Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access FERARI and cargo adaptors coordinate cargo flow through sorting endosomes
FERARI and cargo adaptors coordinate cargo flow through sorting endosomes
It is estimated that about 80% of endocytosed material is recycled back to the plasma membrane. Here, the authors show that kiss-and-run of Rab5 early endocytic and Rab11 recycling vesicles on sorting endosomes allow cargo flow, providing more robustness and fidelity to the sorting process.
- Jachen A. Solinger
- , Harun-Or Rashid
- & Anne Spang
-
Article
| Open Access A density-based enrichment measure for assessing colocalization in single-molecule localization microscopy data
A density-based enrichment measure for assessing colocalization in single-molecule localization microscopy data
Full information gained from single-molecule localisation microscopy (SMLM) isn't exploited by current analysis tools. Here the authors report relative enrichment which uses a density-based colocalisation measure for both 2D and 3D SMLM data; they apply it to both simulated data and cultured neurons.
- Aske L. Ejdrup
- , Matthew D. Lycas
- & Ulrik Gether
-
Article
| Open Access DDX1 vesicles control calcium-dependent mitochondrial activity in mouse embryos
DDX1 vesicles control calcium-dependent mitochondrial activity in mouse embryos
The DEAD box protein DDX1 is known to form large aggregates in the cytoplasm of early mouse embryos. Here the authors identify DDX1-containing vesicles and show that loss of Ddx1 affects their integrity, compromising mitochondria function and causing embryonic lethality.
- Yixiong Wang
- , Lubna Yasmin
- & Roseline Godbout
-
Article
| Open Access Lsm7 phase-separated condensates trigger stress granule formation
Lsm7 phase-separated condensates trigger stress granule formation
Stress granules are non-membranous organelles connected to stress responses and age-related disease. Here, the authors identify a conserved yeast protein, Lsm7, that facilitates stress granule formation through dynamic liquid-liquid phase separation condensates upon 2-deoxy-D-glucose-induced stress.
- Michelle Lindström
- , Lihua Chen
- & Beidong Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Pancreatic α and β cells are globally phase-locked
Pancreatic α and β cells are globally phase-locked
The Ca2+ modulated pulsatile glucagon and insulin secretions by pancreatic α and β cells are critical in glucose homeostasis. Here the authors show that the Ca2+ oscillations of α and β cells are phase-locked, and that the oscillation pattern is tuned by paracrine interactions between α and β cells.
- Huixia Ren
- , Yanjun Li
- & Chao Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging translational control by Argonaute with single-molecule resolution in live cells
Imaging translational control by Argonaute with single-molecule resolution in live cells
Guided by miRNA, Argonaute proteins silence mRNA in multiple ways that are not well understood. Here, the authors develop live-cell biosensors to image the impact tethered regulatory factors, such as Argonaute, have on single-mRNA translation dynamics.
- Charlotte A. Cialek
- , Gabriel Galindo
- & Timothy J. Stasevich
-
Article
| Open Access P-selectin mobility undergoes a sol-gel transition as it diffuses from exocytosis sites into the cell membrane
P-selectin mobility undergoes a sol-gel transition as it diffuses from exocytosis sites into the cell membrane
P-selectin recruits leucocytes to regions of blood vessel damage. Using single molecule imaging, we find newly secreted P-selectin spreads rapidly across the plasma membrane and then becomes immobilized and better-suited to leucocyte capture.
- Nicola Hellen
- , Gregory I. Mashanov
- & Tom Carter
-
Article
| Open Access Open-source personal pipetting robots with live-cell incubation and microscopy compatibility
Open-source personal pipetting robots with live-cell incubation and microscopy compatibility
Liquid handling and pipetting tools can automate repetitive tasks but are far from universally used. Here the authors report the Pipetting Helper Imaging Lid (PHIL), an open-source liquid handling robot designed for inexperienced users, that they use for automated pipetting.
- Philip Dettinger
- , Tobias Kull
- & Timm Schroeder
-
Article
| Open Access Biogenesis of a bacterial metabolosome for propanediol utilization
Biogenesis of a bacterial metabolosome for propanediol utilization
Bacteria have evolved proteinaceous microcompartments (BMCs) to control the passage of metabolites and facilitate catabolism in a micro-environment. Here, Yang et al. apply fluorescence microscopy to characterize the protein-protein interaction and assembly involved in the de novo biogenesis of propanediol-utilization (Pdu) metabolosomes and show that Pdu BMCs undergo a combination of ‘Shell first’ and ‘Cargo first’ assembly.
