Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access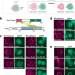 ReLo is a simple and rapid colocalization assay to identify and characterize direct protein–protein interactions
ReLo is a simple and rapid colocalization assay to identify and characterize direct protein–protein interactions
Characterising interactions between proteins that are large and poorly soluble remains challenging. Here, the authors describe ReLo, a rapid and versatile eukaryotic cell culture-based method for detecting and studying direct interactions between structurally complex proteins.
- Harpreet Kaur Salgania
- , Jutta Metz
- & Mandy Jeske
-
Article
| Open Access Single drop cytometry onboard the International Space Station
Single drop cytometry onboard the International Space Station
Real-time lab analysis is key to support clinical research during space missions. Here, the authors show scant test samples can be measured in microgravity using a miniature cytometery-based analyzer, the rHEALTH ONE with specific spaceflight modifications.
- Daniel J. Rea
- , Rachael S. Miller
- & Eugene Y. Chan
-
Article
| Open Access Trophoblast stem cell-based organoid models of the human placental barrier
Trophoblast stem cell-based organoid models of the human placental barrier
The placenta is a transient organ that regulates the fetal environment, but our understanding of placental barrier function has been hampered by the lack of in vitro models. Here they develop human placental organoids that resemble the placental villus and form an intact syncytiotrophoblast barrier when cultured in a column model.
- Takeshi Hori
- , Hiroaki Okae
- & Hirokazu Kaji
-
Article
| Open Access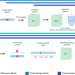 Tigerfish designs oligonucleotide-based in situ hybridization probes targeting intervals of highly repetitive DNA at the scale of genomes
Tigerfish designs oligonucleotide-based in situ hybridization probes targeting intervals of highly repetitive DNA at the scale of genomes
Repetitive DNA intervals play important roles in the nucleus but are difficult to study due to their reiterated nature. Tigerfish introduces a novel computational platform for the design of interval-specific in situ hybridization probes.
- Robin Aguilar
- , Conor K. Camplisson
- & Brian J. Beliveau
-
Article
| Open Access Self-renewing human naïve pluripotent stem cells dedifferentiate in 3D culture and form blastoids spontaneously
Self-renewing human naïve pluripotent stem cells dedifferentiate in 3D culture and form blastoids spontaneously
Blastoids are emerging models for early embryo development exploration in vitro. Here, authors found self-renewing human naïve PSCs spontaneously and efficiently give rise to blastoids upon three-dimensional suspension culture.
- Mingyue Guo
- , Jinyi Wu
- & José C. R. Silva
-
Article
| Open Access Metabolic heterogeneity of tissue-resident macrophages in homeostasis and during helminth infection
Metabolic heterogeneity of tissue-resident macrophages in homeostasis and during helminth infection
Gauging the in vivo metabolism of immune cells at the single-cell level has proven challenging. Here the authors use spectral flow cytometry to investigate metabolic profiles in tissue-resident macrophages from several organs and changes in response to helminth infection.
- Graham A. Heieis
- , Thiago A. Patente
- & Bart Everts
-
Article
| Open Access SEC-seq: association of molecular signatures with antibody secretion in thousands of single human plasma cells
SEC-seq: association of molecular signatures with antibody secretion in thousands of single human plasma cells
Linking proteins secreted from individual cells with other cellular information is challenging. Here, authors report a high-throughput method which uses hydrogel nanovials loaded with single cells to link the secretion profile of individual cells with their surface markers and transcriptomic data.
- Rene Yu-Hong Cheng
- , Joseph de Rutte
- & Richard G. James
-
Article
| Open Access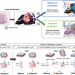 Pacpaint: a histology-based deep learning model uncovers the extensive intratumor molecular heterogeneity of pancreatic adenocarcinoma
Pacpaint: a histology-based deep learning model uncovers the extensive intratumor molecular heterogeneity of pancreatic adenocarcinoma
Rapid and effective molecular subtyping of pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is important for prognosis and treatment. Here, the authors develop PACpAInt, a deep learning model for PDAC molecular subtyping from whole-slide histological imaging that enables the analysis of heterogeneity and prognostic predictions.
