal oxide cathode material.
- Wangda Li
- , Andrei Dolocan
- & Arumugam Manthiram
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional Mo1.33C MXene with divacancy ordering prepared from parent 3D laminate with in-plane chemical ordering
Two-dimensional Mo1.33C MXene with divacancy ordering prepared from parent 3D laminate with in-plane chemical ordering
Vacancies in 2D materials can influence their properties, however controlling their formation remains a challenge. Here the authors show that selective etching of a 3D laminate with in-plane chemical ordering results in formation of MXenes with ordered divacancies, as well as elevated conductance and supercapacitance.
- Quanzheng Tao
- , Martin Dahlqvist
- & Johanna Rosen
-
Article
| Open Access A reversible dendrite-free high-areal-capacity lithium metal electrode
A reversible dendrite-free high-areal-capacity lithium metal electrode
Despite recent technological advances, it remains challenging to realize reversible high-areal-capacity lithium metal anodes. Here, the authors demonstrate such an anode by tailoring the top solid electrolyte interphase layer.
- Hui Wang
- , Masaki Matsui
- & Nobuyuki Imanishi
-
Article
| Open Access Energy scaling of targeted optimal control of complex networks
Energy scaling of targeted optimal control of complex networks
The energy required to control a dynamical complex network can be prohibitively large when there are only a few control inputs. Here the authors demonstrate that if only a subset of the network is targeted the energy requirements decrease exponentially.
- Isaac Klickstein
- , Afroza Shirin
- & Francesco Sorrentino
-
Article
| Open Access Electrochemical generation of sulfur vacancies in the basal plane of MoS2 for hydrogen evolution
Electrochemical generation of sulfur vacancies in the basal plane of MoS2 for hydrogen evolution
In order to fully utilize sulfur vacancies in MoS2 catalysts for industrial applications, a facile and general route for making sulfur vacancies in MoS2 is needed. Here, the authors introduce a scalable route towards generating sulfur vacancies on the MoS2basal plane using electrochemical desulfurization.
- Charlie Tsai
- , Hong Li
- & Frank Abild-Pedersen
-
Article
| Open Access Two-step photon up-conversion solar cells
Two-step photon up-conversion solar cells
Harvesting incident photons with energy below the bandgap may lead to highly efficient solar cells. By introducing InAs quantum dots at the hetero-interface, Asahiet al. achieve efficient two step photon up-conversion resulting in additional photocurrent and very high external quantum efficiency.
- Shigeo Asahi
- , Haruyuki Teranishi
- & Takashi Kita
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance and compact-designed flexible thermoelectric modules enabled by a reticulate carbon nanotube architecture
High-performance and compact-designed flexible thermoelectric modules enabled by a reticulate carbon nanotube architecture
Thermoelectric modules can generate electricity directly from heat and have applications to waste heat-energy conversion. Here Zhouet al. have fabricated a thermoelectric module based on an air-stable n-type single-walled carbon nanotube sheet which can reach a high power factor of 1500 μWm−1K−2.
- Wenbin Zhou
- , Qingxia Fan
- & Sishen Xie
-
Article
| Open Access A class of liquid anode for rechargeable batteries with ultralong cycle life
A class of liquid anode for rechargeable batteries with ultralong cycle life
Ideal energy storage technologies should be efficient, safe and cost-effective. Here, the authors make progress by using dissolved sodium metal in a solution of biphenyl and ethers as a liquid anode for rechargeable sodium beta-alumina batteries.
- Juezhi Yu
- , Yong-Sheng Hu
- & Liquan Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Foldable interpenetrated metal-organic frameworks/carbon nanotubes thin film for lithium–sulfur batteries
Foldable interpenetrated metal-organic frameworks/carbon nanotubes thin film for lithium–sulfur batteries
Lithium sulfur batteries show capacity and cost advantages, but suffer from the insulating sulfur, shuttling effect and volume fluctuation. To address these challenges, the authors synthesize foldable composite electrodes with carbon nanotubes interpenetrating metal-organic frameworks.
- Yiyin Mao
- , Gaoran Li
- & Zhan Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Regenerable Cu-intercalated MnO2 layered cathode for highly cyclable energy dense batteries
Regenerable Cu-intercalated MnO2 layered cathode for highly cyclable energy dense batteries
Manganese oxide cathodes in alkaline solutions combine low cost and high capacity for energy storage, but it has been challenging to combine high capacity and stable cycling in this system. Here authors demonstrate reversible, high-capacity cycling when copper additives are introduced and investigate the transformations involved.