- Mengru Yang
- , Nicolas Wenner
- & Lu-Ning Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Hyperphosphorylated tau self-assembles into amorphous aggregates eliciting TLR4-dependent responses
Hyperphosphorylated tau self-assembles into amorphous aggregates eliciting TLR4-dependent responses
In this work, the authors report that hyperphosphorylated recombinant tau spontaneously assembles into small, amorphous aggregates, which disrupt membranes and induce Toll-like receptor 4-dependent responses in human macrophages.
- Jonathan X. Meng
- , Yu Zhang
- & David Klenerman
-
Article
| Open Access Local and substrate-specific S-palmitoylation determines subcellular localization of Gαo
Local and substrate-specific S-palmitoylation determines subcellular localization of Gαo
How palmitoylated proteins specifically localize is not fully understood. Here, authors created the SwissKASH assay to visualize S-palmitoylation in cells and uncovered a striking substrate selectivity of acyltransferases at the core of this process.
- Gonzalo P. Solis
- , Arghavan Kazemzadeh
- & Vladimir L. Katanaev
-
Article
| Open Access Membrane marker selection for segmenting single cell spatial proteomics data
Membrane marker selection for segmenting single cell spatial proteomics data
Cell segmentation of single-cell spatial proteomics data remains a challenge and often relies on the selection of a membrane marker, which is not always known. Here, the authors introduce RAMCES, a method that selects the optimal membrane markers to use for more accurate cell segmentation.
- Monica T. Dayao
- , Maigan Brusko
- & Ziv Bar-Joseph
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging vesicle formation dynamics supports the flexible model of clathrin-mediated endocytosis
Imaging vesicle formation dynamics supports the flexible model of clathrin-mediated endocytosis
Despite decades of research, the dynamics of clathrin-coated vesicle formation is ambiguous. Here, authors use STAR microscopy to quantify the nanoscale dynamics of vesicle formation, supporting the flexible model of clathrin-mediated endocytosis.
- Tomasz J. Nawara
- , Yancey D. Williams II
- & Alexa L. Mattheyses
-
Article
| Open Access Myosin VI regulates the spatial organisation of mammalian transcription initiation
Myosin VI regulates the spatial organisation of mammalian transcription initiation
The actin-based molecular motors, myosins, have also been linked to transcription, but their precise role has remained elusive. Here the authors show RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) is lost from chromatin upon myosin perturbation and that myosin acts as a molecular anchor to maintain RNAPII spatial organisation.
- Yukti Hari-Gupta
- , Natalia Fili
- & Christopher P. Toseland
-
Article
| Open Access Cytonemes coordinate asymmetric signaling and organization in the Drosophila muscle progenitor niche
Cytonemes coordinate asymmetric signaling and organization in the Drosophila muscle progenitor niche
Asymmetric signaling and organization in the stem cell niche determine cell fates. Here the authors show that polarized contact-dependent signaling through specialized cytonemes forms the basis of niche-specific asymmetric signaling and stem cell organization.
- Akshay Patel
- , Yicong Wu
- & Sougata Roy
-
Article
| Open Access Spatiotemporal expression of regulatory kinases directs the transition from mitosis to cellular morphogenesis in Drosophila
Spatiotemporal expression of regulatory kinases directs the transition from mitosis to cellular morphogenesis in Drosophila
The mechanisms regulating mitosis and differentiation during development are thought to be distinct. Here they show that in Drosophila the mitotic kinase Polo regulates cellular morphogenesis after cell cycle exit.
- Shuo Yang
- , Jennifer McAdow
- & Aaron N. Johnson
-
Article
| Open Access Minimal genetically encoded tags for fluorescent protein labeling in living neurons
Minimal genetically encoded tags for fluorescent protein labeling in living neurons
Site-specific labelling of proteins can be performed with unnatural amino acids combined with bioorthogonal click chemistry. Here the authors establish this in living neurons, using neurofilament light chain; they show combination with CRISPR/Cas9 engineering to tag the endogenous protein.
- Aleksandra Arsić
- , Cathleen Hagemann
- & Ivana Nikić-Spiegel
-
Article
| Open Access Gasdermin D pores are dynamically regulated by local phosphoinositide circuitry
Gasdermin D pores are dynamically regulated by local phosphoinositide circuitry
During pyroptosis, gasdermin D (GSDMD) forms plasma membrane pores that initiate cell lysis. Here, the authors develop optogenetically activatable human GSDMD to assess GSDMD pore behavior and show that they are dynamic and can close, which can be a pyroptosis regulatory mechanism.