- Charlie Saillard
- , Flore Delecourt
- & Jerome Cros
-
Article
| Open Access RAD-TGTs: high-throughput measurement of cellular mechanotype via rupture and delivery of DNA tension probes
RAD-TGTs: high-throughput measurement of cellular mechanotype via rupture and delivery of DNA tension probes
Mechanical forces drive critical cellular processes, but methods to study such cellular forces are typically low-throughput. Here the authors present a method using “Rupture And Deliver” Tension Gauge Tethers, where flow cytometry or sequencing can be used to record the mechanical history of thousands of individual cells.
- Matthew R. Pawlak
- , Adam T. Smiley
- & Wendy R. Gordon
-
Article
| Open Access Comparative analysis of dimension reduction methods for cytometry by time-of-flight data
Comparative analysis of dimension reduction methods for cytometry by time-of-flight data
Dimension reduction (DR) is a key step of Cytometry by Time-of-Flight (CyTOF) data analysis. Here, the authors benchmark 21 DR methods on 110 real and 425 synthetic CyTOF samples, finding a high level of complementarity between the methods, and providing a comprehensive set of user guidelines.
- Kaiwen Wang
- , Yuqiu Yang
- & Tao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access IMC-Denoise: a content aware denoising pipeline to enhance Imaging Mass Cytometry
IMC-Denoise: a content aware denoising pipeline to enhance Imaging Mass Cytometry
Multiplexed imaging technologies can reveal the complex cellular and molecular profiles of tissue. Here, the authors develop and implement a denoising pipeline to significantly enhance imaging mass cytometry quality and improve single-cell analyses.
- Peng Lu
- , Karolyn A. Oetjen
- & Daniel L. J. Thorek
-
Article
| Open Access A conserved tooth resorption mechanism in modern and fossil snakes
A conserved tooth resorption mechanism in modern and fossil snakes
Living snakes replace their teeth without external resorption. Here, the authors use histology to show that odontoclasts resorb dentine internally and investigate this mechanism in fossil snakes.
- A. R. H. LeBlanc
- , A. Palci
- & M. W. Caldwell
-
Article
| Open Access Immune phenotypes that are associated with subsequent COVID-19 severity inferred from post-recovery samples
Immune phenotypes that are associated with subsequent COVID-19 severity inferred from post-recovery samples
The association of specific immune cell types with SARS-CoV-2 severity is not fully understood. Here the authors analyse PBMC from individuals recovered from COVID-19 and propose immune cell signatures post recovery that are associated with disease severity.
- Thomas Liechti
- , Yaser Iftikhar
- & Mario Roederer
-
Article
| Open Access Permian hypercarnivore suggests dental complexity among early amniotes
Permian hypercarnivore suggests dental complexity among early amniotes
Dental development and replacement rates varied greatly among early terrestrial carnivorous and herbivorous amniotes, revealing a complexity that reflected a diversity of feeding behaviours soon after their initial appearance in the fossil record.
- Tea Maho
- , Sigi Maho
- & Robert R. Reisz
-
Article
| Open Access GLI3 regulates muscle stem cell entry into GAlert and self-renewal
GLI3 regulates muscle stem cell entry into GAlert and self-renewal
Primary cilia regulate the processing of the GLI transcription factors and Hedgehog signaling. Here, the authors show that cilia-related GLI3 controls both the quiescence-to-activation transition and self-renewal in muscle stem cells.
- Caroline E. Brun
- , Marie-Claude Sincennes
- & Michael A. Rudnicki
-
Article
| Open Access Clonal barcoding with qPCR detection enables live cell functional analyses for cancer research
Clonal barcoding with qPCR detection enables live cell functional analyses for cancer research
DNA barcoding methods for the analysis of clonal heterogeneity in cancer have been limited in terms of throughput and practical requirements. Here, the authors develop SunCatcher, a rapid and sensitive barcoding approach for live single-cell clonal evolution analysis, and use this method to study breast cancer cell populations.
- Qiuchen Guo
- , Milos Spasic
- & Sandra S. McAllister
-
Article
| Open Access Massive image-based single-cell profiling reveals high levels of circulating platelet aggregates in patients with COVID-19
Massive image-based single-cell profiling reveals high levels of circulating platelet aggregates in patients with COVID-19
The authors report the landscape of circulating platelet aggregates in COVID-19 obtained by massive single-cell image-based profiling and temporal monitoring to elucidate the underlying process of COVID-19-assocaited microvascular thrombosis.