- Gautam G. Yadav
- , Joshua W. Gallaway
- & Sanjoy Banerjee
-
Article
| Open Access Conductive porous vanadium nitride/graphene composite as chemical anchor of polysulfides for lithium-sulfur batteries
Conductive porous vanadium nitride/graphene composite as chemical anchor of polysulfides for lithium-sulfur batteries
Lithium sulfur batteries are a promising next generation storage technology. Their performance, however, is subject to the parasitic shuttle effect. Here the authors report a cathode material comprising porous vanadium nitride nanoribbon and graphene to provide anchoring for polysulfides.
- Zhenhua Sun
- , Jingqi Zhang
- & Feng Li
-
Article
| Open Access Synergy of ammonium chloride and moisture on perovskite crystallization for efficient printable mesoscopic solar cells
Synergy of ammonium chloride and moisture on perovskite crystallization for efficient printable mesoscopic solar cells
The commercialization of solar cells based on hybrid perovskites requires challenges of device stability and scalable production to be addressed. Ronget al. report ambient-processed printable mesoscopic perovskite solar cells with a lifetime of over 130 days in ambient air with 30% relative humidity.
- Yaoguang Rong
- , Xiaomeng Hou
- & Hongwei Han
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of intrinsic twin domains in tetragonal CH3NH3PbI3
Direct observation of intrinsic twin domains in tetragonal CH3NH3PbI3
Using low dose transmission electron microscopy, Rothmann, Li, Zhuet al. report direct evidence for twin domains in tetragonal CH3NH3PbI3perovskite. The relevant scale and transition temperature of these twin domains could have implications for perovskite solar cells.
- Mathias Uller Rothmann
- , Wei Li
- & Yi-Bing Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access The critical role of point defects in improving the specific capacitance of δ-MnO2 nanosheets
The critical role of point defects in improving the specific capacitance of δ-MnO2 nanosheets
Two-dimensional solids are of interest for energy storage due to their large accessible surface area, enabling rapid charge/discharge. Here, the authors quantify the point defects in oxide nanosheets, demonstrating that intentional introduction of charged point defects improves the charge storage behaviour.
- Peng Gao
- , Peter Metz
- & Scott T. Misture
-
Article
| Open Access Reversed thermo-switchable molecular sieving membranes composed of two-dimensional metal-organic nanosheets for gas separation
Reversed thermo-switchable molecular sieving membranes composed of two-dimensional metal-organic nanosheets for gas separation
Reducing membrane thickness to nanometre scale should increase the throughput of gas separation sieves. Here, the authors report a sieving membrane composed of two-dimensional metal-organic framework nanosheets, exhibiting both high permeation flux and thermally switchable behaviour.
- Xuerui Wang
- , Chenglong Chi
- & Dan Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Proton enhanced dynamic battery chemistry for aprotic lithium–oxygen batteries
Proton enhanced dynamic battery chemistry for aprotic lithium–oxygen batteries
Water is believed to undermine the performance of aprotic lithium–air batteries. However, the authors here disclose different battery chemistry, showing that both lithium ions and protons are involved in the battery reactions in the presence of water, leading to an unprecedented dynamic product.
- Yun Guang Zhu
- , Qi Liu
- & Qing Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Self-surface charge exfoliation and electrostatically coordinated 2D hetero-layered hybrids
Self-surface charge exfoliation and electrostatically coordinated 2D hetero-layered hybrids
Synthesis of atomically thin 2D hetero-layered structures remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a scalable approach to fabricating 2D hetero-layered metal chalcogenides of various compositions: self-surface charge exfoliation, followed by electrostatic coupling.
- Min-Quan Yang
- , Yi-Jun Xu
- & Ghim Wei Ho
-
Article
| Open Access Acoustic-optical phonon up-conversion and hot-phonon bottleneck in lead-halide perovskites
Acoustic-optical phonon up-conversion and hot-phonon bottleneck in lead-halide perovskites
Slow cooling of hot charge carriers in lead halide perovskite could be used in photovoltaics devices. Here, Yanget al. study hot carrier dynamics by transient absorption spectroscopy. They relate the phonon bottleneck to the up-conversion of low-energy phonons, facilitated by the presence of organic cations.
- Jianfeng Yang
- , Xiaoming Wen
- & Gavin Conibeer
-
Article
| Open Access Thermal engineering of FAPbI3 perovskite material via radiative thermal annealing and in situ XRD
Thermal engineering of FAPbI3 perovskite material via radiative thermal annealing and in situ XRD
Processing is crucial to ensure material quality and stability in perovskite solar cells. Here, Poolet al. develop a scalable infrared annealing method and use in situXRD to map the processing phase space relative to the device efficiency. This provides a tool to determine processing requirements.