- Ana Beatriz Santa Cruz Garcia
- , Kevin P. Schnur
- & Gary C. H. Mo
-
Article
| Open Access Directly recruited GATA6 + peritoneal cavity macrophages contribute to the repair of intestinal serosal injury
Directly recruited GATA6 + peritoneal cavity macrophages contribute to the repair of intestinal serosal injury
Upon intestinal injury, bone marrow derived monocytes are recruited to the damaged site through the bloodstream. Authors here show that peritoneal cavity macrophages directly migrate to the damaged intestine in an ATP and hyaluronan dependent manner, and participate in the restoration of tissue integrity.
- Masaki Honda
- , Masashi Kadohisa
- & Taizo Hibi
-
Article
| Open Access A turquoise fluorescence lifetime-based biosensor for quantitative imaging of intracellular calcium
A turquoise fluorescence lifetime-based biosensor for quantitative imaging of intracellular calcium
Currently, genetically encoded calcium indicators are not suitable for direct quantification. Here the authors engineer a fluorescence lifetime imaging calcium biosensor, Turquoise Calcium Fluorescence LIfeTime Sensor (Tq-Ca-FLITS), and measure intracellular calcium concentrations in human-derived organoids.
- Franka H. van der Linden
- , Eike K. Mahlandt
- & Joachim Goedhart
-
Article
| Open Access Cilia locally synthesize proteins to sustain their ultrastructure and functions
Cilia locally synthesize proteins to sustain their ultrastructure and functions
Cilia are microtubule-based organelles containing proteins transported from the cell body. Here, the authors show that the multicilia of mouse ependymal cells contain ribosomal components, tubulin mRNA,18 S rRNA and nascent tubulin peptides, suggesting local translation in the ciliary compartment.
- Kai Hao
- , Yawen Chen
- & Xueliang Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering of a fluorescent chemogenetic reporter with tunable color for advanced live-cell imaging
Engineering of a fluorescent chemogenetic reporter with tunable color for advanced live-cell imaging
Fluorescent reporters spanning the visible spectrum are needed for imaging live cells and organisms. Here the authors report a collection of fluorogenic chromophores that cover the visible spectrum from blue to red using a single engineered and optimised protein tag.
- Hela Benaissa
- , Karim Ounoughi
- & Arnaud Gautier
-
Article
| Open Access Mammary tumour cells remodel the bone marrow vascular microenvironment to support metastasis
Mammary tumour cells remodel the bone marrow vascular microenvironment to support metastasis
The visualisation of the bone metastasis process in a spatial temporal manner is lacking. Here, the authors use three-dimensional quantitative imaging and show that mouse mammary tumour cells preferentially home to endothelial subtype type H vessels within the bone marrow and remodel this vasculature by producing granulocyte-colony stimulating factor.
- Raymond K. H. Yip
- , Joel S. Rimes
- & Jane E. Visvader
-
Article
| Open Access The autophagy protein ATG9A enables lipid mobilization from lipid droplets
The autophagy protein ATG9A enables lipid mobilization from lipid droplets
ATG9A is transmembrane autophagic machinery protein that delivers phospholipids to expanding autophagosomes. Mailler et al. show that ATG9A is required to mobilize lipids from lipid droplets for autophagosome expansion as well as mitochondrial fatty acid import and β-oxidation.
- Elodie Mailler
- , Carlos M. Guardia
- & Juan S. Bonifacino
-
Article
| Open Access Optogenetic control of receptors reveals distinct roles for actin- and Cdc42-dependent negative signals in chemotactic signal processing
Optogenetic control of receptors reveals distinct roles for actin- and Cdc42-dependent negative signals in chemotactic signal processing
Here the authors use optogenetic tools to directly measure spatial signal processing in leukocyte chemotaxis. Their results reveal the importance of multiple negative feedback loops for maintaining spatial information in chemotaxis.
- George R. R. Bell
- , Esther Rincón
- & Sean R. Collins
-
Article
| Open Access Directional reorientation of migrating neutrophils is limited by suppression of receptor input signaling at the cell rear through myosin II activity
Directional reorientation of migrating neutrophils is limited by suppression of receptor input signaling at the cell rear through myosin II activity
Neutrophils migrate with remarkably stable front-rear polarization. Using optogenetic receptor control to induce reversal of polarization in restrictive microfluidic channels, the authors find that myosin II promotes this stability by suppressing transmission of receptor inputs at the cell rear.