- Masako Nishikawa
- , Hiroshi Kanno
- & Keisuke Goda
-
Article
| Open Access Cellular model system to dissect the isoform-selectivity of Akt inhibitors
Cellular model system to dissect the isoform-selectivity of Akt inhibitors
Elucidating specific effects of protein kinase Akt isoforms remains challenging. Here, the authors establish an Akt isoform-dependent cellular model system and use it, together with X-ray crystallography and structure-based ligand design, to develop isoform-selective covalent-allosteric Akt inhibitors
- Lena Quambusch
- , Laura Depta
- & Daniel Rauh
-
Article
| Open Access AutoSpill is a principled framework that simplifies the analysis of multichromatic flow cytometry data
AutoSpill is a principled framework that simplifies the analysis of multichromatic flow cytometry data
Flow cytometry allows the simultaneous quantification of many markers in and on a cell, but the analysis of such data is complicated. Here, the authors propose AutoSpill, a framework that facilitates the analysis of such data by automating parts of the analysis and requiring fewer controls.
- Carlos P. Roca
- , Oliver T. Burton
- & Adrian Liston
-
Article
| Open Access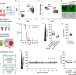 Plasmodium vivax infection compromises reticulocyte stability
Plasmodium vivax infection compromises reticulocyte stability
During Plasmodium intra-erythrocytic developmental, parasites compromise the structural integrity of host red-blood cells. Here, Clark et al. develop a flow cytometric osmotic stability assay to show that P. vivax infection destabilizes host reticulocytes, which are less stable than P. falciparum-infected normocytes.
- Martha A. Clark
- , Usheer Kanjee
- & Manoj T. Duraisingh
-
Article
| Open Access Whole-brain tissue mapping toolkit using large-scale highly multiplexed immunofluorescence imaging and deep neural networks
Whole-brain tissue mapping toolkit using large-scale highly multiplexed immunofluorescence imaging and deep neural networks
It is challenging to map complex processes in brain tissue. Here the authors report a toolkit enabling large-scale multiplexed IHC and automated cell classification whereby they use a conventional epifluorescence microscope and deep neural networks to phenotype all major cell classes of the brain.
- Dragan Maric
- , Jahandar Jahanipour
- & Badrinath Roysam
-
Article
| Open Access A network-based framework for shape analysis enables accurate characterization of leaf epidermal cells
A network-based framework for shape analysis enables accurate characterization of leaf epidermal cells
While cell shape is crucial for function and development of organisms, versatile frameworks for cell shape quantification, comparison, and classification remain underdeveloped. Here, the authors use a network-based framework for Arabidopsis leaf epidermal cell shape characterization and classification.
- Jacqueline Nowak
- , Ryan Christopher Eng
- & Zoran Nikoloski
-
Article
| Open Access Exploiting oxidative phosphorylation to promote the stem and immunoevasive properties of pancreatic cancer stem cells
Exploiting oxidative phosphorylation to promote the stem and immunoevasive properties of pancreatic cancer stem cells
Long-term cultures of pancreatic cancer stem cells (PaCSCs) are difficult to obtain. Here, the authors present a 2D culture method, based on the use of galactose, to establish cell cultures from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma xenotransplants enriched in PaCSCs.
- Sandra Valle
- , Sonia Alcalá
- & Bruno Sainz Jr
-
Article
| Open Access A molecular sensor to quantify the localization of proteins, DNA and nanoparticles in cells
A molecular sensor to quantify the localization of proteins, DNA and nanoparticles in cells
Determining the trafficking of intracellular material is commonly done by colocalisation analysis using microscopy. Here the authors monitor trafficking of select cargo by measuring the conversion of quenched SNAP-tag substrates by subcellularly-localised SNAP-tag and detection by flow cytometry.
- Laura I. FitzGerald
- , Luigi Aurelio
- & Angus P. R. Johnston
-
Article
| Open Access Long-term culture of human pancreatic slices as a model to study real-time islet regeneration
Long-term culture of human pancreatic slices as a model to study real-time islet regeneration
The ability to culture live pancreatic tissue slices for long periods of time would enable longitudinal studies ex vivo. Here the authors culture human and mouse pancreatic slices in a perfluorocarbon-based culture system and show stable endocrine and exocrine function for up to ten days in culture.
