Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Complementarity-determining region clustering may cause CAR-T cell dysfunction
Complementarity-determining region clustering may cause CAR-T cell dysfunction
The challenge of designing chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells for cancer therapy is not limited to finding targetable cellular proteins, but also in optimising the effector properties. Here authors show that single-chain variable fragment targeting moieties could unpredictably prompt spontaneous CAR-T cell activation via CAR clustering, which argues for empirical screening for tonic signalling.
- Tina Sarén
- , Giulia Saronio
- & Magnus Essand
-
Article
| Open Access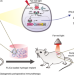 Optogenetic-controlled immunotherapeutic designer cells for post-surgical cancer immunotherapy
Optogenetic-controlled immunotherapeutic designer cells for post-surgical cancer immunotherapy
The induction of long-term systemic immunosurveillance can protect against post-surgery tumor recurrence. Here the authors describe the design of optogenetic-controlled cytokine secreting (IFN-β, TNF-α, and IL-12) engineered mesenchymal stem cells loaded into a hydrogel scaffold, eliciting long-term immune memory and preventing post-operative recurrence in preclinical cancer models.
- Yuanhuan Yu
- , Xin Wu
- & Haifeng Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Targeting CD123 in blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm using allogeneic anti-CD123 CAR T cells
Targeting CD123 in blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm using allogeneic anti-CD123 CAR T cells
Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN) is a rare and highly aggressive hematologic malignancy derived from the precursors of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Here the authors characterize the anti-tumor activity of allogeneic anti-CD123 CAR-T cells in preclinical models of BPDCN.
- Tianyu Cai
- , Agnès Gouble
- & Marina Konopleva
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered osteoclasts as living treatment materials for heterotopic ossification therapy
Engineered osteoclasts as living treatment materials for heterotopic ossification therapy
Heterotopic ossification (HO) is the formation of pathological mature bone within extraskeletal soft tissues, and there are currently no reliable methods for removing these calcified plaques. Here, the authors demonstrate that chemically engineered osteoclasts coated with tetracycline can improve their targeting capacity to ectopic calcifications, which extends their bone resorption functions for the treatment of HO.
- Wenjing Jin
- , Xianfeng Lin
- & Ruikang Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Electrophysiological engineering of heart-derived cells with calcium-dependent potassium channels improves cell therapy efficacy for cardioprotection
Electrophysiological engineering of heart-derived cells with calcium-dependent potassium channels improves cell therapy efficacy for cardioprotection
Strategies to improve the function of damaged hearts with progenitor cells have stalled. Here, the authors show that gene transfer of a calcium-dependent potassium channel enhances the functional properties and ability of explant-derived cells to improve heart function after a heart attack.
- Patrick Vigneault
- , Sandrine Parent
- & Stanley Nattel
-
Article
| Open Access Direct control of CAR T cells through small molecule-regulated antibodies
Direct control of CAR T cells through small molecule-regulated antibodies
Many next-generation antibody therapeutics have enhanced potency but the risk of adverse events. Here the authors develop a conditionally activated, single-module CAR.
- Spencer Park
- , Edward Pascua
- & Javier Chaparro-Riggers
-
Article
| Open Access CD229 CAR T cells eliminate multiple myeloma and tumor propagating cells without fratricide
CD229 CAR T cells eliminate multiple myeloma and tumor propagating cells without fratricide
CD229 is expressed on the surface of multiple myeloma cells, as well as B and T lymphocytes. Here, the authors engineer CD229-specific CAR T cells and, using patient samples and mouse models, show that treatment with these cells reduces tumour burden and results in limited targeting of T cells.
- Sabarinath V. Radhakrishnan
- , Tim Luetkens
- & Djordje Atanackovic
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic TRuC receptors engaging the complete T cell receptor for potent anti-tumor response
Synthetic TRuC receptors engaging the complete T cell receptor for potent anti-tumor response
Supraphysiological T cell activation by chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) contributes to T cell exhaustion and adverse events in CAR T cell therapies. Here the authors engineer a synthetic antigen receptor that integrates into the endogenous TCR complex, preserving natural regulatory circuits and achieving improved performance in mouse tumor models.
- Patrick A. Baeuerle
- , Jian Ding
- & Robert Hofmeister
-
Article
| Open Access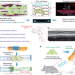 A biodegradable hybrid inorganic nanoscaffold for advanced stem cell therapy
A biodegradable hybrid inorganic nanoscaffold for advanced stem cell therapy
The promise of stem cell therapy for treating central nervous system disease is limited by low stem cell transplantation survival rates and poorly controlled cell fate. Here, the authors develop a biodegradable nanoscaffold for spinal cord injury that enhances transplantation and differentiation of neural stem cells and delivers drugs.
