Featured
-
-
Letter |
 Cis-interactions between Notch and Delta generate mutually exclusive signalling states
Cis-interactions between Notch and Delta generate mutually exclusive signalling states
Notch and Delta are transmembrane proteins that allow neighbouring cells to communicate during development. Here, quantitative time-lapse microscopy has been used to show that the response of Notch to Delta on a neighbouring cell is graded, whereas its response to Delta on the same cell is sharp and occurs at a fixed threshold. A mathematical model explores how this new design principle enhances the sharpness of developmental boundaries set by classical lateral inhibition.
- David Sprinzak
- , Amit Lakhanpal
- & Michael B. Elowitz
-
Article |
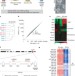 Aberrant silencing of imprinted genes on chromosome 12qF1 in mouse induced pluripotent stem cells
Aberrant silencing of imprinted genes on chromosome 12qF1 in mouse induced pluripotent stem cells
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are generated by the enforced expression of particular transcription factors in somatic cells. The extent to which such cells are equivalent to embryonic stem (ES) cells is an open question. Here, genetically identical mouse ES cells and iPSCs have been compared; the overall expression patterns of messenger RNAs and microRNAs are the same, with the exception of a few transcripts encoded within an imprinted gene cluster on chromosome 12qF1.
- Matthias Stadtfeld
- , Effie Apostolou
- & Konrad Hochedlinger
-
News & Views |
50 & 100 years ago
-
News & Views |
 Extreme makeover of pancreatic α-cells
Extreme makeover of pancreatic α-cells
Most insulin-secreting pancreatic β-cells are irreplaceably lost in type 1 diabetes. In a mouse model, pancreatic α-cells seem to sacrifice their identity to replenish the low stock of β-cells
1 . Two experts discuss what this means for understanding the basic cell biology involved and its relevance to treating diabetes.boxed-text - Kenneth S. Zaret
- & Morris F. White
-
Letter |
 The scaffold protein Ste5 directly controls a switch-like mating decision in yeast
The scaffold protein Ste5 directly controls a switch-like mating decision in yeast
Before mating, a yeast cell must detect a partner cell that is close enough and expresses sufficiently large amounts of a sex pheromone. The mating decision is an all-or-none, switch-like response to pheromone concentration. It is now shown that this decision involves the competition of one kinase and one phosphatase enzyme for multiple phosphorylation sites on a 'scaffold' protein. The results should prompt a re-evaluation of the role of related signalling molecules that have been implicated in cancer.
- Mohan K. Malleshaiah
- , Vahid Shahrezaei
- & Stephen W. Michnick
-
Letter |
 Functional genomic screen for modulators of ciliogenesis and cilium length
Functional genomic screen for modulators of ciliogenesis and cilium length
Primary cilia are tiny hair-like structures expressed on the surface of eukaryotic cells. They participate in a range of processes, such as sensing the extracellular environment and regulating signalling pathways during development. Here, a functional genomic screen is presented that used RNA interference to identify human genes involved in controlling ciliogenesis. Several positive and negative ciliogenesis modulators with broad-ranging functions were found.
- Joon Kim
- , Ji Eun Lee
- & Joseph G. Gleeson
-
Letter |
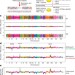 Dissection of genetically complex traits with extremely large pools of yeast segregants
Dissection of genetically complex traits with extremely large pools of yeast segregants
Complex heritable traits — such as human height and many human diseases — are caused by multiple genetic loci, each with small effects. It is hard to identify such loci, however, because of a lack of statistical power. Now, a method has been developed to overcome this problem. The method has been applied to chemical resistance traits and mitochondrial function in yeast, and has identified loci for each of these phenotypes.
- Ian M. Ehrenreich
- , Noorossadat Torabi
- & Leonid Kruglyak
-
Letter |
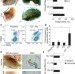 Control of mammary stem cell function by steroid hormone signalling
Control of mammary stem cell function by steroid hormone signalling
The ovarian hormones oestrogen and progesterone increase breast cancer risk but the cellular mechanisms are unclear. Here it is shown that the size of the mammary stem cell pool in mice is regulated by steroid hormone signalling, although these cells lack the receptors for oestrogen and progesterone. The augmented pool could lead to clonal expansion of a mutated cell, possibly accounting for the increased incidence of breast cancer associated with pregnancy.