- Amalia Hadjitheodorou
- , George R. R. Bell
- & Julie A. Theriot
-
Article
| Open Access Extent of myosin penetration within the actin cortex regulates cell surface mechanics
Extent of myosin penetration within the actin cortex regulates cell surface mechanics
Cellular deformations are largely driven by contractile forces generated by myosin motors in the submembraneous actin cortex. Here we show that these forces are controlled not simply by cortical myosin levels, but rather by myosins spatial arrangement, specifically the extent of their overlap with cortical actin.
- Binh An Truong Quang
- , Ruby Peters
- & Ewa K. Paluch
-
Article
| Open Access Intrinsically disordered protein biosensor tracks the physical-chemical effects of osmotic stress on cells
Intrinsically disordered protein biosensor tracks the physical-chemical effects of osmotic stress on cells
Methods to monitor osmolarity-dependent changes in cell are currently lacking. Here the authors use the Arabidopsis intrinsically disordered AtLEA4-5 protein, which is expressed in plants under water deficit, to develop a FRET biosensor (SED1) to monitor osmotic stress.
- Cesar L. Cuevas-Velazquez
- , Tamara Vellosillo
- & José R. Dinneny
-
Article
| Open Access The structural dynamics of macropinosome formation and PI3-kinase-mediated sealing revealed by lattice light sheet microscopy
The structural dynamics of macropinosome formation and PI3-kinase-mediated sealing revealed by lattice light sheet microscopy
Macropinocytosis is a cellular process for the uptake of extracellular fluid. Here, the authors use lattice light sheet microscopy to examine the spatial dynamics of the plasma membrane, PI3K activity, and structural differences of various macrophage cell types during macropinocytosis.
- Shayne E. Quinn
- , Lu Huang
- & Brandon L. Scott
-
Article
| Open Access KRAP tethers IP3 receptors to actin and licenses them to evoke cytosolic Ca2+ signals
KRAP tethers IP3 receptors to actin and licenses them to evoke cytosolic Ca2+ signals
Calcium signals initiated by IP3 receptors in ER membranes regulate most cellular activities. Here, the authors show that KRas-induced actininteracting protein (KRAP) tethers a small subset of IP3 receptors to actin and licenses them to evoke cytosolic calcium signals.
- Nagendra Babu Thillaiappan
- , Holly A. Smith
- & Colin W. Taylor
-
Article
| Open Access Specificities of exosome versus small ectosome secretion revealed by live intracellular tracking of CD63 and CD9
Specificities of exosome versus small ectosome secretion revealed by live intracellular tracking of CD63 and CD9
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) play a role in intercellular communication, however the precise biogenesis of different populations of EVs are not clear. Here, the authors follow the intracellular trafficking of two proteins before their secretion in EVs and report the biogenesis and protein markers of EV subtypes: ectosomes budding from the plasma membrane as well as exosomes from late endosomes.
- Mathilde Mathieu
- , Nathalie Névo
- & Clotilde Théry
-
Article
| Open Access The nanoscale molecular morphology of docked exocytic dense-core vesicles in neuroendocrine cells
The nanoscale molecular morphology of docked exocytic dense-core vesicles in neuroendocrine cells
The molecular organization of exocytic vesicles regulates their transport and fusion. Prasai, Taraska, and colleagues use correlative light and electron microscopy, along with 3D tomography and gold labeling, to directly map proteins on single exocytic organelles at the plasma membrane.
- Bijeta Prasai
- , Gideon J. Haber
- & Justin W. Taraska
-
Article
| Open Access CD45 pre-exclusion from the tips of T cell microvilli prior to antigen recognition
CD45 pre-exclusion from the tips of T cell microvilli prior to antigen recognition
CD45 limits T cell activation, so its exclusion from the T cell immunological synapse is thought to occur as a means to enable TCR signalling. Here the authors use a variety of cellular imaging methods to show that CD45 is indeed excluded from the tips of the T cell microvilli and that this occurs prior to contact with antigen, indicating this exclusion is one of the initiating factors for antigen presentation and T cell activation.