- Letao Yang
- , Sy-Tsong Dean Chueng
- & Ki-Bum Lee
-
Article
| Open Access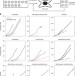 Expansion of functional personalized cells with specific transgene combinations
Expansion of functional personalized cells with specific transgene combinations
Personalised medicine requires cell cultures from defined genetic backgrounds, but providing sufficient numbers of cells is a challenge. Here the authors develop gene cocktails to expand primary cells from a variety of different tissues and species, and show that expanded endothelial and hepatic cells retain properties of the differentiated phenotype.
- Christoph Lipps
- , Franziska Klein
- & Tobias May
-
Article
| Open Access Genetically engineered red cells expressing single domain camelid antibodies confer long-term protection against botulinum neurotoxin
Genetically engineered red cells expressing single domain camelid antibodies confer long-term protection against botulinum neurotoxin
The therapeutic use of single-chain antibodies (VHHs) is limited by their short half-life in the circulation. Here the authors engineer mouse and human red blood cells to express VHHs against botulinum neurotoxin A (BoNT/A) on their surface and show that an infusion of these cells into mice confers long lasting protection against a high dose of BoNT/A.
- Nai-Jia Huang
- , Novalia Pishesha
- & Harvey F. Lodish
-
Article
| Open Access Treatment of ongoing autoimmune encephalomyelitis with activated B-cell progenitors maturing into regulatory B cells
Treatment of ongoing autoimmune encephalomyelitis with activated B-cell progenitors maturing into regulatory B cells
Evidence of how functional Bregs develop in vivo has been lacking. Here the authors show that proB cells exposed in vivoto CpG differentiate into distinct Breg subsets that inhibit autoimmunity by arresting T cells in the lymph nodes via CCL19 and by producing IL-10 at the site of immunopathology.
- Sarantis Korniotis
- , Christophe Gras
- & Flora Zavala
-
Article
| Open Access Microfluidic single-cell transcriptional analysis rationally identifies novel surface marker profiles to enhance cell-based therapies
Microfluidic single-cell transcriptional analysis rationally identifies novel surface marker profiles to enhance cell-based therapies
Unrecognized progenitor cell perturbations underlying a disease state may limit the efficacy of cell therapies. Here, the authors use high-throughput, single-cell transcriptional analysis to identify disease-specific cellular alterations and prospectively isolate restorative cell subpopulations.
- Robert C. Rennert
- , Michael Januszyk
- & Geoffrey C. Gurtner
-
Article
| Open Access Whole-genome mutational burden analysis of three pluripotency induction methods
Whole-genome mutational burden analysis of three pluripotency induction methods
It is feared that reprogramming may introduce DNA mutations. Here Bhutani et al. take three different reprogramming methods and using comparative whole genome analyses do identify nucleotide variations that are different in reprogrammed cells from the original fibroblasts, but none convey oncogenic potential.
- Kunal Bhutani
- , Kristopher L. Nazor
- & Jeanne F. Loring
-
Article
| Open Access Therapeutically engineered induced neural stem cells are tumour-homing and inhibit progression of glioblastoma
Therapeutically engineered induced neural stem cells are tumour-homing and inhibit progression of glioblastoma
Neural stem cells have a tropism for glioblastoma. Here the authors employ fibroblasts directly reprogrammed into induced neural stem cells and loaded with cytotoxic molecules to migrate to xenotransplanted brain tumours in mice, achieving tumour shrinkage and prolonged survival.
- Juli R. Bagó
- , Adolfo Alfonso-Pecchio
- & Shawn D. Hingtgen
-
Article
| Open Access Autonomous beating rate adaptation in human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes
Autonomous beating rate adaptation in human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes
The use of stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes for heart repair is hampered by their immature structural and contractile properties that may cause arrhythmia. Here, Eng et al.show that electrical conditioning of human cardiomyocytes in 3D culture can enhance connectivity and provide resistance to arrhythmia.
- George Eng
- , Benjamin W. Lee
- & Gordana Vunjak-Novakovic
-
Article
| Open Access Sepsis induces long-term metabolic and mitochondrial muscle stem cell dysfunction amenable by mesenchymal stem cell therapy
Sepsis induces long-term metabolic and mitochondrial muscle stem cell dysfunction amenable by mesenchymal stem cell therapy
Sepsis patients often develop muscle atrophy that can last for years. Here the authors show in a mouse model that sepsis causes long-term impairment of the satellite cells, affecting mitochondrial function and energy metabolism, and that injection of mesenchymal stem cells restores satellite cell metabolism and muscle regeneration.
