Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
News Feature |
 How did life begin? One key ingredient is coming into view
How did life begin? One key ingredient is coming into view
A Nobel-prizewinning scientist’s team has taken a big step forward in its quest to reconstruct an early-Earth RNA capable of building proteins.
- Amber Dance
-
News |
 Electrodes build themselves inside the bodies of live fish
Electrodes build themselves inside the bodies of live fish
Substance that transforms into a conductive polymer using the body’s own chemistry could improve implantable electronics.
- Myriam Vidal Valero
-
Article |
 Structure and thiazide inhibition mechanism of the human Na–Cl cotransporter
Structure and thiazide inhibition mechanism of the human Na–Cl cotransporter
Using cryo-electron microscopy, the structures of human Na–Cl cotransporter are determined alone and in complex with a thiazide diuretic.
- Minrui Fan
- , Jianxiu Zhang
- & Liang Feng
-
News & Views |
 Bacterial defence repurposed to fight blight
Bacterial defence repurposed to fight blight
The discovery of bacterial compounds that have antifungal properties opens up opportunities for the development of agents that protect crops from a devastating disease.
- Andrew Mitchinson
-
Where I Work |
 This ecologist uses fake flowers to study India’s insects
This ecologist uses fake flowers to study India’s insects
Shannon Olsson examines the behaviour of insect pollinators to understand their reaction to a changing climate.
- Jack Leeming
-
Article |
 Structure-based design of bitopic ligands for the µ-opioid receptor
Structure-based design of bitopic ligands for the µ-opioid receptor
Bitopic functionalized ligands based on fentanyl can target the sodium ion-binding site of the mu-opioid receptor and selectively modulate downstream signalling pathways, potentially leading to safer analgesics.
- Abdelfattah Faouzi
- , Haoqing Wang
- & Susruta Majumdar
-
Article |
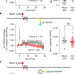 Non-canonical β-adrenergic activation of ERK at endosomes
Non-canonical β-adrenergic activation of ERK at endosomes
β2-adrenergic receptor(β2AR) signalling induces ERK activity at endosomes, but not at the plasma membrane, and this activity is dependent on active, endosome-localized Gαs and requires ligand-stimulated β2AR endocytosis.
- Yonghoon Kwon
- , Sohum Mehta
- & Jin Zhang
-
Research Highlight |
 How to smuggle a drug into cells: add a lipid ‘tail’
How to smuggle a drug into cells: add a lipid ‘tail’
Molecules equipped with a lipid streamer of just the right length can wriggle through a cell’s defensive membrane.
-
Article |
 The E3 ligase adapter cereblon targets the C-terminal cyclic imide degron
The E3 ligase adapter cereblon targets the C-terminal cyclic imide degron
C-terminal cyclic imides are physiological degrons that enable the ubiquitin E3 ligase adapter protein cereblon to target substrates for degradation.
- Saki Ichikawa
- , Hope A. Flaxman
- & Christina M. Woo
-
Article |
 NMR-guided directed evolution
NMR-guided directed evolution
NMR spectroscopy has been used to guide the directed evolution of myoglobin to a Kemp eliminase with high catalytic efficiency, outlining an approach that is likely to be generally applicable to other enzyme activities.
- Sagar Bhattacharya
- , Eleonora G. Margheritis
- & Ivan V. Korendovych
-
Research Briefing |
 Innovative chemistry yields potential antidepressant drugs
Innovative chemistry yields potential antidepressant drugs
Computational simulation of interactions of each of 75 million molecules with a model structure of the 5-HT2A receptor, which mediates the actions of psychedelic drugs, identified molecules that selectively activate the receptor. When tested in mice, two of these compounds had antidepressant-like actions without the side effects of psychedelic drugs.
-
Article |
 Bespoke library docking for 5-HT2A receptor agonists with antidepressant activity
Bespoke library docking for 5-HT2A receptor agonists with antidepressant activity
New agonists of the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor (5-HT2AR) confer high brain permeability and antidepressant activity and—in contrast to classic 5-HT2AR agonists—lack psychedelic activity.
- Anat Levit Kaplan
- , Danielle N. Confair
- & Jonathan A. Ellman
-
News & Views |
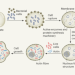 Life brought to artificial cells
Life brought to artificial cells
Can artificial cells be built from basic components? Systems that have complex architectures and functions evocative of natural cells have been prepared by recycling the contents of bacterial cells in synthetic droplets.
- N. Amy Yewdall
-
News & Views |
 Two-drug trick to target the brain blocks toxicity in the body
Two-drug trick to target the brain blocks toxicity in the body
When combined, two drugs alter the activity of a protein complex called target of rapamycin complex 1 such that it is inhibited in the brain but not the body, enabling the treatment of brain tumours in mice without systemic toxicity.
