Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access A randomised Phase IIa trial of amine oxidase copper-containing 3 (AOC3) inhibitor BI 1467335 in adults with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
A randomised Phase IIa trial of amine oxidase copper-containing 3 (AOC3) inhibitor BI 1467335 in adults with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
The authors report data from a Phase IIa randomised, double-blind trial in patients with NASH showing that BI 1467335 strongly and dose-dependently inhibited AOC3 activity (involved in hepatic inflammation) and was well tolerated at all tested doses.
- Philip N. Newsome
- , Arun J. Sanyal
- & Eric Lawitz
-
Article
| Open Access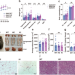 A common East-Asian ALDH2 mutation causes metabolic disorders and the therapeutic effect of ALDH2 activators
A common East-Asian ALDH2 mutation causes metabolic disorders and the therapeutic effect of ALDH2 activators
A common East Asian-specific defect of an alcohol metabolizing enzyme (ALDH2) causes glucose abnormality, obesity, and fatty liver. Here, the authors show an ALDH2 activator can treat these metabolic disorders in mice.
- Yi-Cheng Chang
- , Hsiao-Lin Lee
- & Lee-Ming Chuang
-
Article
| Open Access Biomedical knowledge graph learning for drug repurposing by extending guilt-by-association to multiple layers
Biomedical knowledge graph learning for drug repurposing by extending guilt-by-association to multiple layers
Computational drug repurposing models that leverage biomedical knowledge graphs to associate drugs to diseases, are biased to genes. Here, the authors present DREAMwalk, which extends guilt-by-association for multi-layer knowledge graph learning using a semantic information-guided random walk.
- Dongmin Bang
- , Sangsoo Lim
- & Sun Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying CDK inhibitor selectivity in live cells
Quantifying CDK inhibitor selectivity in live cells
Cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors are widely used both in the clinic and for basic research aimed at dissecting the specific cellular functions of specific CDKs. Here, the authors report the development of a panel of fluorescent reporter probes and provide a comprehensive profile of the inhibitory activity of several CDK inhibitors towards all 21 CDKs in living cells.
- Carrow I. Wells
- , James D. Vasta
- & Matthew B. Robers
-
Article
| Open Access AZD7648 is a potent and selective DNA-PK inhibitor that enhances radiation, chemotherapy and olaparib activity
AZD7648 is a potent and selective DNA-PK inhibitor that enhances radiation, chemotherapy and olaparib activity
DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) plays a major role in the DNA damage response upon double-strand break formation. Here, the authors show that the DNA-PK inhibitor AZD7648, enhances the activity of radiotherapy, chemotherapy and the PARP inhibitor olaparib in multiple mouse tumour models.
- Jacqueline H. L. Fok
- , Antonio Ramos-Montoya
- & Elaine B. Cadogan
-
Article
| Open Access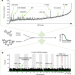 The germline genetic component of drug sensitivity in cancer cell lines
The germline genetic component of drug sensitivity in cancer cell lines
Little is known about the contribution of germline genetic variants to cancer drug sensitivity. Here, the authors devise an approach for joint analysis of germline variants and somatic mutations, identifying substantial germline contributions to variation in drug sensitivity.
- Michael P. Menden
- , Francesco Paolo Casale
- & Oliver Stegle
-
Article
| Open Access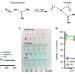 PolyMetformin combines carrier and anticancer activities for in vivo siRNA delivery
PolyMetformin combines carrier and anticancer activities for in vivo siRNA delivery
The anti-diabetic drug Metformin also possesses anti-tumour activity. Here, the authors synthesize polymeric Metformin-based nanoparticles that still exert intrinsic biological activity through AMPK and mTOR regulation and can systematically deliver VEGF siRNA, significantly reducing lung cancer growth in mice.
- Yi Zhao
- , Wei Wang
- & Leaf Huang
-
Article
| Open Access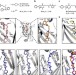 Identification of pyrazolopyridazinones as PDEδ inhibitors
Identification of pyrazolopyridazinones as PDEδ inhibitors
PDEδ is a widely expressed factor that sustains the spatial organization and signalling of Ras family proteins. Here the authors describe the activity of Deltazinone 1, a new highly selective PDEδ inhibitor of KRAS-dependent cancer cell growth with low cytotoxic side effects.
- Björn Papke
- , Sandip Murarka
- & Philippe I.H. Bastiaens
-
Article
| Open Access A phosphotyrosine switch regulates organic cation transporters
A phosphotyrosine switch regulates organic cation transporters
Organic cation transporters are important drug transporters that influence therapeutic outcomes. Here, the authors find that these transporters are regulated by tyrosine phosphorylation and propose that tyrosine kinase inhibitors can influence drug transporter function through post-translational mechanisms.