- Marie-Liesse Asselin-Labat
- , François Vaillant
- & Jane E. Visvader
-
News |
 What's in a name? Fly world is abuzz
What's in a name? Fly world is abuzz
Proposed reorganization of Drosophila fruitfly genus might throw out its most celebrated member.
- Rex Dalton
-
Article |
 Generation of a novel wing colour pattern by the Wingless morphogen
Generation of a novel wing colour pattern by the Wingless morphogen
Here, the generation and evolution of the complex spotted wing pattern of Drosophila guttifera are investigated. The findings show that wing spots are induced by the Wingless morphogen, and that the elaborate spot pattern evolved from simpler schemes by co-option of Wingless expression at new sites. This type of process is likely to occur in other animals, too.
- Thomas Werner
- , Shigeyuki Koshikawa
- & Sean B. Carroll
-
Article |
 Conversion of adult pancreatic α-cells to β-cells after extreme β-cell loss
Conversion of adult pancreatic α-cells to β-cells after extreme β-cell loss
In the pancreas, insulin-producing β-cells are long-lived and generally replicate seldom. They can do so, however, after increased metabolic demand or after injury. Here, a new transgenic model is developed in which β-cells are nearly completely ablated in mice. If given insulin, these mice survive, and grow new β-cells. Lineage-tracing shows that these new β-cells come from α-cells, revealing a previously disregarded degree of pancreatic cell plasticity.
- Fabrizio Thorel
- , Virginie Népote
- & Pedro L. Herrera
-
Research Highlights |
Developmental biology: Hidden differences
-
Letter |
 Exceptional dinosaur fossils show ontogenetic development of early feathers
Exceptional dinosaur fossils show ontogenetic development of early feathers
Study of two specimens of the feathered dinosaur Similicaudipteryx shows that the morphology of dinosaur feathers changed dramatically as the animals matured. Moreover, the morphology of feathers in dinosaurs was much more varied than one would expect from looking at feathers in modern birds.
- Xing Xu
- , Xiaoting Zheng
- & Hailu You
-
Letter |
 Control of cortical GABA circuitry development by Nrg1 and ErbB4 signalling
Control of cortical GABA circuitry development by Nrg1 and ErbB4 signalling
Although several synaptic adhesion proteins have been identified as genetic risk factors in schizophrenia, it is unclear as to what role they play in disease progression. Here, it is shown that two such proteins — neuregulin 1 and its receptor ErbB4 — function to regulate the connectivity of specific cortical circuits. The study not only implicates these proteins in the wiring of inhibitory synapses, about which little is known, but also provides a new perspective on their involvement in schizophrenia.
- Pietro Fazzari
- , Ana V. Paternain
- & Beatriz Rico
-
Letter |
 Evolution of self-compatibility in Arabidopsis by a mutation in the male specificity gene
Evolution of self-compatibility in Arabidopsis by a mutation in the male specificity gene
Self-fertilisation (selfing) in plants is prevented mainly by the self-incompatibility recognition system, which consists of male and female specificity genes and modifier genes. Selfing does occur in Arabidopsis plants, but it is not known how it arose. Here it is reported that selfing in Arabidopsis results from a geographically widespread, 213-base-pair inversion within the male specificity gene. When this inversion is returned to its original orientation, selfing is prevented once more.
- Takashi Tsuchimatsu
- , Keita Suwabe
- & Kentaro K. Shimizu
-
News |
 Gene flaw found in induced stem cells
Gene flaw found in induced stem cells
Key difference between reprogrammed adult mouse cells and embryonic stem cells discovered.
- Elie Dolgin
-
Article |
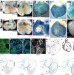 Coronary arteries form by developmental reprogramming of venous cells
Coronary arteries form by developmental reprogramming of venous cells
Prevailing models propose that coronary arteries in the developing heart are formed from progenitor cells originating in the proepicardium. It is found here, however, that these arteries arise from angiogenic sprouts of the major vein that returns circulating blood to the embryonic heart. Thus some differentiated venous cells retain developmental plasticity and respond to local signals to convert to coronary arteries, capillaries and veins.
- Kristy Red-Horse
- , Hiroo Ueno
- & Mark A. Krasnow
-
Letter |
 Zebrafish heart regeneration occurs by cardiomyocyte dedifferentiation and proliferation
Zebrafish heart regeneration occurs by cardiomyocyte dedifferentiation and proliferation
Zebrafish are able to replace lost heart muscle efficiently, and are used as a model to understand why natural heart regeneration — after a heart attack, for instance — is blocked in mammals. Here, and in an accompanying paper, genetic fate-mapping approaches reveal which cell population contributes prominently to cardiac muscle regeneration after an injury approximating myocardial infarction. The results show that cardiac muscle regenerates through activation and expansion of existing cardiomyocytes, without involving a stem-cell population.