- Mirza Muhammad Fahd Qadir
- , Silvia Álvarez-Cubela
- & Juan Domínguez-Bendala
-
Article
| Open Access Virtual-freezing fluorescence imaging flow cytometry
Virtual-freezing fluorescence imaging flow cytometry
High throughput imaging flow cytometry suffers from trade-offs between throughput, sensitivity and spatial resolution. Here the authors introduce a method to virtually freeze cells in the image acquisition window to enable 1000 times longer signal integration time and improve signal-to-noise ratio.
- Hideharu Mikami
- , Makoto Kawaguchi
- & Keisuke Goda
-
Article
| Open Access Automated optimized parameters for T-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding improve visualization and analysis of large datasets
Automated optimized parameters for T-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding improve visualization and analysis of large datasets
Visualisation tools that use dimensionality reduction, such as t-SNE, provide poor visualisation on large data sets of millions of observations. Here the authors present opt-SNE, that automatically finds data set-tailored parameters for t-SNE to optimise visualisation and improve analysis.
- Anna C. Belkina
- , Christopher O. Ciccolella
- & Jennifer E. Snyder-Cappione
-
Article
| Open Access Functional analysis of genetic variants in the high-risk breast cancer susceptibility gene PALB2
Functional analysis of genetic variants in the high-risk breast cancer susceptibility gene PALB2
PALB2 is an established breast cancer risk gene but the pathogenicity of many variants remains uncharacterised. Here, the authors present a cDNA-based system for the functional analysis of PALB2 variants of unknown significance.
- Rick A. C. M. Boonen
- , Amélie Rodrigue
- & Haico van Attikum
-
Article
| Open Access Meiotic crossovers characterized by haplotype-specific chromosome painting in maize
Meiotic crossovers characterized by haplotype-specific chromosome painting in maize
Meiotic crossovers (COs) are essential for proper chromosome segregation and generating novel combinations of alleles. Here, the authors develop haplotype-specific oligos on maize chromosome 10 for fluorescence in situ hybridization and analyze CO patterns in an intermated recombinant population derived from B73 and Mo17.
- Lívia do Vale Martins
- , Fan Yu
- & Jiming Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access iFISH is a publically available resource enabling versatile DNA FISH to study genome architecture
iFISH is a publically available resource enabling versatile DNA FISH to study genome architecture
DNA FISH allows for the visual analysis of chromosomal organisation in individual cells. Here the authors present iFISH, an open-source repository of ready-to-use DNA FISH probes along with tools for probe design.
- Eleni Gelali
- , Gabriele Girelli
- & Magda Bienko
-
Article
| Open Access Probing aggrephagy using chemically-induced protein aggregates
Probing aggrephagy using chemically-induced protein aggregates
Autophagic clearance of aggregates, aggrephagy, is essential for cellular homeostasis but tools to induce and monitor it are limited. Here the authors present a fluorescence-based aggrephagy induction assay to study spatiotemporal dynamics and control mechanisms driving protein aggregate clearance.
- Anne F. J. Janssen
- , Eugene A. Katrukha
- & Lukas C. Kapitein
-
Article
| Open Access Single cell analysis of kynurenine and System L amino acid transport in T cells
Single cell analysis of kynurenine and System L amino acid transport in T cells
Kynurenine is an immunomodulatory aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) ligand. Here the authors show, using a new flow cytometry based method, that kynurenine needs to be transported across the plasma membrane of activated T cells by the transporter protein SLC7A5 to activate the AHR.
- Linda V. Sinclair
- , Damien Neyens
- & Doreen A. Cantrell
-
Article
| Open Access Expansion of functional personalized cells with specific transgene combinations
Expansion of functional personalized cells with specific transgene combinations
Personalised medicine requires cell cultures from defined genetic backgrounds, but providing sufficient numbers of cells is a challenge. Here the authors develop gene cocktails to expand primary cells from a variety of different tissues and species, and show that expanded endothelial and hepatic cells retain properties of the differentiated phenotype.
