Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Structure of dynein–dynactin on microtubules shows tandem adaptor binding
Structure of dynein–dynactin on microtubules shows tandem adaptor binding
The structure of the complete dynein–dynactin complex and its interaction with microtubules and cargo adaptors are visualized using cryo-electron microscopy.
- Sami Chaaban
- & Andrew P. Carter
-
Article |
 Cryo-EM shows how dynactin recruits two dyneins for faster movement
Cryo-EM shows how dynactin recruits two dyneins for faster movement
Cryo-electron microscopy and single-molecule studies reveal that the adaptors BICDR1 and HOOK3 recruit two dynein molecules to dynactin and thereby increase the force and speed of the dynein–dynactin microtubule motor.
- Linas Urnavicius
- , Clinton K. Lau
- & Andrew P. Carter
-
Research Highlights |
How cells maintain chains
-
Letter |
 MAP and kinesin-dependent nuclear positioning is required for skeletal muscle function
MAP and kinesin-dependent nuclear positioning is required for skeletal muscle function
Skeletal muscle cells are multinucleate, and improper positioning of the nuclei contributes to muscle dysfunction.
- Thomas Metzger
- , Vincent Gache
- & Mary K. Baylies
-
-
Letter |
 MEC-17 is an α-tubulin acetyltransferase
MEC-17 is an α-tubulin acetyltransferase
In eukaryotic cells, a subset of microtubules undergo post-translational modifications such as acetylation, which alters microtubule dynamics and trafficking of motors. These authors identify MEC-17 as the enzyme that directly acetylates α-tubulin in vitro and in vivo and in both invertebrates and vertebrates. This is the identification of the long-sought enzyme that acetylates microtubules.
- Jyothi S. Akella
- , Dorota Wloga
- & Jacek Gaertig
-
Letter |
 A spindle-independent cleavage furrow positioning pathway
A spindle-independent cleavage furrow positioning pathway
The mitotic spindle plays a key part in determining the site of the cleavage furrow in dividing metazoan cells. But are other mechanisms also involved? Here evidence is provided for a spindle-independent pathway for furrow positioning that occurs during asymmetric divisions of Drosophila neuroblast cells. The pathway involves the Pins protein complex, which polarizes furrow-forming proteins to the basal cortex of the cell. This mechanism might also occur in other highly polarized cell types.
- Clemens Cabernard
- , Kenneth E. Prehoda
- & Chris Q. Doe
-
Letter |
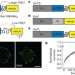 Measuring mechanical tension across vinculin reveals regulation of focal adhesion dynamics
Measuring mechanical tension across vinculin reveals regulation of focal adhesion dynamics
The ability of cells to respond to physical forces is central to development and physiology, but until now it has been difficult to directly measure forces across proteins in vivo. Here, however, a calibrated biosensor is described that can measure forces with high sensitivity across specific proteins in cells. This is applied to the vinculin protein, and a regulatory mechanism is revealed in which the force applied to vinculin determines whether focal adhesions assemble or disassemble.
- Carsten Grashoff
- , Brenton D. Hoffman
- & Martin A. Schwartz

 Structural basis of actin filament assembly and aging
Structural basis of actin filament assembly and aging The crystal structure of dynamin
The crystal structure of dynamin