- Chris Jopling
- , Eduard Sleep
- & Juan Carlos Izpisúa Belmonte
-
Letter |
 Primary contribution to zebrafish heart regeneration by gata4+ cardiomyocytes
Primary contribution to zebrafish heart regeneration by gata4+ cardiomyocytes
Zebrafish are able to replace lost heart muscle efficiently, and are used as a model to understand why natural heart regeneration — after a heart attack, for instance — is blocked in mammals. Here, and in an accompanying paper, genetic fate-mapping approaches reveal which cell population contributes prominently to cardiac muscle regeneration after an injury approximating myocardial infarction. The results show that cardiac muscle regenerates through activation and expansion of existing cardiomyocytes, without involving a stem-cell population.
- Kazu Kikuchi
- , Jennifer E. Holdway
- & Kenneth D. Poss
-
Article |
 Neurogenic radial glia in the outer subventricular zone of human neocortex
Neurogenic radial glia in the outer subventricular zone of human neocortex
In the mammalian brain, the subventricular zone (SVZ) produces neural progenitor cells that migrate into the cortex to populate the upper layers. In humans this region is massively expanded, producing an outer SVZ (OSVZ). Here, live-cell imaging of developing human tissue was used to show that the OSVZ has similar characteristics to the SVZ, with progenitor cells proliferating in a way that depends on the Notch protein. The findings have implications for our understanding of how the complex human brain evolved.
- David V. Hansen
- , Jan H. Lui
- & Arnold R. Kriegstein
-
-
Research Highlights |
Regenerative biology: Pregnancy boosts repair
-
News & Views |
 Plumbing the heart
Plumbing the heart
Ever since Leonardo da Vinci sketched the heart vessels in his anatomical notebook in the late fifteenth century, the origin of the coronary vasculature has been in question. We might just have come upon the answer.
- Paul Riley
-
News Feature |
 Ageing: Much ado about ageing
Ageing: Much ado about ageing
Questions about a laboratory assay are making Sirtris, a high-profile biotechnology company, the talking point of the ageing field. Heidi Ledford investigates.
- Heidi Ledford
-
Letter |
 Chromatin signature of embryonic pluripotency is established during genome activation
Chromatin signature of embryonic pluripotency is established during genome activation
To study the changes in chromatin structure that accompany zygotic genome activation and pluripotency during the maternal–zygotic transition (MZT), the genomic locations of histone H3 modifications and RNA polymerase II have been mapped during this transition in zebrafish embryos. H3 lysine 27 trimethylation and H3 lysine 4 trimethylation are only detected after MZT; evidence is provided that the bivalent chromatin domains found in cultured embryonic stem cells also exist in embryos.
- Nadine L. Vastenhouw
- , Yong Zhang
- & Alexander F. Schier
-
News |
 Bizarre models for human diseases
Bizarre models for human diseases
Plants shed light on disfigured faces, and yeast and blood vessels find common ground.
- Janelle Weaver
-
News |
 A direct hit for thalidomide
A direct hit for thalidomide
The drug stunts limb development in zebrafish and chicks by binding to a protein called cereblon.
- Janet Fang
-
Letter |
 Systematic genetic analysis of muscle morphogenesis and function in Drosophila
Systematic genetic analysis of muscle morphogenesis and function in Drosophila
A genome-wide RNA interference screen to systematically test the genetic basis for formation and function of the Drosophila muscle is described. A role in muscle for 2,785 genes is identified; many of these genes are phylogenetically conserved.
- Frank Schnorrer
- , Cornelia Schönbauer
- & Barry J. Dickson
-
Research Highlights |
Cancer biology: Arsenic activation
-
News & Views |
 An avian sexual revolution
An avian sexual revolution
Hormones are not all-powerful in determining whether birds develop with male or female features. Chickens that are genetic sexual mosaics reveal that individual cells also have a say in the matter.
- Lindsey A. Barske
- & Blanche Capel
-
News |
 Chicken's split sex identity revealed
Chicken's split sex identity revealed
Half-male, half-female fowl explain sex determination.