- Matthias P. Wymann
- & Chiara Borsari
-
Article
| Open Access Brain-restricted mTOR inhibition with binary pharmacology
Brain-restricted mTOR inhibition with binary pharmacology
The combination of the brain-permeable mTOR inhibitor RapaLink-1 and the brain-impermeable FKBP12 ligand RapaBlock enable brain-specific inhibition of mTOR.
- Ziyang Zhang
- , Qiwen Fan
- & Kevan M. Shokat
-
Article |
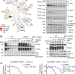 CDK11 regulates pre-mRNA splicing by phosphorylation of SF3B1
CDK11 regulates pre-mRNA splicing by phosphorylation of SF3B1
CDK11 associates with SF3B1 and phosphorylates threonine residues at the N terminus of SF3B1 during spliceosome activation, and the inhibition of CDK11 blocks the activation and leads to widespread intron retention and the accumulation of non-functional spliceosomes on pre-mRNAs and chromatin.
- Milan Hluchý
- , Pavla Gajdušková
- & Dalibor Blazek
-
Article |
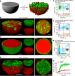 Living material assembly of bacteriogenic protocells
Living material assembly of bacteriogenic protocells
A bacteriogenic strategy for constructing membrane-bounded, molecularly crowded, and compositionally, structurally and morphologically complex synthetic cells provides opportunities for the fabrication of new synthetic cell modules and augmented living/synthetic cell constructs.
- Can Xu
- , Nicolas Martin
- & Stephen Mann
-
Article |
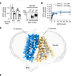 Methotrexate recognition by the human reduced folate carrier SLC19A1
Methotrexate recognition by the human reduced folate carrier SLC19A1
Cryo-EM structures provide insight into how the antifolate methotrexate, a chemotherapy drug, is recognized by the reduced folate carrier.
- Nicholas J. Wright
- , Justin G. Fedor
- & Seok-Yong Lee
-
Research Highlight |
 The AI system that picks carcinogens out of the chemical crowd
The AI system that picks carcinogens out of the chemical crowd
An algorithm trained on the properties of more than 35,000 compounds can identify novel cancer-causing substances.
-
Nature Video |
 The geometry of life: when mathematics meets synthetic biology
The geometry of life: when mathematics meets synthetic biology
How researchers created complex tiling patterns with bioengineered bacteria
- Sara Reardon
-
News & Views |
 Sticky logic programs bacteria to form multicellular patterns
Sticky logic programs bacteria to form multicellular patterns
The engineering of cells to express synthetic adhesion molecules creates a simple logic for patterning cell populations with visible boundaries. The approach paves the way for smart living materials and programmable biosensors.
- Luis Ángel Fernández
-
Article |
 Autoantibody mimicry of hormone action at the thyrotropin receptor
Autoantibody mimicry of hormone action at the thyrotropin receptor
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the thyrotropin receptor reveal the basis for the activation of the receptor by autoantibodies in patients with Graves’ disease.
- Bryan Faust
- , Christian B. Billesbølle
- & Aashish Manglik
-
Article
| Open Access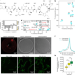 Teixobactin kills bacteria by a two-pronged attack on the cell envelope
Teixobactin kills bacteria by a two-pronged attack on the cell envelope
Using a combination of methods, the mechanism of the antibiotic teixobactin is revealed.
- Rhythm Shukla
- , Francesca Lavore
- & Markus Weingarth
-
Article |
 Recording gene expression order in DNA by CRISPR addition of retron barcodes
Recording gene expression order in DNA by CRISPR addition of retron barcodes
Retro-Cascorder, a system for time-ordered recording of transcriptional output, uses retrons as a tag to mediate DNA barcode acquisition in a CRISPR array.
- Santi Bhattarai-Kline
- , Sierra K. Lear
- & Seth L. Shipman
-
Article |
 C. elegans as a model for inter-individual variation in metabolism
C. elegans as a model for inter-individual variation in metabolism
Using differences among strains as a model for inter-individual variation, this paper identifies a conserved metabolicadaptation in C. elegans that compensates for genetic variation.
- Bennett W. Fox
- , Olga Ponomarova
- & Albertha J. M. Walhout
-
News & Views |
 Synthesis reveals unexpected biological targets of a traditional medicine
Synthesis reveals unexpected biological targets of a traditional medicine
A compound made by plants used in traditional medicine has been prepared by chemical synthesis, providing enough for biological testing. The unexpected finding that it acts at opioid receptors raises prospects for drug discovery.