- Jason A. Sprowl
- , Su Sien Ong
- & Navjotsingh Pabla
-
Article
| Open Access IL-1 receptor antagonist ameliorates inflammasome-dependent inflammation in murine and human cystic fibrosis
IL-1 receptor antagonist ameliorates inflammasome-dependent inflammation in murine and human cystic fibrosis
IL-1-mediated inflammation contributes to the pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis. Here the authors show that this is largely due to NLRP3 activation, whereas NLRP4 induces IL-1Ra, limiting the overall inflammasome activity and providing a therapeutic angle to ameliorate the disease.
- Rossana G. Iannitti
- , Valerio Napolioni
- & Luigina Romani
-
Article
| Open Access Network-based in silico drug efficacy screening
Network-based in silico drug efficacy screening
Attempts to predict novel use for existing drugs rarely consider information on the impact on the genes perturbed in a given disease. Here, the authors present a novel network-based drug-disease proximity measure that provides insight on gene specific therapeutic effect of drugs and may facilitate drug repurposing.
- Emre Guney
- , Jörg Menche
- & Albert-László Barábasi
-
Article
| Open Access Perfluorocarbon nanoparticles enhance reactive oxygen levels and tumour growth inhibition in photodynamic therapy
Perfluorocarbon nanoparticles enhance reactive oxygen levels and tumour growth inhibition in photodynamic therapy
Photodynamic therapy is used in cancer treatment and generates reactive oxygen species to kill tumour cells but is limited by the availability of oxygen. Here, the authors modify a photodynamic sensitiser so that it produces excess oxygen species and show enhanced tumour cell killing in vitro and in vivo.
- Yuhao Cheng
- , Hao Cheng
- & Yiqiao Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Tumour-associated macrophages act as a slow-release reservoir of nano-therapeutic Pt(IV) pro-drug
Tumour-associated macrophages act as a slow-release reservoir of nano-therapeutic Pt(IV) pro-drug
Drug-loaded nanoparticles allow controlled release and enhanced delivery, yet understanding in vivobehavior has been difficult. Here, the authors develop a platinum prodrug coupled to a polymer platform, and use intravital imaging to show that the nanoparticle accumulates in macrophages, from the which drug redistributes to neighboring tumour cells.
- Miles A. Miller
- , Yao-Rong Zheng
- & Ralph Weissleder
-
Article
| Open Access Carbohydrate scaffolds as glycosyltransferase inhibitors with in vivo antibacterial activity
Carbohydrate scaffolds as glycosyltransferase inhibitors with in vivo antibacterial activity
The inhibition of bacterial glycosyltransferase has the potential to be an effective therapeutic target against drug resistance bacteria. Here, the authors present a novel class of inhibitor compounds based on a monosaccharide scaffold, which are able to eliminate bacterial infections in mice.
- Johannes Zuegg
- , Craig Muldoon
- & Matthew A. Cooper
-
Article |
 Amplification of oxidative stress by a dual stimuli-responsive hybrid drug enhances cancer cell death
Amplification of oxidative stress by a dual stimuli-responsive hybrid drug enhances cancer cell death
Cancer cells have elevated levels of reactive oxygen species. Here the authors show that cancer cells can be selectively killed in vitro and in vivoby an oxidative stress-activated drug, which amplifies the generation of reactive oxygen species while blocking the cells’ antioxidant defense.
- Joungyoun Noh
- , Byeongsu Kwon
- & Dongwon Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Triaminopyrimidine is a fast-killing and long-acting antimalarial clinical candidate
Triaminopyrimidine is a fast-killing and long-acting antimalarial clinical candidate
The emergence of resistant Plasmodiumstrains fuels the search for new antimalarials. Here, the authors present a new class of potent antimalarial compounds, the triaminopyrimidines, that display low toxicity and long half-life in animal models.
- Shahul Hameed P.
- , Suresh Solapure
- & Vasan K. Sambandamurthy
-
Article
| Open Access PPARγ contributes to PKM2 and HK2 expression in fatty liver
PPARγ contributes to PKM2 and HK2 expression in fatty liver
Molecular factors, regulating the expression of specific glycolytic enzymes that favour biosynthetic processes, have remained unknown. Panasyuket al. identify PPARγ as a novel transcription factor turning on pyruvate kinase M2 and hexokinase 2, which are frequently upregulated in pathophysiological growth.
- Ganna Panasyuk
- , Catherine Espeillac
- & Mario Pende

 Associations of semaglutide with incidence and recurrence of alcohol use disorder in real-world population
Associations of semaglutide with incidence and recurrence of alcohol use disorder in real-world population