- Janet Fang
-
Letter |
 A computational model of teeth and the developmental origins of morphological variation
A computational model of teeth and the developmental origins of morphological variation
Genotype and phenotype cannot be connected simply by one-to-one mapping; instead they are linked by the nonlinear process of development. Here, a computational model is described — based on real data about the development of seal teeth — that attempts to combine the three. The results show that a few genetic parameters regulating signalling during cusp development may explain variation among individuals. But a cellular parameter regulating epithelial growth may explain tooth-to-tooth variation along the jaw.
- Isaac Salazar-Ciudad
- & Jukka Jernvall
-
Letter |
 Changes in Hox genes’ structure and function during the evolution of the squamate body plan
Changes in Hox genes’ structure and function during the evolution of the squamate body plan
The organization of Hox clusters in several different reptiles is investigated, showing that the Hox clusters in squamates — lizards and snakes — have unexpectedly accumulated transposable elements, reflecting extensive genomic rearrangements of coding and non coding regulatory regions. Comparative expression analyses between two species showing different axial skeletons, the corn snake and the whiptail lizard, revealed major alterations in Hox13 and Hox10 expression features during snake somitogenesis, in line with the expansion of both caudal and thoracic regions.
- Nicolas Di-Poï
- , Juan I. Montoya-Burgos
- & Denis Duboule
-
-
Letter |
 Transcriptional control of preadipocyte determination by Zfp423
Transcriptional control of preadipocyte determination by Zfp423
An understanding of how fat cells (adipocytes) develop will contribute to our understanding of obesity. The differentiation of committed preadipocytes into adipocytes is known to be controlled by PPARγ and several other transcription factors. But what turns a cell into a preadipocyte? Here, the zinc-finger protein Zfp423 is identified as a transcriptional regulator of preadipocyte determination.
- Rana K. Gupta
- , Zoltan Arany
- & Bruce M. Spiegelman
-
Letter |
 Control of Arabidopsis apical–basal embryo polarity by antagonistic transcription factors
Control of Arabidopsis apical–basal embryo polarity by antagonistic transcription factors
During development in Arabidopsis plants, populations of shoot stem cells and root stem cells are established at the embryo's apical and basal poles, respectively. PLETHORA genes are master regulators of root fate, but the regulators of shoot fate were unknown. Here, CLASS III HOMEODOMAIN-LEUCINE ZIPPER genes are identified as master regulators of apical/shoot fate, and are shown to be sufficient to convert the embryonic root pole into a second shoot pole.
- Zachery R. Smith
- & Jeff A. Long
-
Brief Communications Arising |
Location of corneal epithelial stem cells
- Tung-Tien Sun
- , Scheffer C. Tseng
- & Robert M. Lavker
-
Letter |
 An essential role for XBP-1 in host protection against immune activation in C. elegans
An essential role for XBP-1 in host protection against immune activation in C. elegans
The unfolded protein response, known to contribute to the defence against infectious agents and toxins, is shown here to protect Caenorhabditis elegans larvae against detrimental effects of the innate immune response to infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The findings establish innate immunity as a physiologically relevant inducer of ER stress during C. elegans development.
- Claire E. Richardson
- , Tristan Kooistra
- & Dennis H. Kim
-
Research Highlights |
Developmental biology: Heads or tails
-
Research Highlights |
 Biology: Colour-blind
Biology: Colour-blind
-
News & Views |
 Cell reprogramming gets direct
Cell reprogramming gets direct
In a feat of biological wizardry, one type of differentiated cell has been directly converted into another, completely distinct type. Notably, the approach does not require a stem-cell intermediate stage.
- Cory R. Nicholas
- & Arnold R. Kriegstein
-
News |
 NIH may allow stem-cell lines from younger embryos
NIH may allow stem-cell lines from younger embryos
Lines derived from pre-blastocyst stage embryos could be eligible for agency funding.
- Meredith Wadman
-
Letter |
 Targeted deletion of the 9p21 non-coding coronary artery disease risk interval in mice
Targeted deletion of the 9p21 non-coding coronary artery disease risk interval in mice
Sequence variations in a 58-kilobase interval on human chromosome 9p21 have been associated with an increased risk of coronary artery disease. However, this interval contains no protein-coding genes and the mechanism underlying the increased risk has been unclear. Here, the corresponding interval has been deleted from mouse chromosome 4, revealing that this part of the chromosome regulates the cardiac expression of two nearby genes, Cdkn2a and Cdkn2b, and the proliferation dynamics of vascular cells.