- Christoph Lipps
- , Franziska Klein
- & Tobias May
-
Article
| Open Access High-efficiency RNA-based reprogramming of human primary fibroblasts
High-efficiency RNA-based reprogramming of human primary fibroblasts
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have potential for regenerative medicine applications, but are generated with very low efficiency. Here, the authors show highly efficient reprogramming of human primary fibroblasts to iPSCs via the synergistic activity of synthetic modified mRNAs, mature miRNA mimics, and optimized culture methods.
- Igor Kogut
- , Sandra M. McCarthy
- & Ganna Bilousova
-
Article
| Open Access 3D microniches reveal the importance of cell size and shape
3D microniches reveal the importance of cell size and shape
Little is known about how geometric cues affect cell function and gene expression in 3D settings. Here the authors use microniches of different geometries to control cell volume and shape, and by extension cell phenotype and lineage.
- Min Bao
- , Jing Xie
- & Wilhelm T. S. Huck
-
Article
| Open Access Visual analysis of mass cytometry data by hierarchical stochastic neighbour embedding reveals rare cell types
Visual analysis of mass cytometry data by hierarchical stochastic neighbour embedding reveals rare cell types
Single cell profiling yields high dimensional data of very large numbers of cells, posing challenges of visualization and analysis. Here the authors introduce a method for analysis of mass cytometry data that can handle very large datasets and allows their intuitive and hierarchical exploration.
- Vincent van Unen
- , Thomas Höllt
- & Boudewijn P. F. Lelieveldt
-
Article
| Open Access Multiscale cytometry and regulation of 3D cell cultures on a chip
Multiscale cytometry and regulation of 3D cell cultures on a chip
3D cell culture is more relevant than the two-dimensional format, but methods for parallel analysis and temporal regulation of the microenvironment are limited. Here the authors develop a droplet microfluidics system to perform long-term culture of 3D spheroids, enabling multiscale cytometry of individual cells within the spheroid.
- Sébastien Sart
- , Raphaël F.-X. Tomasi
- & Charles N. Baroud
-
Article
| Open Access RNA-aptamers-in-droplets (RAPID) high-throughput screening for secretory phenotypes
RNA-aptamers-in-droplets (RAPID) high-throughput screening for secretory phenotypes
Screening libraries of genetically engineered microbes for secreted products is limited by the available assay throughput. Here the authors combine aptamer-based fluorescent detection with droplet microfluidics to achieve high throughput screening of yeast strains engineered for enhanced tyrosine or streptavidin production.
- Joseph Abatemarco
- , Maen F. Sarhan
- & Adam R. Abate
-
Article
| Open Access Mfsd2a+ hepatocytes repopulate the liver during injury and regeneration
Mfsd2a+ hepatocytes repopulate the liver during injury and regeneration
Hepatocytes are highly specialized cells and their fate is determined by their position in the liver as either periportal or perivenous hepatocytes. Here, Pu et al. show through genetic lineage tracing for Mfsd2 that periportal hepatocytes proliferate and reprogram into pericentral hepatocytes during liver regeneration and injury.
- Wenjuan Pu
- , Hui Zhang
- & Bin Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access A centrosome interactome provides insight into organelle assembly and reveals a non-duplication role for Plk4
A centrosome interactome provides insight into organelle assembly and reveals a non-duplication role for Plk4
The centrosome is a large intracellular structure that serves as the microtubule-organising center, but how it is accurately assembled is not known. Here the authors generate a ‘domain-level’ centrosome interactome and show that Plk4 positions the essential centriole component Asterless by phosphorylating Cep135.
- Brian J. Galletta
- , Carey J. Fagerstrom
- & Nasser M. Rusan
-
Article
| Open Access Human serum-derived protein removes the need for coating in defined human pluripotent stem cell culture
Human serum-derived protein removes the need for coating in defined human pluripotent stem cell culture
Improved culture methods are needed to reliably grow human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) on a large scale. Here, the authors identify a xeno-free medium with a supplement of Inter-α-inhibitor that supports long-term propagation and improved single-cell passaging of hPSCs on uncoated plastic.