- Nicholas P. R. Onuska
- & Joshua G. Pierce
-
Article |
 De novo design of discrete, stable 310-helix peptide assemblies
De novo design of discrete, stable 310-helix peptide assemblies
A study demonstrates the rational de novo design of water-soluble assemblies constructed from long 310-helical peptides, and details their characterization by circular dichroism spectroscopy, analytical ultracentrifugation and X-ray crystallography.
- Prasun Kumar
- , Neil G. Paterson
- & Derek N. Woolfson
-
Article |
 An exercise-inducible metabolite that suppresses feeding and obesity
An exercise-inducible metabolite that suppresses feeding and obesity
A newly identified exercise-induced signalling metabolite—an amidated conjugate of lactate and phenylalanine—can reduce food intake and improve blood glucose homeostasis.
- Veronica L. Li
- , Yang He
- & Jonathan Z. Long
-
Article |
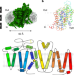 Structural basis of GABA reuptake inhibition
Structural basis of GABA reuptake inhibition
Structural determination of GAT1 using cryo-electron microscopy provides insights into the biology and pharmacology of this GABA transporter.
- Zenia Motiwala
- , Nanda Gowtham Aduri
- & Cornelius Gati
-
Article
| Open Access Potentiating adoptive cell therapy using synthetic IL-9 receptors
Potentiating adoptive cell therapy using synthetic IL-9 receptors
Synthetic chimeric orthogonal IL-2 receptors that incorporate the intracellular domain of receptors for other γ-chain cytokines such as IL-9 can reroute orthogonal signalling and alter the phenotype of T cells to improve anti-tumour responses.
- Anusha Kalbasi
- , Mikko Siurala
- & K. Christopher Garcia
-
News & Views |
 Designer protein circuits enable safe cancer immunotherapy
Designer protein circuits enable safe cancer immunotherapy
Synthetic receptor proteins can enable customized and flexible control of immune cells called T lymphocytes. A defined framework for the proteins’ design now improves their potential for use in cancer immunotherapy.
- Mohamad Hamieh
- & Maria Themeli
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of non-squalene triterpenes
Discovery of non-squalene triterpenes
Chimeric triterpene synthases are identified that catalyse non-squalene-dependent triterpene biosynthesis.
- Hui Tao
- , Lukas Lauterbach
- & Tiangang Liu
-
Review Article |
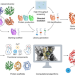 The road to fully programmable protein catalysis
The road to fully programmable protein catalysis
Recent progress in computational enzyme design, active site engineering and directed evolution are reviewed, highlighting methodological innovations needed to deliver improved designer biocatalysts.
- Sarah L. Lovelock
- , Rebecca Crawshaw
- & Anthony P. Green
-
Article
| Open Access A prebiotically plausible scenario of an RNA–peptide world
A prebiotically plausible scenario of an RNA–peptide world
Peptide synthesis can take place directly on RNA, which suggests how a nucleic acid–protein world might have originated on early Earth.
- Felix Müller
- , Luis Escobar
- & Thomas Carell
-
News & Views |
 A possible path towards encoded protein synthesis on ancient Earth
A possible path towards encoded protein synthesis on ancient Earth
How did the biological machinery for protein synthesis evolve from simple chemicals on ancient Earth? Experiments suggest an intriguing role for modified RNA nucleotides in directing stepwise peptide synthesis.
- Claudia Bonfio
-
Nature Podcast |
 Retinas revived after donor's death open door to new science
Retinas revived after donor's death open door to new science
A new method for reviving retinal cells, and the likelihood that life originated as RNA.
- Shamini Bundell
- & Benjamin Thompson
-
Article |
 Mosquito brains encode unique features of human odour to drive host seeking
Mosquito brains encode unique features of human odour to drive host seeking
Select chemical compounds enriched in human odour activate an olfactory glomerulus in the brain of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes, which strengthens host-seeking behaviour and helps explain their strong preference for biting humans.
- Zhilei Zhao
- , Jessica L. Zung
- & Carolyn S. McBride
-
Research Briefing |
 The impact of protected areas on waterbird populations worldwide
The impact of protected areas on waterbird populations worldwide
Protected areas are a cornerstone of conservation policies, but many are not benefiting target species. These areas need to be managed better if they are to achieve conservation goals.
-
Article |
 Human gut bacteria produce ΤΗ17-modulating bile acid metabolites
Human gut bacteria produce ΤΗ17-modulating bile acid metabolites
Bacterially produced bile acids inhibit TH17 cell function, which may be relevant to the pathophysiology of inflammatory disorders such as inflammatory bowel disease.