- Axel Visel
- , Yiwen Zhu
- & Len A. Pennacchio
-
Letter |
 Rere controls retinoic acid signalling and somite bilateral symmetry
Rere controls retinoic acid signalling and somite bilateral symmetry
The vertebrate body plan shows marked bilateral symmetry, although this can be disrupted in conditions such as scoliosis. Here, a mutation in Rere is found that leads to the formation of asymmetrical somites in mouse embryos; furthermore, Rere is shown to control retinoic acid signalling, which is required to maintain somite symmetry by interacting with Fgf8. The results provide insight into how bilateral symmetry is maintained.
- Gonçalo C. Vilhais-Neto
- , Mitsuji Maruhashi
- & Olivier Pourquié
-
Letter |
 Telomere elongation in induced pluripotent stem cells from dyskeratosis congenita patients
Telomere elongation in induced pluripotent stem cells from dyskeratosis congenita patients
Here, iPS cell technology is used to study the mechanisms underlying dyskeratosis congenita in humans. Reprogramming restores telomere elongation in dyskeratosis congenita cells despite genetic lesions affecting telomerase. The reprogrammed cells were able to overcome a critical limitation in telomerase RNA component (TERC) levels to restore telomere maintenance and self-renewal, and multiple telomerase components are targeted by pluripotency-associated transcription factors.
- Suneet Agarwal
- , Yuin-Han Loh
- & George Q. Daley
-
Letter |
 Proviral silencing in embryonic stem cells requires the histone methyltransferase ESET
Proviral silencing in embryonic stem cells requires the histone methyltransferase ESET
Endogenous retroviruses (ERVs) are widely dispersed in mammalian genomes, and are silenced in somatic cells by DNA methylation. Here, an ERV silencing pathway independent of DNA methylation is shown to operate in embryonic stem cells. The pathway involves the histone H3K9 methyltransferase ESET and might be important for ERV silencing during the stages in embryogenesis when DNA methylation is reprogrammed.
- Toshiyuki Matsui
- , Danny Leung
- & Yoichi Shinkai
-
Letter |
 Blood stem cells emerge from aortic endothelium by a novel type of cell transition
Blood stem cells emerge from aortic endothelium by a novel type of cell transition
One of two papers showing the generation of haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) from the ventral wall of the dorsal aorta in live zebrafish embryos. Here, using imaging of live zebrafish, HSCs are shown to emerge directly from the aorta floor. This process does not involve cell division but movement of single endothelial cells out of the aorta ventral wall into the sub aortic space, where they transform into haematopoietic cells.
- Karima Kissa
- & Philippe Herbomel
-
Letter |
 In vivo imaging of haematopoietic cells emerging from the mouse aortic endothelium
In vivo imaging of haematopoietic cells emerging from the mouse aortic endothelium
De novo emergence of phenotypically defined haematopoietic stem cells (Sca1+, c kit+, CD41+) directly from ventral aortic haemogenic endothelial cells is shown in mice. Although the study did not visualize live embryos, it instead developed a dissection procedure to visualize the deeply located aorta.
- Jean-Charles Boisset
- , Wiggert van Cappellen
- & Catherine Robin
-
Letter |
 Haematopoietic stem cells derive directly from aortic endothelium during development
Haematopoietic stem cells derive directly from aortic endothelium during development
One of two papers showing the generation of haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) from the ventral wall of the dorsal aorta in live zebrafish embryos. Here, combined fluorescent reporter transgenes, confocal time-lapse microscopy and flow cytometry identify and isolate the stepwise intermediates as aortic haemogenic endothelium transitions to nascent HSCs. HSCs generated from this haemogenic endothelium are the lineal founders of virtually all of the adult haematopoietic system.
- Julien Y. Bertrand
- , Neil C. Chi
- & David Traver
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Ageing
- Angiogenesis
- Bone development
- Bone remodelling
- Cartilage development
- Cell growth
- Cell proliferation
- Ciliogenesis
- Differentiation
- Disease model
- Embryogenesis
- Embryology
- Epigenetic memory
- Experimental organisms
- Germline development
- Haematopoiesis
- Intrauterine growth
- Lymphangiogenesis
- Morphogenesis
- Neurogenesis
- Organogenesis
- Pattern formation
- Pluripotency
- Reprogramming
- Self-renewal
- Senescence
- Stem-cell niche
- Stem cells
- Transdifferentiation

 A dicer-independent miRNA biogenesis pathway that requires Ago catalysis
A dicer-independent miRNA biogenesis pathway that requires Ago catalysis Time for teeth
Time for teeth