- Sara Pijuan-Galitó
- , Christoffer Tamm
- & Cecilia Annerén
-
Article
| Open Access Flow cytometry combined with viSNE for the analysis of microbial biofilms and detection of microplastics
Flow cytometry combined with viSNE for the analysis of microbial biofilms and detection of microplastics
The interpretation of high-dimensional flow cytometry data is difficult and time consuming. Here, Sgier et al.present an improved method that combines stain-free flow cytometry with viSNE data visualization for the analysis of microbial biofilms.
- Linn Sgier
- , Remo Freimann
- & Alexandra Kroll
-
Article
| Open Access Optical painting and fluorescence activated sorting of single adherent cells labelled with photoswitchable Pdots
Optical painting and fluorescence activated sorting of single adherent cells labelled with photoswitchable Pdots
Isolation of individual cells from mixed populations is desirable for many biomedical applications. Here the authors use photoswitchable Pdots to allow 'optical painting', where cells of interest are marked based on their visual characteristics, and can then be isolated by fluorescence activated cell sorting.
- Chun-Ting Kuo
- , Alison M. Thompson
- & Daniel T. Chiu
-
Article
| Open Access Mito-priming as a method to engineer Bcl-2 addiction
Mito-priming as a method to engineer Bcl-2 addiction
Apoptosis often requires mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization, a process targeted by Bcl-2-binding BH3 mimetics. Here the authors describe and apply 'mito-priming', a method that allows triggering mitochondrial apoptosis in a synchronous manner, facilitating the investigation of mitochondrial apoptosis and its regulation by Bcl-2 proteins.
- Jonathan Lopez
- , Margaux Bessou
- & Stephen W. G. Tait
-
Article
| Open Access Live-cell protein labelling with nanometre precision by cell squeezing
Live-cell protein labelling with nanometre precision by cell squeezing
The direct observation of intracellular processes through microscopy can provide key insight into biological pathways. Here the authors demonstrate the combination of microfluidic cell squeezing and fluorescent label delivery to native proteins for high throughput live cell super-resolution imaging.
- Alina Kollmannsperger
- , Armon Sharei
- & Robert Tampé
-
Article
| Open Access Label-free cell cycle analysis for high-throughput imaging flow cytometry
Label-free cell cycle analysis for high-throughput imaging flow cytometry
Imaging flow cytometry enables high-throughput acquisition of fluorescence, brightfield and darkfield images of biological cells. Here, Blasi et al.demonstrate that applying machine learning algorithms on brightfield and darkfield images can detect cellular phenotypes without the need for fluorescent stains, enabling label-free assays.
- Thomas Blasi
- , Holger Hennig
- & Paul Rees
-
Article
| Open Access A distributed cell division counter reveals growth dynamics in the gut microbiota
A distributed cell division counter reveals growth dynamics in the gut microbiota
Research on the gut microbiota would benefit from improved methods to study microbial population growth. Here, Myhrvold et al. present a ‘mark and recapture’ method that uses genetically encoded fluorescent particles to measure the growth rates of gut microbes in live animals.
- Cameron Myhrvold
- , Jonathan W. Kotula
- & Pamela A. Silver
-
Article
| Open Access A synthetic hydrogel for the high-throughput study of cell–ECM interactions
A synthetic hydrogel for the high-throughput study of cell–ECM interactions
Multiple extracellular matrix parameters influence cellular behaviour, but it is difficult to dissect their cooperative contributions. Here the authors describe a hydrogel system in which ligand density and substrate stiffness can be tuned orthogonally to study the contribution of combinations of these parameters simultaneously.
- Andrew D. Rape
- , Mikhail Zibinsky
- & Sanjay Kumar
-
Article
| Open Access Digital microfluidic immunocytochemistry in single cells
Digital microfluidic immunocytochemistry in single cells
The ability to measure signalling responses in single cells following short pulses of stimulus would shed insight into temporal thresholds for cell activation. Here the authors introduce a microfluidic platform that allows downstream phosphorylation cascades to be observed following as little as one second of stimulus exposure.
- Alphonsus H. C. Ng
- , M. Dean Chamberlain
- & Aaron R. Wheeler

 Hepatocytes differentiate into intestinal epithelial cells through a hybrid epithelial/mesenchymal cell state in culture
Hepatocytes differentiate into intestinal epithelial cells through a hybrid epithelial/mesenchymal cell state in culture