- P. Rocheteau
- , L. Chatre
- & F. Chrétien
-
Article
| Open Access Rescue of neonatal cardiac dysfunction in mice by administration of cardiac progenitor cells in utero
Rescue of neonatal cardiac dysfunction in mice by administration of cardiac progenitor cells in utero
The protein Speg is expressed in the developing mouse heart, where its absence leads to neonatal cardiac disease. Here the authors trace the cardiomyopathy of Speg KO mice back to defects in cardiac progenitor cells (CPCs) and rescue it with injections of wild type CPCs into the foetal heart.
- Xiaoli Liu
- , Sean R. R. Hall
- & Mark A. Perrella
-
Article
| Open Access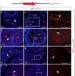 Resident c-kit+ cells in the heart are not cardiac stem cells
Resident c-kit+ cells in the heart are not cardiac stem cells
The issue whether the cell surface protein c-kit identifies resident cardiac stem cells (CSC) is controversial. By using novel reporter mouse models, Sultana et al. show that c-kit+cells represent a subpopulation of endothelial cells in the developing and adult heart and do not exhibit CSC traits in health or disease.
- Nishat Sultana
- , Lu Zhang
- & Chen-Leng Cai
-
Article
| Open Access Directing cell therapy to anatomic target sites in vivo with magnetic resonance targeting
Directing cell therapy to anatomic target sites in vivo with magnetic resonance targeting
Cell therapy requires the targeting of cells to specific sites in the body. Here Muthana et al.use a standard MRI scanner to direct oncolytic macrophages, labelled with magnetic nanoparticles, to primary and metastatic tumour sites in mice, and demonstrate that this leads to reduced tumour growth.
- Munitta Muthana
- , Aneurin J. Kennerley
- & Claire Lewis
-
Article |
 An authentic imaging probe to track cell fate from beginning to end
An authentic imaging probe to track cell fate from beginning to end
The availability of tracers to track the health of cells over long periods of time will be of value to optimize cell-based therapy. Here, Lee et al.design a nanoparticle that fluoresces red in living cells, but fluoresces green when cells begin to die from apoptosis or necrosis.
- Seung Koo Lee
- , Luke J. Mortensen
- & Ching-Hsuan Tung
-
Article |
 FOXO1 inhibition yields functional insulin-producing cells in human gut organoid cultures
FOXO1 inhibition yields functional insulin-producing cells in human gut organoid cultures
The transcription factor FOXO1 has been shown to control the differentiation of enteroendocrine cells in mice. Here the authors extend these findings to humans by showing that FOXO1-expressing cells also exist in the human gut, and that inhibition of FOXO1 generates insulin-secreting cells in human gut organoid cultures.
- Ryotaro Bouchi
- , Kylie S. Foo
- & Domenico Accili
-
Article
| Open Access hESC-derived Olig2+ progenitors generate a subtype of astroglia with protective effects against ischaemic brain injury
hESC-derived Olig2+ progenitors generate a subtype of astroglia with protective effects against ischaemic brain injury
Astroglia are heterogeneous in phenotype and not all astrocytes are equivalent in their ability to repair injured brain. Here, the authors show that two defined subtypes of astroglia generated from hESC-derived Olig2-positive versus Olig2-negative neural progenitors, exhibit distinct properties and neuroprotective effects.
- Peng Jiang
- , Chen Chen
- & Wenbin Deng
-
Article |
 An ex vivo gene therapy approach to treat muscular dystrophy using inducible pluripotent stem cells
An ex vivo gene therapy approach to treat muscular dystrophy using inducible pluripotent stem cells
Patient-specific induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells hold great potential for regenerative cell therapies. Here Filareto et al. genetically correct iPS cells from mice with muscular dystrophy and use these cells to treat the same animals, providing a proof-of-principle for autologous iPS cell therapy.
- Antonio Filareto
- , Sarah Parker
- & Rita C. R. Perlingeiro
-
Article
| Open Access Muscle-derived stem/progenitor cell dysfunction limits healthspan and lifespan in a murine progeria model
Muscle-derived stem/progenitor cell dysfunction limits healthspan and lifespan in a murine progeria model
The function of adult stem cells is diminished with age but the role this dysfunction plays in the aging process is unknown. Here, the injection of muscle-derived stem/progenitor cells from young mice rescues symptoms in progeroid mice and is shown to regenerate tissues independent of engraftment.
- Mitra Lavasani
- , Andria R. Robinson
- & Johnny Huard

 Autologous cell transplantation for treatment of colorectal aganglionosis in mice
Autologous cell transplantation for treatment of colorectal aganglionosis in mice