- Yunmin Jung
- , Lai Wen
- & Klaus Ley
-
Article
| Open Access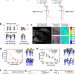 Ceramide structure dictates glycosphingolipid nanodomain assembly and function
Ceramide structure dictates glycosphingolipid nanodomain assembly and function
Gangliosides such as GM1 present in the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane of eukaryotic cells are essential for many cellular functions and pathogenic interactions. Here the authors show that the acyl chain structure of GM1 determines the establishment of nanodomains when actively clustered by actin, which depended on membrane cholesterol and phosphatidylserine or superimposed by the GM1-binding bacterial cholera toxin.
- Senthil Arumugam
- , Stefanie Schmieder
- & Ludger Johannes
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time imaging of cellular forces using optical interference
Real-time imaging of cellular forces using optical interference
Studying dynamic processes in mechanobiology has been challenging due to lack of appropriate tools. Here, the authors present an interference-based method, illuminated via two rapidly alternating wavelengths, which enables real-time mapping of nanoscale forces with sub-second mechanical fluctuations.
- Andrew T. Meek
- , Nils M. Kronenberg
- & Malte C. Gather
-
Article
| Open Access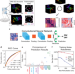 Deep learning connects DNA traces to transcription to reveal predictive features beyond enhancer–promoter contact
Deep learning connects DNA traces to transcription to reveal predictive features beyond enhancer–promoter contact
Recent advances in super-resolution microscopy have made it possible to measure chromatin 3D structure and transcription in thousands of single cells. Here, authors present a deep learning-based approach to characterise how chromatin structure relates to transcriptional state of individual cells and determine which structural features of chromatin regulation are important for gene expression state.
- Aparna R. Rajpurkar
- , Leslie J. Mateo
- & Alistair N. Boettiger
-
Article
| Open Access Live-cell imaging reveals the spatiotemporal organization of endogenous RNA polymerase II phosphorylation at a single gene
Live-cell imaging reveals the spatiotemporal organization of endogenous RNA polymerase II phosphorylation at a single gene
During transcription, RNA polymerase II (RNAP2) is recruited to promoters and phosphorylated stepwise; so far, these steps have not been visualized in a single-copy gene in live cells. Here the authors use single-molecule microscopy to visualize endogenous phosphorylated RNAP2 and nascent mRNA synthesis at a single locus in living cells.
- Linda S. Forero-Quintero
- , William Raymond
- & Timothy J. Stasevich
-
Article
| Open Access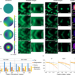 Subcellular three-dimensional imaging deep through multicellular thick samples by structured illumination microscopy and adaptive optics
Subcellular three-dimensional imaging deep through multicellular thick samples by structured illumination microscopy and adaptive optics
Optical aberrations in Structured Illumination Microscopy (SIM) can lead to loss of resolution and artifacts making it unsuitable for thick samples. Here the authors combine Adaptive Optics and SIM (AO-3DSIM) to improve the 3D resolution and reduce artifacts, performing 3D-SIM in C.elegans.
- Ruizhe Lin
- , Edward T. Kipreos
- & Peter Kner
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule imaging reveals replication fork coupled formation of G-quadruplex structures hinders local replication stress signaling
Single-molecule imaging reveals replication fork coupled formation of G-quadruplex structures hinders local replication stress signaling
In the genome, repetitive guanine-rich sequences have the potential to spontaneously fold into non-canonical DNA secondary structures known as G-quadruplex (G4). Using novel single-molecule imaging approaches, the authors reveal that G4 formation within active replication forks locally perturb replisome dynamics and damage response signaling, which require RPA and FANCJ for regulation.
- Wei Ting C. Lee
- , Yandong Yin
- & Eli Rothenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Democratising deep learning for microscopy with ZeroCostDL4Mic
Democratising deep learning for microscopy with ZeroCostDL4Mic
Deep learning methods show great promise for the analysis of microscopy images but there is currently an accessibility barrier to many users. Here the authors report a convenient entry-level deep learning platform that can be used at no cost: ZeroCostDL4Mic.
- Lucas von Chamier
- , Romain F. Laine
- & Ricardo Henriques
-
Article
| Open Access Cargo sorting zones in the trans-Golgi network visualized by super-resolution confocal live imaging microscopy in plants
Cargo sorting zones in the trans-Golgi network visualized by super-resolution confocal live imaging microscopy in plants
The trans-Golgi network (TGN) serves as a platform to sort and transport proteins to their final destinations. Here the authors show that the TGN of Arabidopsis consists of spatially and temporally distinct subregions and propose that these zones may sort cargo to different destinations.