- Vanessa L. Pool
- , Benjia Dou
- & Michael F. Toney
-
Article
| Open Access Intragranular cracking as a critical barrier for high-voltage usage of layer-structured cathode for lithium-ion batteries
Intragranular cracking as a critical barrier for high-voltage usage of layer-structured cathode for lithium-ion batteries
Cycling-induced fracture can limit conditions for stable operation for various lithium-ion electrode materials. Here, the authors characterize fracture in nickel-manganese-cobalt oxide microscopically and provide evidence for dislocation-assisted, intragranular fracture operating above a critical voltage threshold.
- Pengfei Yan
- , Jianming Zheng
- & Chong-Min Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Long-term efficient organic photovoltaics based on quaternary bulk heterojunctions
Long-term efficient organic photovoltaics based on quaternary bulk heterojunctions
Organic photovoltaics suffer from degradation. Here, Namet al. develop a quaternary blend and fabricate devices which lose 28% of their initial efficiency after one year of operation at 65 °C.
- Minwoo Nam
- , Minjeong Cha
- & Doo-Hyun Ko
-
Article
| Open Access Super-emitters in natural gas infrastructure are caused by abnormal process conditions
Super-emitters in natural gas infrastructure are caused by abnormal process conditions
A large proportion of methane emissions from natural gas production sites are released by a fraction of high-emitting sources. Here, using Monte Carlo simulations, the authors reveal that super-emitters occur due to abnormal process conditions, explaining component and site-based inventory discrepancies.
- Daniel Zavala-Araiza
- , Ramón A Alvarez
- & Steven P. Hamburg
-
Article
| Open Access High power rechargeable magnesium/iodine battery chemistry
High power rechargeable magnesium/iodine battery chemistry
Rechargeable magnesium batteries suffer from slow solid-state Mg2+diffusion in the intercalation cathode. Here the authors show magnesium/iodine chemistry in which the liquid–solid two-phase reaction leads to increased rate capabilities by overcoming the sluggish kinetics.
- Huajun Tian
- , Tao Gao
- & Chunsheng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Augmenting light coverage for photosynthesis through YFP-enhanced charge separation at the Rhodobacter sphaeroides reaction centre
Augmenting light coverage for photosynthesis through YFP-enhanced charge separation at the Rhodobacter sphaeroides reaction centre
Photosynthesis uses only a limited range of solar radiation. Here, Graysonet al. genetically incorporated the yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) chromophore into a bacterial photosystem, and show that energy harvested by reaction centre–YFP complexes can augment photosynthesis in vivo.
- Katie J. Grayson
- , Kaitlyn M. Faries
- & C. Neil Hunter
-
Article
| Open Access A stable lithiated silicon–chalcogen battery via synergetic chemical coupling between silicon and selenium
A stable lithiated silicon–chalcogen battery via synergetic chemical coupling between silicon and selenium
Lithium-based batteries employing silicon anodes and sulfur cathodes are promising for combining low cost and high capacity, but have been limited in terms of cycling stability. Here authors present cycling and characterization data supporting beneficial synergies between a selenium disulfide cathode and a silicon anode.
- KwangSup Eom
- , Jung Tae Lee
- & Thomas F. Fuller
-
Article
| Open Access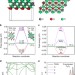 Ti3C2 MXene co-catalyst on metal sulfide photo-absorbers for enhanced visible-light photocatalytic hydrogen production
Ti3C2 MXene co-catalyst on metal sulfide photo-absorbers for enhanced visible-light photocatalytic hydrogen production
Solar hydrogen production through photocatalytic water splitting requires active and stable co-catalysts to replace platinum. Here, the authors use DFT to identify Ti3C2nanoparticles as potential co-catalysts, and assess their photocatalytic hydrogen production activity.
- Jingrun Ran
- , Guoping Gao
- & Shi-Zhang Qiao
-
Article
| Open Access Origin of stabilization and destabilization in solid-state redox reaction of oxide ions for lithium-ion batteries
Origin of stabilization and destabilization in solid-state redox reaction of oxide ions for lithium-ion batteries
Energy storage by metal redox reactions sets strict limits on capacity in metal oxide cathode materials used in lithium-ion batteries. Here authors study stabilization of redox reactions at oxygen sites and demonstrate a cathode with a high reversible capacity enabled by the process.
- Naoaki Yabuuchi
- , Masanobu Nakayama
- & Toshiaki Ohta

 Oscillatory vapour shielding of liquid metal walls in nuclear fusion devices
Oscillatory vapour shielding of liquid metal walls in nuclear fusion devices