- Donggi Paik
- , Lina Yao
- & A. Sloan Devlin
-
News & Views |
 Promising reversible protein inhibitors kept on target
Promising reversible protein inhibitors kept on target
Compounds that form reversible covalent bonds with lysine amino-acid residues in proteins have high potential for drug discovery. A chemical group has been reported that prolongs the time for which such compounds bind to their targets.
- Stephan M. Hacker
-
Article |
 Discovery of a Ni2+-dependent guanidine hydrolase in bacteria
Discovery of a Ni2+-dependent guanidine hydrolase in bacteria
A bacterial enzyme is characterized and demonstrated to have Ni2+-dependent activity and high specificity for free guanidine enabling the bacteria to use guanidine as the sole nitrogen source for growth.
- D. Funck
- , M. Sinn
- & J. S. Hartig
-
Article |
 Overcoming universal restrictions on metal selectivity by protein design
Overcoming universal restrictions on metal selectivity by protein design
An alternative approach to metalloprotein design shows that it is possible to overcome the restrictions of the Irving–Williams series and achieve both flexibility and specificity in the binding of metal ions.
- Tae Su Choi
- & F. Akif Tezcan
-
Article
| Open Access The bacterial toxin colibactin triggers prophage induction
The bacterial toxin colibactin triggers prophage induction
The bacterial genotoxin colibactin triggers prophage-mediated lysis of neighbouring bacteria, a finding that provides insight into the dynamics of microbial communities and relationships between bacterial metabolite production and phage behaviour.
- Justin E. Silpe
- , Joel W. H. Wong
- & Emily P. Balskus
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism-based traps enable protease and hydrolase substrate discovery
Mechanism-based traps enable protease and hydrolase substrate discovery
Light-activated trapping is used in a mechanism-based assay to capture and identify substrates of protein hydrolases.
- Shan Tang
- , Adam T. Beattie
- & Jason W. Chin
-
News |
 Last-resort cancer therapy holds back disease for more than a decade
Last-resort cancer therapy holds back disease for more than a decade
Two of the first people treated with CAR-T-cell cancer therapies are still in remission 12 years on.
- Heidi Ledford
-
News & Views |
 Nanoparticle asymmetry shapes an immune response
Nanoparticle asymmetry shapes an immune response
The chirality, or handedness, of nanoparticles is shown to be a key factor in determining how well such particles engage with the immune system — a finding that might help to inform the design of vaccines and anticancer therapeutics.
- Alexander Hooftman
- & Luke A. J. O’Neill
-
Nature Podcast |
 Why mutation is not as random as we thought
Why mutation is not as random as we thought
Challenging the dogma of gene evolution, and how chiral nanoparticles could give vaccines a boost.
- Shamini Bundell
- & Benjamin Thompson
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into inhibitor regulation of the DNA repair protein DNA-PKcs
Structural insights into inhibitor regulation of the DNA repair protein DNA-PKcs
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit bound to ATPγS and four inhibitors (wortmannin, NU7441, AZD7648 and M3814) provide molecular details and insights useful for drug design.
- Shikang Liang
- , Sherine E. Thomas
- & Tom L. Blundell
-
Article |
 A naturally inspired antibiotic to target multidrug-resistant pathogens
A naturally inspired antibiotic to target multidrug-resistant pathogens
The discovery and synthesis of a colistin congener provide a promising clinical lead against mcr-1-encoding colistin-resistant pathogens, which are responsible for an increasing number of deaths from antibiotic-resistant infections.
- Zongqiang Wang
- , Bimal Koirala
- & Sean F. Brady
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Biocatalysis
- Biophysical chemistry
- Biosynthesis
- Carbohydrates
- Chemical ecology
- Chemical genetics
- Chemical libraries
- Chemical modification
- Chemical tools
- Cheminformatics
- Combinatorial libraries
- Computational chemistry
- DNA
- Drug delivery
- Enzyme mechanisms
- Enzymes
- Glycobiology
- Glycomics
- Ion channels
- Kinases
- Lipidomics
- Lipids
- Mechanism of action
- Membranes
- Metabolic pathways
- Metabolomics
- Metals
- Natural products
- Networks and systems biology
- Nucleic acids
- Peptides
- Pharmacology
- Post-translational modifications
- Proteases
- Protein design
- Protein folding
- Proteins
- Proteomics
- RNA
- Screening
- Small molecules
- Synthetic biology
- Target identification
- Target validation
- Transporters

 Autoregulation of GPCR signalling through the third intracellular loop
Autoregulation of GPCR signalling through the third intracellular loop