- Yutaro Shimizu
- , Junpei Takagi
- & Akihiko Nakano
-
Article
| Open Access Properties of repression condensates in living Ciona embryos
Properties of repression condensates in living Ciona embryos
While recent studies suggest that transcriptional activators form condensates at active loci, less is known about the distribution of repressor proteins. Here, the authors develop an expression assay in living Ciona embryos and visualize puncta of Hes repressors, with the Groucho/TLE corepressor, observing that the Hes.a/Gro puncta have the properties of viscous liquid droplets that undergo limited fusion events due to association with DNA.
- Nicholas Treen
- , Shunsuke F. Shimobayashi
- & Michael Levine
-
Article
| Open Access Morphological bases of phytoplankton energy management and physiological responses unveiled by 3D subcellular imaging
Morphological bases of phytoplankton energy management and physiological responses unveiled by 3D subcellular imaging
Phytoplankton account for a large proportion of global primary production and comprise a number of phylogenetically distinct lineages. Here, Uwizeye et al. use FIB-SEM to study ultrastructural plasticity of 7 distinct taxa and describe how subcellular organisation is linked to energy metabolism.
- Clarisse Uwizeye
- , Johan Decelle
- & Giovanni Finazzi
-
Article
| Open Access Live-cell single particle tracking of PRC1 reveals a highly dynamic system with low target site occupancy
Live-cell single particle tracking of PRC1 reveals a highly dynamic system with low target site occupancy
How PRC1 recognises and interacts with its target genes remains poorly understood. Here, the authors use genome engineering and single particle tracking to dissect how PRC1 binds to chromatin in live mouse embryonic stem cells, revealing that this repressor is highly dynamic, with only a small fraction stably interacting with chromatin.
- Miles K. Huseyin
- & Robert J. Klose
-
Article
| Open Access Effects of individual base-pairs on in vivo target search and destruction kinetics of bacterial small RNA
Effects of individual base-pairs on in vivo target search and destruction kinetics of bacterial small RNA
Bacterial small RNA SgrS binds and regulates its primary target, ptsG mRNA. Here the authors employ Sort-Seq and super resolution imaging to investigate in vivo target recognition and rejection kinetics of SgrS.
- Anustup Poddar
- , Muhammad S. Azam
- & Taekjip Ha
-
Article
| Open Access Analysing the mechanism of mitochondrial oxidation-induced cell death using a multifunctional iridium(III) photosensitiser
Analysing the mechanism of mitochondrial oxidation-induced cell death using a multifunctional iridium(III) photosensitiser
Mitochondrial oxidation-induced cell death is an important physiological process activated by cancer therapeutics, but its investigation is challenging. Here, the authors report a multifunctional iridium(III) photosensitiser, Ir-OA, able to induce mitochondrial oxidative stress and monitor the corresponding changes in mitochondrial properties.
- Chaiheon Lee
- , Jung Seung Nam
- & Tae-Hyuk Kwon
-
Article
| Open Access A versatile and customizable low-cost 3D-printed open standard for microscopic imaging
A versatile and customizable low-cost 3D-printed open standard for microscopic imaging
Open standard microscopy is urgently needed to give low-cost solutions to researchers and to overcome the reproducibility crisis in science. Here the authors present a 3D-printed, open-source modular microscopy toolbox UC2 (You. See. Too.) for a few hundred Euros.
- Benedict Diederich
- , René Lachmann
- & Rainer Heintzmann
-
Article
| Open Access Spatiotemporal dynamics of 53BP1 dimer recruitment to a DNA double strand break
Spatiotemporal dynamics of 53BP1 dimer recruitment to a DNA double strand break
53BP1 is a crucial factor involved in double strand break repair which blocks DNA end resection affecting DNA repair pathway choice. Here the authors reveal by live cell nuclear architecture analysis the spatiotemporal dynamics of 53BP1 oligomerization during a DSB DNA damage response.
- Jieqiong Lou
- , David G. Priest
- & Elizabeth Hinde
-
Article
| Open Access Organized cannabinoid receptor distribution in neurons revealed by super-resolution fluorescence imaging
Organized cannabinoid receptor distribution in neurons revealed by super-resolution fluorescence imaging
Despite the importance of G-protein-coupled receptors in many cellular functions, their intracellular organisation is largely unknown. The authors identified periodically repeating clusters of cannabinoid receptor 1 hotspots within neuronal axons that are dynamically regulated by CB1 agonists.
- Hui Li
- , Jie Yang
- & Guisheng Zhong

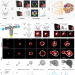 Multiscale light-sheet organoid imaging framework
Multiscale light-sheet organoid imaging framework